13 Diagnostic Tests for Hepatobiliary Disease
1/52
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
53 Terms
Icterus
What is the BIGGEST finding on clinical exam with hepatic disease?
CBC, Chem, UA
What is a "minimum database"
Microcytosis (from impaired transport of iron)
What type of RBC changes occur with hepatobiliary disease from portosystemic shunts?
Iron deficiency anemia, portosystemic shunting (NO anemia), GI bleed
What 3 things cause microcytosis?
Hemolytic anemia
What might cause regenerative MACROCYTIC anemia if the patient is jaundice?
Poiklocytes, acanthocytes
What SHAPE might RBC be in animals with portosystemic shunts or hepatobiliary disease?
ALT, AST
What are the two Chem. markers that measure hepatocellular membrane damage/leakage?
SAP (ALP), GGT
What are the two Chem. markers that measure the biliary tract and cholestasis?
Hepatocytes (fairly specific for liver cell injury)
WHERE is ALT normally found?
Extent of hepatic injury
The magnitude of ALT elevation on chem. tells you extent of hepatic injury OR prognosis/reversibility?
Cats
note: this is because it is also found in muscle especially in the dog, making it less specific than ALT
AST is more reliable predictor of hepatocellular damage in dogs or cats?
Steroids/phenobarb, bone (esp. puppies), and liver
ALP has isoenzymes where, especially for dogs?
Cats
note: meaning any elevation of ALP at ALL is significant, and this is not the same for dogs
Which animal has smaller stores and shorter half lives of ALP, cats or dogs?
GGT
What is the best specific enzyme for cholestasis in dogs and cats?
Liver function synthetic parameters
note: when bilirubin is elevated, it will elevate in bloodstream before you see it in mucous membranes, and there are 3 differentials: prehepatic hemolytic anemia, intrahepatic functional problems, or posthepatic
Bilirubin is used as a marker for WHAT?
Glucose, cholesterol, albumin, BUN
note: this is because the liver has a large role in making these
What are the 4 tests that ESTIMATE hepatic function?
Cats
Which animals have Heinz bodies (oxidized, denatured hemoglobin) with liver disease (hepatic lipidosis)?
Oxidative stress events: unregulated diabetes, unregulated hyperthyroidism, lymphoma
Besides hepatic lipidosis, what would be some differentials for a cat with heinz bodies?
CATS
Bilirubinuria is ALWAYS abnormal in which animal, even if it is trace amounts?
Serum bile acids, ammonia
What are more sensitive ways to assess liver function?
From cholesterol in liver
Where are bile acids made?
Bile acids will be increased
note: bile acids are made from cholesterol in the liver. So, if the liver is not working properly (cholestasis), they cannot be excreted into the intestines and will instead back up into liver cells and the blood stream
If the liver is not functioning, what will this do to bile acids?
Collect pre fasted bile acids, Fast patient, give small amount of food with fat, 2 hrs later collect post sample
How do you do a bile acid stimulation test?
Urine bile acids
What reflects the average blood level of serum bile acids during the interval of the urine formation?
Hepatobiliary disease/PSS
Urine bile acids tend to elevate well with hepatobiliary disease/PSS OR hepatic neoplasia?
Proteins in amino acids
Where do you mainly get ammonia naturally produced in your body?
Urea
What does the liver turn ammonia to to make it safer?
Ionized
When ammonia is ionized or nonionized, it becomes trapped in the gut and cannot reenter enterohepatic circulation, so it must be pooped out, called "ammonia trapping", good for treating hepatic encephalopathy
Ammonia
What is the biggest thing during liver disease that can cause hepatic encephalopathy
Bile acids (more stable)
Which is tested more often for liver disease, bile acids or ammonia testing?
Buccal mucosal bleeding test, thrombocytopenia and platelet function testing, PT, and APTT
You need to be careful with liver disease because it is so important for normal hemostasis. What coagulation tests can you do to see how these pathways are functioning?
PT
Which coagulation test looks at the extrinsic pathway of coagulation (very importantly, factor VII)?
APTT
Which coagulation test looks at intrinsic pathway of coagulation?
70-80% = NONSENSITIVE MARKER
How many clotting factors need to be nonfunctional for the PT/APTT to go up in liver disease?
Buccal mucosal bleeding
What is the only cage side test available to practitioners as a coagulation test?
Caudal shift
What will happen to the gastric axis with hepatomegaly?
Cranial shift
What will happen to the gastric axis with microhepatica?
Structure
Ultrasound looks at structure or function
Portosystemic shunts and 3D rendering
What hepatic abnormality is computed tomography best at imaging?
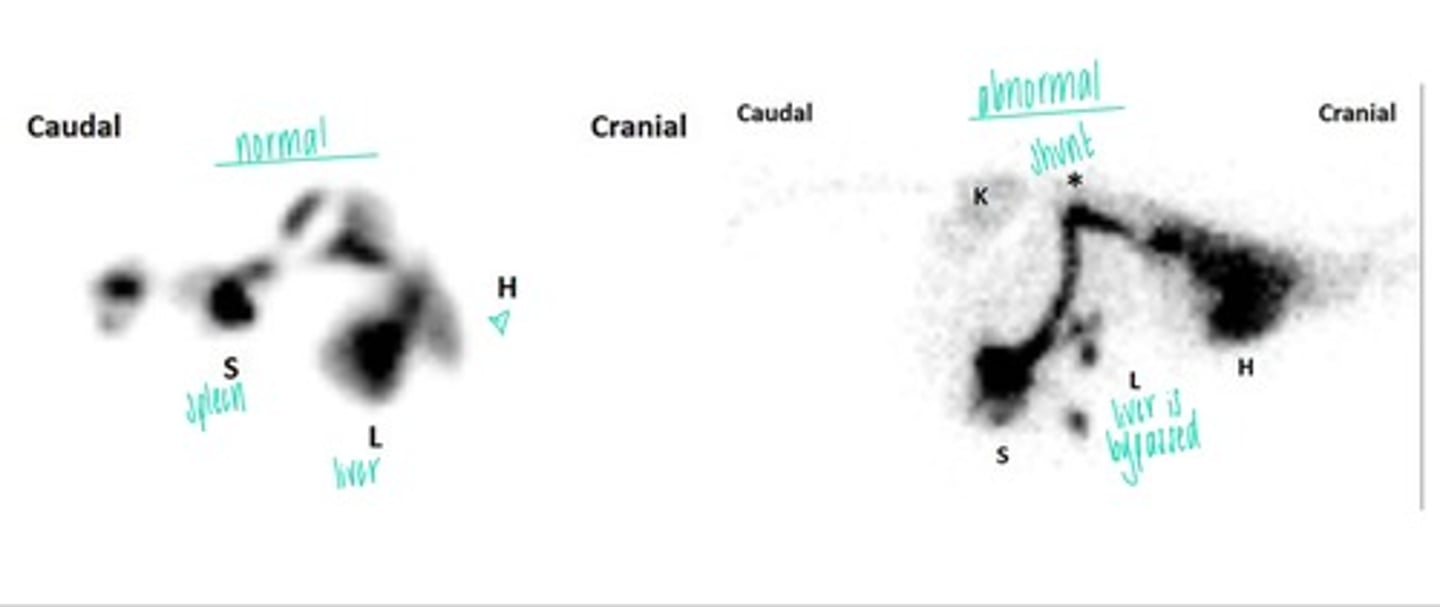
Scintigraphy
What imaging technique utilizes uptake of Technetium 99m and radioactive isotopes taken up by the tissue?
Post
When testing bile acids, should post or pre be higher?
Bile acids
Which test relies on intact enterohepatic circulation, ammonia or bile acids?
Cholestatic
(because a lot of factors are made by vitamin K, and if there is a decreased flow of bile, the coag. factors may not work)
With which type of liver disease should you be MOST worried about your coag. factors not working?
1. explain hepatomegaly
2. stage neoplasia
3. assess response to treatment
4. evaluate progression of disease
5. explain abnormal test results
6. determine hepatic involvement in systemic disease
Why do you want to do a cytology/biopsy of the liver?
Cytology (FNA)
Which sampling of the liver is minimally invasive and better for cells that suck up into your needle and exfoliate, where you don't need to look at tissue architecture
For neoplasia
Where is Tru-Cut biopsies best, what is it best to look at?
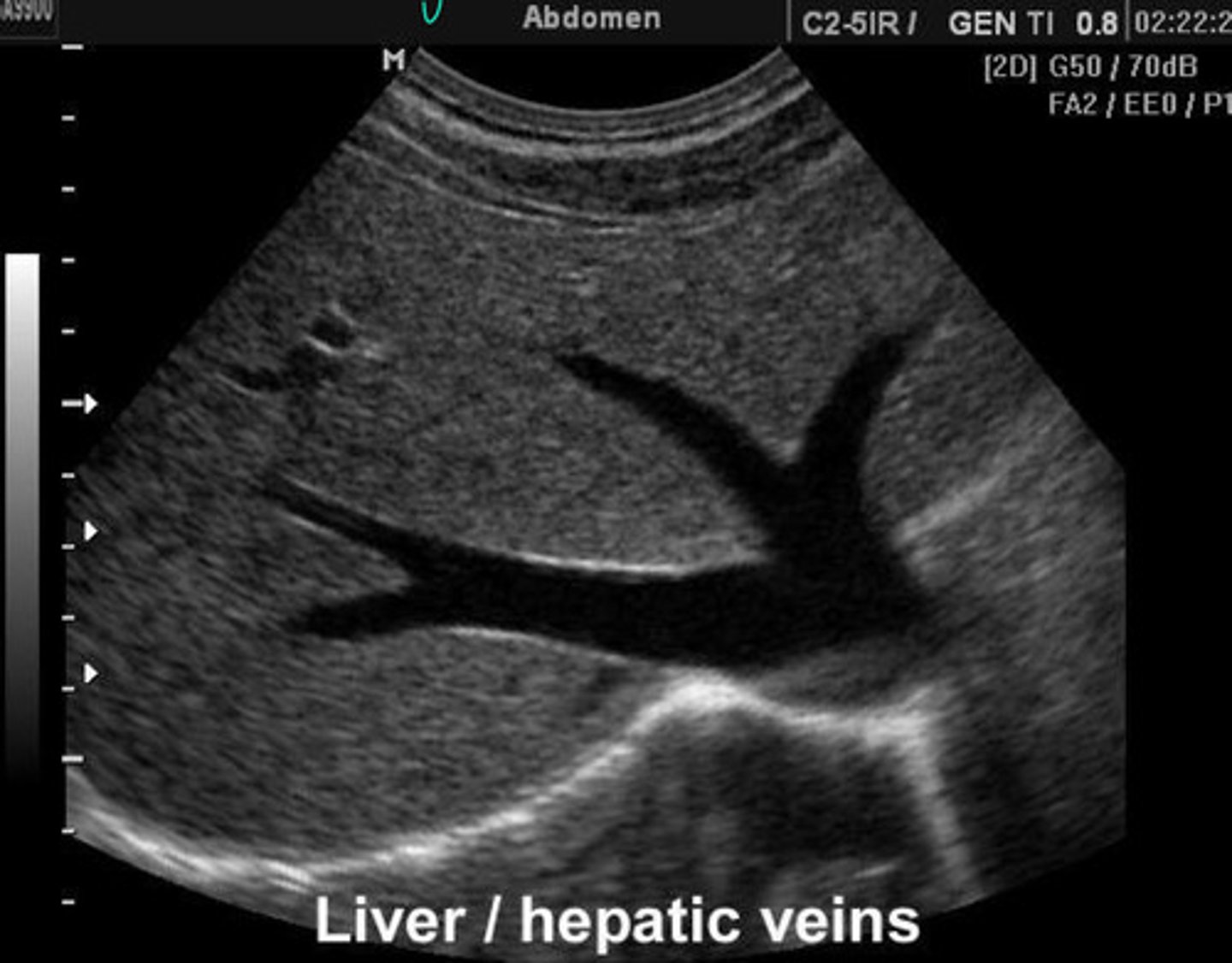
Abnormal = vessels are MASSIVE and congested
What is going on here? Is this normal or abnormal?
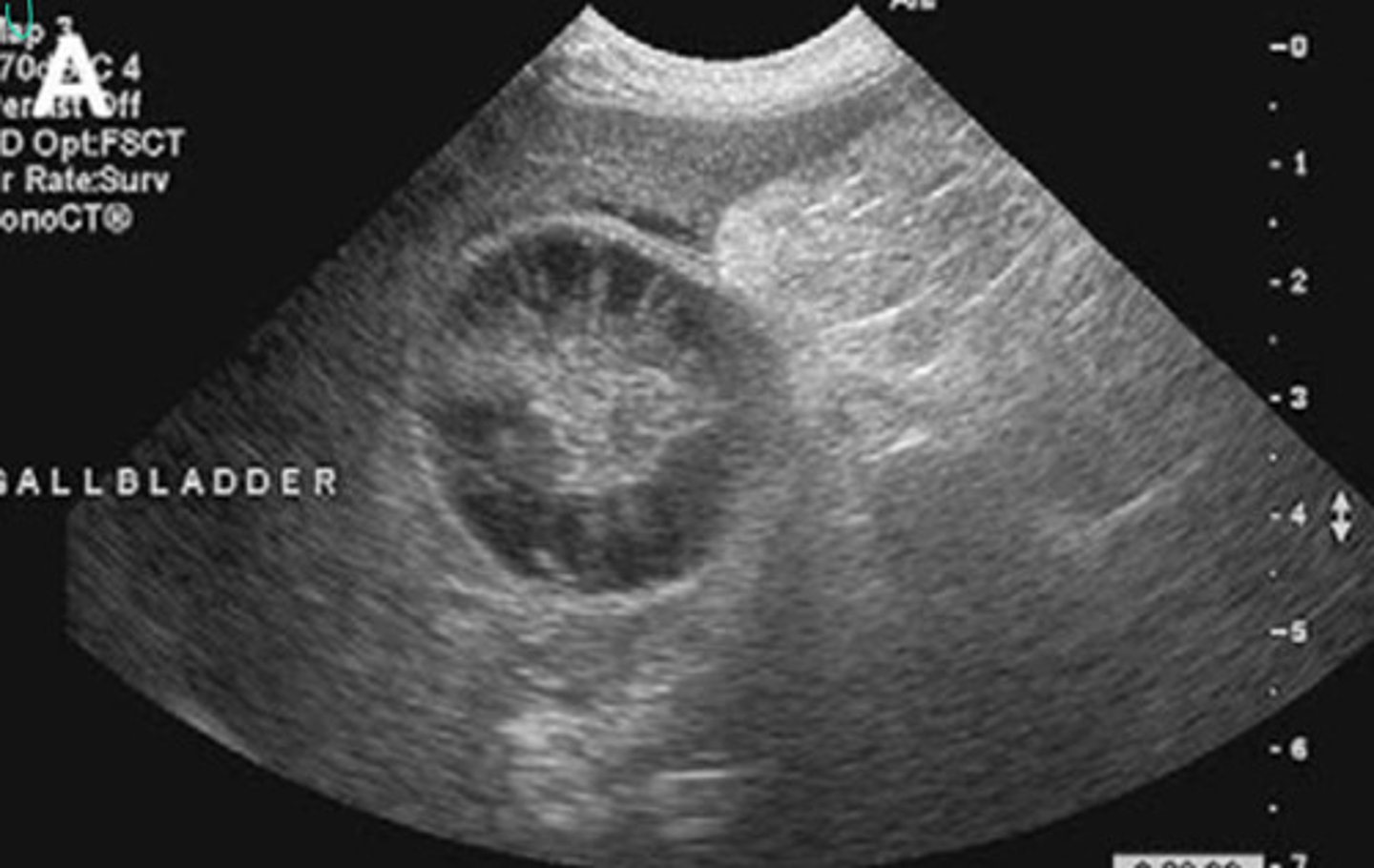
Abnormal = mucocele in the gallbladder
What is going on here? Is this normal or abnormal?
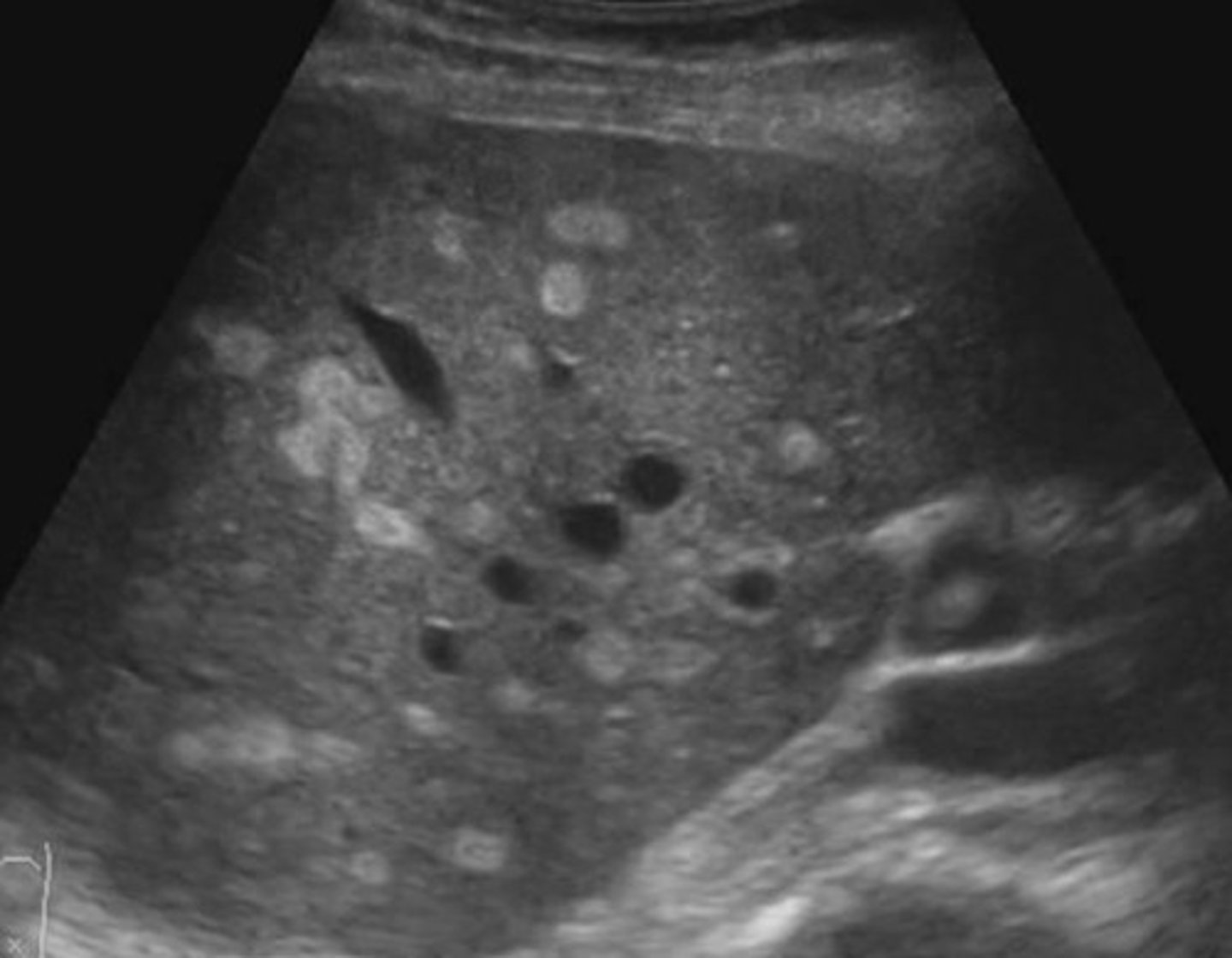
Abnormal = Hyperechoic areas are lipoma lesions in the liver
What is going on here? Is this normal or abnormal?
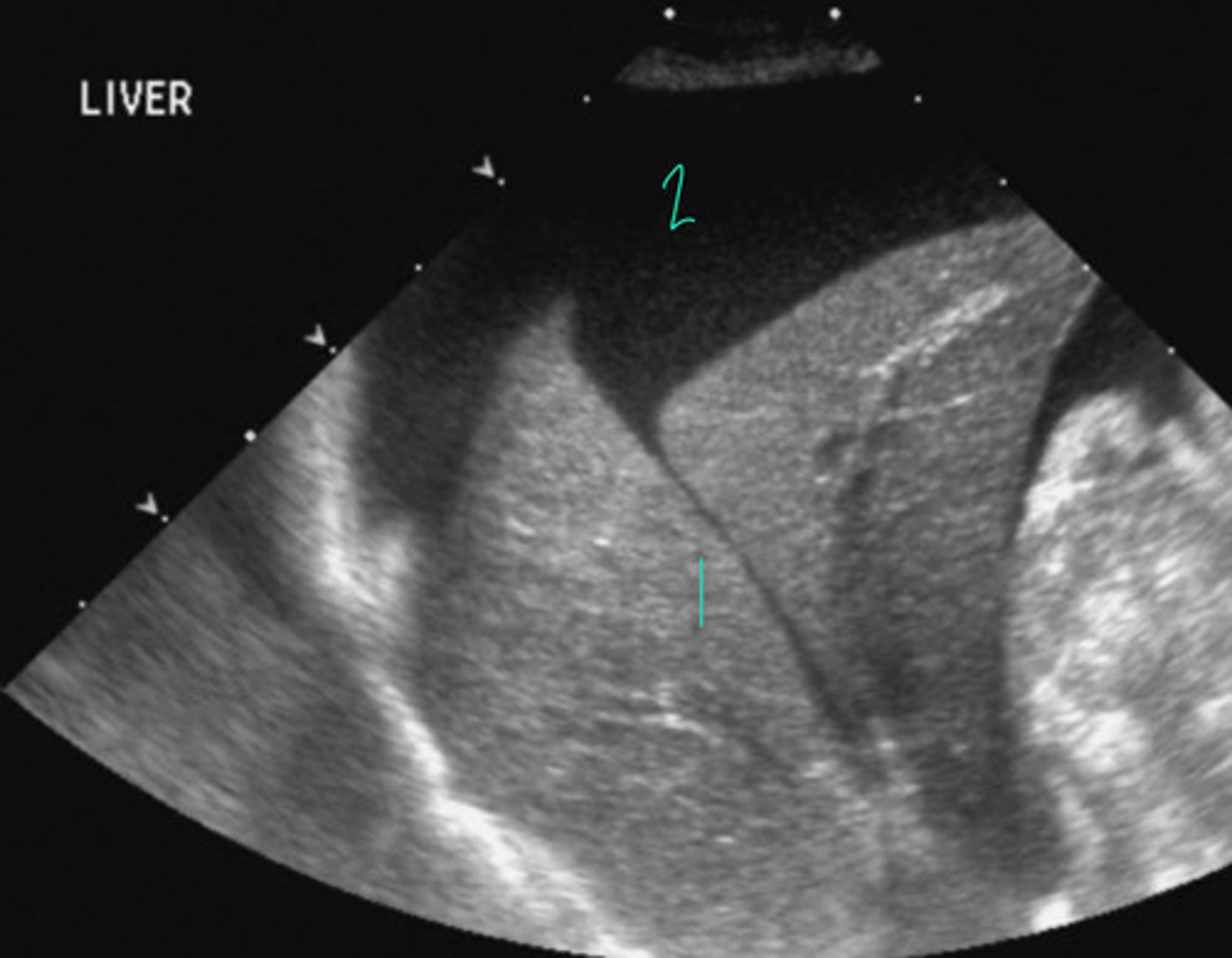
This is normal liver listed at 1, abnormal ascites going on at 2
What is going on here? Is this normal or abnormal?
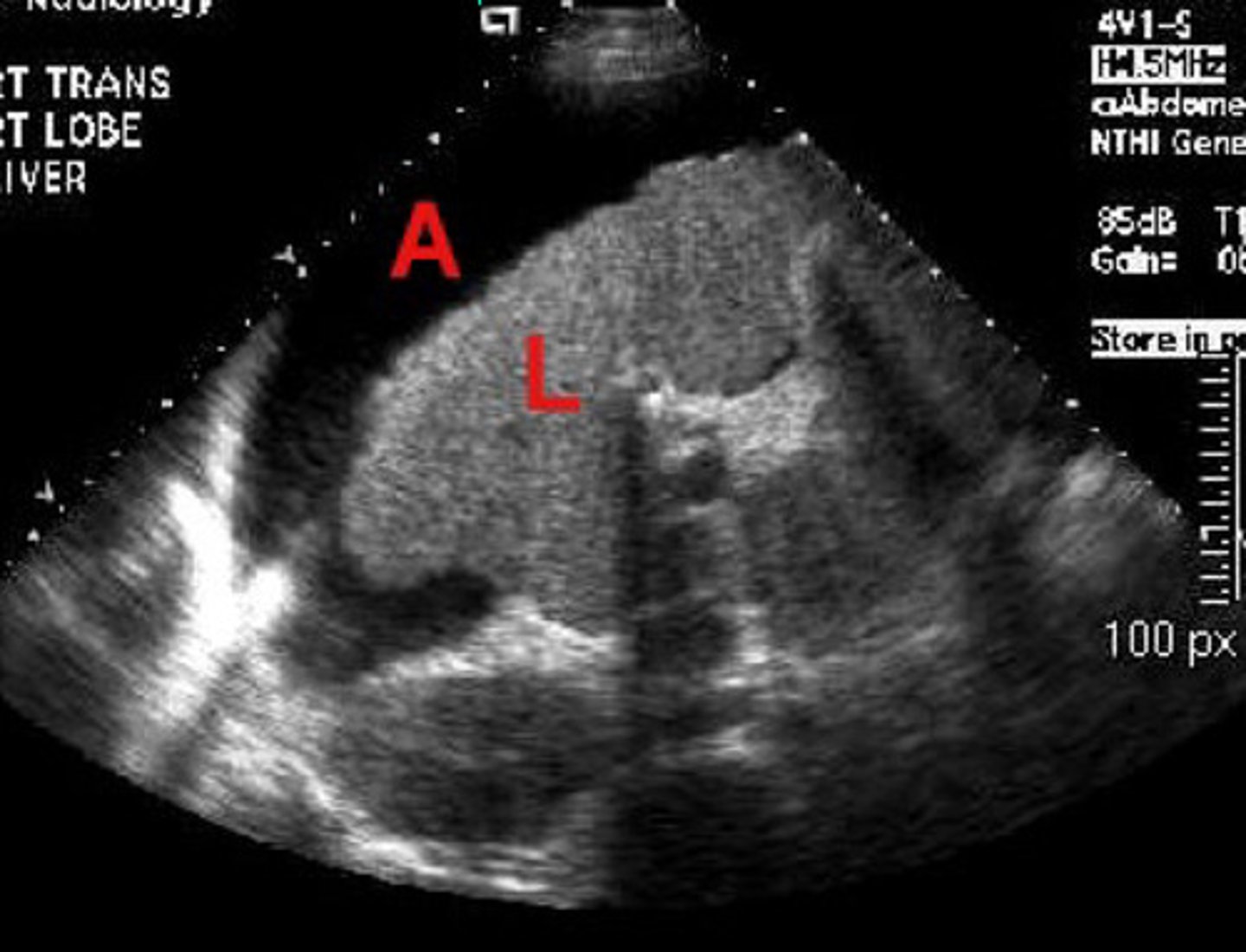
Abnormal = small irregularly marginated liver at L and ascites at A = chronic hepatitis and scar tissue present
What is going on here? Is this normal or abnormal?
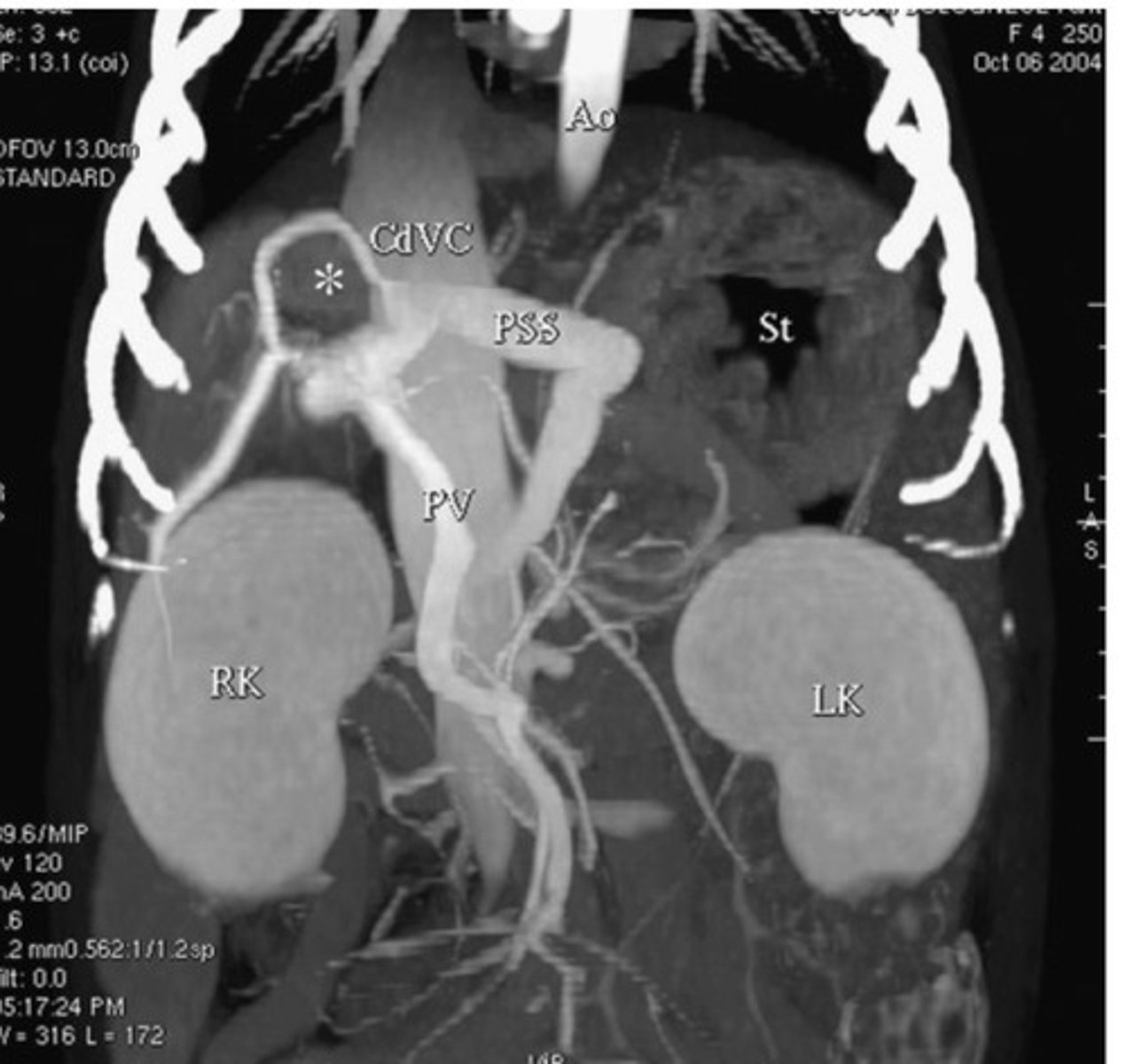
CT
What form of imaging is this?
Nuclear scintigraphy
What form of imaging is this?