The Collective Honors physics knowt
1/431
Earn XP
Description and Tags
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
432 Terms
Instantaneous velocity
average velocity over infinitesimally small time interval
Tangent line
straight line connecting a pair of infinitely close points on a curve
Time derivative
rate of value a function changes over time
acceleration
vector that is a derivative of velocity (m/s²)
constant accelerated motion
motion w/ constant acceleration
Instantaneous acceleration
average acceleration over infinitesimally small interval
Equations of motion
equations that describe an object’s displacement and velocity when acceleration is constant
v = vi + at
Equation of motion (velocity)
C, B, D, F, G, A, E
Unscramble these terms in order of their derivatives:
A: crackle
B: velocity
C: position
D: acceleration
E: pop
F: jerk
G: snap
a = delta v/ delta t
acceleration equation
v= at + vi
velocity vs. time slope intercept formula
negative velocity
if one were to take the tangent of a point on the descending part of the curve on this position vs. time graph, what would be the velocity
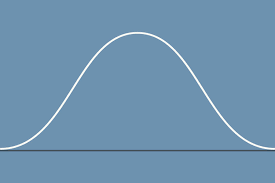
0 velocity
if one were to take the tangent of a point on the peak part of the curve on this position vs. time graph, what would be the velocity
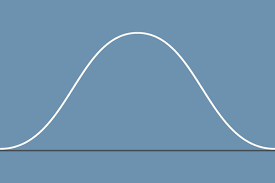
positive velocity
if one were to take the tangent of a point on the acsending part of the curve on this position vs. time graph, what would be the velocity?
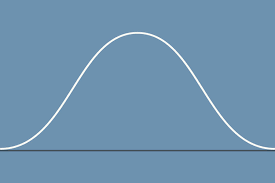
negative acceleration
if one were to take the tangent of a point on the descending part of the curve on this velocity vs. time graph, what would be the acceleration?
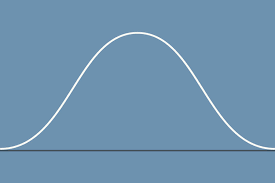
0 acceleration
if one were to take the tangent of a point on the peak part of the curve on this velocity vs. time graph, what would be the acceleration?
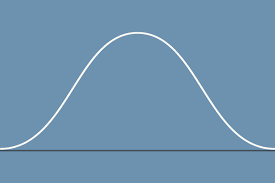
acceleration is positve
if one were to take the tangent of a point on the acsending part of the curve on this velocity vs. time graph, what would be the acceleration?
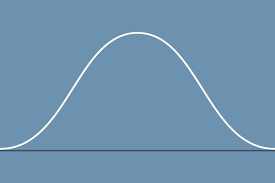
acceleration
the slope for a velocity vs.time graph is
object faced down
if one were to take the tangent of a point on the descending part of the curve on this acceleration vs. time graph, what would be the jerk?
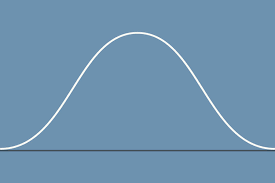
no jerk
if one were to take the tangent of a point on the peak part of the curve on this acceleration vs. time graph, what would be the jerk?
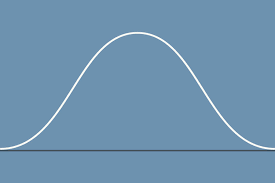
Object faced up
if one were to take the tangent of a point on the ascending part of the curve on this acceleration vs. time graph, what would be the jerk?
position
a measurement of where an object is at a particular time in respect to a reference point
Displacement
object’s change of position
Distance traveled
total length of path between two positions
change in d = df - di
displacement equation
scalar quantity
quantity with now direction but magnitude/size
vector quantity
quantity having both magnitude and direction
d = (x)x^ + (y)y^
components
IdI = sqrt((x)²+(y)²)
displacement
Resultant
vector that is a sum of two or more vectors
motion diagram
displays object’s position at equal increments in time
Dot diagram
motion diagram where object is represented by a dot
uniform motion
straight line motion when change interval is equal
nonuniform motion
position dose not change the same amount
position graph
position as a function of time
velocity
a measure of amount of change in position at specified time
speed
measurement of distance traveled in amount of time
v = delta d/delta t
velocity slope equation
d = vt +di
slope intercept form for position vs. time graph
displacement
area under velocity vs. time graph
negative
If an object is returning to it’s original position, the velocity will be ____
equal, opposite
If two non-zero vectors are added together, and the resultant vector is zero, what must be true of the two vectors?
they have ___ magnitude and ___ direction
integral
the area under a curve under a graph
delta d= vit+1/2at2
equation of motion for displacement
free fall
the falling motion of an object without resistance under the influence of Earth’s gravity
acceleration due to gravity
the constant acceleration towards the center of Earth experienced by a body in free fall near Earth’s surface
delta y= vit+1/2gt2
equations of motion for free fall (product is displacement in the y-direction)
v=vi+gt
Equations of motion free fall (product is velocity)
v=(x)x^+(y)y^
velocity in components
sqrt((x)²+(y)²)
velocity’s magnitude
independent
horizontal and vertical components are _________ of each other
x, y
when adding two velocities, it is like displacement. Add_______ to x and ______ to y to make components for resultant vector
Pythagorean theorem
when you add two resultant vectors, what equation will you use?
projectile
object moving through air that is only affected by gravity
projectile motion
combo of uniform motion parallel to earth’s surface and free-fall motion perpendicular to earth’s surface
separating
projectile motion is analyzed by ______ the two-dimensions into separate dimensions
uniform, does not
horizontal motion is _______ and velocity __________ change
free-fall, increases
vertical motion is ___________ and __________ if going down
t
accelerated motion that is a parabola will have a _____ x-axis
x
trajectory graph will have a _____ on the x axis
y(x)=ax²+bx+c
parabola problem
trajectory graph
2 dimensional dot plot that displays total trajectory
delta x= vxt
horizontal equation of motion
vy=viy+gt
Velocity equation of motion with answer as vertical velocity component
delta y = viyt + ½gt²
Velocity equation of motion with vertical displacement component as the answer
x
trajectory is a quadratic function of __
t
Change in y position is a quadratic function of __
delta x, vx, t
X motion variables
delta y, g, t, vy, viy
y motion variables
viy=0
If an object is launched horizontally off a table, then _____
0
If launched upwards, and object’s y velocity at maximum ______
constant
vx is ______
vy
viy and vy are the same absolute value, but ___ is negative
uniform circular motion
The motion observed when an object travels in a circular path at constant speed
constant, changes
in uniform circular motion, the magnitude of velocity is _____, and velocity _______
Centripetal vector
A vector quantity that is always directed towards the center of the circle
centripetal acceleration
acceleration of an object in uniform circular motion
ac = v²/R
centripetal acceleration equation
oscillatory motion
any motion in which an object repeats the same pattern of motion while repeatedly returning to the same position
x=Rcos((v/R)t)
oscillatory motion x equation
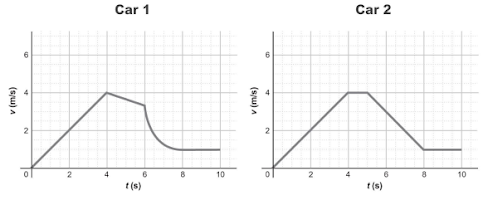
The area is greater under car 2’s graph
Car 2 has a larger displacement. How would you find this out?
y= Rsin((v/R)t)
oscillary motion y equation
It would take longer because no outside velocity besides free fall is affecting them and deceleration is directly related to the speed.
If a student throws up a ball with twice it’s initial speed, how would the air time change?
the point, after
When a problem asks for the instantaneous value from a graph, you should take the _____ and the point _____ it
There is gravitational acceleration to speed it up
Why do objects fall faster on earth than in a vaccuum?
Split it into a triangle and rectangle and add the two values together
if you’re looking for the displacement under a graph and you encounter a irregular shape, you should ____
ΣF=ma
Newton’s seconds law of motion (force)
Newton’s first law of motion
a law that states that an object remains at rest or continue with uniform motion in a straight line unless some action causes a change in motion
ΣF= delta p/ delta t
Newton’s Seconds Law of motion with momentum
p= mv
Momentum equation
Inertia
object’s resistance to change
Mass
measure of object’s inertia (measured in the SI unit of kg)
Force
The cause of a change in motion or change in shape resulting from the unopposed interaction between two objects
net force
vector sum of all net forces
momentum
product of mass and velocity of an object; represents object’s total quantity of motion
Newton’s third law of motion
interaction between two objects can be represented as forces having equal magnitude and opposite directions
Third Law pair
the two related action-related forces described by newton’s third law
Contact Force
an interaction between objects due to direct contact with each other
noncontact force (field force)
interaction between two objects that are separated by some distance
gravitational force (gravity)
the noncontact attractive interaction between tow objects having mass