Williams Drugs
1/34
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
35 Terms
Name an oral abortifacient and it’s PG receptor
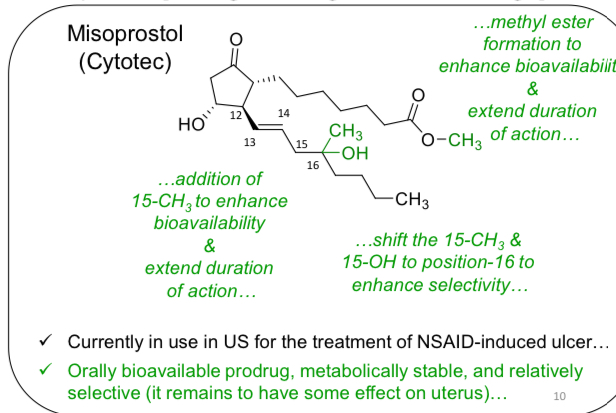
Misoprostol: PGE1
Name an oral contraceptive and it’s PG receptor
Mifepristone; PGE1
Name an abortifacient suppository and it’s PG receptor
Dinoprostol; PGE2
Name an abortifacient injection and it’s PG receptor
Carboprost tromethamine; PGF2a
Name a drug used to treat erectile dysfunction and it’s PG receptor
Alprostadil; PGE1
Name a cytoprotection drug that can treat ulcers and it’s receptor
Misoprostol; PGE1
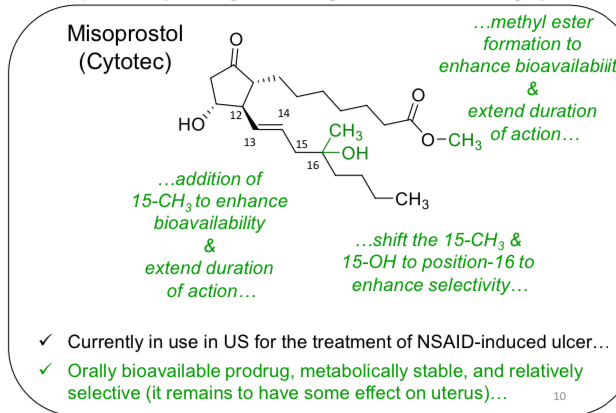
Name a drug (s) that can treat glaucoma and their receptor
Latanoprost (Xatalan)
Bimatoprost (Lumigan)
Travoprost
PGF2a
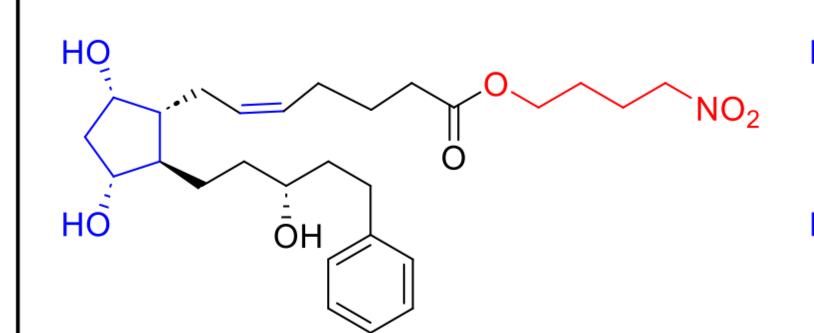
Name a drug(ss that can treat Pulmonary Arterial HTN ( or PAH) and their receptors
Epoprostenol
Iloprost
Treprostinil
PGI2
What are the symptoms to PAH treatment
Flushing, Jaw pain, headache , & Nausea
Name the drug to treat Ductus Arteriosus Maintenance and the PG receptor. What is the route of administration?
Alprostadil, PGE1, and the route of administration is intravenous.
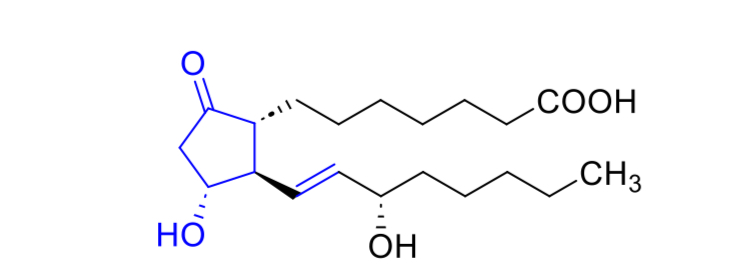
Name the drug to treat Ductus Arteriosus Closure
Indomethacin
Failure to close Ductus Arteriosus leads to ______, ________ & ________
Pulmonary HTN, CHF & Arrhythmia
Drug thats used to replace morphine in some cases for post operative pain
Ketorolac
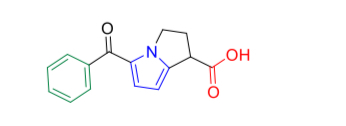
Dug that elevated transaminase
• Increased risk of fluid retention
Longest. Acting salicylate
Diflunisal
Drug that May impair the anti-platelet and anti-inflammatory effects of ASA
Ibuprofen
Drug that Twice the GI bleeding incidence as Ibuprofen
– Seems to be less likely to cause adverse cardiovascular side effects
– Contraindicated in hepatic disease
Naproxen
inhibits both COX and LOX
Ketoprofen
“ Cox-2” Selective drugs
Piroxicam
Oxaprozin
Etolodac
Celecoxib
Therapeutic applications for ASA’s anti-platelet function
prevent ischemia,
angina, infarction, thrombosis
COX1 is responsible for ________________
-COX2 specific drugs target _______________________
COX1 is responsible for normal processes;
inflamed tissue,
while sparing physiological COX-1 processesological COX-1 processes
Finish the pathway:
COX 1 —> ________——>TXA2——> Thrombus formation
and vasoconstriction ——>____________
Platelets; increase adverse CV effects
Finish the pathway:
COX 2 —> _________——>______——> Inhibit platelets and
and vasodilation
Endothelial cells ; PGI2
ASA P450 mediated oxidation
n acetyl-p- benzoquinone imine, NAPQ
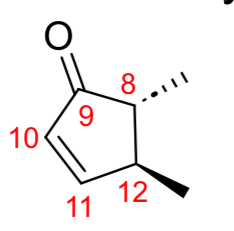
PGA
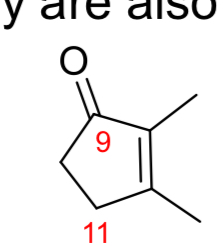
PGB
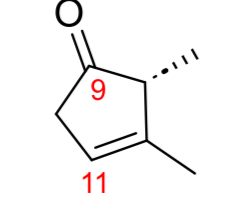
PGC
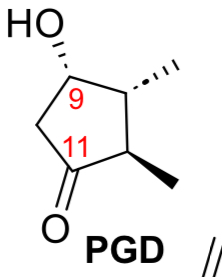
PGD
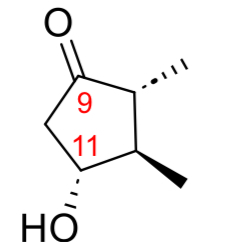
PGE
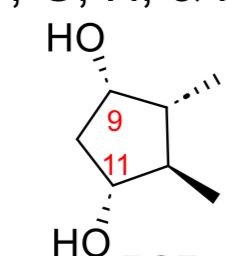
PGF
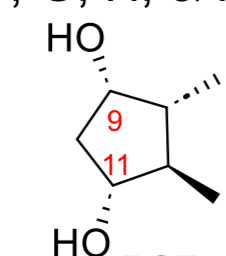
PGF
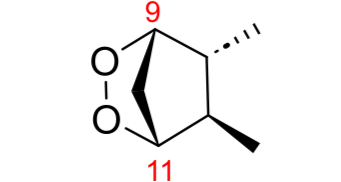
PGG and PGH
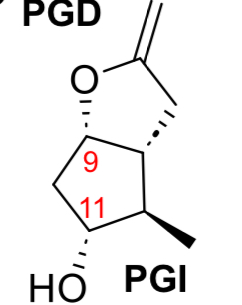
PGI