5.2.2 Enthalpy and entropy
1/31
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
32 Terms
Define lattice enthalpy?
the enthalpy change when 1 mole of a solid ionic compound is formed from its gaseous ions under standard conditions
what happens to lattice enthalpy when ionic radius increases?
lattice enthalpy becomes less negative as the attraction between ions decreases
melting point decreases
define enthalpy change of atomisation?
the enthalpy change when 1 mole of gaseous ions are formed from the element in its standard state under standard conditions
define first ionization energy?
the enthalpy change required to remove 1 electron from each atom in 1 mol of gaseous atoms to form 1 mol of gaseous 1+ ions
Na(g)→Na+(g) +e-
define first electron affinity?
the enthalpy change when 1 electron is added to each atom in 1 mole of gaseous atoms to form 1 mol of gaseou 1- ions
Cl(g) + e- → Cl-(g)
why are first electron affinities exothermic?
because the electron added is attracted to the positive nucleus
why are second electron affinities endothermic?
a second ion is being gained by a negative ion so the electron is repelled
energy must be put in to force
Define standard enthalpy change of solution?
the enthalpy change when 1 mol of an ionic compound dissolves in a solvent
is enthalpy change of solution endothermic or exothermic?
can be either
state what occurs when an ionic compound dissolves in water?
the ionic lattice breaks up forming separate gaseous ions
the separate gaseous ions interact with polar water molecules to form hydrated aqueous ions
define standard enthalpy change of hydration?
the enthalpy change when 1 mole of gaseous ions dissolve in water to form 1 mole of aqueous ions
what 2 factors influence enthalpy change of hydration?
charge
size of ion
state how a higher ionic charge influences enthalpy change of hydration?
ions with a higher charge attract water molecules more strongly
more ebergy is released when a bond is made
more exothermic enthalpy of hydraton
th larger the charge the greater the enthalpy of hydration
state how the size of an ion influences enthalpy change of hydration?
smaller ions have a higher charge than larger ions
they attract water molecules more strongly
more exothermic enthalpy of hydration
smaller ion means greater enthalpy change of hydration
how does increased ionic charge affect lattice enthalpy?
bigger charge means stronger electrostatic attraction between ions
more energy needed to overcome these forces
lattice enthalpy becomes more negative(more exothermic) as attraction between ions increases
melting point therefore increases
Define enthalpy change of formation?
the enthalpy change when 1 mole of a compound is formed from its elements in their standard states under standard conditions
is enthalpy change of formation endo or exo thermic?
can be either
Define entropy?
the dispersion of energy within chemicals which make up a chemical system in jk-1 mol-1
what does a greater entropy mean?
the greater the dispersal of energy and the greater the disorder
state the order of increasing entropies in solids, liquids and gas?
solid, liquid , gas
when can enthalpically unfavourable reactions(endotermic) still occur?
if changes in entropy overcome changes in enthalpy
what is the value of entropy at 0 kelvin?
0
state the entropy when reactants have more gas moles than products?
negative
state the entropy when products have more gas moles than reactants?
positive
give the entropy change formula?

what does gibbs free energy tell us?
if a reaction is feasible or not
define feasibility?
if a reaction will be able to happen
state the gibbs free energy equation?
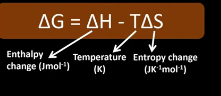
state the units of gibbs free energy?
Jmol-1
If Delta G is negative ($< 0$):
The reaction is spontaneous. It can occur without outside energy
If $\Delta G$ is positive ($> 0$):
The reaction is non-spontaneous. It requires work or energy to be put in.
If $\Delta G = 0$:
the system is at equilibrium.