Genetics Final
1/161
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
162 Terms
Bacteria grow and divide into two identical daughter cells by a process called what?
binary fission
We identify and count individual chromosomes in a cell by counting each chromosome's ______________ (i.e., the waist of the chromosome).
centromere
Cleavage furrows in human cells are caused by the actions of myosin motor proteins and cytoskeletal proteins called...
actin microfilaments
Chromosomes that contain the same genes, are the same size and shape and are inherited from separate parents are together called..
homologs
Different sequence variants of the same gene that occur within an individual or a population are called...
alleles
A new variety of the common garden pea has a diploid chromosome number of 4. Assuming no crossing-over events happen, how many possible genetically different types of reproductive gametes can an individual plant produce via meiosis?
4
Gametophytes ultimately produce gametes by what cellular process? mitosis, meiosis or fertilization
mitosis
The position of a single gene on a particular chromosome is called it's ________________.
locus
A cell containing the following number of sets of chromosomes can undergo mitosis?
diploid, triploid, haploid (all)
What is the name given to microtubules that extend through/around the nuclear DNA during prometaphase but don't specifically bind to each of the chromosomes?
polar microtubules
A woman from Venus generates her gametes through meiosis, just like human females do. Her secondary oocytes have 12 chromosomes, however. This means her diploid number is...
24
During oogenesis, the second meiotic division...occurs
only after fertilization by a sperm cell
In oogenesis, unequal cytoplasmic division result in a(n) __________________, a cell containing DNA but with very little cytoplasm.
polar body
Which of the following organelles contain genomic DNA?
nucleus
Crossing over actually occurs in ______________, a substage of prophase I in meiosis.
pachytene
Spectral karyotyping can be used to identify which of the following mutations in DNA?
translocations of DNA from one chromosome to another
In human spermatogenesis, how many chromosomes can be identified at the middle of anaphase I, the beginning of metaphase II and the middle of anaphase II, respectively?
46,23,46
What is the name of the stem cell that has decided to undergo meiosis to produce four sperm cells and has replicated its DNA already, but not divided yet?
primary spermatocyte
For a karyotype, DNA from white blood cells is harvested during what phase of the cell cycle?
Metaphase
A cell that exits the cell cycle is said to enter into a Go phase. If the cell stays in this phase and never divides again, it is said to be permanently resting, or...
senescent
If two characters are always inherited together (i.e., complete linkage), what is the expected ratio of offspring from a dihybrid cross?
3:1
In a dihybrid testcross, what is the total fraction of individuals demonstrating recombinant (i.e., non-parental) phenotypes?
1/2
You already have two kids, both girls. You want to have 5 kids total. What is the probability that you would have 3 girls and 2 boys in the end?
3/8
Carriers of a trait are often indicated by what in a family pedigree?
half shade
Mendel's Law of Segregation is explained mechanistically by the events of...
anaphase of Meiosis I
Mendel investigated specific traits that showed only this number of variants?
2
Flipping four pennies at the same time is expected to yield two heads and two tails how often?
3/8
Flipping three pennies in succession (i.e., one after another) is expected to yield heads, then tails, then heads again how often?
1/8
What is the following cross called: AaBbCc X aabbcc
a trihybrid test cross
The number of different types of genotypes produced in the offspring of a dihybrid self-cross is...
9
What is the scientific name of the pea plant Mendel used for his crosses?
pisum sativum
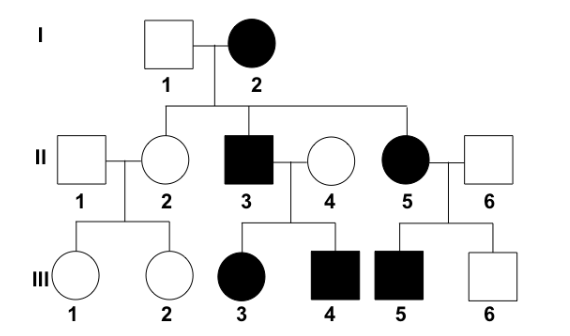
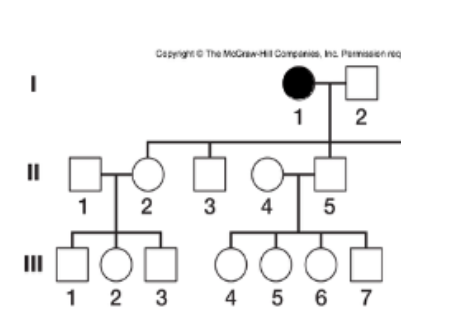
This is a dominant disorder. What is the probability that individual I-2 is homozygous?
0
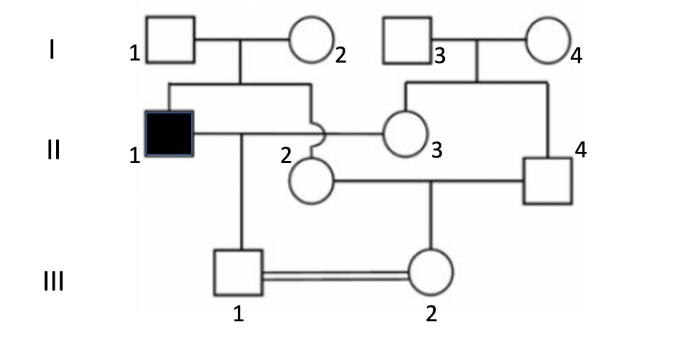
The disease depicted above is an autosomal recessive disorder.
What is the probability that II-2 is a heterozygote?
2/3
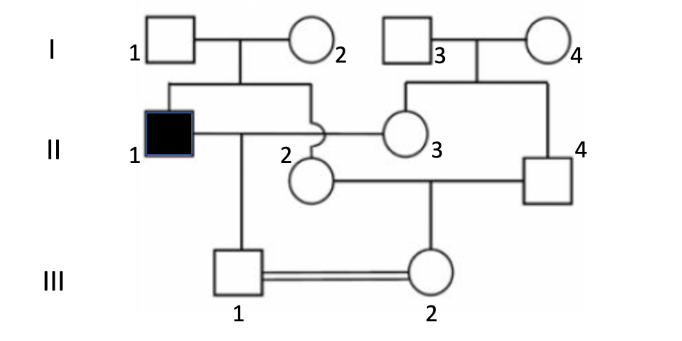
If III-1 and III-2 decide to have a child, what is the probability that it would have the disease?
1/4
The disease depicted above is an autosomal recessive disorder.
If III-1 and III-2 have kids, what is the probability that their first one WON'T have the disease?
35/36
In a family pedigree, the first reported diseased individual being studied is called the...
proband
How many alleles are required to show a recessive phenotype?
2
Which of the following is a true breeder?
AAbbccdd
W+W+ : Number of recessive alleles are ( ) Phenotype is "mutant" or "WT" .
2; WT
W+W : Number of recessive alleles are ( ) Phenotype is "mutant" or "WT"
1; mutant
w+w+ : Number of recessive alleles are ( )Phenotype is "mutant" or "WT" .
0; WT
ww+ : Number of recessive alleles are ( ) Phenotype is "mutant" or "WT"
1; WT
ww : Number of recessive alleles are ( )Phenotype is "mutant" or "WT" .
2; mutant
A male fruit fly increases expression of the X chromosome 2 fold by use of the __________________ complex.
dosage compensation
Female chickens are considered the _______________ sex, meaning that they produce two different gametes that will decide the sex of the offspring.
heterogametic
_______________ pattern of inheritance is when each parent passes their phenotype to their opposite-sex offspring.
criss cross
Dull spikes in porcupines is a sex-influenced trait. The Dull spiked allele acts recessive in males but dominant in females. If two heterozygous porcupines mate, what is the proportion of sharp spiked sows (i.e., female porcupines) that will be born from all offspring?
1/8
The presence of a 5th eye in Martian males (compared to the normal 4) is a sex-limited, dominant trait in males. Predict the ratios of the offspring phenotypes (including sex) from the breeding of two individuals that carry this mutation.
0 -5th eye females: 4- normal females: 3- 5th eyed males: 1- normal male
0/8, 4/8, 3/8, 1/8
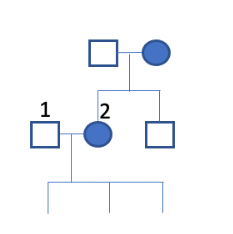
Brown spotting of teeth in humans is a dominant X-linked disease. If man 1 and woman 2 decide to have three children, what is the probability they will have two daughters with brown teeth and a son with normal teeth
3/64
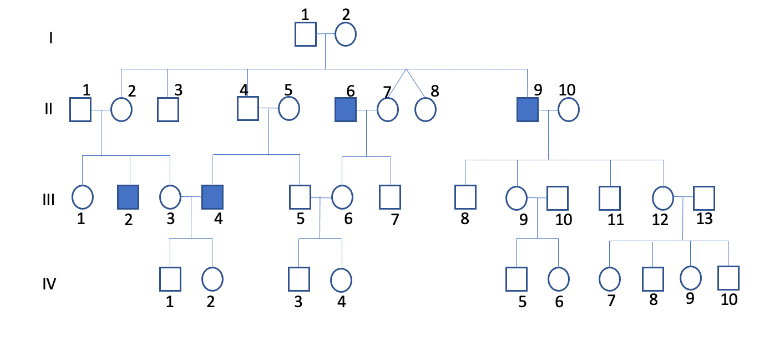
The following pedigree is for an X-linked recessive disorder. If individual IV-2 marries IV-3, what is the probability that their first child will be colorblind?
1/4
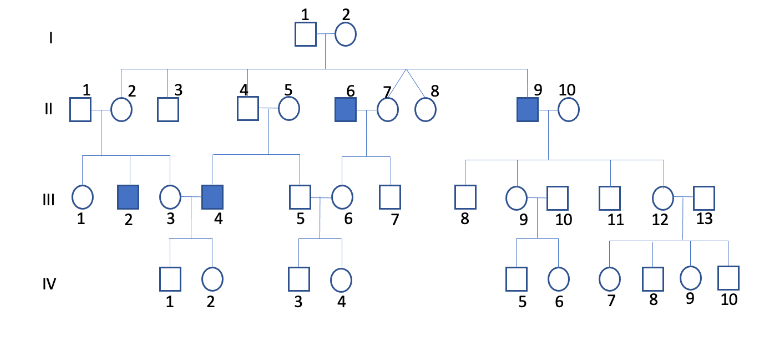
The following pedigree is for an X-linked recessive disorder. If individual II-1 and II-2 decide to have two more children, what is the probability that 1 would be colorblind while the other has normal vision?
3/8
The Lyon hypothesis has been used to explain the phenotype of "brindle" and "calico" cats. What is the mechanistic cause of this phenotype?
the random inactivation of the X chromosome in females
The urge to be awake (E, the energized gene on Chr 2 in humans) is due to a balanced mutation (i.e., heterozygous advantage) that occurs in a protein that forms a dimer (two E proteins need to work together). The extremes of the condition, either the “early riser” or the “night owl”, occur in individuals that are homozygous and result in difficulties staying awake either late at night or early in the morning, respectively. If two super ability parents (they are each both early risers and night owls) are looking to have a child, what is the probability that it would be a daughter who possessed both of these super abilities?
1/4
In blood typing biochemistry, the FUT1 protein completes the H structure by adding a fucose sugar. This addition then allows the ABO enzyme to either add an N-acetyl-galactosamine (IA allele) or galactose (IB allele). If the enzyme is inactive (i allele), no sugar modification is subsequently added. If two individuals, genotypes Ff IAi and ffIBi, decide to have children, what is the probability of an “O” blood type in their 1st child?
5/8
What is the expected fraction of hypostatic individuals with a recessive phenotype with a trait controlled by dominant epistasis in the following cross where “A” is the epistatic gene: AaBb x Aabb
1/8
Two genes are involved in producing the pigment that gives hair a red tint. Assuming a decreasing gene dosage model for no tint, pink and flaming red occur as phenotype groups (IN THAT ORDER), what is the expected phenotypic outcomes of this cross: Rrpp X RrPp3 No tint: 4 pink: 1 flaming red
3/8 none, 4/8 pink, 1/8 red
Double-jointed thumbs is an autosomal dominantly inherited disorder that shows incomplete penetrance (75%). If a double-jointed heterozygous couple decide to have a child, what is the chance they will have double joints
?Achondroplasia (dwarfism) results from the inheritance of a single defective allele. This trait is also recessively lethal. If Gimli (a dwarf of short stature) finds his dwarven soul mate (who is also a dwarf of short stature), what is the probability that they would have a normal height child that would be shunned and need to leave the colony in normal height shame?
1/3
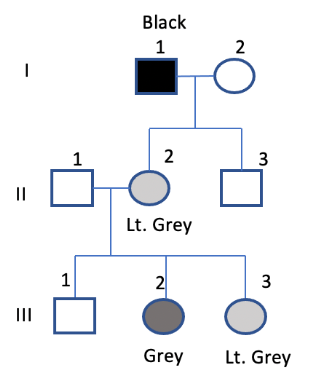
The figure above shows an autosomal dominant trait such as Polydactyly with variable expressivity and incomplete penetrance (50%). If individual II-1 and II-2 decide to have another child, what is the probability they would NOT show the trait. Assume I-2 and II-1 are non-carriers
Mutations in a specific biochemical pathway leave a person feeling melancholy (i.e. sad). Assuming complementary gene action to feel "happy", what is the proportion of individuals that are expected to be melancholy if crossing two individual with the following genotypes:
AaBbccDd x AabbCcdd
Expression of a deletion or mutant version of the AS (the Angelman syndrome) gene results in a disease characterized by delayed development, intellectual disability and severe speech impairment…Children typically have a happy, excitable demeanor with frequent smiling, laughter and hand-flapping movements. Predict the chance of having a child with this disease from a father who carries the deletion and a mother with two normal alleles.
0%
Chlamydomonas is a haploid, single-cell algae. After fusion of two cells (one mt+, the other mt-), the zygote undergoes meiosis to produce four daughter cells. Which answer is true concerning chloroplast inheritance?
all offspring inherit their chloroplasts from the mt+ parent
de novo imprinting in humans means that a brand new __________ group is added to a cytosine base in genomic DNA in only a single parent.
methyl
Erasure of imprinting occurs during
spermatogenesis and oogenesis
BIG is an autosomal, paternally imprinted (& expressed) gene in Martians that represses body size. Therefore, having a single mutant allele (B-) of this gene results in gigantism if its the allele that is expressed. If a BB- normal size male mates with a B-B- giant female, what is the probability of having a giant son?
½ giant x ½ male = ¼
Igf2 Igf2 (mom) x 1gf2- Igf2- (dad) Igf2 controls normal growth of mice. A mutant allele when expressed causes dwarfism. Which is of the following is true concerning this cross?
the father imprints, turning his alleles on. Their offspring will only express this gene from the father and will be dwarf sized
D is the dextral allele, d is the sinistral allele.
Parent are both heterozygous (Dd). Their shell shapes are both sinistral.
What is the phenotypic ratios (snail shell spiraling) of the offspring
all dextral
D is the dextral allele, d is the sinistral allele.
The Male parent's shell is dextral shape, the female parent's shell spiral is sinistral shape.
The male is homozygous recessive. The female is homozygous dominant.
What is the phenotypic ratios (snail shell spiral) of the offspring?
all dextral
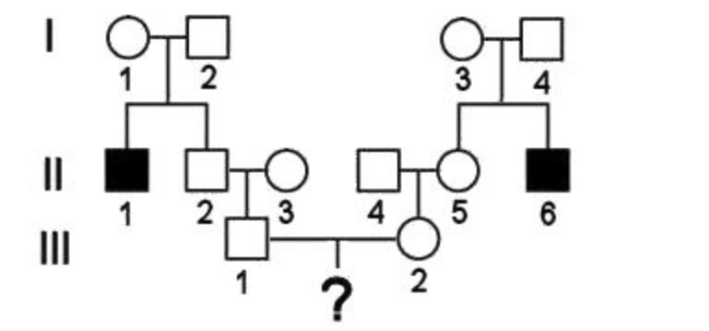
If you were to shade in the rest of this pedigree, which individuals below should be expected to show this maternal inheritance trait?
II-2
________________ is the term we use to describe a cell that contains multiple mitochondria which are similar in their chromosomal DNA sequences.
homoplasmy
The mitochondrial genome contains some of the genes needed for mitochondrial function. In other words, there are some mitochondrial genes located in the nucleus.
true
Plant cells have only chloroplasts; animal cells only have mitochondria.
false
Explain why variegation (the random patches of green and white colors) occurs to the leaves of some plant species.
Since the female gamate is larger the offspring inherit all of their chloroplasts from the mother (maternal inheritance). If the mother's chloroplasts are all white or all green then the offspring will be all white or green. However, if the mother is variegated, meaning a mixture of both green and white, the offspring can have variegation. This is due to the unequal distribution of chloroplasts during cytokinesis. Some areas may have all white, all green, or a mixture of green and white chloroplast cells.
If a single crossover forms across non sister chromatids between the two genes in the dihybrid individual of a dihybrid test cross, we will see two recombinant phenotypes in the offspring.
true
Which phenotypic reciprocal class occurs most often in a trihybrid testcross of three linked genes?
non crossover reciprocal class
A trihybrid female drosophila fly for the sex linked traits yellow body (y), miniature wings (m) and white eye (w) mutations was test crossed and produced the following offspring. What alleles are on each of the original, parental female fly's chromosomes? Make sure to use Morgan fruit fly nomenclature to describe the mutant and wild type alleles. Note: for this question, you don't need to tell me what gene is in the middle.
For example write: 1st chromosome has ___, ___, and ___ alleles; 2nd has ___, ___, and ___
WT - 758
miniature wings - 401
white eyes - 1
white eyes, miniature wings -16
yellow - 12
yellow, white - 317
yellow, white, miniature - 700
1st chromosome has : y+, w+, m+
2nd chromosome has: y, w, m
A trihybrid female drosophila fly for the sex linked traits yellow body (y), miniature wings (m) and white eye (w) mutations was test crossed and produced the following offspring. What gene is in the middle?
WT - 758
miniature wings - 401
white eyes - 1
white eyes, miniature wings -16
yellow - 12
yellow, white - 317
yellow, white, miniature - 700
the white eye gene (w)
A trihybrid female drosophila fly for the sex linked traits yellow body (y), miniature wings (m) and white eye (w) mutations was test crossed and produced the following offspring. What are the most accurate distances between the genes? I need three separate answers: Y-M; Y-W; and M-W
WT - 758
miniature wings - 401
white eyes - 1
white eyes, miniature wings -16
yellow - 12
yellow, white - 317
yellow, white, miniature - 700
y-m = 33.91 mu
y-w = 1.31 mu
m-w = 32.61 mu
We can see (with a microscope) the actual site of where crossing over has already occurred across a pair of homologs in meiosis during what subphase of Prophase I?
diplotene
What is the expected fraction of recombinant phenotypes in a dihybrid testcross with two independently assorting genes showing Mendelian inheritance?
1/2
The main reason that a dihybrid testcross is conducted is to determine the identity of the second alleles for each gene in a phenotypically dominant (for both genes) individual.
false
Mitotic crossing over in a dihybrid individual can inadvertently lead to _________________, an unusual phenotype where adjacent tissues display separate recessive mutant phenotypes not displayed anywhere else in a wildtype organism.
twin spotting
Nonallelic homologous recombination could be the cause of a duplicated region in a chromosome
true
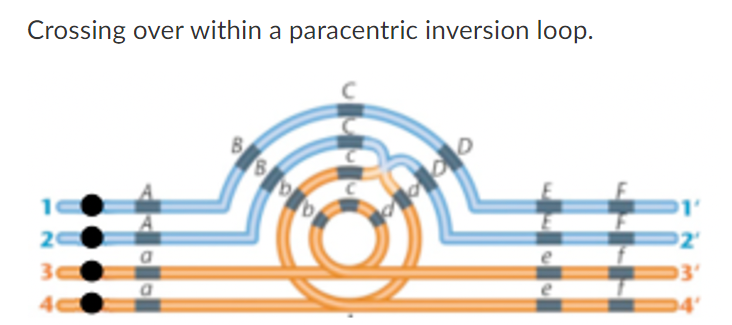
In the above figure, the black dots represent centromeres. The positions of each of the genes (A through F) have been indicated. A single crossing over event has taken place between the C and D genes. The non-recombinant chromosomes are summarized here with the + sign indicating the centromere:
chromosome 1: +ABCDEF
chromosome 3: +adcbef
Notice the inversion in chromosome 3. For this question, indicate what chromosome 2 and 4 will look like after crossing over has completed. Indicate the position of a centromere by using a + sign as well:
2: +ABCda+ -dicentric chromosome
4: FEDcbef -accentric fragment
The majority of autosomal aneuploid conditions are lethal, but sex chromosome aneuploids are commonly viable.
true
An allotetraploid individual can be fertile if psuedodiploid. Explain a case in which the allotetraploid individual would NOT be fertile.
The allotetraploid would not be fertile if the chromosomes could not pair during meiosis. An example that comes to mind is when a horse and donkey make a mule. The mule is viable but cannot have offspring because its chromosomes do not match up and pair during meiosis. An individual can have 6 sets of chromosomes but since they cannot be split into 3 and 3 in meiosis they are non-viable gametes.
During ______________________ segregation of a translocation cross, all gamete cells that form will be able to produce viable offspring.
alternative
A chromosome with its centromere that is slightly off center (thus creating arms of different sizes) is morphologically called a ________________ chromosome.
submetacentric
What is the common name given to a q-arm, q-arm fusion mutation?
Robertsonian Translocation
Crossing over inside a pericentric inversion loop results in how many different gametic chromosomes?
4
A _______________ deletion is the loss of genomic material from the end of a chromosome.
terminal
Reciprocal translocations can be the result of _____________________ recombination (crossover), an accidental repair mechanism using repetitive sequences on two unrelated chromosomes. For example if crossing over occurred between chromosome 5 and 10.
nonhomologous
Familial Down syndrome occurs due to a q-arm q-arm fusion involving chromosome 21 and another chromosome such as chromosome 14. If a phenotypically normal child is born from a man who is known to carry this translocation (wife is a non carrier), what is the probability that this child will carry the translocation? (think this through before answering)
1/2
Variations in complete sets of chromosomes is referred to as
euploidy
Failure to separate chromosomes properly into the two daughter cells is referred to as.......
nondisjunction
Polytene chromosomes in only the salivary gland cells of the fruit fly is an example of _____________, meaning that the different tissues of the fly contain different sets of chromosomes.
endopolyploidy
A reciprocal translocation is a genomic alteration that involves the transfer of DNA from one chromosome to another non-homologous chromosome.
false
Treatment of heat killed S-type bacterial extracts by Avery, MacLeod, McCarty with which reagent prevented the conversion of R-type to S-type in their hands?
DNase
What is the gap size of the minor groove in B-DNA? Make sure to use a label for units.
12 A
Chargaff's data/ratios ultimately indicates that for any species
A+C = T+G