bio2
1/29
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
30 Terms
cell
most basic unit of life
characteristics of cell
1. Microscopic
2. Membrane
3. Cytoplasm
Eukaryotic cells
-has a nucleus and other membrane bound organelles.
-may be single or multicellular organisms.
-has a cytoskeleton.
Cytoplasm
-important contributor to cell structure
-made up of mostly water
-many chemical reactions
Mitochondria
-cells “powerhouse”
-supplies energy to cell
-chemical reactions converts food into usable energy
Chloroplasts
-carries out photosynthesis
-highly compartmentalized
-contains thylakoids (disc-shaped sacs)
Cell Membrane
-forms boundary between cell and outside
-controls passage of materials
-selectively permeable - some methods of transport require energy, some do not
-double layer of phospholipids
-receptors made of proteins. when bind make ligands and change shape. affects how receptor interacts with other molecules.
Phospholipids
-molecule composed of 2 basic parts
-phosphate and glycerol form “head” (loves water)
-fatty acid forms “tail” (hates water)
Molecules embedded in membrane
-cholesterol - support
-proteins - gates
-carbohydrates - “identification tags”
Fluid Mosaic Model
describes arrangement of molecules in cell membrane.
Passive transport
no energy needed to pass
Diffusion
-high concentration to region of low concentration
-plays important role in movement of carbon dioxide and oxygen molecules
-facilitated diffusion - larger molecules can still diffuse through opens formed by transport proteins (still passive)
When concentration is equal in a concentration gradient
reaches dynamic equilibrium
Osmosis
diffusion of water molecul,es
Active Transport
-requires energy by cell to move materials in or out of cell
-uses energy from ATP molecule
-“cell eating”
-key role in immune system (white blood cells)
Exocytosis
-releases substances from cell
-vesicle moves to cell membrane, fuses, and then lets go of its contents out the cell
-occurs constantly in body
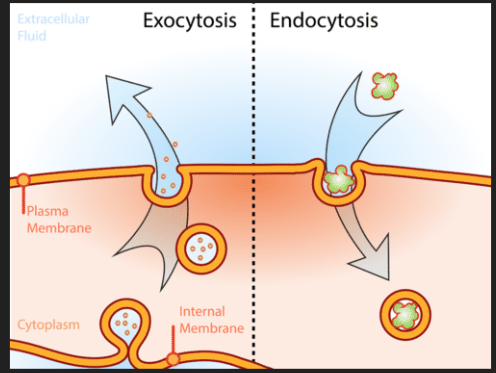
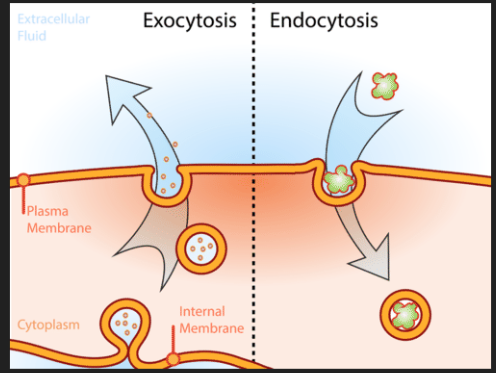
Nucleus
-storehouse for genetic material
-2 demands: protects DNA and must be available for use at proper time
-encased in nuclear envelope with pores that allow molecules to go in
Nucleolus
makes ribosomes
Rough ER
-studded with ribosomes
-makes proteins and lipids
Smooth ER
-makes lipids
-helps break down drugs and alcohol
Ribosomes
-composed of RNA and proteins
-site of protein production
Golgi Apparatus
-cells “post office”
-packages/stores/delivers proteins
Vesicles
-stores separate reactants for various chemical reactions
-membrane bound sacs
-transports materials
Vacuole
-fluid-filled storage sacs
-stores water, food, inorganic ions, enzymes
Lysosomes
-”destruction” sacs
-defends cell from invading viruses and bacteria
-breaks down damaged and worn-out cell parts
-not in plant cells
Centrosome
-small region of cytoplasm that produces microtubules
-in animal cells, contains two centrioles; cylinder-shaped organelles made of microtubules
-helps cell division in animal cells
Cilia and flagella
made of microtubles