MCAT Organic Chemistry - Aldehydes and Ketones I: Electrophilicity and Oxidation— Reduction
1/14
Earn XP
Description and Tags
whoever rated this one star: really?
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
15 Terms
carbonyl group
a double bond between a carbon and an oxygen; strong dipole moment; no hydrogen bonding; electrophilic carbon
ketone
has two alkyl groups bonded to the carbonyl; never a terminal group
IUPAC: alkane - -e + -one
common names: alphabetical alkyl gorups + ketone; acetone, ethylmethylketone
substituents: oxo-/keto-
ring: -carbaldehyde
aldehyde
has one alkyl group and one hydrogen; always a terminal group
IUPAC: alkane - -e + -al
common names: formaldehyde, acetaldehyde, propionaldehyde, butyraldehyde, valeraldehyde
substituents: oxo-
ring: -carbaldehyde
pyridinium chlorochromate (PCC; C5H5NH[CrO3Cl])
weak oxidant; turns terminal/primary alcohol to aldehyde
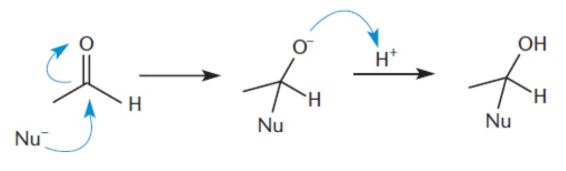
Nucleophilic addition reaction
The nucleophile attacks the carbonyl carbon, opening the carbonyl. The carbonyl cannot reform because there is no good leaving group; thus, the O– is protonated to generate an alcohol
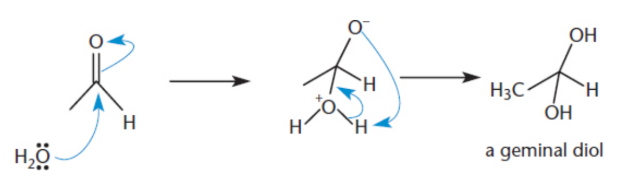
Hydration of carbonyls
In the presence of water, aldehydes and ketones react to form geminal diols 1,1-diols)
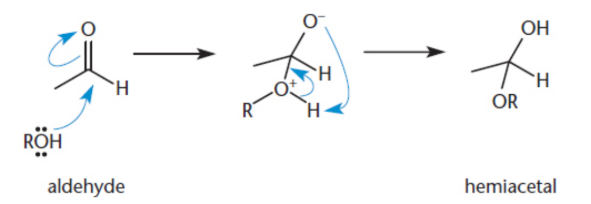
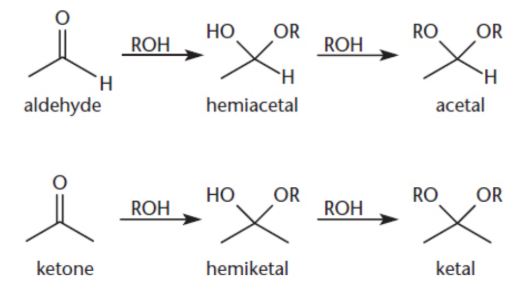
hemiacetal/hemiketal
when aldehydes and ketones are treated by one equivalent of alcohol
acetal/ketal
when aldehydes and ketones are treated by one equivalent of alcohol
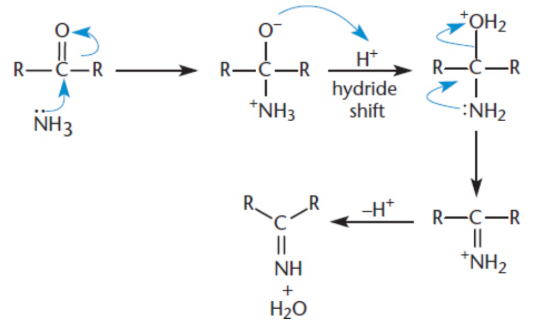
imine
a compound with a nitrogen atom double-bonded to a carbon atom; Ammonia is added to the carbonyl, resulting in the elimination of water and generation of an imine
nucleophilic substitution (SN1/SN2)
leaving group is replaced by nucleophile
common ammonia derivatives that react with aldehydes and ketones
hydroxylamine (H2N−OH) → oximes
hydrazine (H2N−NH2) → hydrazones
semicarbazide (H2N−NH−C(O)NH2) → semicarbazones
enamines
Imines and related compounds can undergo tautomerization to contain both a double bond and a nitrogen-containing group
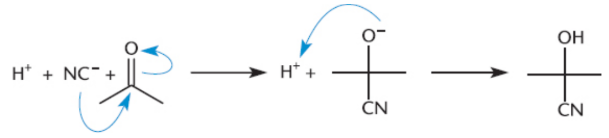
cyanohydrins
hydrogen cyanide (HCN; pKa 9.2) with aldehydes and ketones
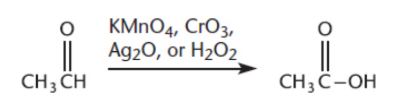
Oxidation of Aldehydes
form carboxylic acids
oxidzing agents: potassium permanganate (KMnO4), chromium trioxide (CrO3), silver(I) oxide (Ag2O), and hydrogen peroxide (H2O2)
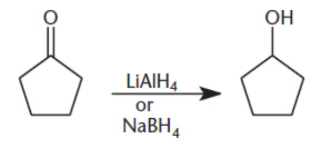
Reduction by Hydride Reagents
lithium aluminum hydride (LiAlH4) and sodium borohydride (NaBH4)