Chapter 14-16
1/35
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
36 Terms
Aggregate Demand (AD)
Total spending on goods and services in a period of time at a given price level (Price level vs real GDP)
inverse relationship (lower average price level = high average demand)
Long Run Aggregate Demand (LRAD)
AD = C + I + G + (X - M) where C is consumption, I is investment, G is government spending, X is exports, and M is imports.
Non-price determinants of Consumption:
TWICED
NPDC: Income Taxes
higher income = higher consumption
higher income tax = lower consumption (less disposable income)
NPDC: Wealth
Higher house prices or stock value = higher consumption.
NPDC: Interest Rates
higher interest rates = less borrowing -> lower consumption
lower interest rates = higher consumption (ceteris paribus)
NPDC: Consumer Confidence
Higher consumer confidence leads to higher consumption.
NPDC: Debt
easy to borrow money + low interest = higher debt willingness + consumption
Non-price determinant of investments
IB-TBD
NPDI: Interest
higher interest rate = lower investments
NPDI: Business Confidence
optimistic about future = higher investments
NPDI: Technology
increase in tech = higher investments
NPDI: Business Taxes
higher taxes = reduced post-tax profits = lower investments
NPDI: Corporate indebtedness
easy to borrow money + low interest = higher debt willingness + investment
Non-price determinants of Government Spending:
economic + political priorities
commitment to support industry = higher spending
correct market failure = higher spending
Non-price determinant of net exports: Imports
higher domestic income = higher imports
higher exchange rate = higher imports
lower restrictions on trade = higher imports
lower inflation rates of foreign partners = higher imports
Non-price determinant of net exports: Exports
increased foreign incomes = higher exports
higher exchange rate of currency = lower exports
lower restrictions on trade = higher exports
higher inflation rate = lower exports
Aggregate Supply (AS)
Total amount of goods and services produced by all industries at every price level.
Short Run Aggregate Supply (SRAS)
period of time where FoP do not change; fixed price of labour, positive relationship between price level and real GDP.
Non-price determinant of SRAS: Cost of Resources
wage rates (increase in wages = increase in cost of FoP -> lower AS)
cost of raw materials (higher costs = lower AS)
dependent on how widely used the material is
price of imports (increase in price = higher cost of production -> lower AS)
Non-price determinant of SRAS: Government Intervention
subsidies (increased subsidies = higher AS)
taxes (increased taxes = lower AS)
regulations (more regulations = lower AS)
Non-price determinant of SRAS: Supply Shocks
natural disasters or wars = less supply
Long Run Aggregate Supply (LRAS)
keynesian and neo-classical views
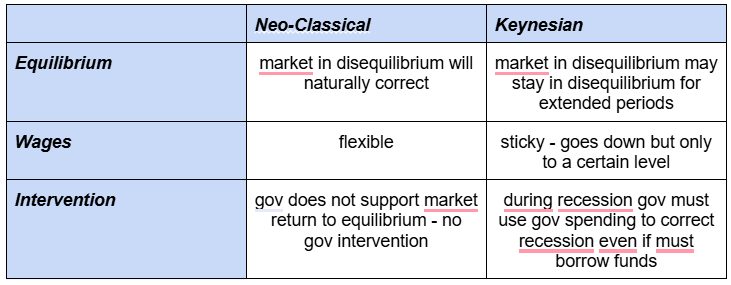
Neo-classical view of LRAS
Belief in market efficiency and minimal government intervention
LRAS = perfectly inelastic
full employment level
independent of price level
Keynesian view of AS
3 phases:
1. AS is perfectly elastic
spare capacity
increase output without high costs
2: approaching potential output
use up spare capacity
FoP more scarce
FoP cost more
rising price levels
3: full capacity
impossible to increase output
AS perfectly inelastic
Non-price determinants of LRAS:
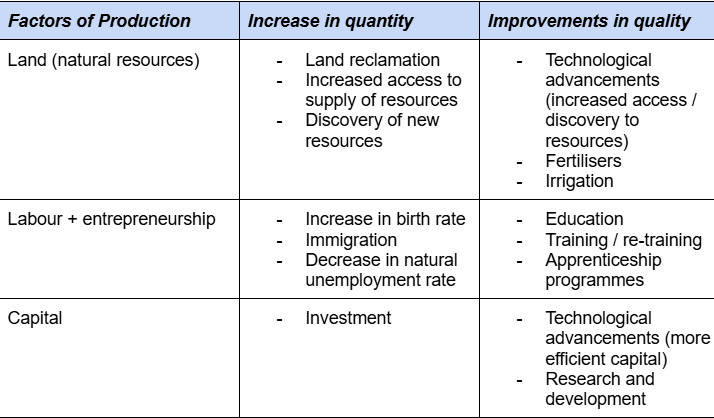
Change in quantity or quantities of FoPs
Technological improvements
Increase in efficiency
Changes in institutions
Factors influencing quality / quantity of FoPs:
Short run equilibrium
State when AD meets AS; no incentives for price or output to change, no inflation/deflation
Long run equilibrium (neo-classical)
When AD equals LRAS, indicating an economy at full employment.
Recessionary Gap
Equilibrium level of real output is less than potential output due to decreased AD.
Inflationary Gap
Equilibrium level of real output exceeds potential output due to increased AD.
Stagflation
inflation but no economic growth
Long Run Equilibrium:
short run = inflationary and recessionary gaps exists
long run = equilibrium point must return to LRAS (full employment)
Long run equilibrium (Keynesian)
Economy at equilibrium below full employment levels due to AD
AS = perfectly elastic -> spare capacity + unused FoP
Shifts in AD
first shift -> no change in price, only change in output
second shift -> slight inflationary pressure, increased price + output
third shift -> purely inflationary shift, only change in price, no change in output
Neo-classical vs Keynesian equilibrium