Chapter 2 - The Brain & The Nervous System
1/30
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
31 Terms
Phrenology
Pseudoscience that attributed the moral character of a person to the shape/bumps on their skull
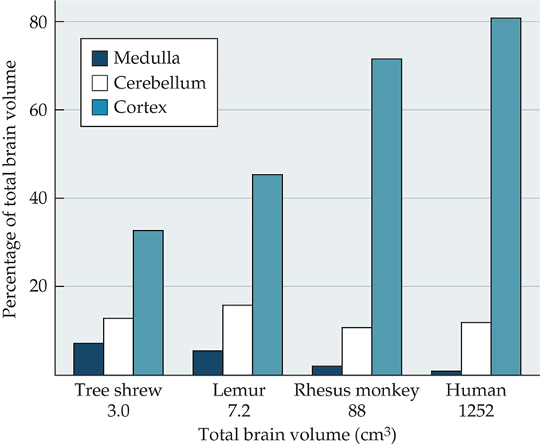
Brain Size in Humans
Compared to our close evolutionary relatives, our cortex is much larger and more layered relative to brain size
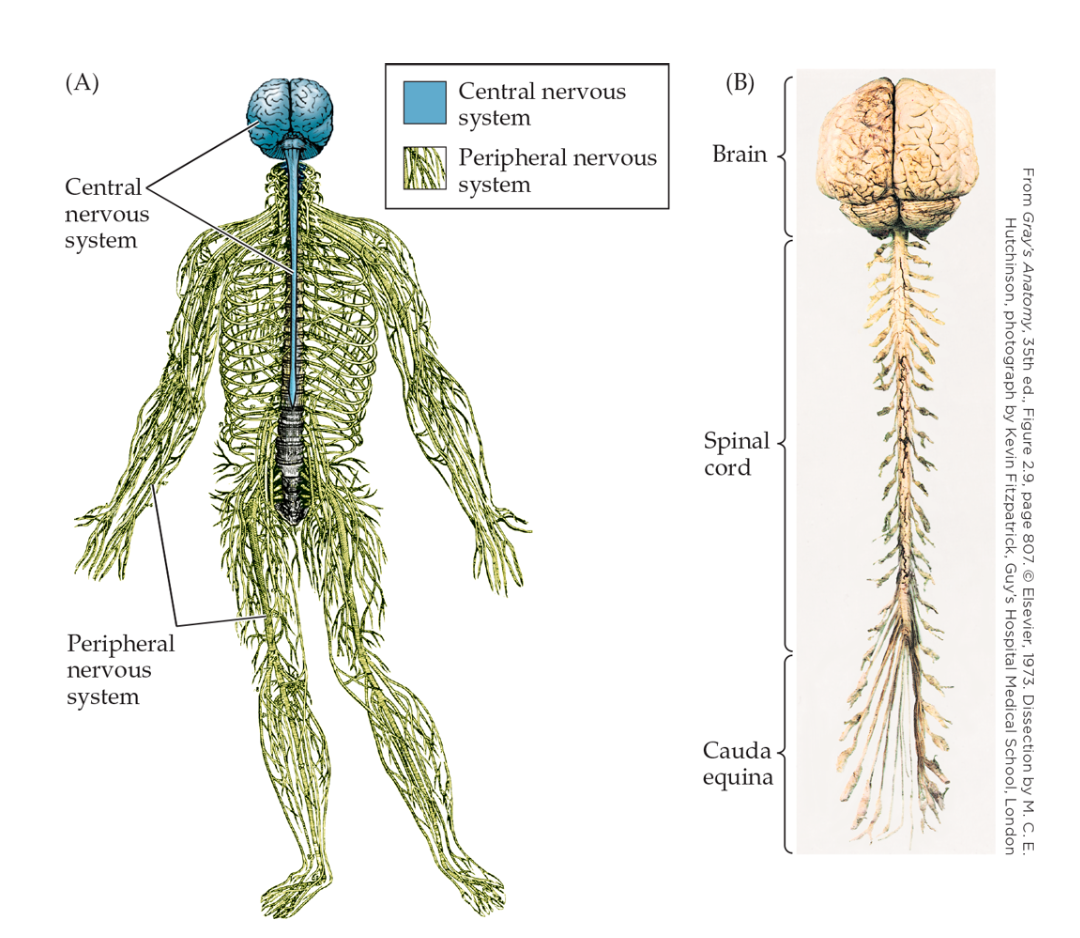
The Central Nervous System (CNS)
Brain and Spinal cord
The Peripheral Nervous System (PNS)
Everything Else
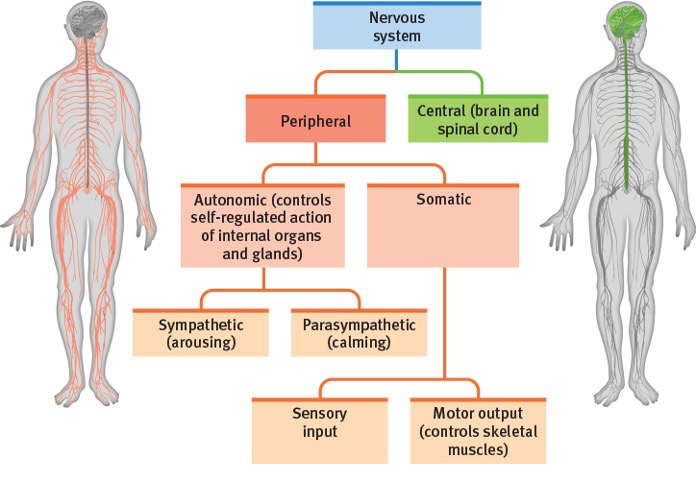
The Peripheral Nervous System’s Divisions
Somatic Nervous System and Autonomic Nervous System
Purpose of the Somatic Nervous System
Sensing and musculoskeletal output (motor control; voluntary and involuntary reflexes)
Part 1 of the Somatic Nervous System
Cranial Nerve: 12 nerves that are directly connected to our brain; generally transmit motor and sensory info from the head/face - vagus nerve is the exception that involves internal organ signaling and sensing
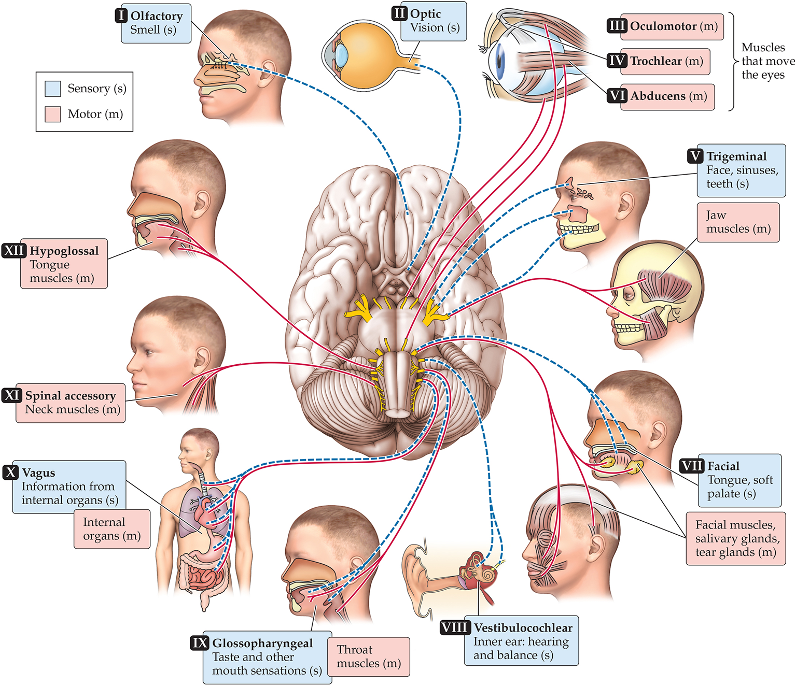
Part 2 of the Somatic Nervous System
Spinal Nerves: 31 pairs of nerves that act as the communication pathway between the CNS and the rest of the body - 8 cervical, 12 thoracic, 5 lumbar, 5 sacral, and 1 coccygeal
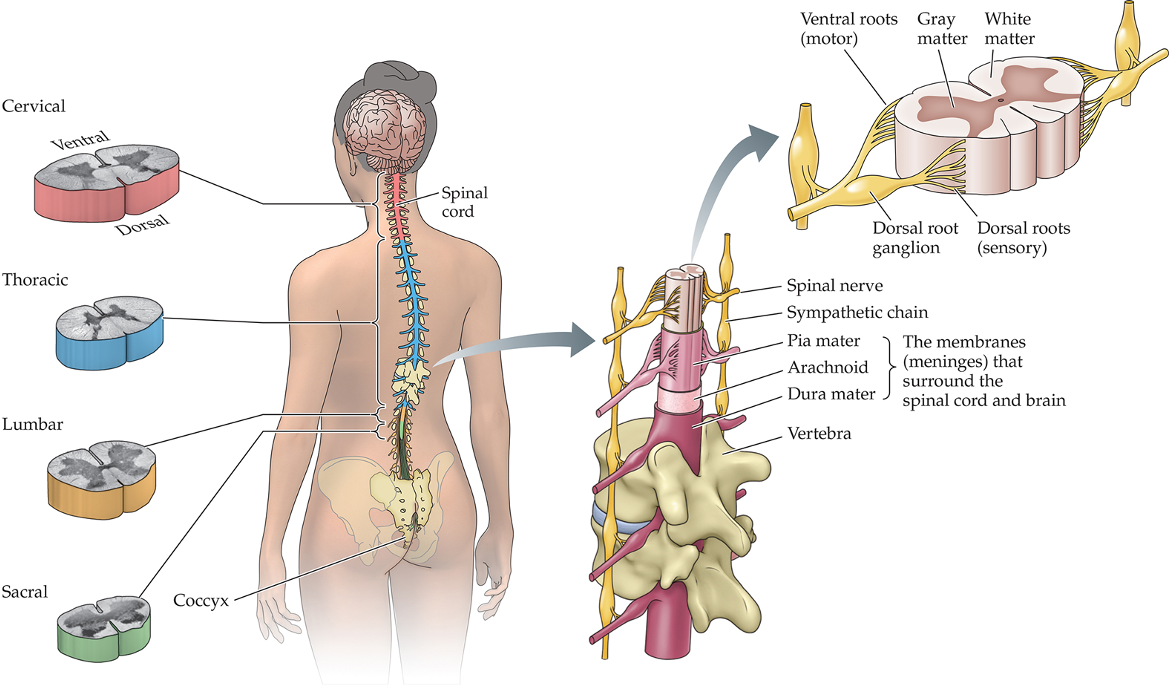
Purpose of the Autonomic Nervous System
Controlling involuntary bodily functions (internal organs; regulatory processes)
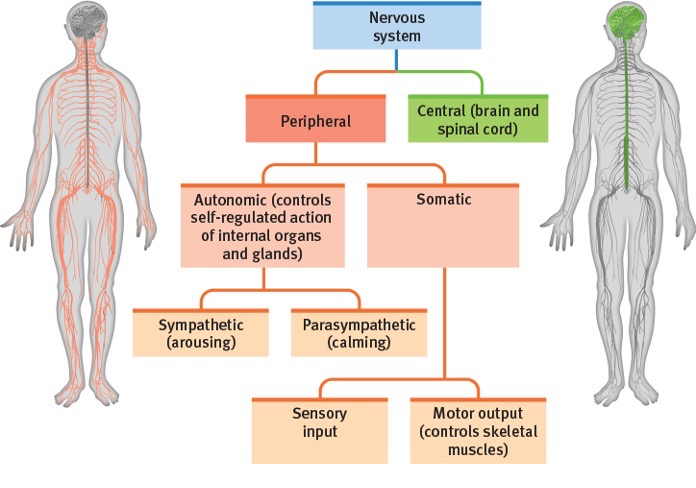
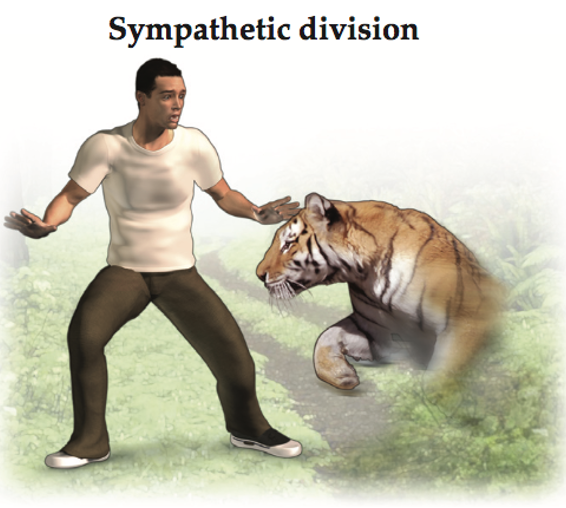
Part 1 of the Autonomic Nervous System
Sympathetic Division: “fight or flight”
releases noradrenaline/norepinephrine;
signals via a ganglion near the spinal cord

Part 2 of the Autonomic Nervous System
Parasympathetic Division: “rest and digest”
releases acetylcholine
signal via a ganglion near target organ

Anatomical Planes of the Brain
Horizontal Plane, Sagittal Plane, and Coronal Plane
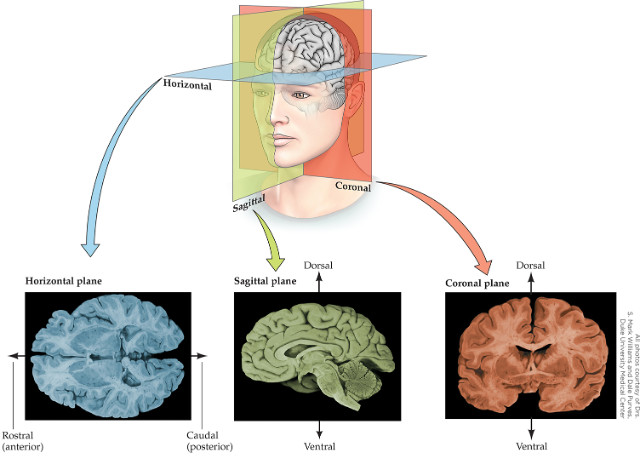
Anat Term: Medial
towards the middle
Anat Term: Lateral
towards the outside
Anat Term: Rostral
towards the front
Anat Term: Caudal
towards the back
Anat Term: Dorsal
towards the top
Anat Term: Ventral
towards the bottom
Brain Organization: Cortex
Thick outermost layer of gray matter on the brain;
Contains two hemispheres connected by the corpus callosum, with each hemisphere carrying 4 lobes
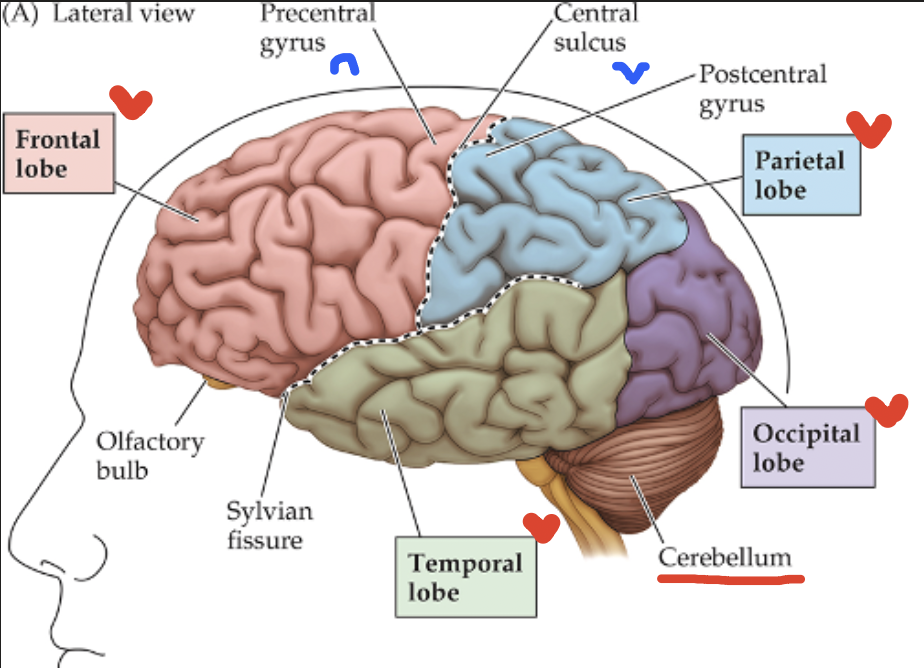
Cortex Surface features
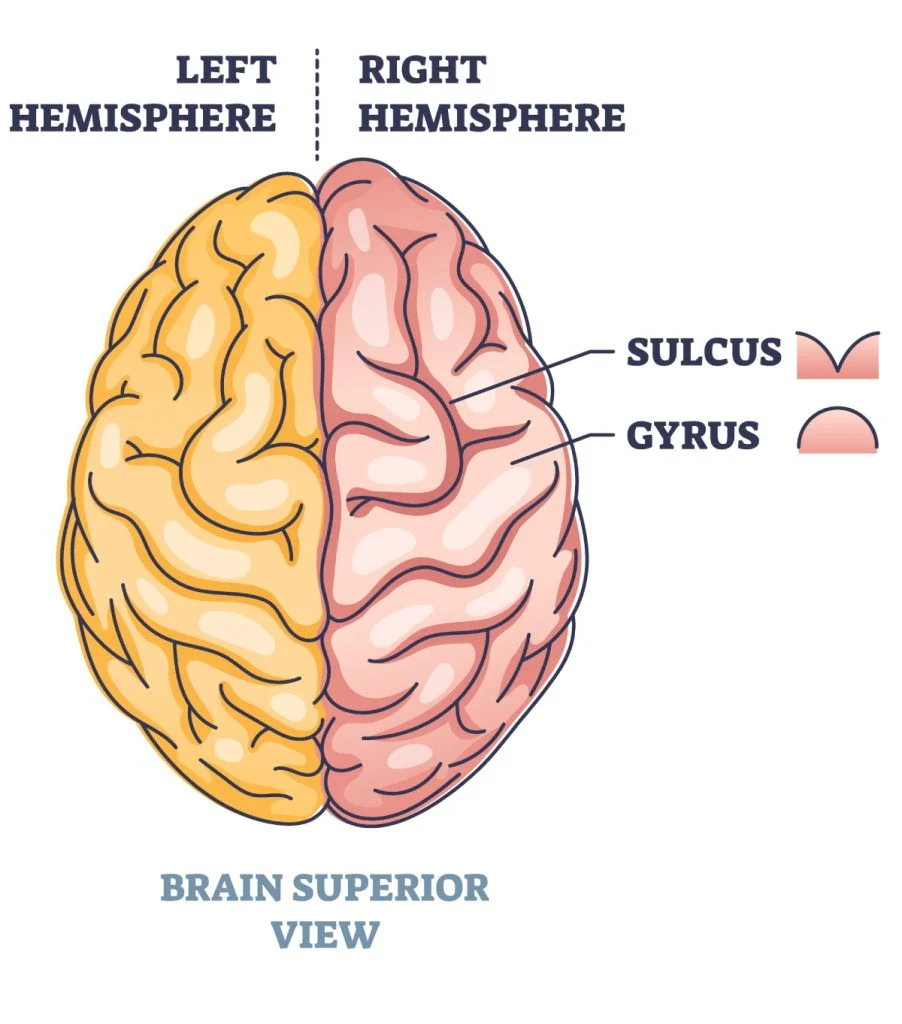
Gyri (gyrus): rounded ridges of the cortex;
Sulci(sulcus): furrowed grooves between the gyri
Cortex: red lobe
Frontal Lobe
Cortex: blue lobe
Parietal Lobe
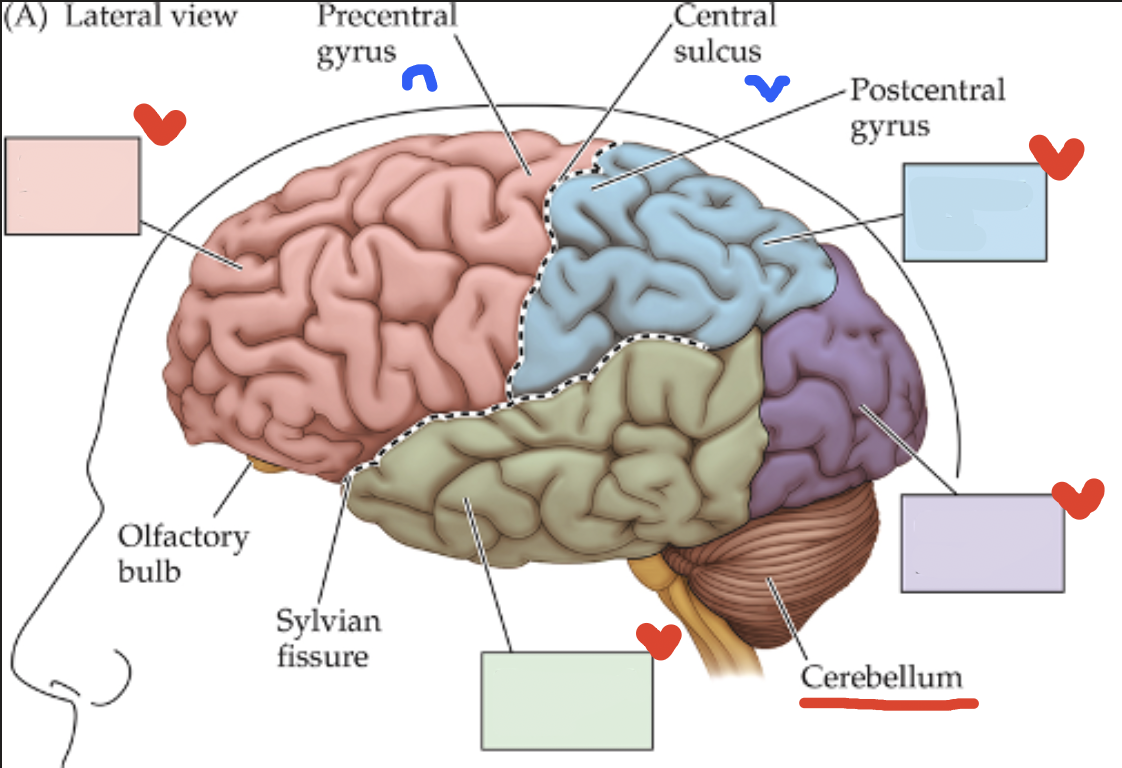
Cortex: green lobe
Temporal Lobe
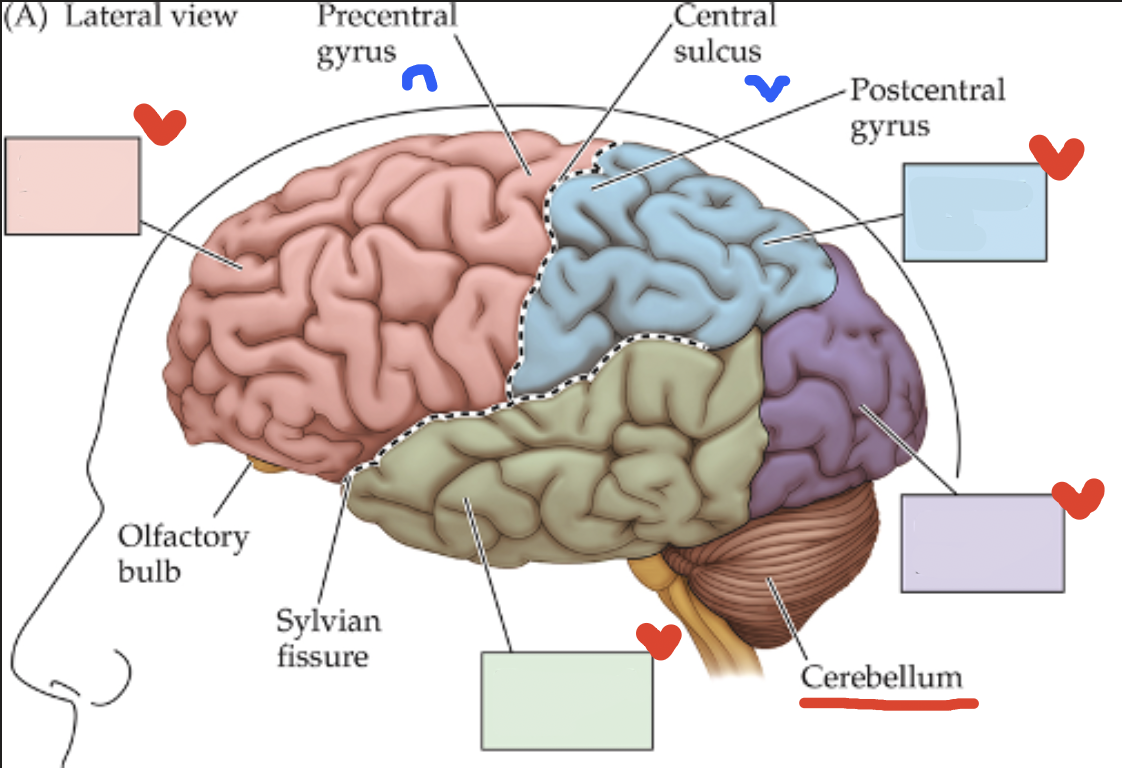
Cortex: purple lobe
Occipital Lobe
Brain Organization: Diencephalon
Thalamus: sensory processing unit with over 50 individual regions;
Hypothalamus: maintains internal body balance (homeostasis)
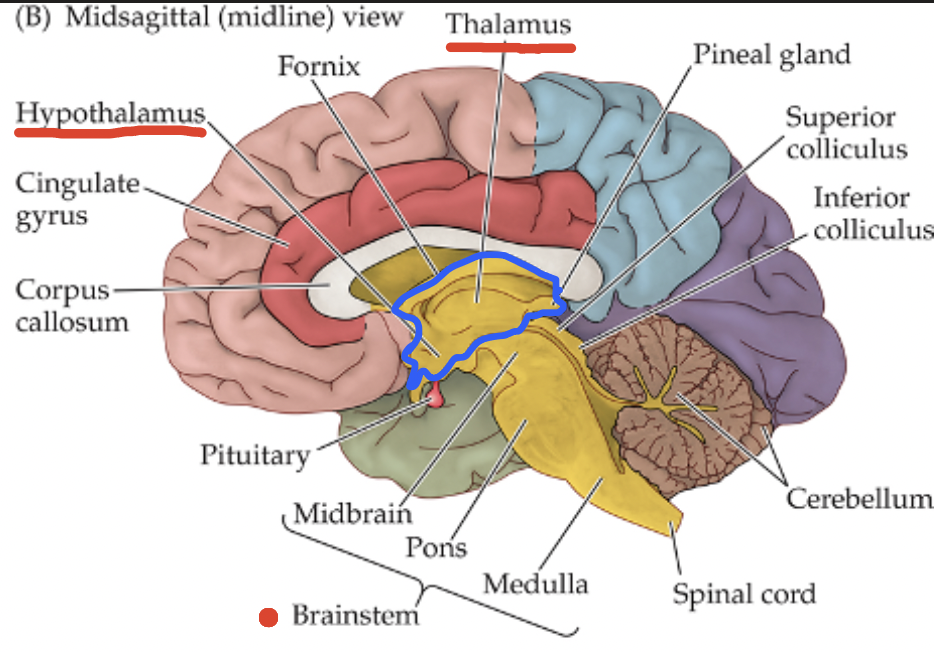
Brain Organization: Brainstem
Midbrain: aids in motor control and sensory processing;
Pons: regulates circadian rhythm, arousal, and basic sensory functions;
Medulla: involves critical involuntary function that support life (breathing, heart rate, etc.)
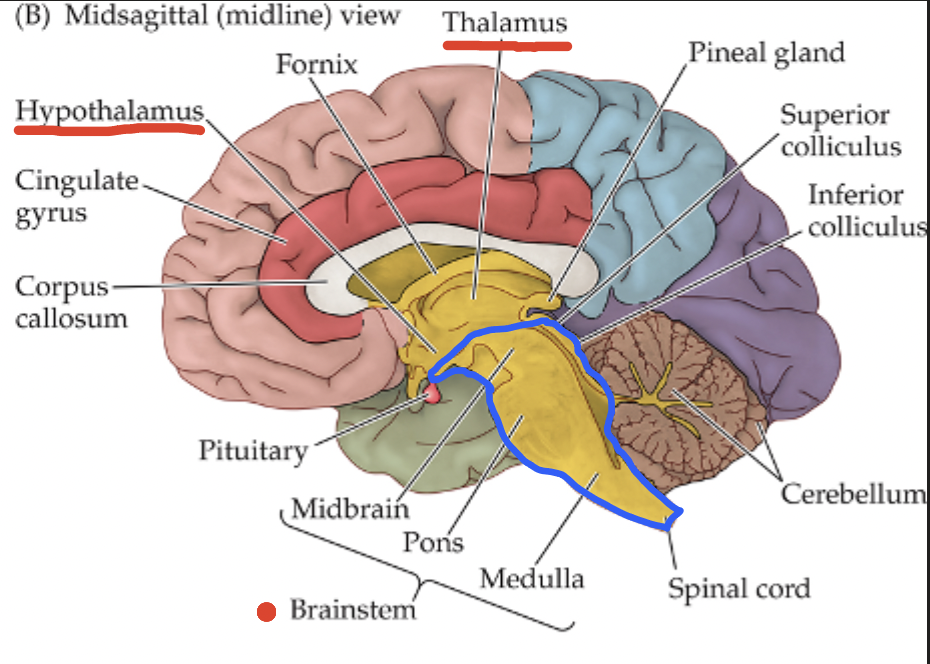
Brain Organization: Cerebellum
Coordinates voluntary movement and balance;
Contains more neurons than the cortex
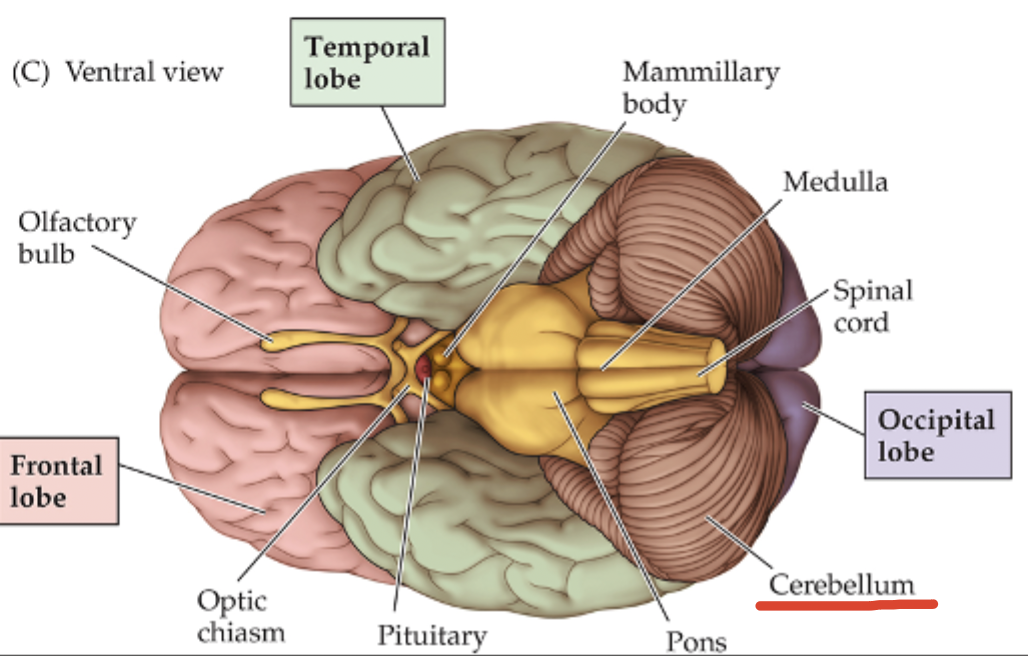
Brain Organization: The Cerebral Ventricles
4 empty, fluid-filled venticles;
Lateral ventricles (2), third ventricle, and fourth ventricle;
Keeps the brain cushioned in cerebral spinal fluid
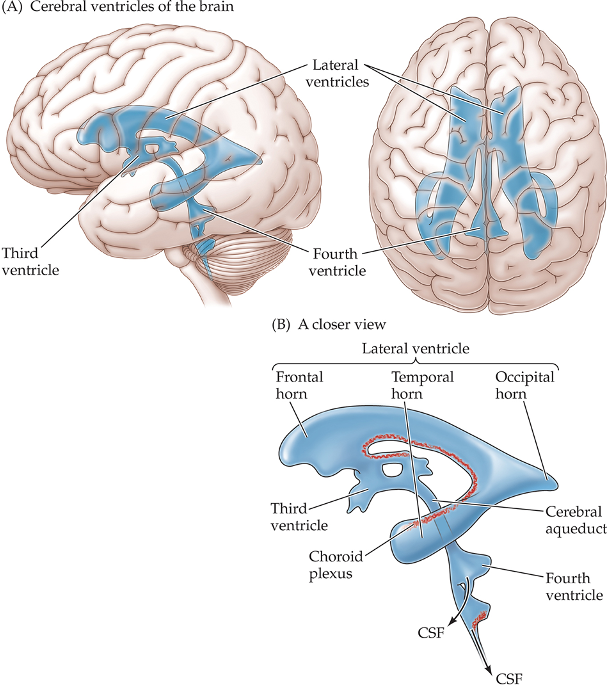
Brain Organization: The Cerebrovascular System
3 major arteries (anterior, middle, and posterior) supply blood to the brain;
Blood flow to the brain is tightly regulated by the blood brain barrier
Stroke
Occurs when flood flow to the brain is disrupted;
Hemorrhagic Stroke: a vessel has burst to let blood leak;
Ischemic Stroke: a clog has blocked blood flow
Brain Organization: The Glymphatic System
Brain’s drainage system to clear waste and debris