AP Micro Unit 2 - Supply and Demand
5.0(2)
Card Sorting
1/50
Last updated 8:58 AM on 1/25/23
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
51 Terms
1
New cards
Market
* A system that brings together producers that supply goods and consumers that demand them
2
New cards
Demand
* The desire for a good or service, as well as the willingness and ability to pay for it
3
New cards
Law of Demand
* As the price of a good increases, the quantity demanded decreases
* As the price of a good decreases, the quantity demanded increases
* As the price of a good decreases, the quantity demanded increases
4
New cards
Substitution Effect
* When the price of a good increases, consumers will usually buy less of that good and more of a substitute good that is similar but cheaper
5
New cards
Income Effect
* When the price of a good increases, a consumer’s purchasing power decreases because they can buy less of the good with the same amount of income
* A consumer will buy less of the good and more of other, cheaper goods to make their income stretch further
* When the price of a good decreases, a consumer’s purchasing power increases as they can now buy more of the good with their same income
* A consumer will buy less of the good and more of other, cheaper goods to make their income stretch further
* When the price of a good decreases, a consumer’s purchasing power increases as they can now buy more of the good with their same income
6
New cards
Determinants of Demand
* INSECT
* Income
* changes in consumers’ income
* Number of consumers
* change in consumer population in the market
* Substitute
* availability of substitutes
* Expectation
* expectations about the future
* Complement
* availability of complements
* Taste
* changes in tastes and preferences
* Income
* changes in consumers’ income
* Number of consumers
* change in consumer population in the market
* Substitute
* availability of substitutes
* Expectation
* expectations about the future
* Complement
* availability of complements
* Taste
* changes in tastes and preferences
7
New cards
Supply
* The quantity of a good or service a producer is willing and able to offer for sale at a given price in a given time period
8
New cards
Law of Supply
* As the price of a good increases, the quantity supplied increases
* As the price of a good decreases, the quantity supplied decreases
* As the price of a good decreases, the quantity supplied decreases
9
New cards
Determinants of Supply
* Resource costs
* cost of the resources used to produce
* Taxes and subsidies
* government actions
* Technology/Productivity
* advances in technology
* Expectations
* expectations for future market conditions
* Number of Sellers/Producers
* number of sellers in the market
* cost of the resources used to produce
* Taxes and subsidies
* government actions
* Technology/Productivity
* advances in technology
* Expectations
* expectations for future market conditions
* Number of Sellers/Producers
* number of sellers in the market
10
New cards
Price Elasticity of Demand (PED)
* Measure a consumer’s sensitivity to price changes
* %ΔQd / %ΔP
* Percent change in Quantity Demanded divided by percent change in Price
* We use absolute value of the PED Coefficient (what we solve for)
* %ΔQd / %ΔP
* Percent change in Quantity Demanded divided by percent change in Price
* We use absolute value of the PED Coefficient (what we solve for)
11
New cards
Perfectly Inelastic Demand
* Demand coefficient of 0
* Quantity demanded does not change regardless of price changes
* Examples: necessities of food, water, and shelter; insulin, etc.
* Doesn’t realistically exist
* Quantity demanded does not change regardless of price changes
* Examples: necessities of food, water, and shelter; insulin, etc.
* Doesn’t realistically exist
12
New cards
Relatively Inelastic Demand
* Demand coefficient between 0 and 1
* Quantity demanded is slightly responsive to price changes
* Examples: gasoline
* Quantity demanded is slightly responsive to price changes
* Examples: gasoline
13
New cards
Unit Elasticity of Demand
* Demand coefficient of 1
* Quantity demanded is exactly proportional to price changes
* Examples: Luxury goods
* Quantity demanded is exactly proportional to price changes
* Examples: Luxury goods
14
New cards
Relatively Elastic Demand
* Demand coefficient greater 1 but less than infinity
* Quantity demanded is highly responsive to price changes
* Examples: Leisure activities (concerts)
* Quantity demanded is highly responsive to price changes
* Examples: Leisure activities (concerts)
15
New cards
Perfectly Elastic Demand
* Demand coefficient of infinity
* Quantity demanded becomes infinite as the price approaches zero and becomes zero as the price increases
* Examples: product with many substitutes
* Doesn’t realistically exist
* Quantity demanded becomes infinite as the price approaches zero and becomes zero as the price increases
* Examples: product with many substitutes
* Doesn’t realistically exist
16
New cards
Total Revenue
* Measure of the amount of money a business brings in
* TR = P \* Q
* TR = P \* Q
17
New cards
Total Revenue Test
* Connect TR to price elasticity by defining rules for how TR responds to price changes under certain elasticities
* Elastic Demand
* When P increases, TR will decrease
* When P decreases, TR will increase
* Inelastic Demand
* When P increases, TR will increase
* When P decreases, TR will decrease
* Unit Elastic Demand
* Increase or decrease in P will not affect TR
* Elastic Demand
* When P increases, TR will decrease
* When P decreases, TR will increase
* Inelastic Demand
* When P increases, TR will increase
* When P decreases, TR will decrease
* Unit Elastic Demand
* Increase or decrease in P will not affect TR
18
New cards
Price Elasticity of Supply (PES)
* Measurement of how responsive firms are to a change of a good or service in the market
* %ΔQs / %ΔP
* Percent change in Quantity Supplied divided by percent change in Price
* Big factor is time - time to adjust production or retrieve resources
* Think about short run vs long run
* %ΔQs / %ΔP
* Percent change in Quantity Supplied divided by percent change in Price
* Big factor is time - time to adjust production or retrieve resources
* Think about short run vs long run
19
New cards
Perfectly Inelastic Supply
* Supply coefficient of 0
* Quantity supplied does not change regardless of price changes
* Examples: monopoly goods
* Quantity supplied does not change regardless of price changes
* Examples: monopoly goods
20
New cards
Relatively Inelastic Supply
* Supply coefficient between 0 and 1
* Quantity supplied is not very responsive to price changes
* Examples
* Supply for a company that has a large fixed cost
* Quantity supplied is not very responsive to price changes
* Examples
* Supply for a company that has a large fixed cost
21
New cards
Unit Elasticity of Supply
* Supply coefficient of 1
* Quantity supplied is exactly proportional to price changes
* Quantity supplied is exactly proportional to price changes
22
New cards
Relatively Elastic Supply
* Supply coefficient between 1 and infinity
* Quantity supplied is very responsive to price changes
* Examples
* Type of supply that a firm can quickly increase production of in response to higher prices
* Quantity supplied is very responsive to price changes
* Examples
* Type of supply that a firm can quickly increase production of in response to higher prices
23
New cards
Perfectly Elastic Supply
* Supply coefficient of infinity
* Quantity supplied becomes infinite as the price increases
* Examples
* Type of supply that has an unlimited number of suppliers (commodities)
* Quantity supplied becomes infinite as the price increases
* Examples
* Type of supply that has an unlimited number of suppliers (commodities)
24
New cards
Income Elasticity of Demand
* Measure of the sensitivity of quantity demanded to changes in income
* %ΔQd / %ΔI
* Percent change in Quantity Demanded divided by percent change in Income
* Can show if a good in normal or inferior
* %ΔQd / %ΔI
* Percent change in Quantity Demanded divided by percent change in Income
* Can show if a good in normal or inferior
25
New cards
Normal Good
* A good that increases in quantity demanded when income increases
* Higher quality products that, when we have more income, we buy more readily
* Positive Coefficient
* Higher quality products that, when we have more income, we buy more readily
* Positive Coefficient
26
New cards
Inferior Good
* A good that decreases in quantity demanded when income increases
* Lower quality products that, when we have more income, we change what we buy
* Negative Coefficient
* Lower quality products that, when we have more income, we change what we buy
* Negative Coefficient
27
New cards
Sticky Good
* A good that has no change in quantity demanded when income changes
* Coefficient of 0
* Coefficient of 0
28
New cards
Cross-Price Elasticity of Demand
* Describes the sensitivity quantity demanded for one good to the price of another good
* Determines if two goods are substitutes or complements or neither
* %ΔQda / %ΔPb
* Percent change in Quantity Demanded of good A divided by percent change in Price of good B
* Positive Coefficient - substitutes
* Negative Coefficient - complements
* Coefficient of 0 - no relation to each other
* Determines if two goods are substitutes or complements or neither
* %ΔQda / %ΔPb
* Percent change in Quantity Demanded of good A divided by percent change in Price of good B
* Positive Coefficient - substitutes
* Negative Coefficient - complements
* Coefficient of 0 - no relation to each other
29
New cards
Market Equilibrium
* A condition in a market where the quantity supplied equals the quantity demanded at an optimal price level
* Point where everything supplied is consumed
* Where Qd = Qs
* Occurs from voluntary exchange
* This is allocative efficiency
* Point where everything supplied is consumed
* Where Qd = Qs
* Occurs from voluntary exchange
* This is allocative efficiency
30
New cards
Voluntary Exchange
* The act of consumers and firms are mutually benefitting in the marketplace, as utility and profits are maximized
31
New cards
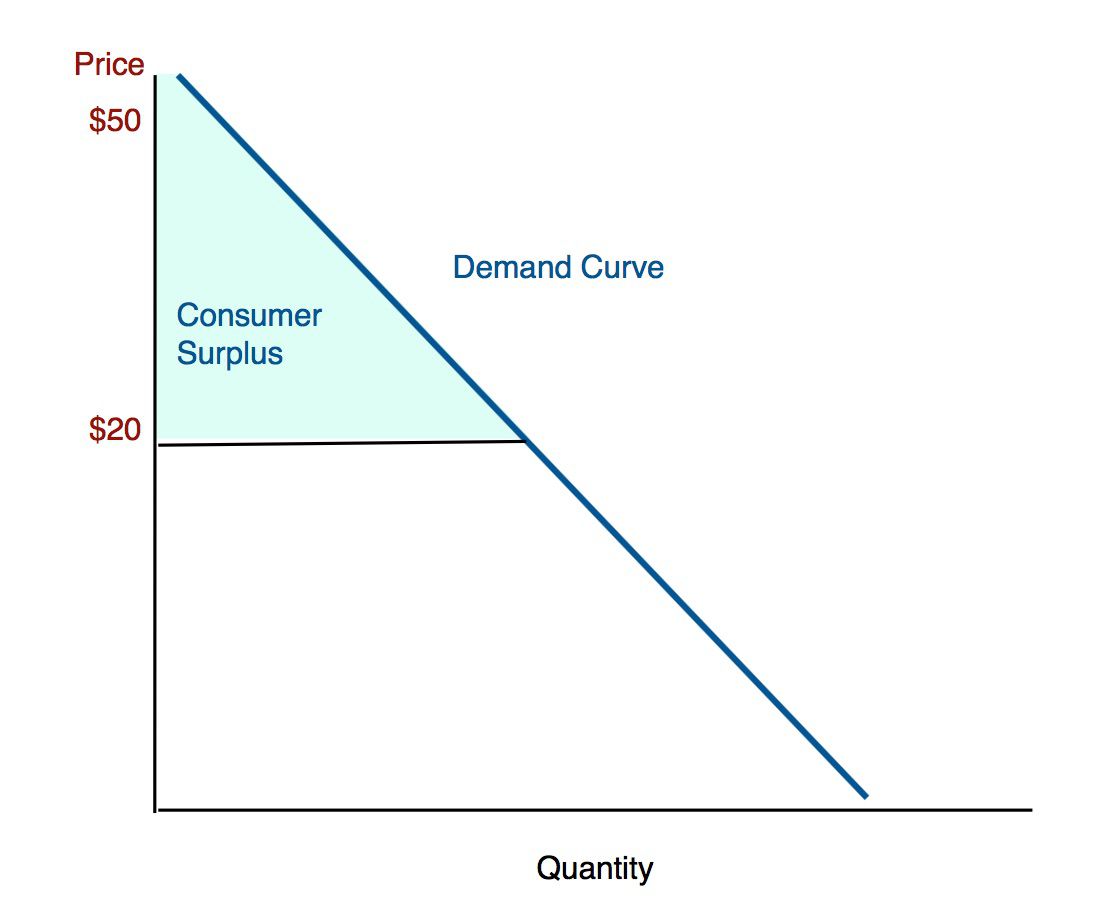
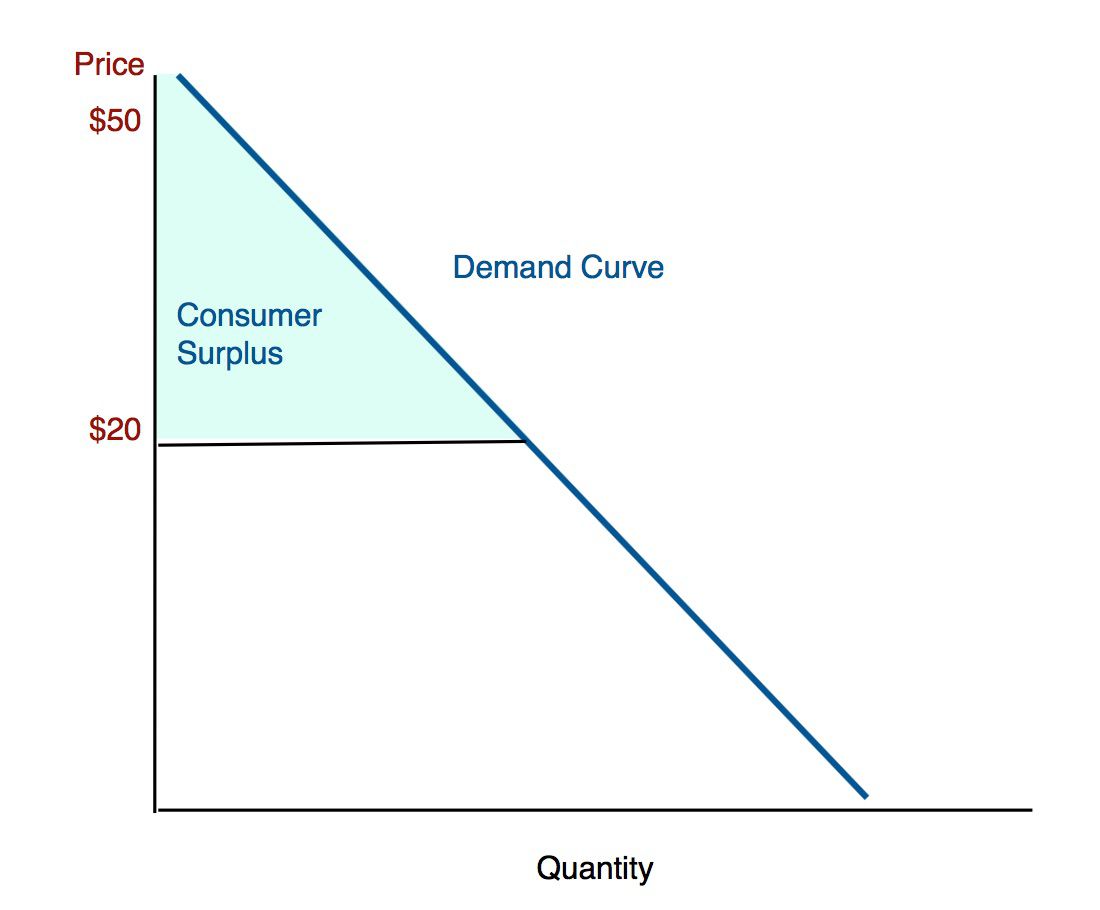
Consumer Surplus
* The difference between the total amount that consumers are willing and able to pay for a good or service and the total amount they actually pay
* Shaded triangle above the equilibrium price
* Shaded triangle above the equilibrium price
32
New cards
Individual Consumer Surplus
* Difference between a buyer’s maximum price and what the market price is
33
New cards
Total Consumer Surplus
* All the individual consumer surpluses added together
* Shaded triangle above the equilibrium price
* Shaded triangle above the equilibrium price
34
New cards
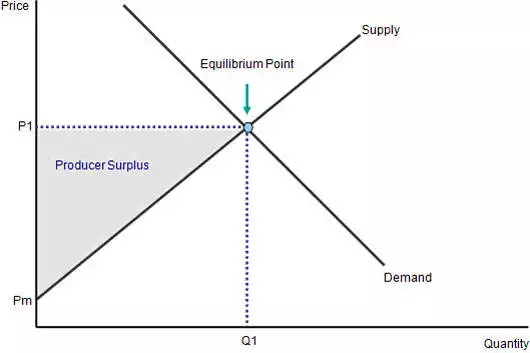
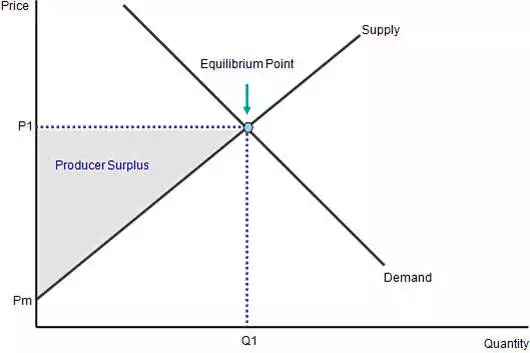
Producer Surplus
* The difference between the total amount firms are willing and able to sell a good or service for and the total amount they actually receive when selling it
* Shaded triangle below the equilibrium price
* Shaded triangle below the equilibrium price
35
New cards
Individual Producer Surplus
* Difference between a seller’s minimum price and the market equilibrium price
36
New cards
Total Producer Surplus
* All the individual producer surpluses added together
* Shaded triangle below the equilibrium price
* Shaded triangle below the equilibrium price
37
New cards
Market Disequilibrium
* A state at which the quantity demanded does not equal the quantity supplied
* Usually caused by a price above or below the equilibrium price
* Consumer or Producer surplus will lose out in disequilibrium
* Usually caused by a price above or below the equilibrium price
* Consumer or Producer surplus will lose out in disequilibrium
38
New cards
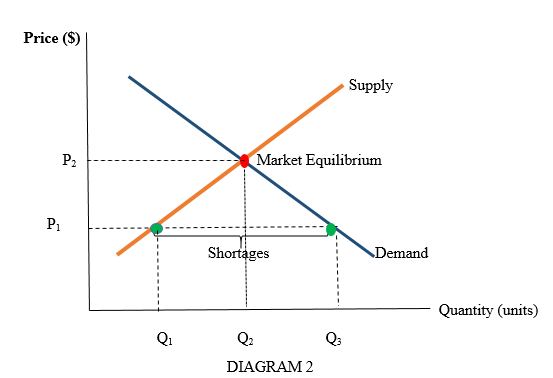
Shortage
* Quantity demanded is higher than quantity supplied
* Too many people want a good compared to how many firms are willing to sell it
* Too many people want a good compared to how many firms are willing to sell it
39
New cards
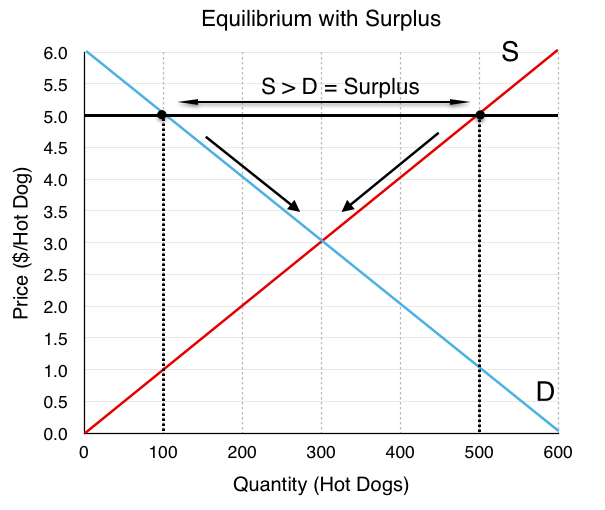
Surplus
* Quantity supplied is higher than quantity demanded
* Too many firms are willing to sell a good, but not many people want to or are able to purchase it
* Too many firms are willing to sell a good, but not many people want to or are able to purchase it
40
New cards
When there is disequilibrium, in the long run, the market will shift towards…
market equilibrium
41
New cards
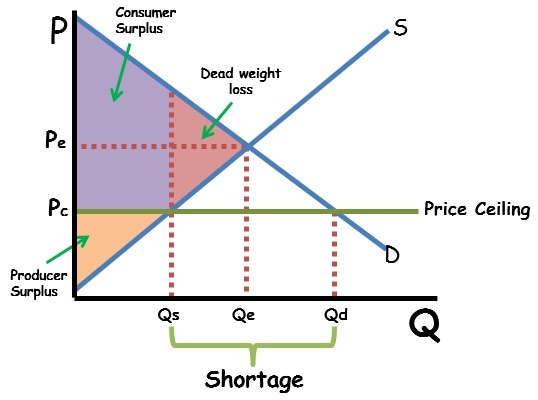
Deadweight Loss
* Lost surplus
* Triangle shaded that is not the Consumer Surplus or the Producer Surplus
* Triangle shaded that is not the Consumer Surplus or the Producer Surplus
42
New cards
Double Shift
* Both the supply and demand shift
43
New cards
Government power in microeconomics
* Has power over markets
* Can control prices with price ceilings and price floors
* Can impact the price of goods through excise (aka per-unit) taxes
* Can control prices with price ceilings and price floors
* Can impact the price of goods through excise (aka per-unit) taxes
44
New cards
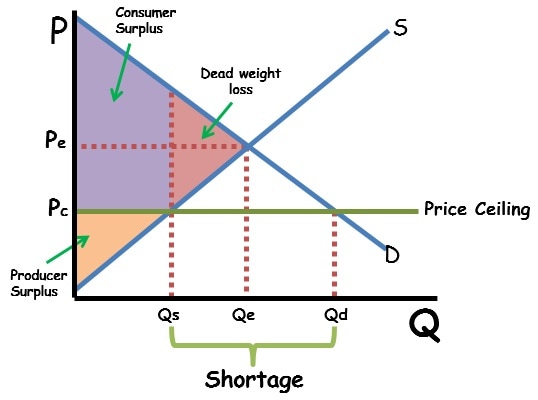
Price Ceiling
* A price maximum set by the government - firms cannot sell above the price ceiling
* Only effective below the market equilibrium
* Examples:
* Rent control
* Only effective below the market equilibrium
* Examples:
* Rent control
45
New cards
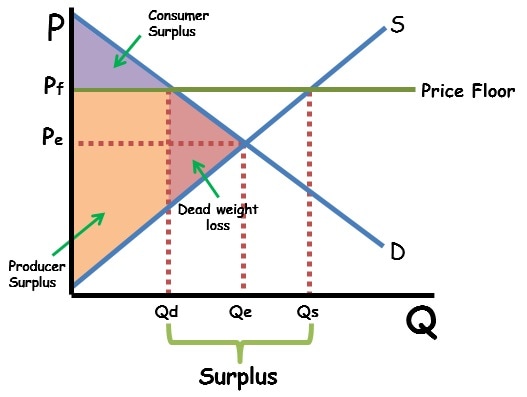
Price Floor
* A price minimum set by the government - firms cannot sell below the price floor
* Only effective above market equilibrium
* Examples:
* Minimum wage
* Only effective above market equilibrium
* Examples:
* Minimum wage
46
New cards
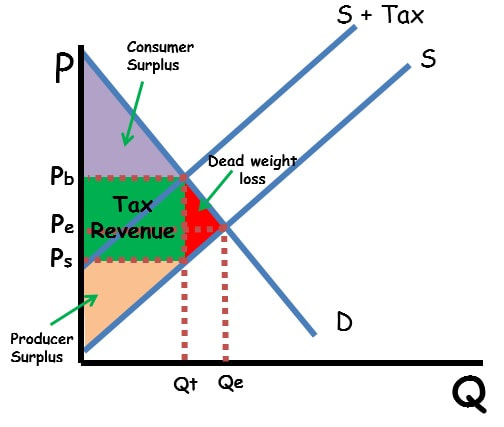
Excise Tax
* AKA per-unit tax
* A tax on every item produced
* A tax on every item produced
47
New cards
Lump Sum Tax
* Independent of quantity
* Doesn’t increase in size as quantity increases - it’s a fixed price
* Doesn’t increase in size as quantity increases - it’s a fixed price
48
New cards
Tax Incidence
* Both producers and consumers share part of the excise tax
* Based on elasticity of demand and supply, consumers or producers may carry more of the burden
* Elasticities are equal - consumers and producers equally pay
* Demand is more inelastic - consumers pay more
* Demand is more elastic - consumers pay less
* Based on elasticity of demand and supply, consumers or producers may carry more of the burden
* Elasticities are equal - consumers and producers equally pay
* Demand is more inelastic - consumers pay more
* Demand is more elastic - consumers pay less
49
New cards
Public Policy
* The laws and regulations that govern economic activity
50
New cards
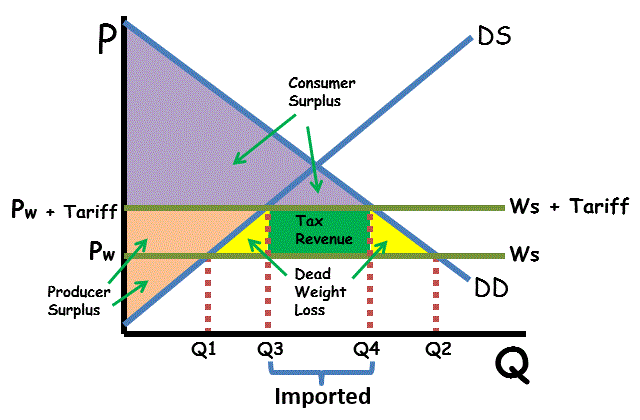
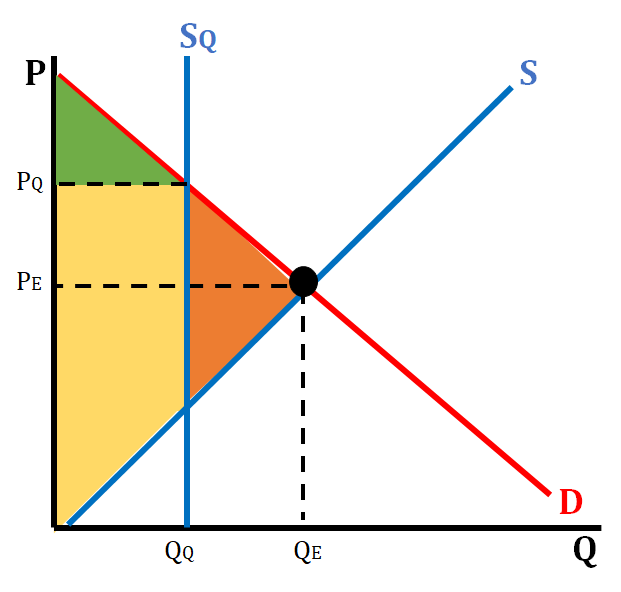
Quotas
* A government-imposed limit on production levels
* Limits the amount of a particular good that can come into a country from somewhere else
* Trade barrier to protect domestic industries that produce similar goods
* Limits the amount of a particular good that can come into a country from somewhere else
* Trade barrier to protect domestic industries that produce similar goods
51
New cards
Tariffs
* A tax on foreign goods coming into a country
* Effort to reduce the amount of a particular good coming into a country by raising the price of the good
* Effort to reduce the amount of a particular good coming into a country by raising the price of the good