Hemoglobin, oxygen dissociation curve, o2/CO2 transport
1/41
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
42 Terms
How long does it take for oxygen to fully diffuse into the capillaries in relation to the time it has?
It completely diffuses in 1/3 of the total pulmonary capillary transit time it has so lots of buffer time to ensure full exchange this is due to the large pressure gradient
What are the 2 forms of which oxygen is in while in the blood?
Less than 2 percent is dissolved, the rest is bound to hemoglobin (98%)
This is due to the low solubility of oxygen
What is hemoglobin?
Iron containing protien in RBCs
What is the makeup of hemoglobin?
4 alpha and beta chain, each one has a heme unit
Each of these iron containing heme units binds one oxygen
How many oxygen molecules can one hemoglobin carry?
four, one for each heme unit
What is the relationship between oxygen and hemoglobin?
Oxygen binds hemoglobin reversibly, so that it can on load at the lungs and off load at the tissues
What two words describe Hemoglobin binding?
Cooperative and saturable
What is meant by cooperative Hb binding?
The binding of each successive oxygen molecule facilitates the next, increases affinity
And
The release of each successive oxygen molecule facilitates the offloading of the next
What produces the sigmoidal shape of the Hb-O2 dissociation curve?
The cooperative nature of Hb-O2 binding and release
What is meant by saturable Hb binding?
Every site in the hemoglobin can be bound
What is the oxygen dissociation curve?
X axis is PO2 and Y is percent saturation
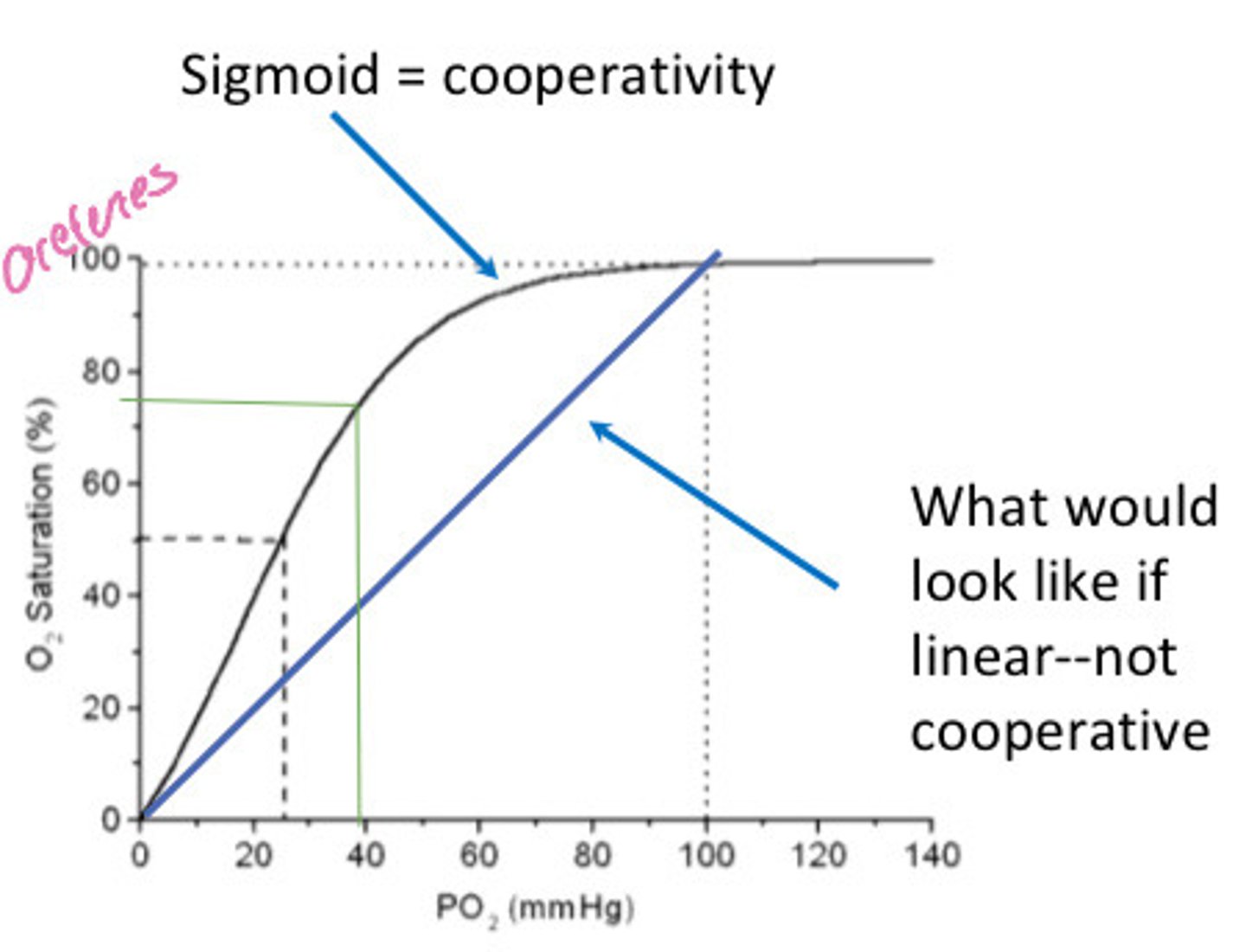
What 4 states shift the oxygen dissociation curve?
pH
Temperature
CO2
2,3 DPG
Is shifting of the oxygen dissociation bad?
No, it can be normal and wanted
What does a right shift of the oxygen dissociation curve indicate?
That at any given PO2 Hb is less saturation due to decreased affinity causing more oxygen offloading
This is normal in active tissues as it increases the oxygen available to them
What variables can cause a right shift?
Increased H+ concentration (ie decreased pH)
Increases PCO2
Increased temperature
Increased concentration of 2,3-DPG in RBCs
What does a left shift of the oxygen dissociation curve indicate?
Increased saturation of Hb at any given pO2 meaning there is an increased oxygen affinity and therefore less offloading
This is normal in the lungsn
What variables cause a left shift?
Decreased H+ concentration (ie increased pH)
Decreased PCO2
Decreased temperature
Decreased 2,3-DPG concentration in RBCs
How is fetal Hb compared to adult Hb?
Left shifted so O2 with Bind during placental circulation
What allows for the normal on loading/offloading of Hb-O2?
In the lungs there is decreased CO2 and H+ causing a left shift increasing onloading
In the tissues there is increased CO2 and H+ causing a right shift increasing offloading
What is the carbonic acid equation?
CO2 + H2O <-> H2CO3 <-> HCO3- + H+
What enzyme is required to make carbonic acid from carbon dioxide and water?
Carbonic anhydrase
What is occurring when oxygen is onloading at the lungs?
O2 in the alveoli diffuse into the capillaries and most of it binds hemoglobin and a bit of it dissolves into the plasma
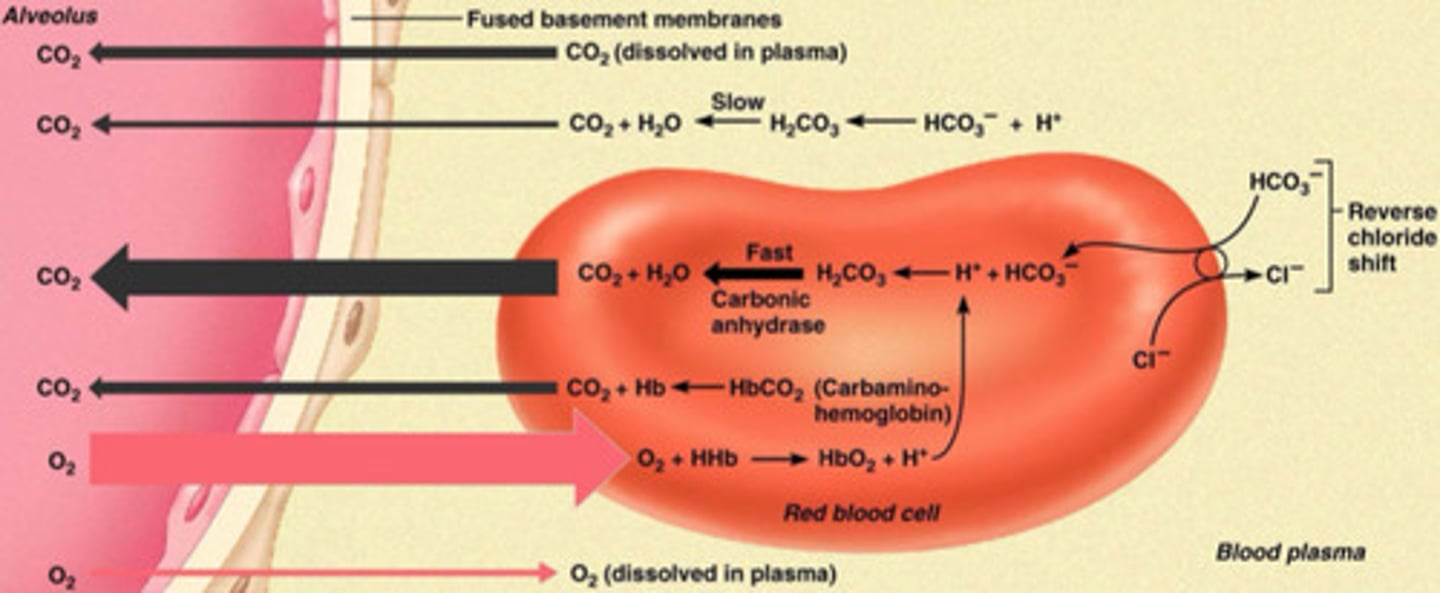
What does the total oxygen content of the blood equal?
The sum of o2 dissolved and o2 chemically combined with HB
What is occurring when oxygen gets offloaded at the tissues?
Dissolved O2 directly offloads into the tissues
Increased temp, carbon dioxide, and decreased pH causes O2 to offload from the RBCs
Why is anemia so dangerous?
Hemoglobin in RBCs play such a big role in carrying o2 and with decreased RBCs it severely affects oxygen levels
As you can never get enough o2 from just the plasma
What are the 3 ways oxygen can be measured?
Partial pressure of oxygen in arterial blood (mmHg)
Saturation of Hb with oxygen from artery
(%)
Oxygen content in arterial blood (ml O2/dl)
What is oxygen delivery the product of?
DO2= Total O2 content (CaO2) x cardiac output
What 3 things negatively affect oxygen delivery?
Decreased Hb levels
Decreased PaO2 (hypoxemia)/SaO2(hemoglobin saturation)
Decreased cardiac output
What is the normal arterial blood CO2 level?
40 mmHg
Why does carbon dioxide concentration matter?
It's the primary CNS trigger for ventilation and it acts as an acid in the body so it affects the pH
Where is carbonic anhydrase found in high concentrations?
red blood cells to catalyze the conversion of CO2 and H2O to carbonic acid (H2CO3)
What are the 3 forms of CO2 carriage?
Dissolved in blood (more soluble than O2 is)
As bicarbonate (90%)
Carbamino compounds (bound to Hb)
When does hemoglobin start to grab CO2?
When oxygen offloads, so in acidic environments when Hb has a reduced affinity
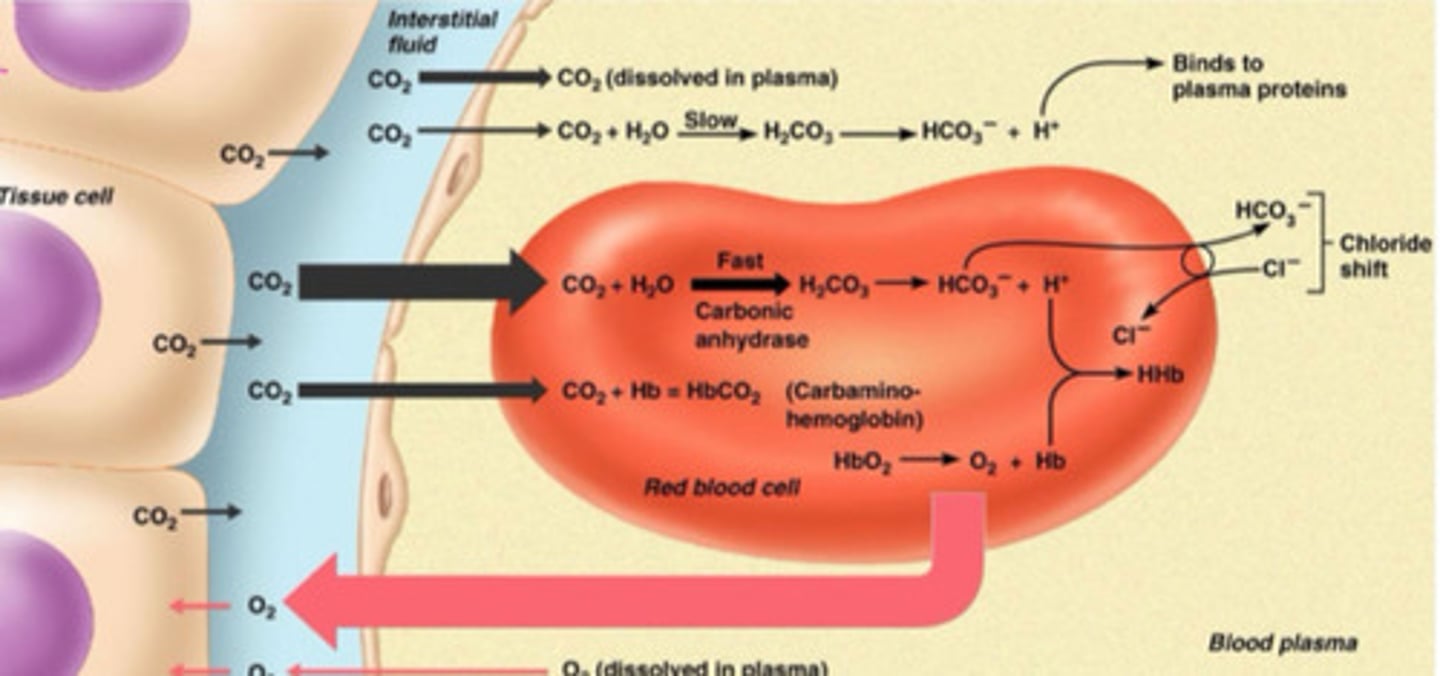
How does CO2 get uptook into hemoglobin?
CO2 combines with H2O in the RBC via carbonic anhydrase (fast) to make carbonic acid (H2CO3)
Carbonic acid then dissociates to H+ and HCO3-
HCO3- diffuses out of the RBC and Cl- exchanges with it to maintain electro neutrality
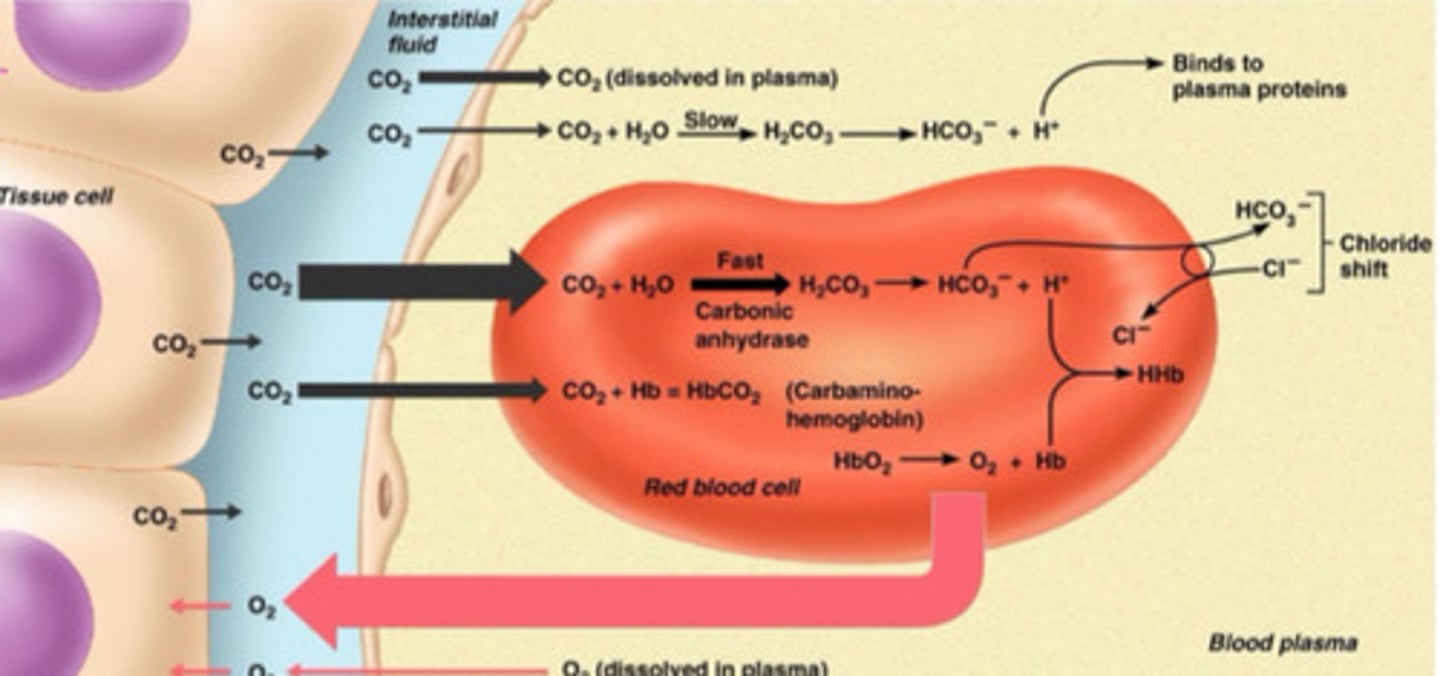
What type of hemoglobin has an increased capacity to carry CO2?
Deoxygenated, so favorable at tissue level, some H+ binds
What type of hemoglobin has an decreased capacity to carry CO2?
Oxygenated, which is good at alveoli
What is the process of CO2 release into the alveoli?
Opposite of what happen with onloading
Chloride shift occurs and HCO3 enters the RBC and combines with H+ to make carbonic acid
It then is catalyzed by carbonic acid to carbon dioxide and water and it then diffuses into the alveoli
What maintains the concentration gradient for carbon dioxide offloading from RBCs?
Ventilation
What is venous O2 level?
40 mmHg
What is arterial O2 level?
100 mmHg
How is oxygen transported into the tissues?
Diffuses down its concentration gradient from artery into tissue, large gradient
How is CO2 transported out of the tissue?
Diffuses across interstitial space into capillary down its concentration gradient, smaller gradient that oxygens (difference of 45 in artery and 40 in vein)