Food Animal Growth and Development Test 1
1/332
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
333 Terms
what are the 3 main parts of the cell
cell membrane, nucleus, cytoplasm
what color is the nucleus on a slide
blue
what is growth
refers to the increase in size of an animal
what are the two major components of growth
cellular growth and extracellular growth
what are the two types of cellular growth
hypertropy and hyperplasia
what is hypertropy
increase in size
what is hyperplasia
increase in number
what is extracellular growth
accretion of materials in the extracellular space
what is development
refers to increase in complexity
what is the process that goes from a single cell to an adult animal called
animal development
what are the three components of development
growth, differentiation, and morphogenesis
what does differentiation refer to
being specialized
what is morphogenesis
shaping and patterning of body
what are the two parts of growth of major tissues
true growth and fattening
true growth
growth of muscle and bone
fattening
growth of adipose tissue
why do we study animal growth and development
sufficient knowledge means right size and shape, right composition, and high efficiency
cell
basic structural and functional unit of all living organisms
tissue
groups of closely associated cells and cell products that act together to perform specific functions
organ
recognizable structure that performs complex functions
what are the 4 types of primary tissues
epithelial tissue
connective tissue
muscle tissue
nervous tissue
primary tissue is ? distributed
broadly
epithelial tissue
a thin layer of tissue that covers the surface of the body, lining body cavities and hollow organs throughout the body, and form glands
what are the two environments the epithelium separates
external and internal environment as well as internal and internal environment
what are cells like in epithelial tissue
tightly organized and polarized
what is extracellular space like in epithelial tissue
limited (they do have it just limited)
is epithelial tissue vascularized
no it is avascular → it gets it nutrients from surrounding tissue
simple epithelium
composed of a single layer of cells
where is simple epithelium tissue located
in well protected areas where maximal secretion and absorption are needed
stratified epithelium
multiple layers of cells
where is stratified epithelium tissue located
exposed areas where there is friction with the outer environment (skin, extremities of digestive tract)
pseudostratified
single layer, but the cell nuclei are positioned at different levels and suggestive of being stratified
example of where pseudo-stratified tissue is
lining of respirratory tract
squamous
thin and flat
cuboidal
box-like
columnar
slender, elongated
transitional
cell shape changes
simple squamous location
endothelium, epithelium of lung, mesothelium
simple cuboidal location
some kidney tubules, thryoid gland, sweat gland
simple columnar location
digestive tract
pseudo-stratified columnar location
trachea and epididymis
stratified squamous location
epidermis, oral mucosa, vagina, anal mucosa
stratified cuboidal location
sweat gland duct
stratified columnar location
trachea, epiglottis
transitional location
bladder, ureter
basic simple and stratified epithelium function
simple - secretes
stratified - protects
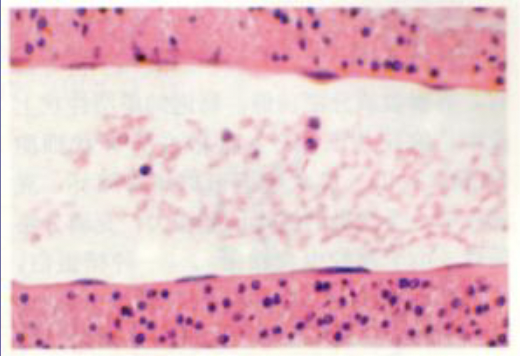
what is this
simple squamous epithelial tissue
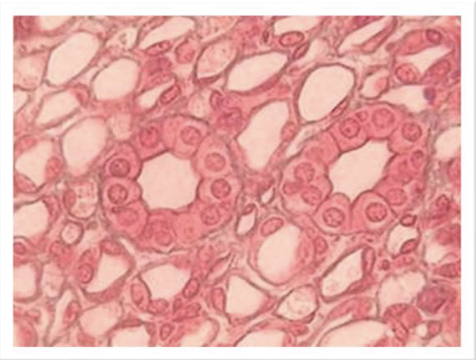
what is this
simple cuboidal epithelial tissue
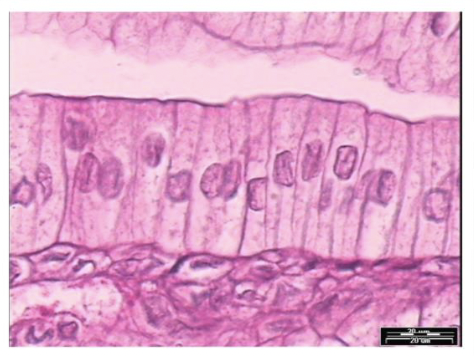
what is this
simple columnar
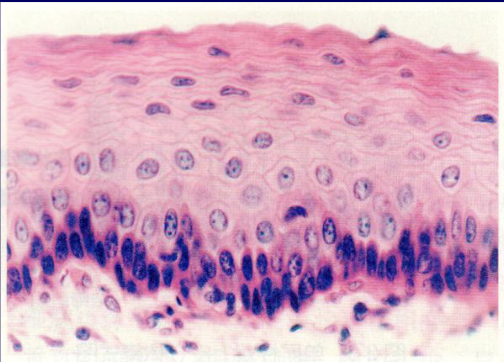
what is this
stratified squamous
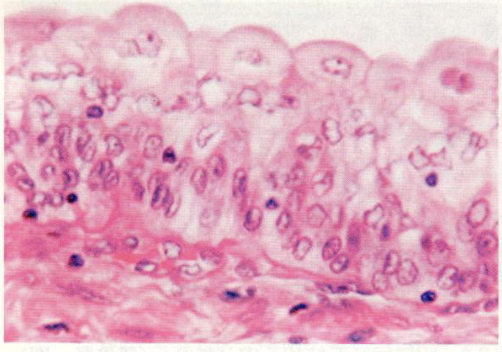
what is this
transitional
what is a special organelle of epithelial tissue
ciliac
cilia
slender (hair-like) extensions of cell membrane almost every cell has a primary cilium
what are the four functions of epithelial tissue
protection
transportation (absorption, excretion)
secretion
sensation
connective tissue cell characterisitics
sparse
connective tissue extracellular space characterisitcs
rich
is connective tissue vascularized
yes but not all
what are the two types of connective tissue
connective tissue proper and specialized connective tissue
connective tissue proper types
loose connective tissue and dense connective tissue
specialized connective tissue types
adipose tissue
cartilage and bone
blood and lymph
connective tissue cell shape
stellate, with multiple dendrites
what are the two types of cells in connective tissue
fixed and wandering
fixed cells
fibroblast
adipocyte
tendon cell
wandering cells
mast cell and macrophage
what are the two parts of the extracellular matrix in connective tissue
ground substance and fibers
what is the ground substance of the extracellular matrix in connective tissue
tissue “fluid”
3 types of fibers
collagenous
reticular
elastic
what is the most abundant protein in the body
collagen
what are collagen fibers synthesized from
fibroblasts
procollagen
alpha helices linked by disulfide bonds in the non-helical portion of molecule
what does cross linking of collagen do
gives it strength
what part of the molecule in collagen fiber provides stability
helical part
how many known collagen types are there
11
true or false: there is one single type of collagen
false - there is not one single type
how are reticular fibers formed
formed similarly to collagen but without large bundles
reticular fibers characteristics
small and delicate within abundant ground substance
where is reticular fiber found
in connective tissue surrounding parenchyma of many organs
characteristics of elastic fibers
very elastic and capable of reversibly stretching to double their length
what is elastin primarily composed of
desmosine and isodesmosine
what are elastic fibers secreted as
a precursor molecule, then cross linked
where are elastic fibers location
blood vessels, ligaments, lungs, and skin
5 characteristics of collagenous
thick
composed of collagen
great tensile strength
abundant in dense CT
hold structures together
where are collagenous fibers
tendons, ligaments
what are 4 characteristics of reticular fibers
very thin
composed of collagen
highly branched
form supportive networks
3 characteristics of elastic fibers
bundles of microfibrils embedded in elastin
fibers branch
elastic
where are elastic fibers found
vocal cords
air passages
blood vessels
what does loose connective tissue contain
few collagen and elastin fibers
what does loose connective tissue provide
loosely associated so it provides maximum flexibility and provides structure to blood vessels and nerves
loose connective tissue is not ? or ?
strong or rigid
loose connective tissue is ? and contains ?
highly vascularized and contains numerous cells
what does loose connective tissue act as
packing material between some organs
what does dense connective tissue contain
numerous collagen and elastin fibers for maximal strength and little flexibility
what is regular dense CT
fibers arranged in parallel bundles
where is regular dense CT found
tendons and muscles
tendons
muscle to bone
ligaments
bone to bone
what is irregular dense CT
thick mat of fibers running in all directions
where is irregular dense CT found
dermis of skin and mammary gland
what does supportive connective tissue include
bone and cartilage
what are the 6 functions of CT
connection
support
transport (nutrients and wastes)
protection
immunity
storage