Biomolecules
1/370
Earn XP
Description and Tags
[UPDATE: would love to inform everyone that the flashcards contain cards from both my coaching material and NCERT and there's just so many I don't know if any have been repeated, though I've tried to make sure they aren't. If they are, forgive me. Also I made the NCERT flashcards wayyy later so now the order of cards is messed up according to the progression of the chapter, forgive me for that too.] Everything in Biomolecules chapter except for calculations for Isoelectronic Point. Answer mode: Answer with Definition. Question mode: flashcards only. Almost-Comprehensive flashcards for the entire Biomolecules chapter, suitable for JEE Mains, IAT, NCERT.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
371 Terms
What is the general formula for carbohydrates?
C_x(H_2O)_y
where x and y are any natural number
What are the two groups that vitamins can be sorted into?
Fat soluble vitamins
Water soluble vitamins
Which vitamins are fat-soluble?
Vitamins A, D, E, and K.
Where are fat-soluble vitamins stored in humans?
They are stored in liver and adipose (fat storing) tissues.
Which vitamins are water-soluble?
Vitamins B (and subgroups) and C.
Which water-soluble vitamin can be stored in the body?
B12
What are vitamins?
They are generally regarded as organic compounds required in the diet in small amounts to perform specific biological functions for normal maintenance of optimum growth and health of the organism.
Why are vitamins called vitamins?
The term “Vitamine” was coined from the word vital + amine since the earlier identified compounds had amino groups. Later work showed that most of them did not contain amino groups, so the letter ‘e’ was dropped and the term vitamin is used these days.
How are enzymes generally named?
They are generally named after the compound or class of compounds upon which they work.
Sometimes enzymes are also named after the reaction, where they are used.
What is a native protein?
Protein found in a biological system with a unique three-dimensional structure and biological activity is called a native protein.
Protein found in a biological system with a unique three-dimensional structure and biological activity is called a _____________.
Protein found in a biological system with a unique three-dimensional structure and biological activity is called a native protein.
The melting points and solubility in water of amino acids are generally higher than that of the corresponding halo acids. Explain.
Due to the dipolar behaviour of the zwitter ion, amino acids have strong electrostatic interactions within them and with water. But halo-acids do not exhibit such dipolar behaviour.
For this reason, the melting points and the solubility of amino acids in water is higher than those of the corresponding halo-acids.
What is a tripeptide?
If a third amino acid combines to a dipeptide, the product is called a tripeptide.
What is the difference between a polypeptide and a protein?
A polypeptide with more than hundred amino acid residues, having molecular mass higher than 10,000u is called a protein. However, the distinction between a polypeptide and a protein is not very sharp. Polypeptides with fewer amino acids are likely to be called proteins if they ordinarily have a well defined conformation of a protein.
Insulin contains how many amino acids?
51
Most naturally occurring amino acids have ____-configuration.
(D / L)
Most naturally occurring amino acids have L-configuration.
Most naturally occurring amino acids have L-configuration. L-Aminoacids are represented by writing the –NH2 group on ____ hand side.
(left / right)
Most naturally occurring amino acids have L-configuration. L-Aminoacids are represented by writing the –NH2 group on left hand side.
Are amino acids soluble in water?
yes
Why is glycine named glycine?
Glycine is so named since it has sweet taste (in Greek glykos means sweet)
Cellulose is a ______ chain of \beta-D-glucose.
(straight / branched)
straight
What has been used for a long time as an instant source of energy by ‘Vaids’ in ayurvedic system of medicine?
Honey
Is maltose a reducing sugar or non-reducing sugar?
reducing
Why are maltose and lactose reducing sugars while sucrose is a non-reducing sugar?
In disaccharides, if the reducing groups of monosaccharides i.e., aldehydic or ketonic groups are bonded, these are non-reducing sugars, e.g., sucrose. On the other hand, sugars in which these functional groups are free, are called reducing sugars, for example, maltose and lactose (the functional groups get freed in solution)
Is lactose a reducing sugar or non-reducing sugar?
reducing
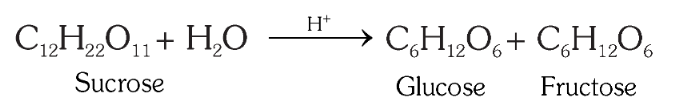
How does hydrolysis of sucrose bring about a change in rotation from dextrorotatory to leavorotatory?
Sucrose is dextrorotatory but after hydrolysis gives dextrorotatory glucose and laevorotatory fructose. Since the laevorotation of fructose (–92.4°) is more than dextrorotation of glucose (+ 52.5°), the mixture is laevorotatory. Thus, hydrolysis of sucrose brings about a change in the sign of rotation, from dextro (+) to laevo (–).
What is an invert sugar?
Hydrolysis of sucrose brings about a change in the sign of rotation, from dextro (+) to laevo (–) and the product is named as invert sugar.
Is sucrose dextrorotatory or leavorotatory?
dextrorotatory
What is glycosidic linkage? How is it formed?
Two monosaccharides are joined together by an oxide linkage formed by the loss of a water molecule. Such a linkage between two monosaccharide units through oxygen atom is called glycosidic linkage.
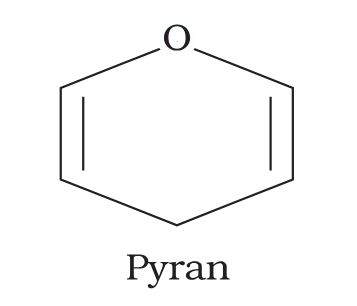
What is the structure of pyran?
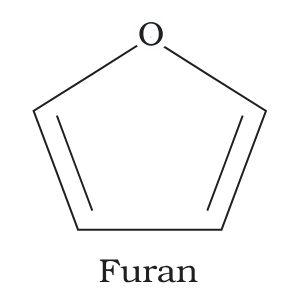
What is the structure of furan?
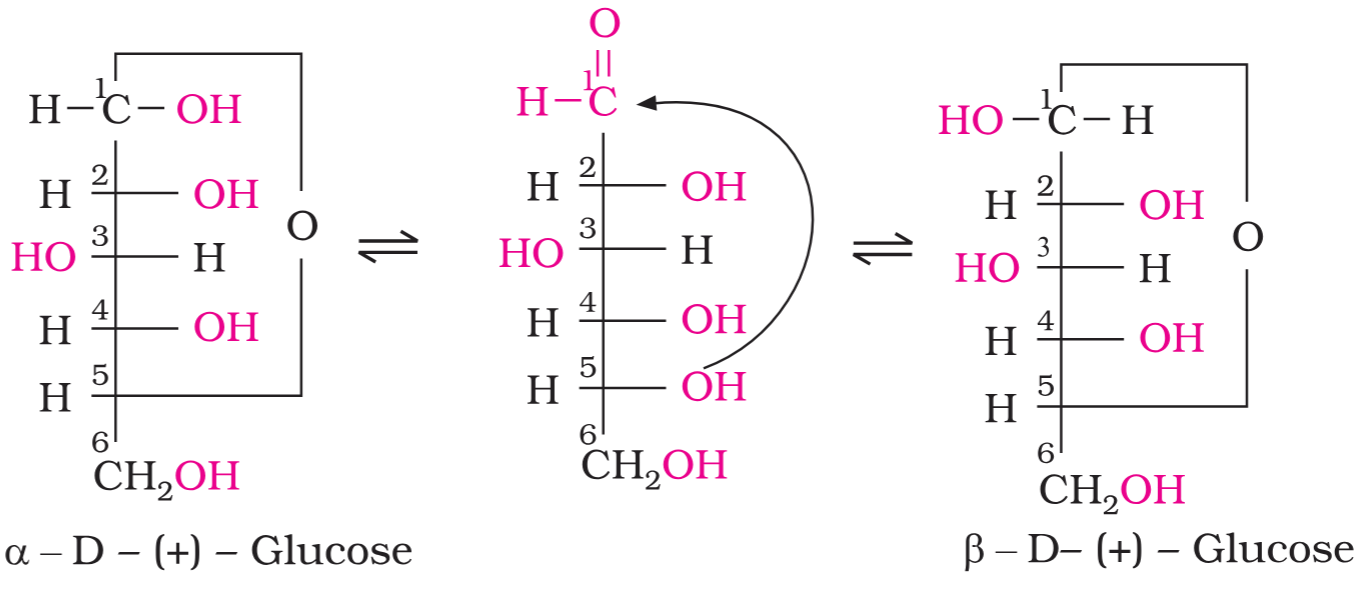
Depict how the cyclic forms of glucose can be formed from the aliphatic form of glucose.
Despite the aliphatic chain having an aldehyde group, why does glucose not give Schiff’s test?
It was proposed that one of the —OH groups may add to the —CHO group and form a cyclic hemiacetal structure. It was found that glucose forms a six-membered ring in which —OH at C-5 is involved in ring formation. This explains the absence of —CHO group
Despite the aliphatic chain having an aldehyde group, why does glucose not form the hydrogen sulphite addition product with NaHSO_3?
It was proposed that one of the —OH groups may add to the —CHO group and form a cyclic hemiacetal structure. It was found that glucose forms a six-membered ring in which —OH at C-5 is involved in ring formation. This explains the absence of —CHO group
Why does glucose pentaacetate not react with hydroxylamine?
absence of free —CHO group in the cyclic structure of glucose.
The pentaacetate of glucose does not react with hydroxylamine. What does this indicate?
Absense of free —CHO group in the cyclic structure of glucose.
Which has a higher melting point, α-form of glucose or β-form of glucose?
β-form of glucose (m.p. 423 K) > α-form of glucose (m.p. 419 K)
How can the α-form of glucose be obtained from a solution of glucose?
The α-form of glucose (m.p. 419 K) is obtained by crystallisation from concentrated solution of glucose at 303 K.
How can the β-form of glucose be obtained from a solution of glucose?
the β-form (m.p. 423 K) is obtained by crystallisation from hot and saturated aqueous solution at 371 K.
What is the structure of glucose pentaacetate?
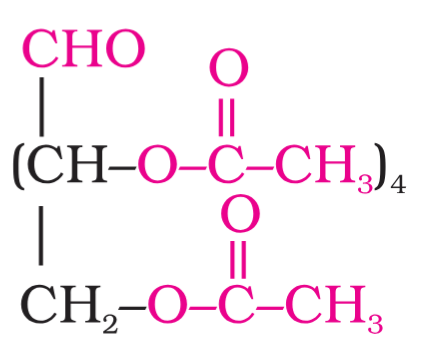
What is the sugar present in milk?
Lactose.
What does the “+” in D(+)-glucose represent?
dextrorotatory nature of the molecule
What does the “D” in D(+)-glucose represent?
relative configuration of a particular stereoisomer of a compound with respect to configuration of some other compound, configuration of which is known
The letters ‘D’ or ‘L’ before the name of any compound indicate the relative configuration of a particular stereoisomer of a compound with respect to configuration of some other compound, configuration of which is known.
How does this work in the case of carbohydrates?
In the case of carbohydrates, this refers to their relation with a particular isomer of glyceraldehyde. Glyceraldehyde contains one asymmetric carbon atom and exists in two enantiomeric forms.
All those compounds which can be chemically correlated to D (+) isomer of glyceraldehyde are said to have D—configuration whereas those which can be correlated to ‘L’ (–) isomer of glyceraldehyde are said to have L—configuration.
What are the two enantiomeric forms of glyceraldehyde?
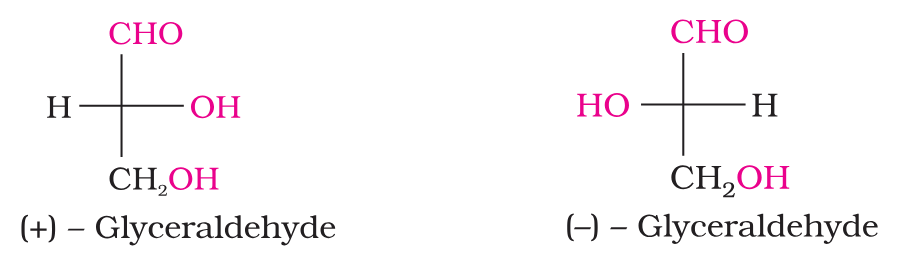
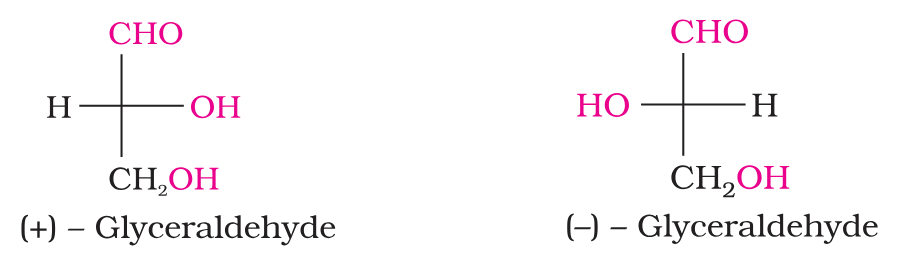
Which isomer has D configuration and which one has L configuration?
(+) Isomer of glyceraldehyde has ‘D’ configuration.
(–) isomer of glyceraldehyde has ‘L’ configuration.
How is the configuration of monosaccharides determined?
For assigning the configuration of monosaccharides, it is the lowest asymmetric carbon atom (as shown below) which is compared. As in (+) glucose, —OH on the lowest asymmetric carbon is on the right side which is comparable to (+) glyceraldehyde, so (+) glucose is assigned D-configuration. Other asymmetric carbon atoms of glucose are not considered for this comparison.
The structure of glucose and glyceraldehyde is written in a way that most oxidised carbon (in this case –CHO)is at the top.
True or false?
True.
What is the formula of Glucose? (in hydrate form as well)
C_6H_{12}O_6 or C_6(H_2O)_6
Is acetic acid a carbohydrate?
It is not.
What is the chemical formula of rhamnose?
C_6H_{12}O_5
The chemical formula of rhamnose is C_6H_{12}O_5
Is rhamnose a carbohydrate?
yes, it is an exception to the rule.
What is the definition of a carbohydrate?
Carbohydrates are optically active polyhydroxy- aldehyde or ketone which produce simpler units on hydrolysis.
What are sugars?
Carbohydrates that are sweet in taste.
What is a monosaccharide, or simple sugar?
A sugar that cannot be hydrolysed into simpler units.
How many monosaccharides are known to occur in nature?
about 20
What is the general formula of monosaccharides?
C_nH_{2n}O_n
What is an oligosaccharide?
Carbohydrates that produce 2-10 simpler units of monosaccharides.

If an aldehyde is present in a monosaccharide, what is it called?
aldose.
If a ketone is present in a monosaccharide, what is it called?
ketose
What is a disaccharide?
a carbohydrate that produces 2 units of monosaccharides on hydrolysis.
What is a trisaccharide?
a carbohydrate that produces 3 units of monosaccharides on hydrolysis.
What are polysaccharides?
These are the non-sugars which yield a large number of monosaccharide units on hydrolysis.
What is the general formula of polysaccharides?
(C_6H_{10}O_5)_n
Why are polysaccharides also called non-sugars?
They are not sweet in taste.
What is a reducing sugar?
A sugar that reduces Tollen’s reagent, Fehling’s reagent, Benedict’s reagent
What is a non-reducing sugar?
A sugar that does not reduce Tollen’s reagent, Fehling’s reagent, Benedict’s reagent.
All monosaccharides are ________ sugars.
(reducing / nonreducing)
reducing
Which one has a free -CHO group, a reducing sugar or a non-reducing sugar?
a reducing sugar
Is sucrose a reducing sugar or a non-reducing sugar?
a non-reducing sugar.
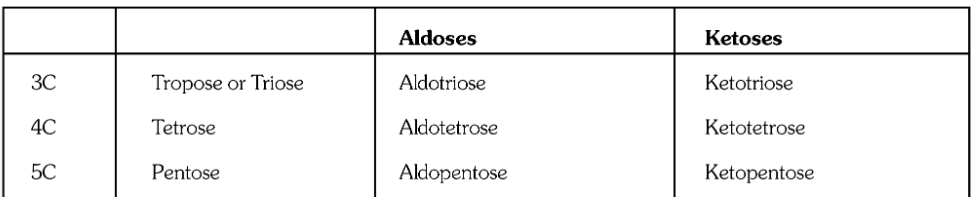
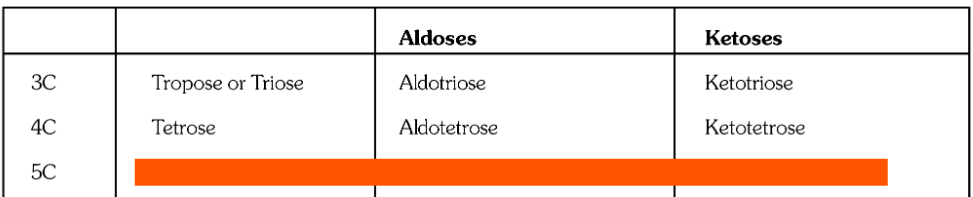
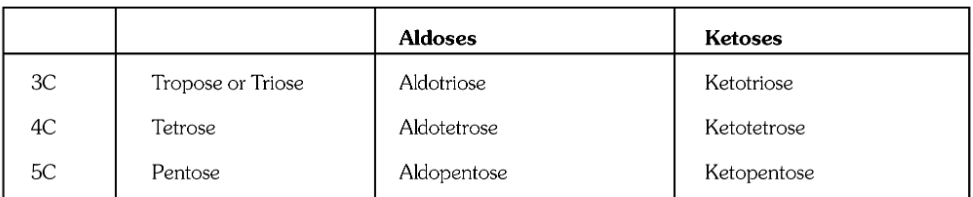
Is Glucose an aldose or a ketose?
aldose
Glucose is an aldo____
(number of carbon atoms)
aldohexose
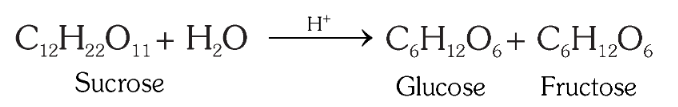
How would you produce glucose from sucrose? What is the reagent?
By boiling with dilute HCl or H_2SO_4 in alcoholic solution.
How would you produce glucose from starch? What is the reagent? At which temperature? At which pressure?
By boiling with dilute H_2SO_4 at 393K under 2-3 atm.
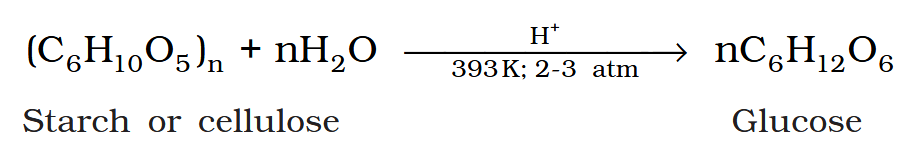
What is dextrose?
Glucose is also known as dextrose.
Which is the most abundant organic compound on earth?
glucose
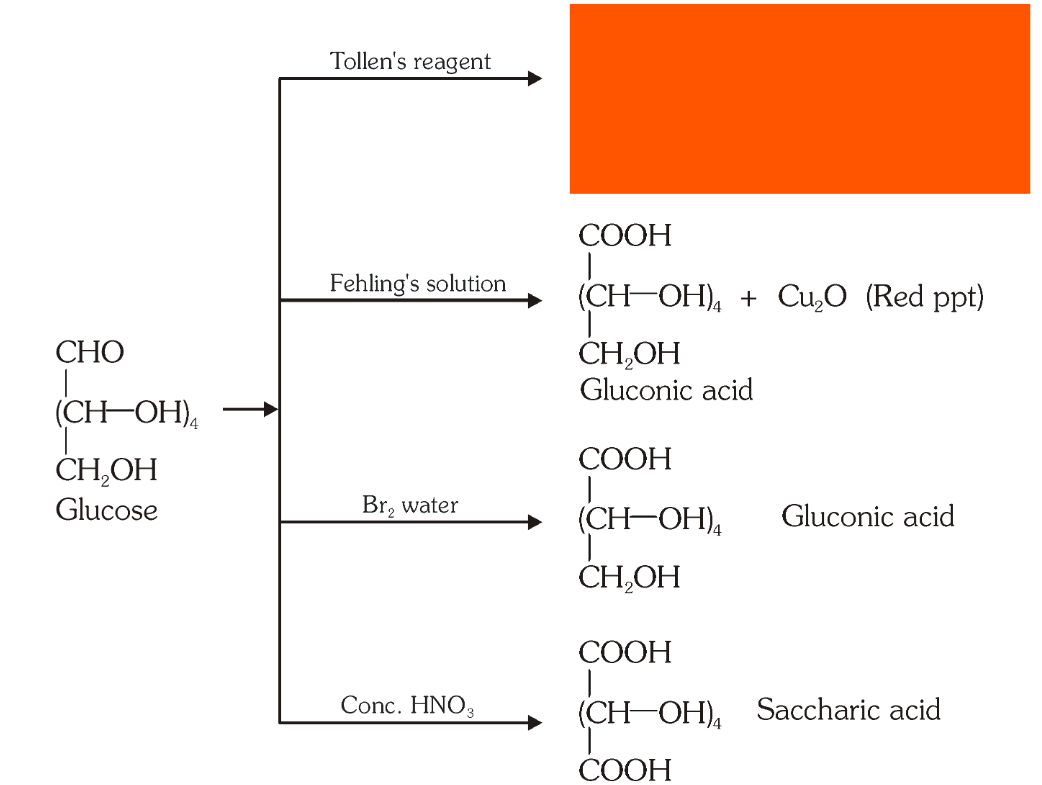
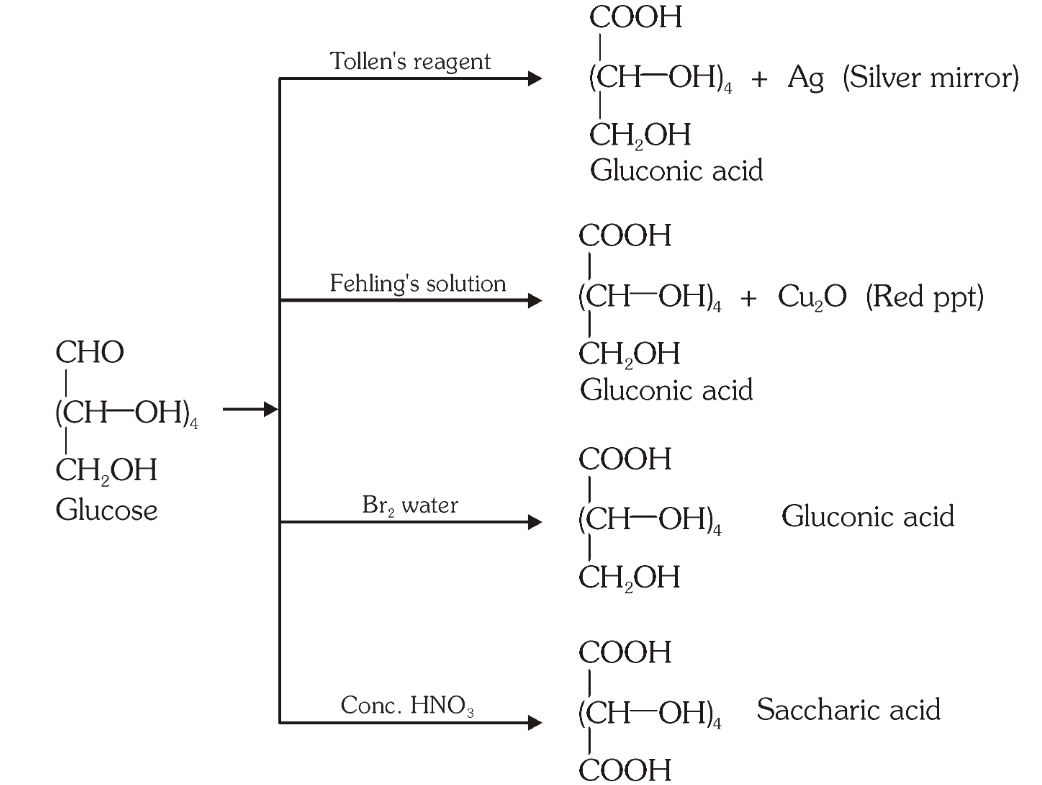
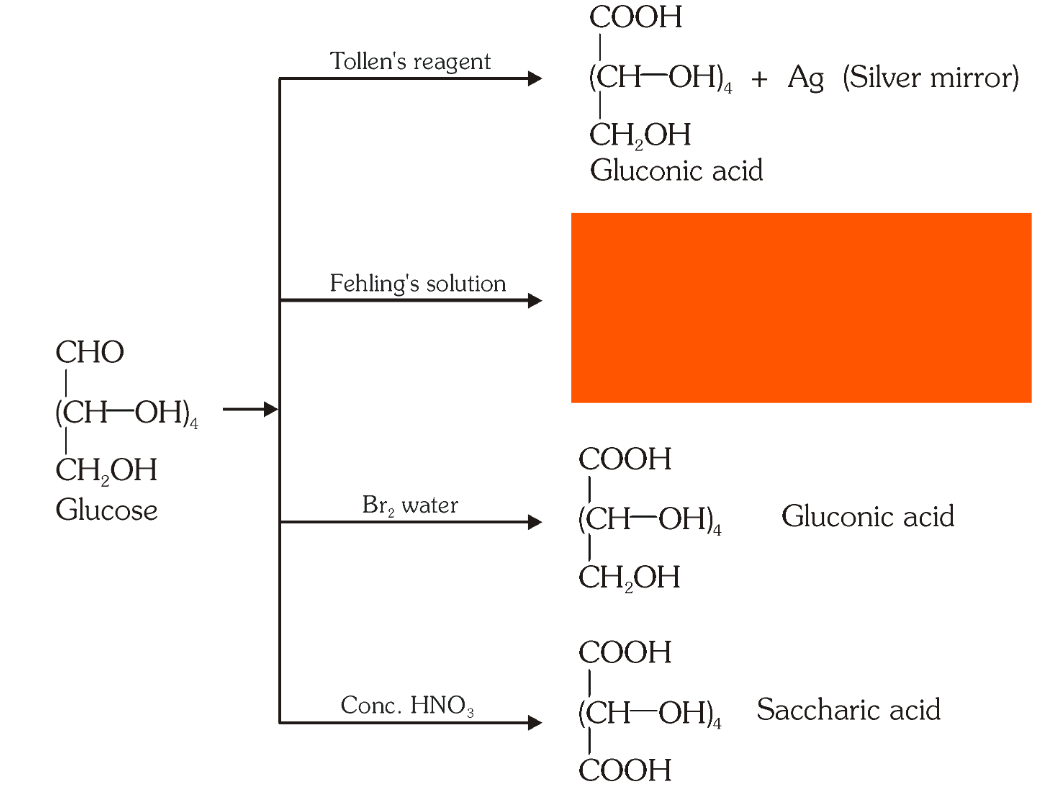
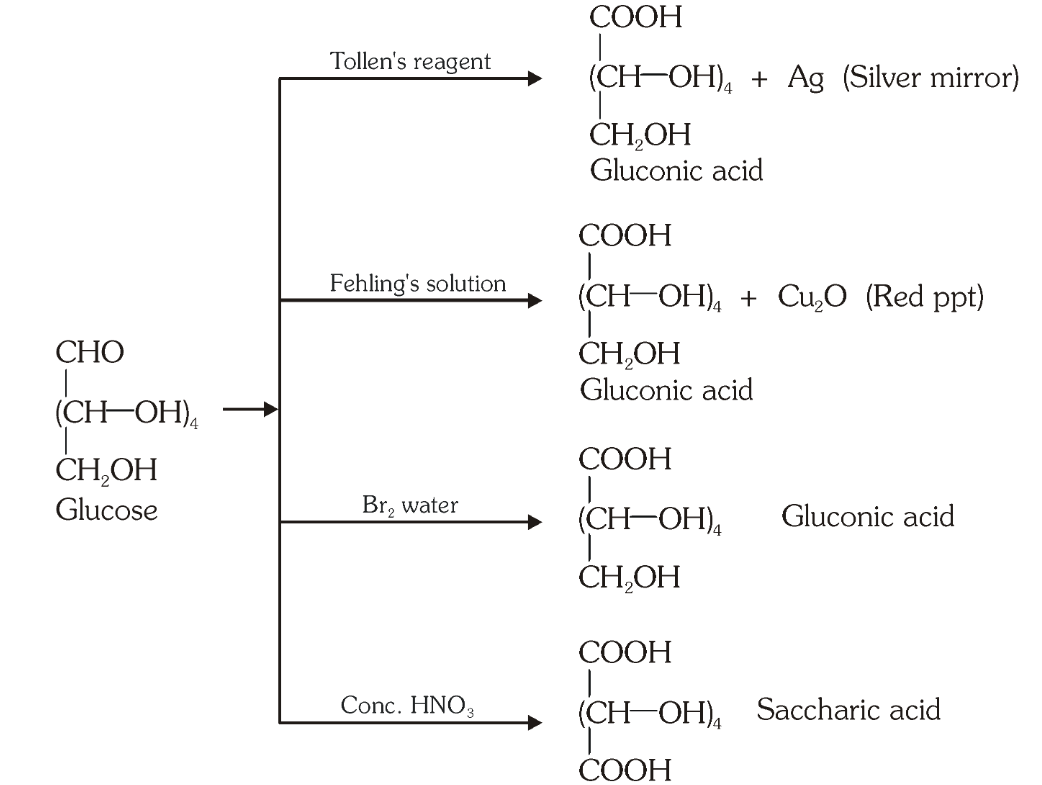

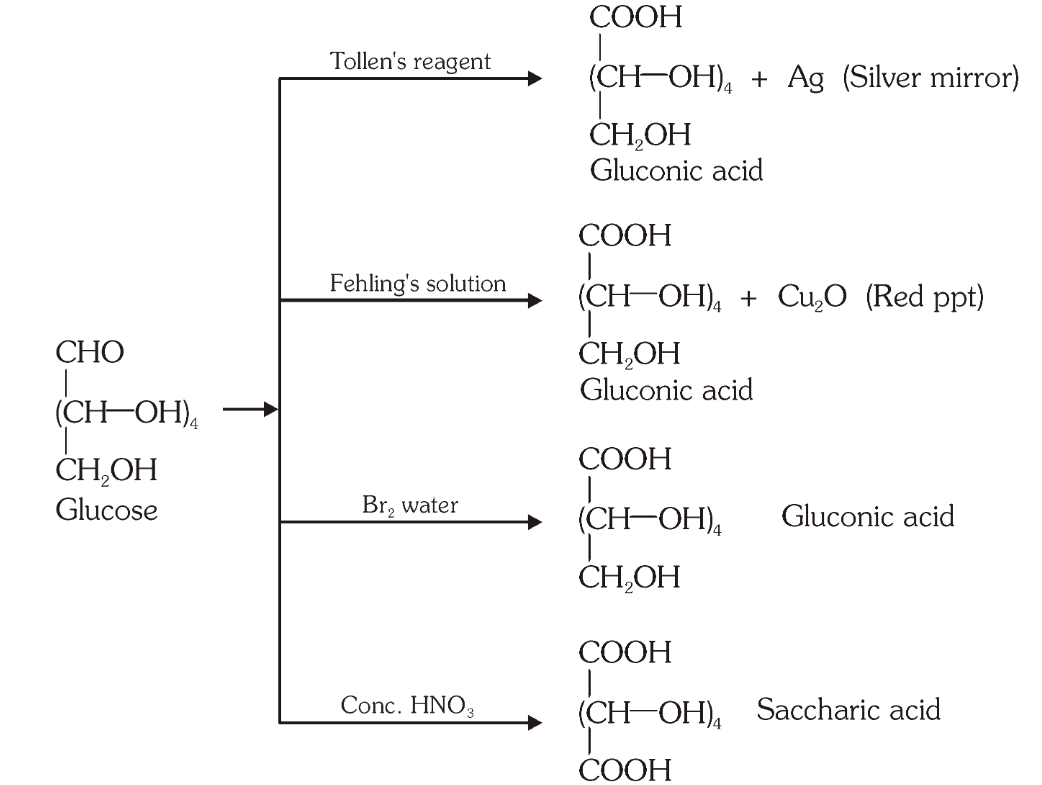
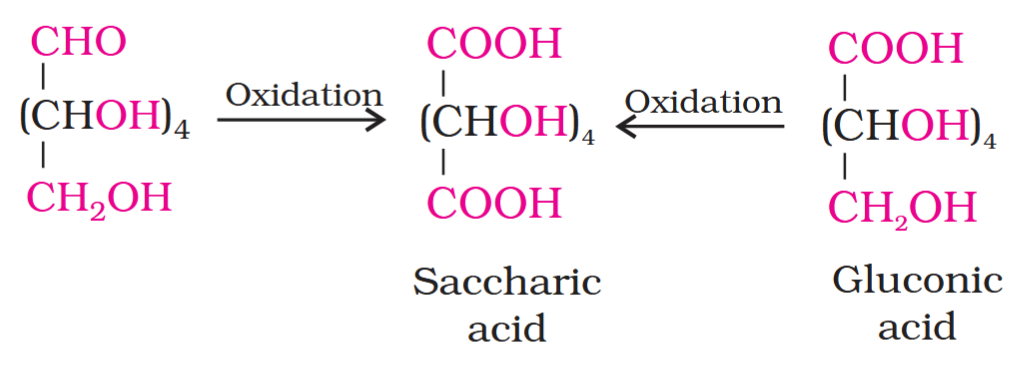
Which reaction indicates that the carbonyl group present on glucose is an aldehydic group?
Glucose gets oxidised to six carbon carboxylic acid (gluconic acid) on reaction with a mild oxidising agent like bromine water. This indicates that the carbonyl group is present as an aldehydic group.
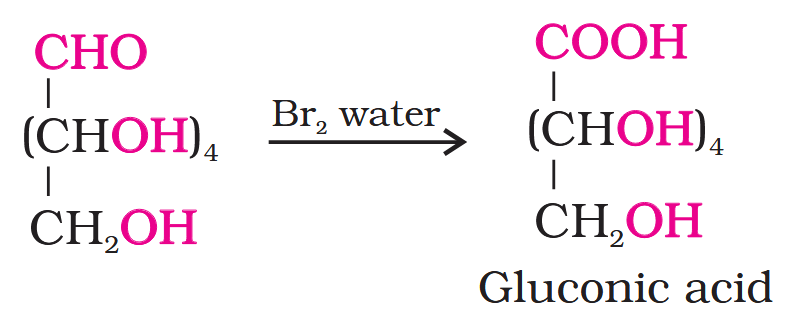
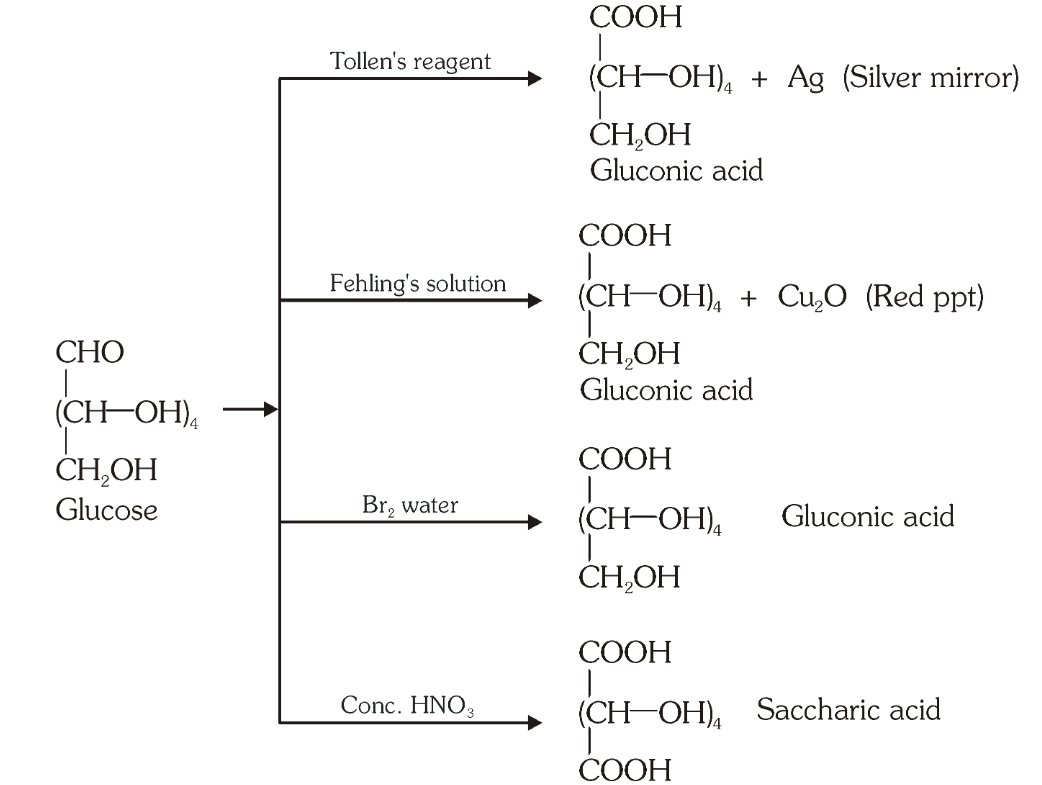
What is the silver mirror test?
Glucose is reacted with Tollen’s reagent to form gluconic acid and AgCl.
What do you get when you react glucose with Fehling’s solution?
Gluconic acid and a red precipitate of Cu_2O.
What do you get when you react glucose with bromine water?
gluconic acid
What do you get when you react glucose with concentrated HNO_3?
saccharic acid
What do you get when you oxidise gluconic acid with nitric acid?
saccharic acid
Which reactions indicate the presence of a primary alcoholic group in glucose?
On oxidation with nitric acid, glucose as well as gluconic acid both yield a dicarboxylic acid, saccharic acid. This indicates the presence of a primary alcoholic (–OH) group in glucose.
What is the structure of gluconic acid?
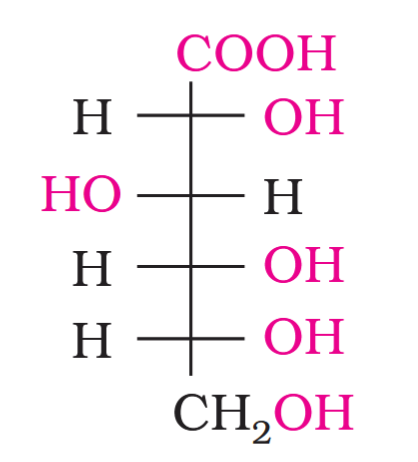
What is the structure of saccharic acid?
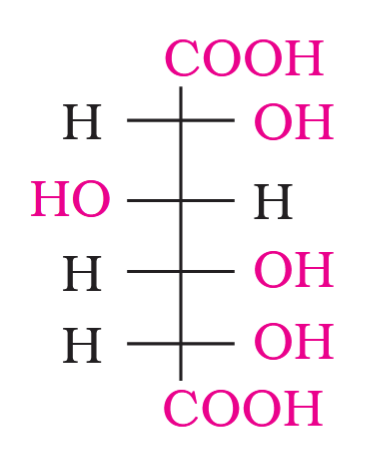
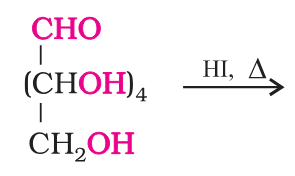
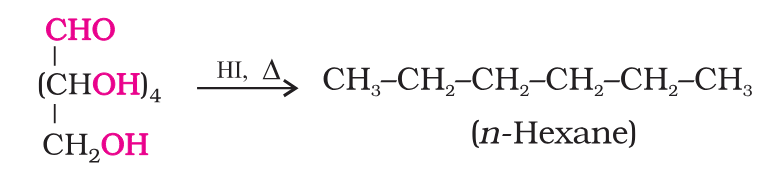
Which reaction suggests that glucose is a straight chain of 6 carbons?
On prolonged heating with HI, it forms n-hexane, suggesting that all the six carbon atoms are linked in a straight chain.
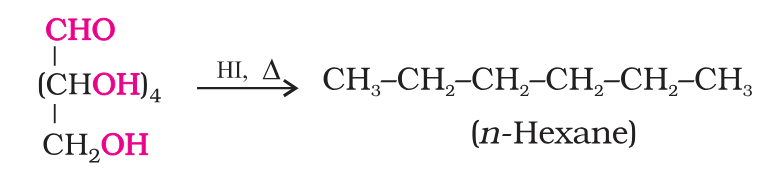

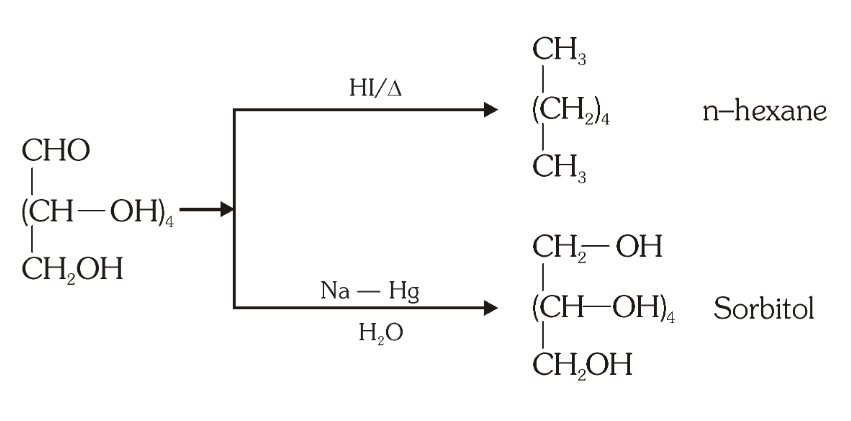
What do you get when you react glucose with HI and red phosphorus?
n-hexane
What do you get when you react glucose with any reducing agent like NaBH_4, LiAlH_4, H_2/Ni, Na-Hg/C_2H_5OH etc?
sorbitol
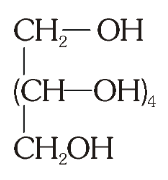
What is the structure of sorbitol?
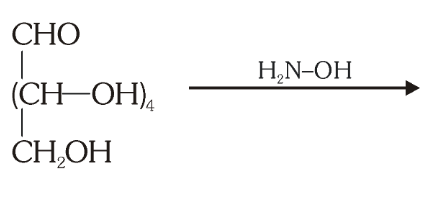
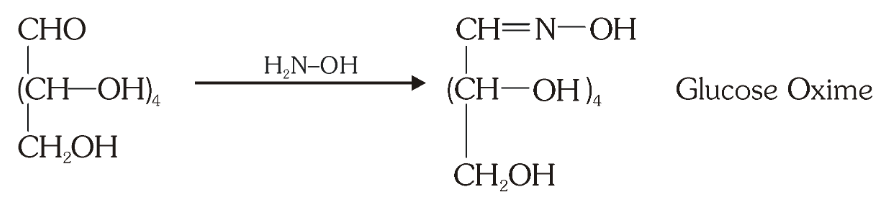
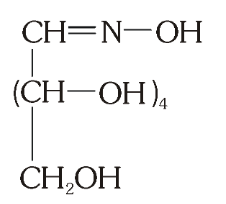
What do you get when you react glucose with hydroxyl amine?
glucose oxime