Chapter 15 Haloalkanes
1/28
Earn XP
Description and Tags
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
29 Terms
define haloalkanes
compounds containing carbon, hydrogen, and at least one halogen
why is the C-Halogen bond polar
1) halogen atoms are more electronegative that carbon atoms
2) the electron pair in the c-halogen bond is closer to the halogen atom than the c atom
define nucleophile
electron pair donor
name three common nucleophiles
hydroxide ions, water molecules, ammonia molecules
define hydrolysis
a chemical reaction involving water or a an aqueous solution of a hydroxide that causes the breaking of a bond in a molecule resulting in the molecule being split into two products
steps of nucleophilic addition of a haloalkane
1) the nucleophile approaches the c atom attached to the halogen atom on the opposite side of the molecule from the halogen atom
2) this direction of attack by the nucleophile minimises repulsion between the nucleophile and the delta negative halogen atom
3) a lone pair of electrons on the nucleophile is attracted and donated to the delta positive c atom
4) the c-halogen bond breaks by heterolytic fission
6) an alcohol and a halide ion are formed
diagram of nucleophilic substitution mechanism for the hydrolysis of chloroethane
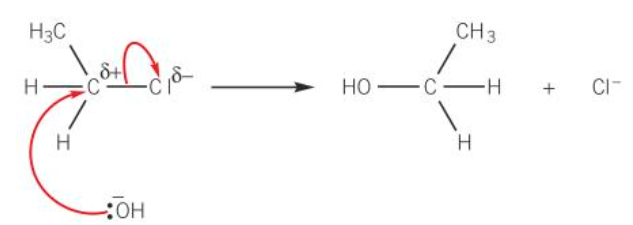
describe how haloalkanes be converted to alcohols
aqueous sodium hydroxide
heated under reflux to obtain a good yield of product
equation for the hydrolysis of 1-bromobutane
CH3CH2CH2CH2Br + NaOH → CH3CH2CH2CH2OH + NaBr
3 predictions that can be made from the bond enthalpy of c-halogen bonds
1) iodoalkanes react faster than bromoalkanes
2) bromoalkanes react faster than chloroalkanes
3) fluoroalkanes are unreactive
general equation for the hydrolysis of haloalkanes in water
CH3CH2CH2CH2X +H2O = CH3CH2CH2CH2OH + X-
how can the rate of hydrolysis reactions of haloalkanes be measured
carrying out the reaction in the presence of aqueous silver nitrate
general equation for the reaction of aqueous silver nitrate and haloalkanes
Ag+ (aq) + X- (aq) = AgX (s)
why is the hydrolysis of haloalkanes reaction done in the presence of an ethanol solvent
ethanol allows water and the haloalkane to mix and produce a single solution rather than two layers
steps of hydrolysis of haloalkanes
1) set up three test tubes and add 1cm3 of ethanol and 2 drops of 1-chloro/bromo/iodobutane in each separate test tube
2) stand the tubes in a water bath at 60°c
3) place a test tube containing 0.1moldm-3 silver nitrate in the water bath and allow all tubes to reach a constant temperature
4) add 1cm3 of the silver nitrate quickly to each test tube. start stopwatch
5) observe test tubes for 5 minutes and record the time taken for precipitate to form
observation of hydrolysis of 1-chlorobutane
white precipitate forms very slowly
observation of hydrolysis of 1-bromobutane
cream precipitate forms slower that 1-iodobutane but faster that 1-chlorobutane
observation of hydrolysis of 1-iodobutane
yellow precipitate forms rapidly
define organohalogen compound
molecules containing at least one halogen atom joined to a carbon chain
uses of organohalogen compounds
pesticides, dry cleaning solvents, flame retardants, general solvents, making polymers, refrigerants
equations for ozone formation
O2 → 2O
O2 + O → O3
why are CFCs very stable
strength of the carbon-halogen bonds within their molecules
how does the stability of CFCs affect the ozone layer
long residence time
takes them years to reach the stratosphere which has UV radiation to break down the ozone layer
equation for the photodissociation of CF2Cl2
CF2Cl3 = CF2Cl radical + Cl radical
propagation steps of ozone depletion
Cl radical + O3 = ClO radical + O2
ClO radical + O = Cl radical + O2
overall equation for the propagation steps of ozone depletion
O3 + O = 2O2
how are nitrogen oxide radicals formed
lightning strikes and aircraft travel in stratosphere
propagation steps of ozone depletion involving NO
NO radical + O3 = NO2 radical + O2
NO2 radical + O = NO radical + O2
overall equation for propagation steps of ozone depletion involving NO
O3 + O = 2O2