Lab Practical 2 - BIOL 320
0.0(0)
Card Sorting
1/115
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Last updated 9:53 PM on 4/11/23
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
116 Terms
1
New cards
What are the 2 main groups of the digestive system?
1. alimentary canal
2. accessory digestive organs
2
New cards
5 processes of digestion
1. ingestion
2. propulsion
3. mechanical and enzymatic digestion
4. absorption
5. elimination
3
New cards
small intestine segments
1. duodenum
2. jejunum
3. ileum
4
New cards
large intestine segments
1. colon
* ascending
* transverse
* descending
2. rectum
5
New cards
lipid digestion main points
liver: produces bile to help move lipids through small intestine
stomach: little digestion occurs
pancreas: enzyme lipase
small I: most digestion occurs here
stomach: little digestion occurs
pancreas: enzyme lipase
small I: most digestion occurs here
6
New cards
CHO digestion main points
mouth: begins digestion with chewing and salivary amylase
liver: converts fructose and galactose to glucose
stomach: HCl acid
pancreas: contributes enzymes
small I: remaining disaccharides are broken down
liver: converts fructose and galactose to glucose
stomach: HCl acid
pancreas: contributes enzymes
small I: remaining disaccharides are broken down
7
New cards
paired arteries
1. renal a.
2. adrenal lumbar a.
3. iliac lumbar a.
4. external iliac a.
5. internal iliac a.
8
New cards
unpaired arteries
1. celiac a.
2. superior mesenteric a.
3. inferior mesenteric a.
4. medial sacral a.
9
New cards
what makes the left kidney different?
extra artery (gonadal)
10
New cards
celiac a. branches
1. splenic a.
2. left gastric a.
3. hepatic a.
11
New cards
superior mesenteric a. branches
1. middle colic a.
2. ileocolic a.
3. intestinal a.
4. posterior pancreatic duodenal a.
12
New cards
inferior mesenteric a. branches
1. left colic a.
2. superior rectal a.
13
New cards
what artery is in humans but not in cats?
common iliac a. but cats have veins
14
New cards
what veins combine to for the hepatic portal vein?
splenic vein and superior mesenteric
15
New cards
muscles of inspiration
1. sternocleidomastoid
2. scalenes
3. external intercostals
4. diaphragm
16
New cards
muscles of expiration
1. internal intercostals
2. diaphragm
3. external oblique
4. internal oblique
5. transversus abdominus
6. rectus abdominus
17
New cards
Boyles law
at a constant temp, the pressure of a gas varies inversely with its volume
18
New cards
inhalation vs exhalation (pressure and volume)
inhalation: increase volume and decrease pressure
exhalation: decrease volume and increase pressure
exhalation: decrease volume and increase pressure
19
New cards
tissue of the alveoli?
elastic connective tissue for expansion
20
New cards
function of pulmonary capillaries?
exchange gases with alveoli and tissues
21
New cards
lobes of the lungs
right:
1. superior lobe
2. middle lobe
3. inferior lobe
left:
1. superior lobe
2. inferior lobe
1. superior lobe
2. middle lobe
3. inferior lobe
left:
1. superior lobe
2. inferior lobe
22
New cards
4 lung volumes
1. inspiratory reserve volume (1900ml F, 3100ml M)
2. tidal volume (500ml)
3. expiratory reserve volume (700ml F, 1200ml M)
4. reserve volume (1100ml F, 1200ml M)
23
New cards
which volume is not recorded by spirometry?
reserve volume
24
New cards
5 lung capacities
1. inspiratory capacity (2400ml F, 3600ml M)
2. expository capacity (1200ml F, 1700ml M)
3. vital capacity (3100ml F, 4800ml M)
4. functional residual capacity (1800ml F, 2400ml M)
5. total lung capacity (4200ml F, 6000ml M)
25
New cards
inspiratory capacity equation
IC\=TV+IRV
26
New cards
expiratory capacity equation
EC \= TV + ERV
27
New cards
vital capacity equation
VC \= TV + IRV + ERV
28
New cards
functional residual capacity equation
FRC \= ERV + RV
29
New cards
total lung capacity equation
TLC \= VC + RV
30
New cards
pontine respiratory center
refine transitions between inhalation and exhalation
31
New cards
eupnea
clinical term for a normal breathing rate
32
New cards
hypercapnia
high CO2 in blood (decrease pH)
1. hypercapnia
2. aortic arch
3. chemoreceptor
4. DRG
5. VRG
6. increase ventilation rate
1. hypercapnia
2. aortic arch
3. chemoreceptor
4. DRG
5. VRG
6. increase ventilation rate
33
New cards
Hypernea vs hyperventilation
hypernea: increase breathing rate and depth that matches metabolic need (exercise)
hyperventilation: increased breathing rate and depth that exceeds body need (anxiety attack)
hyperventilation: increased breathing rate and depth that exceeds body need (anxiety attack)
34
New cards
chronic obstructive pulmonary disease (COPD)
emphysema and chronic bronchitis
irreversible lung damage
irreversible lung damage
35
New cards
dyspnea
clinical term for difficult or labored breathing and symptom of COPD
36
New cards
Emphysema
permanent enlargement of the alveoli due to destruction of the alveolar walls
37
New cards
factors influencing breathing
lung stretch receptors: keep from overfilling
irritant response: sneezing
higher brain center: Brain influence
chemicals: chemoreceptors
irritant response: sneezing
higher brain center: Brain influence
chemicals: chemoreceptors
38
New cards
Ratio of FEV1/FVC
normal = 80%
obstructive disorder < 80%
restrictive disorder > 80%
mixed disorder < 80%
obstructive disorder < 80%
restrictive disorder > 80%
mixed disorder < 80%
39
New cards
blood flow through kidney
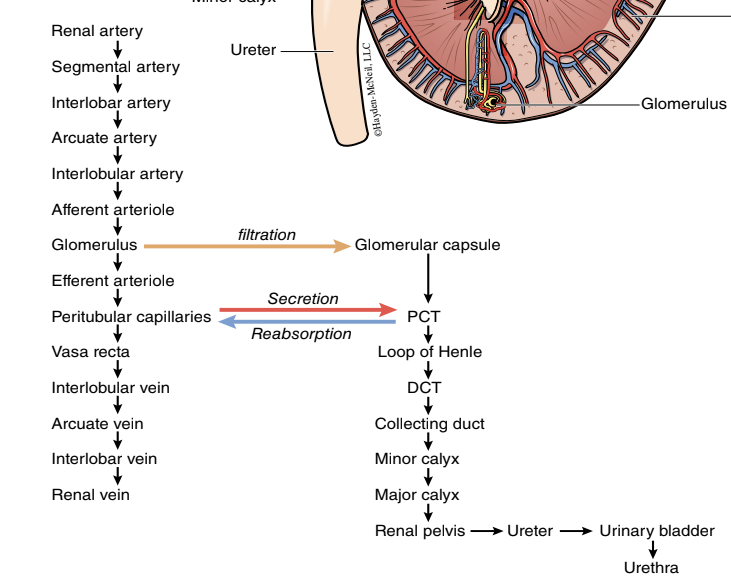
40
New cards
female gonads
ovaries - primary reproductive organ, produce both estrogen and progesterone
41
New cards
fallopian tubes
site of fertilization
42
New cards
infundibulum
the funnel-shaped opening into the fallopian tube near the ovary that catches oocyte
43
New cards
Layers of the uterus
1. perimetrium
2. myometrium
3. endometrium
* functional (shed during mensuration)
* basal (produce new functional layer)
44
New cards
function of uterus
site of embryo implantation
45
New cards
cervix
internal os: opening into the uterus
external os: opening into the vagina
external os: opening into the vagina
46
New cards
cervix cells
endocervical canal: ciliated simple columnar epithelial
ectocervix: stratified squamous epithelial
ectocervix: stratified squamous epithelial
47
New cards
vagina layers and cells
between the bladder and rectum
layers:
1. fibroelastic adventitia
2. muscularis
3. inner mucosa
stratified squamous epithelial
layers:
1. fibroelastic adventitia
2. muscularis
3. inner mucosa
stratified squamous epithelial
48
New cards
Bartholin's glands
produce a mucus to lubricate and moisten the vagina
49
New cards
homologous structures
labia majora - male scrotum
labia minora - vental penis
bartholins glands - bulbourethral gland
clitoris - penis
labia minora - vental penis
bartholins glands - bulbourethral gland
clitoris - penis
50
New cards
corpus spongiosum vs corpus cavernosa
corpus cavernous becomes engorged with arterial blood
51
New cards
sperm development order
1. seminiferous tubules
2. rete testis
3. efferent ductules
4. epididymis
5. vas deferens
52
New cards
seminiferous tubules
site of sperm production
53
New cards
Epididymis
site of maturation of sperm
54
New cards
vas deferens
transport sperm from epididymis to urethra
55
New cards
ejaculatory duct
fusion of vas deferens and seminal vesticle duct
56
New cards
bulbourethral glands
produce fluid that serves to lubricate urethra and neutralize any acidity from urine
57
New cards
Digestive system layers
1. Lumen
2. Mucosa
* epithelium
* laminate propia
* muscularis mucosa
3. Submuscosa
4. Muscularis
* circular muscle
* longitudinal muscle
5. Serosa
58
New cards
What can be seen in the slides of the duodenum?
Brunners glands (alkaline) in submucosa
59
New cards
What can be seen in the ileum and colon slides?
Peyers patch's in submucosa
60
New cards
On lips...
Keratin on outer region and glands on inner region
61
New cards
What can be seen on colon slides?
Thick layer of submucosa and large goblet cells
62
New cards
exocrine vs endocrine glands
Exocrine have epithelial attachment
63
New cards
Exocrine gland shapes
1. Simple tubulan
2. Simple branched tubulan
3. Simple coiled tubulan
4. Simple acinar
5. Simple branched acinar
64
New cards
Endocrine gland shapes
1. Cord and clump
2. Follicular type
65
New cards
Lymph follicles
Located in cortex
maturation of B cells
primary follicle: immature B cells
secondary follicle: activation of B cells
maturation of B cells
primary follicle: immature B cells
secondary follicle: activation of B cells
66
New cards
What can be seen on lingual tonsil slides?
Muscle and salivary glands
67
New cards
What can be seen on pharyngeal slide?
Pseudostratified ciliated columnar epithelial
68
New cards
Thymus
Made up of lobules with septoe separating them
maturation of T cells
contain Hassan's capsule
maturation of T cells
contain Hassan's capsule
69
New cards
spleen
Filter RBCs
divided into 2 regions
* white pulp = WBC
* red pulp = RBC
divided into 2 regions
* white pulp = WBC
* red pulp = RBC
70
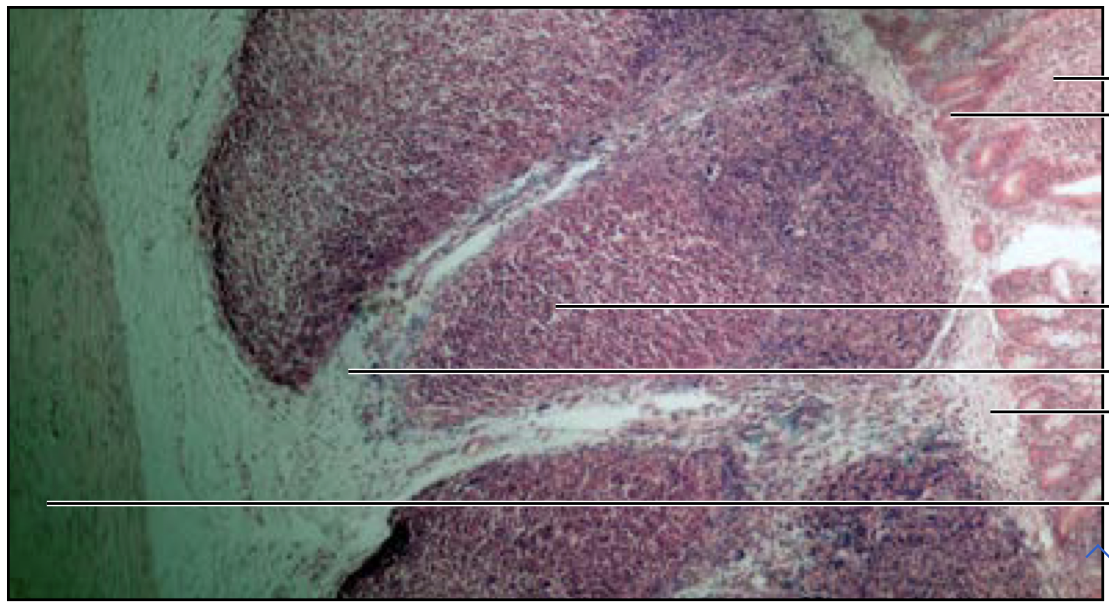
New cards
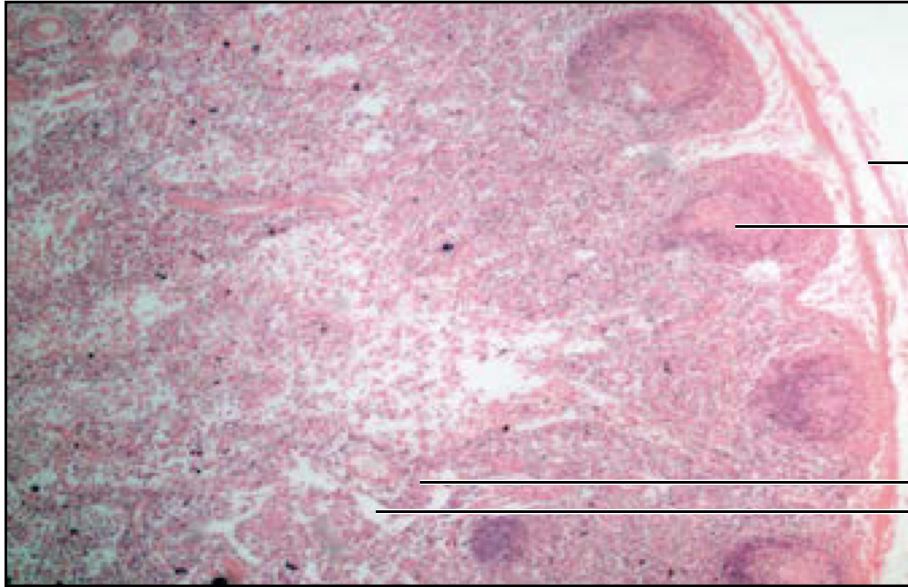
Lymph node
71
New cards
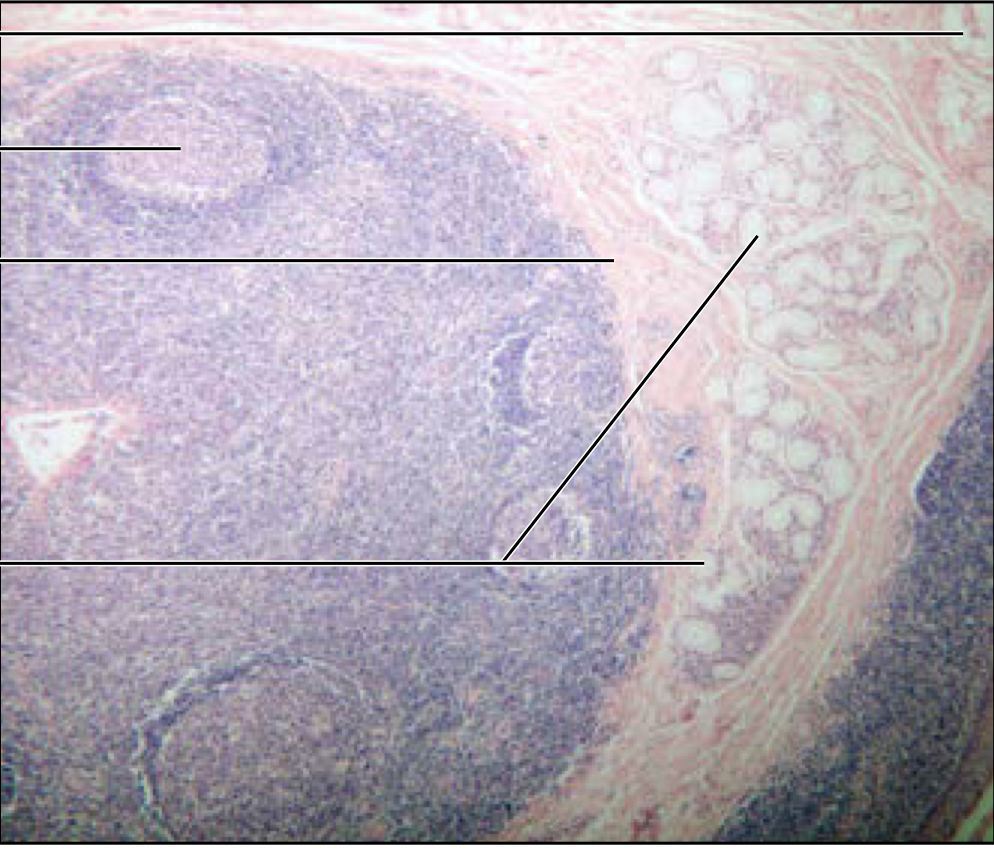
Lingual tonsil
72
New cards
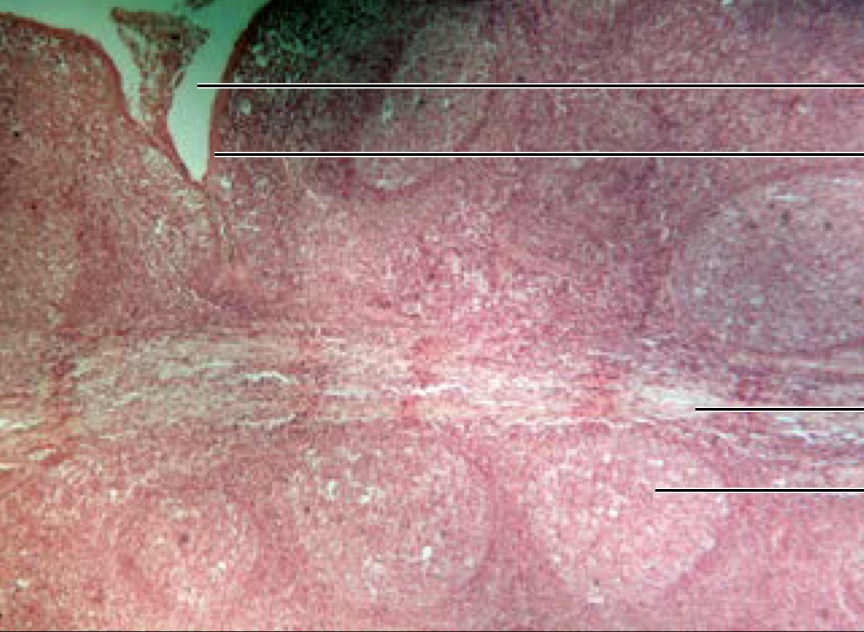
Palatine tonsil
73
New cards
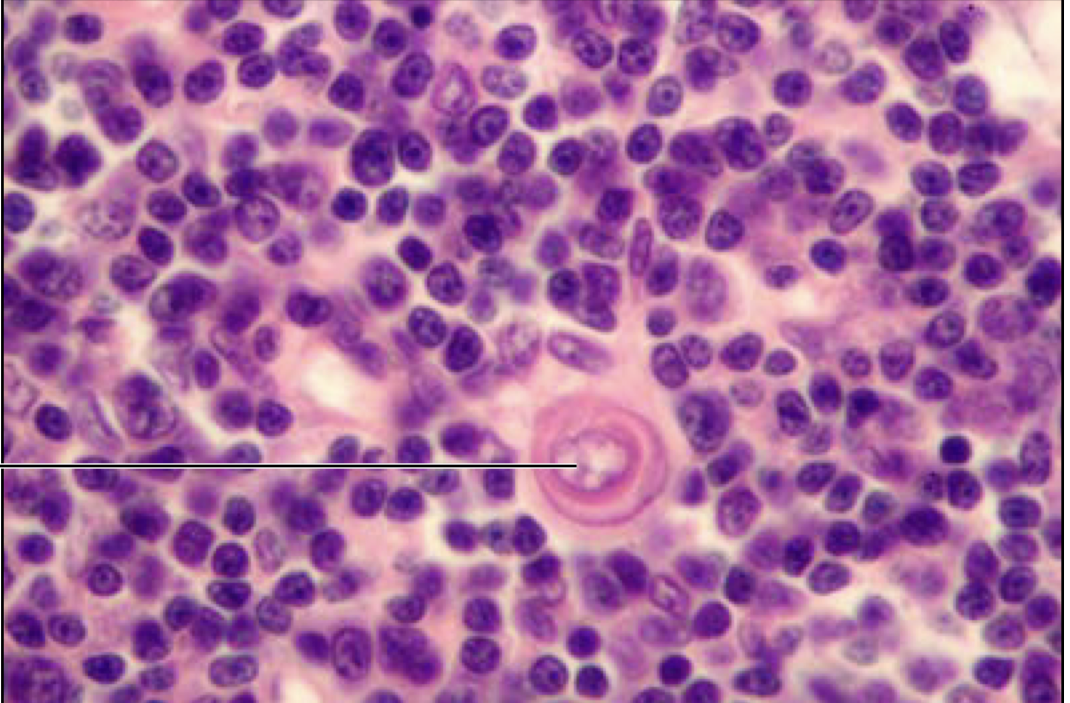
Thymus
hassalls corpuscles
hassalls corpuscles
74
New cards
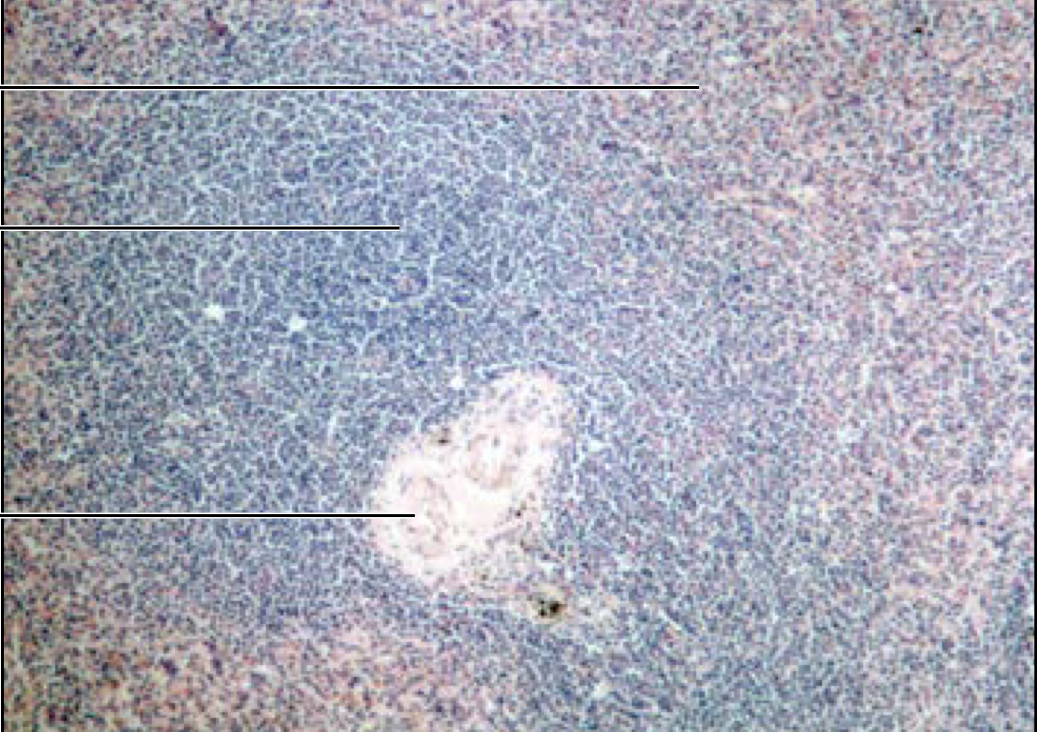
Spleen
white pulp = blue
red pulp = red
white pulp = blue
red pulp = red
75
New cards
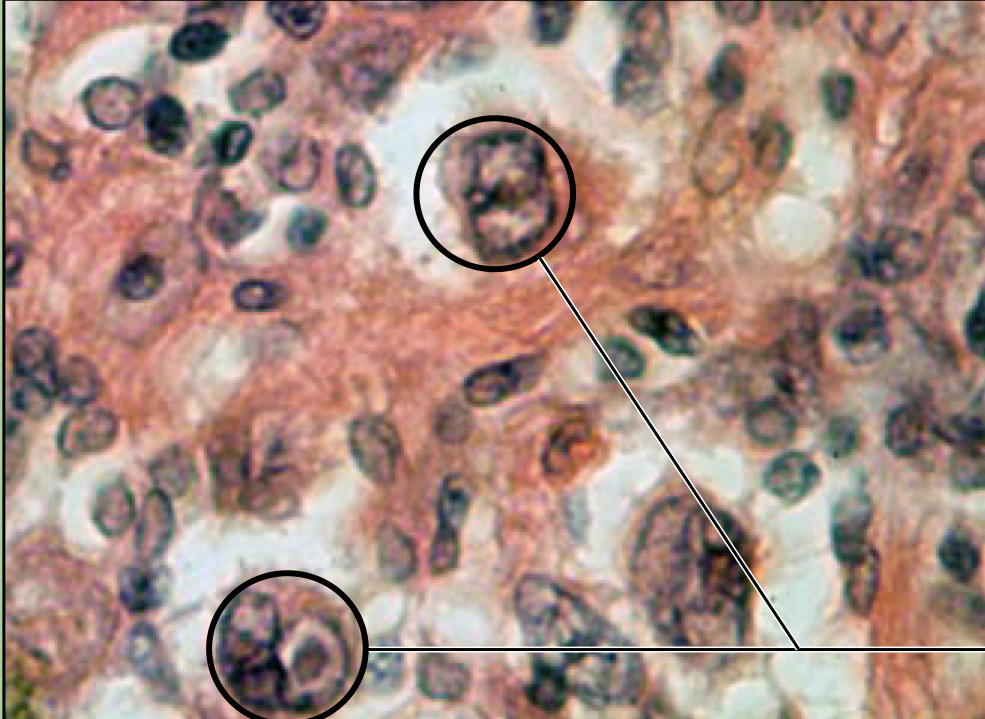
what disease is this?
Hodgkins granuloma - cancer of lymphatic system. can lead to breakdown of splenic pulps
Reed-Sternberg cells
Reed-Sternberg cells
76
New cards
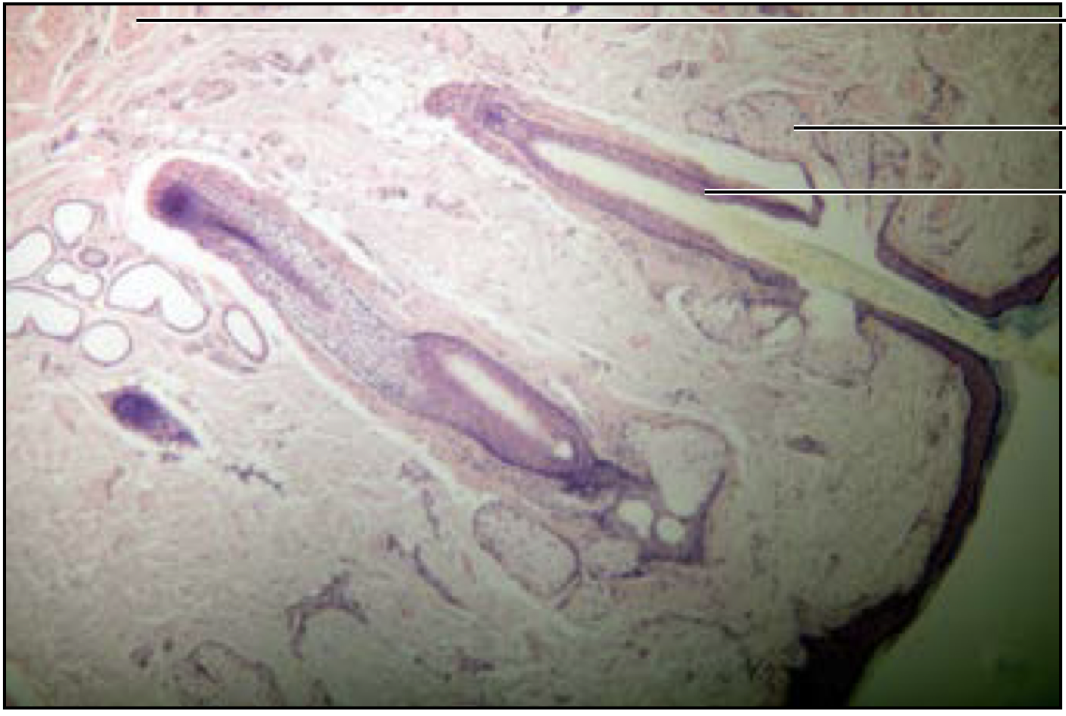
Lip
77
New cards
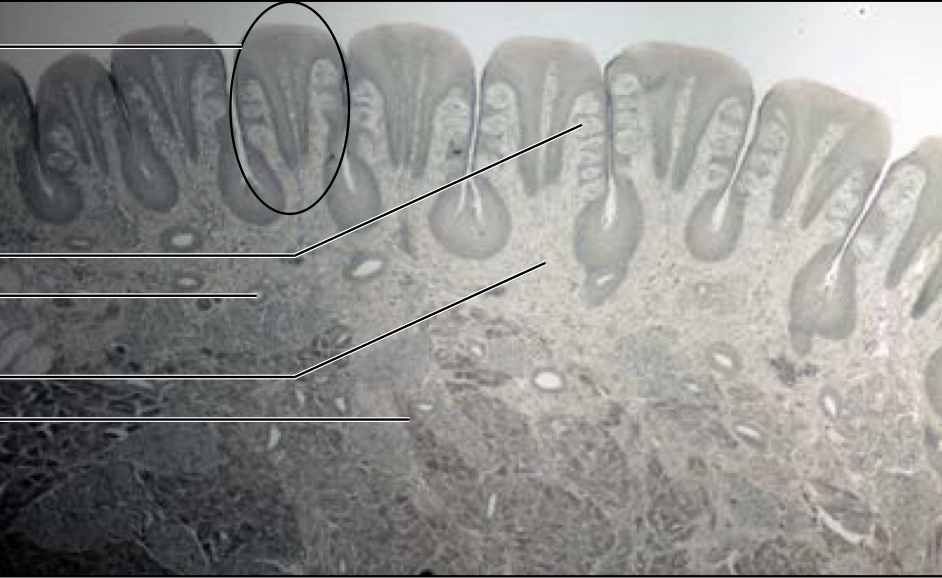
Tongue - taste bub
papilla containing taste buds
papilla containing taste buds
78
New cards
Tooth
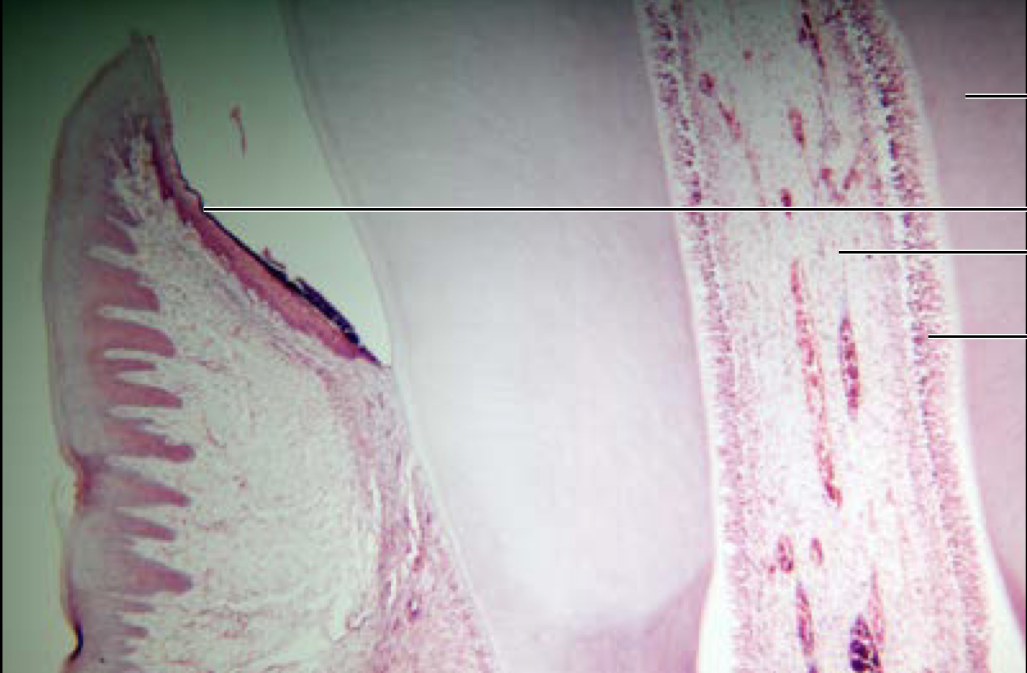
79
New cards
Esophagus
80
New cards
Parotid gland
one of the 3 major salivary glands, located on superficial masseter on both sides of head
one of the 3 major salivary glands, located on superficial masseter on both sides of head
81
New cards
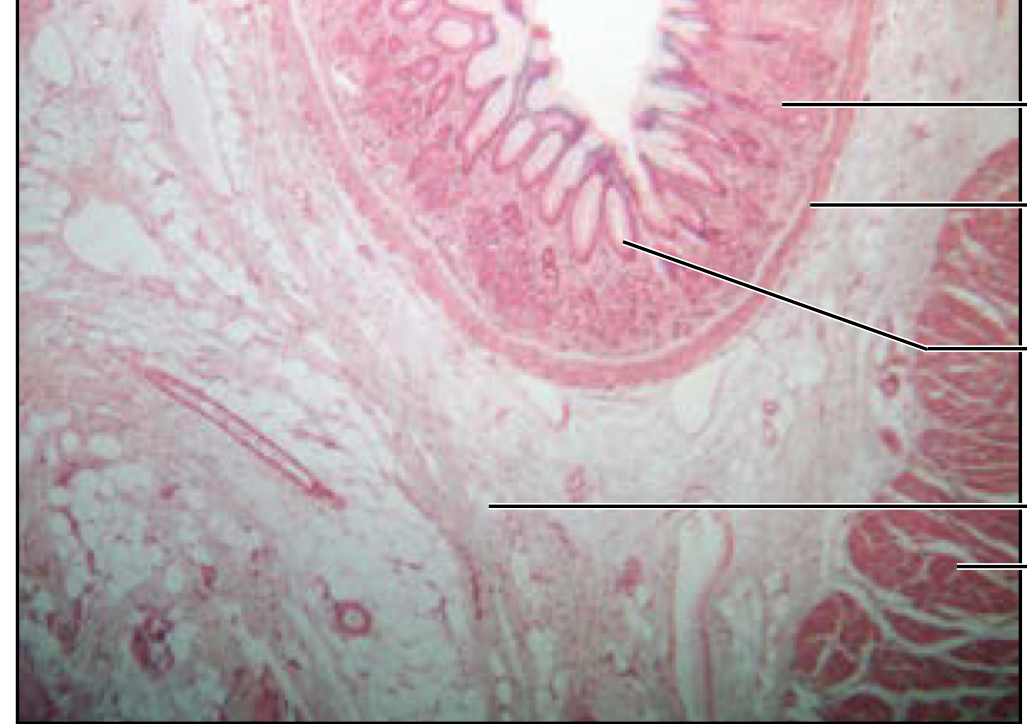
Stomach
contain gastric pits and glands
contain gastric pits and glands
82
New cards
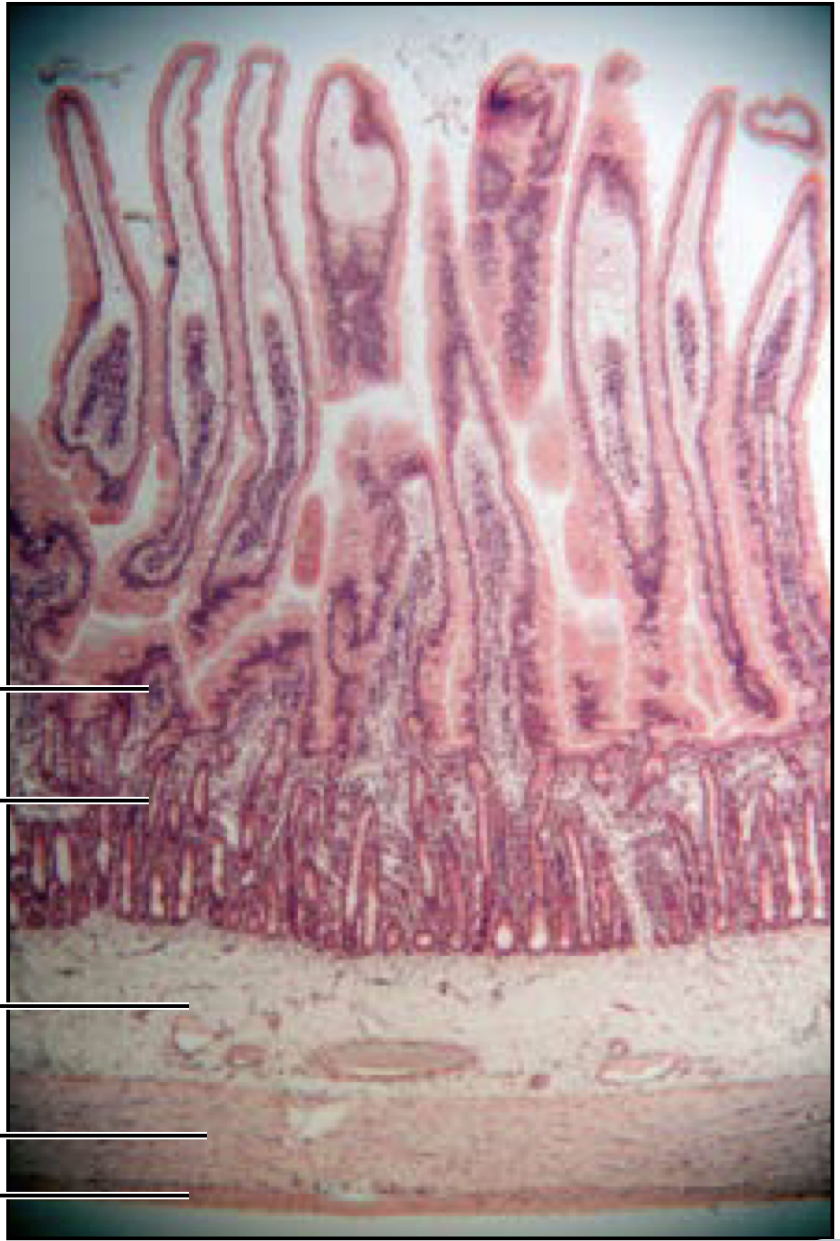
Duodenum
brunners gland and goblet cells
brunners gland and goblet cells
83
New cards
Jejunum
84
New cards
Ileum
85
New cards
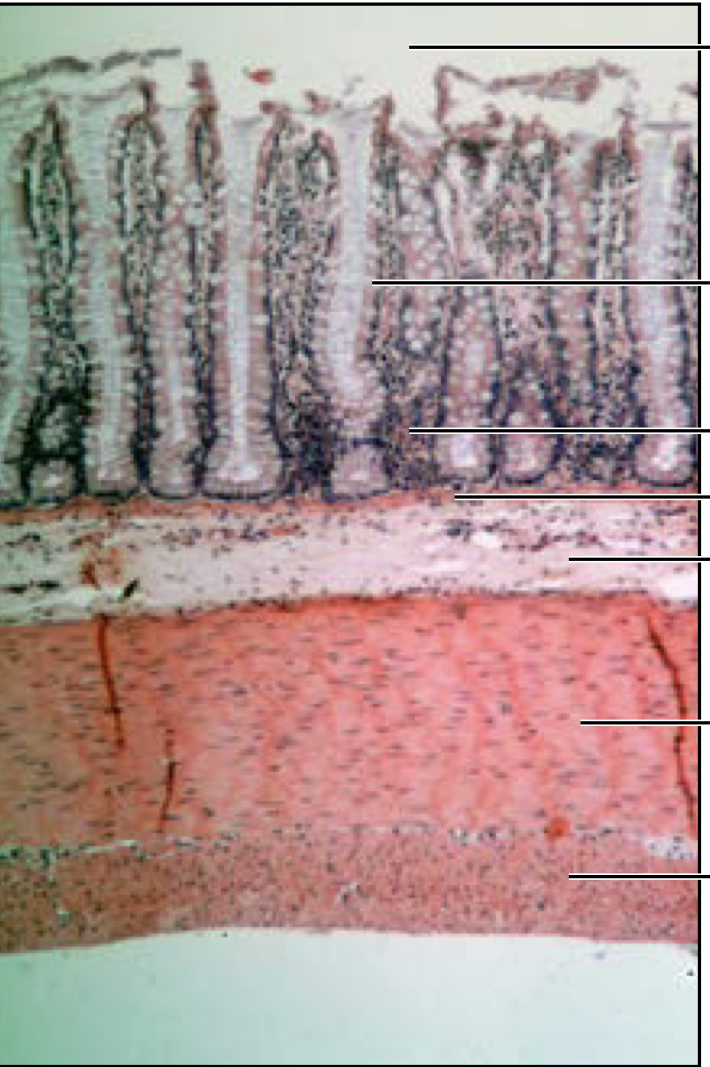
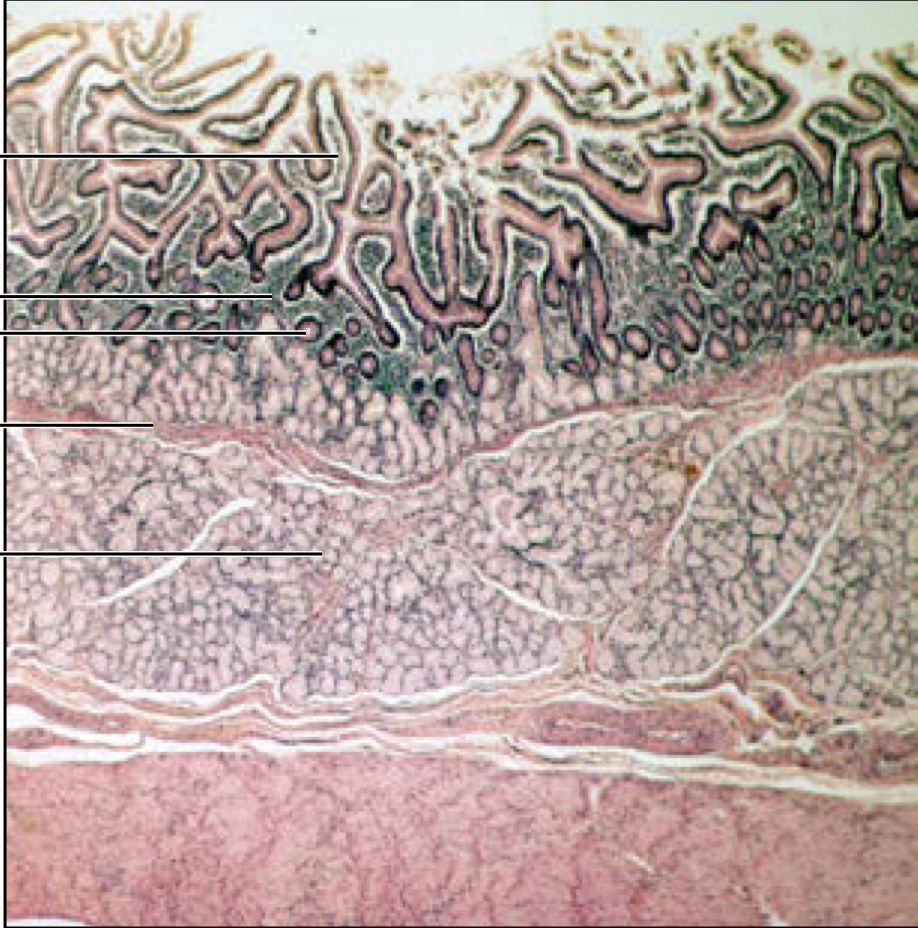
Colon
86
New cards
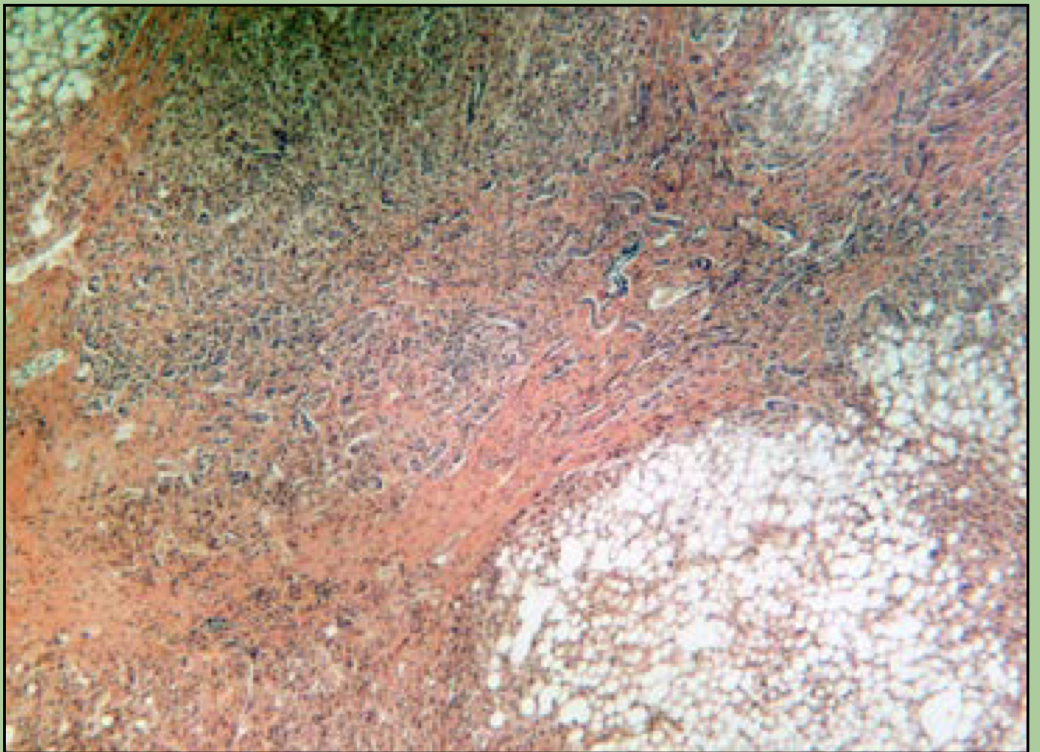
What disorder is this?
Cirrhosis
fibrous fatty deposits in liver
fibrous fatty deposits in liver
87
New cards
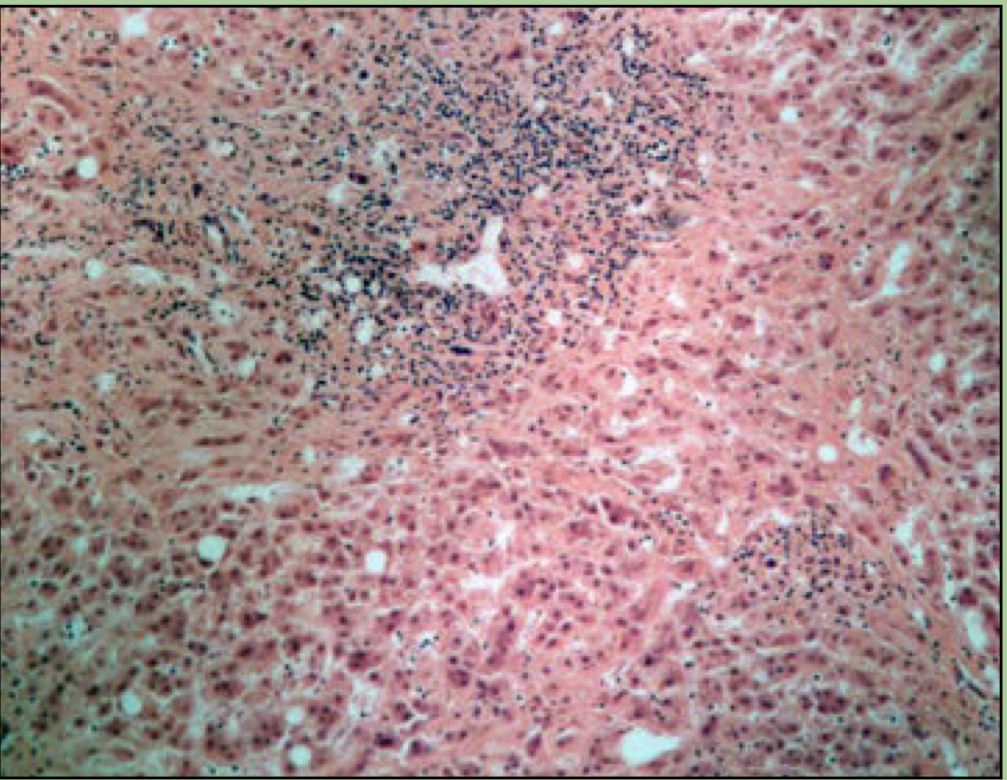
What disorder is this?
Hepatitis
viral infection of the liver
viral infection of the liver
88
New cards
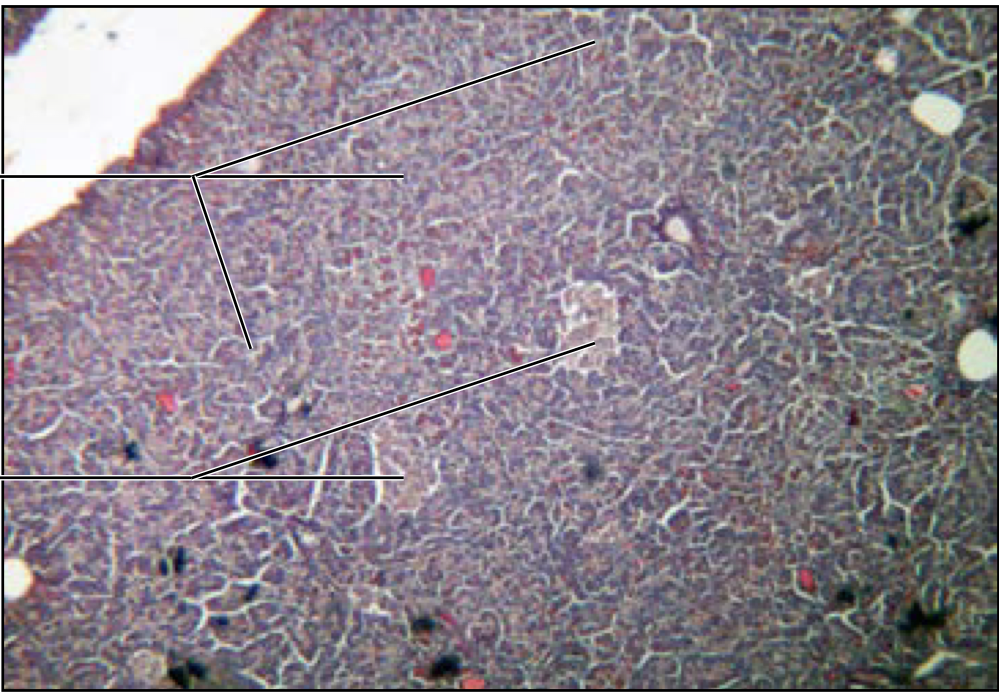
Pancreas
beta and alpha cells
islets of langerhans
beta and alpha cells
islets of langerhans
89
New cards
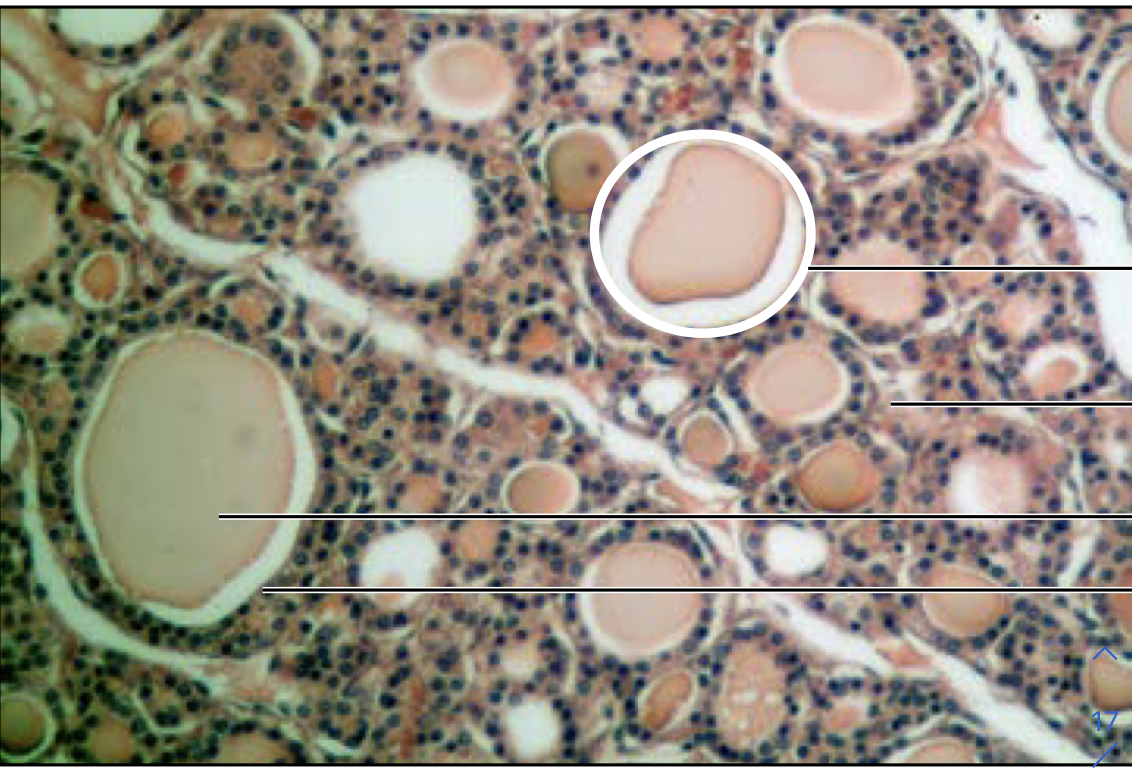
Thyroid gland
parafollicular cells secrete calcitonin
parafollicular cells secrete calcitonin
90
New cards
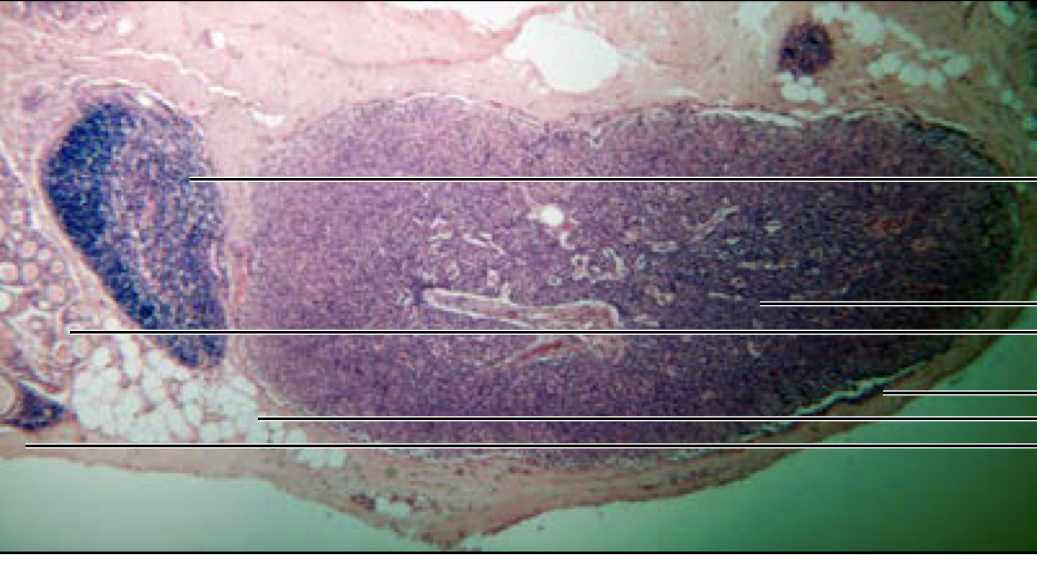
\
parathyroid gland
secrete parathyroid hormone
secrete parathyroid hormone
91
New cards
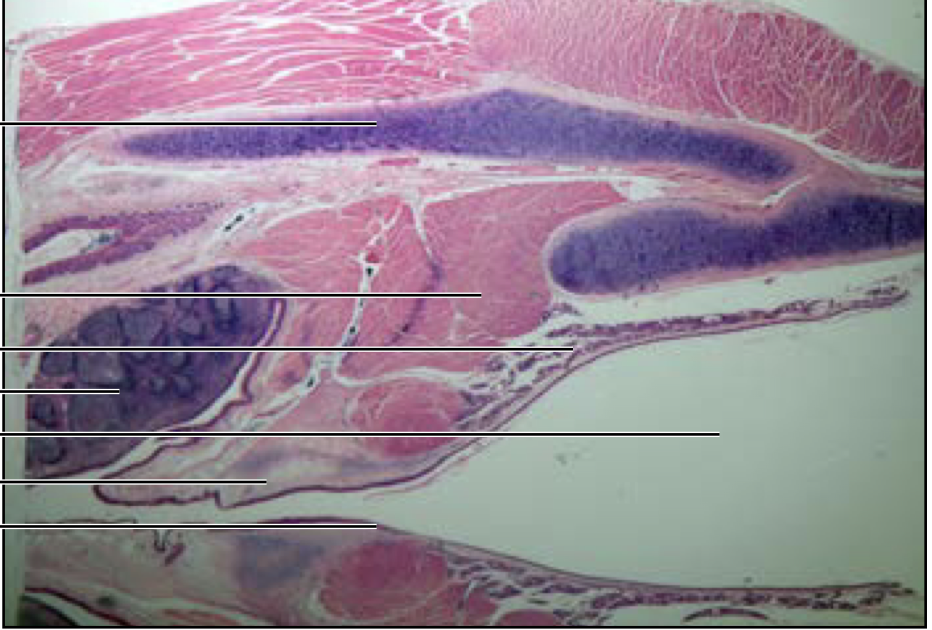
Larynx
contain vocal cords
contain vocal cords
92
New cards
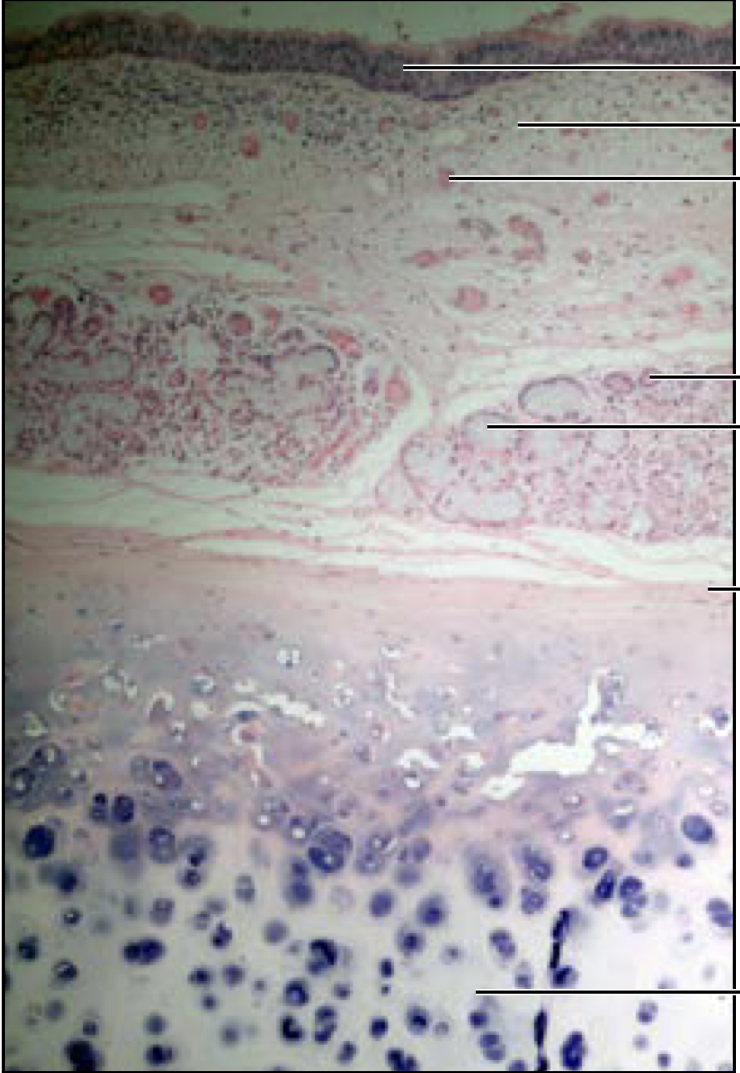
Trachea
93
New cards
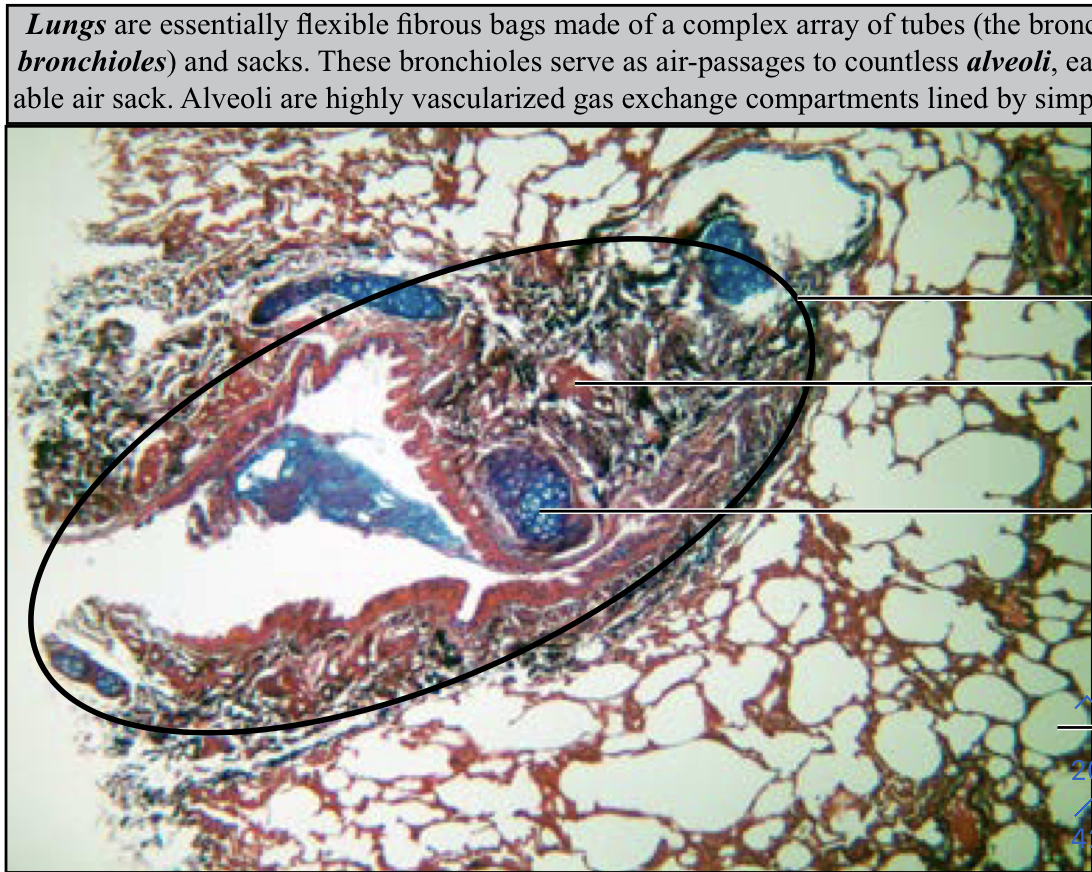
Lung
94
New cards
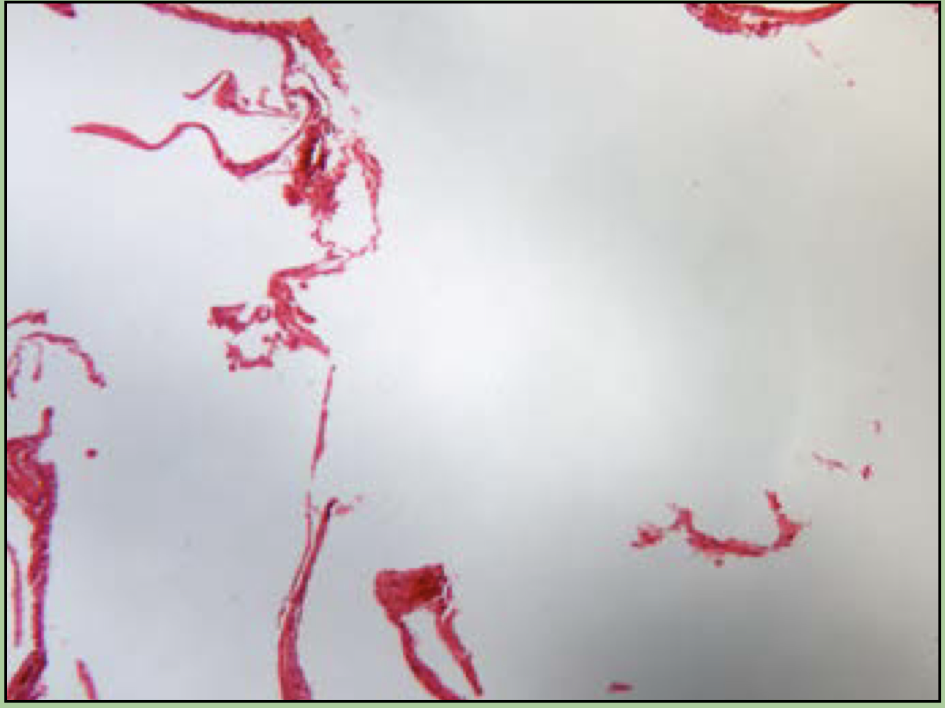
What disorder is this?
Emphysema
COPD
breakage and collapse of alveoli
COPD
breakage and collapse of alveoli
95
New cards
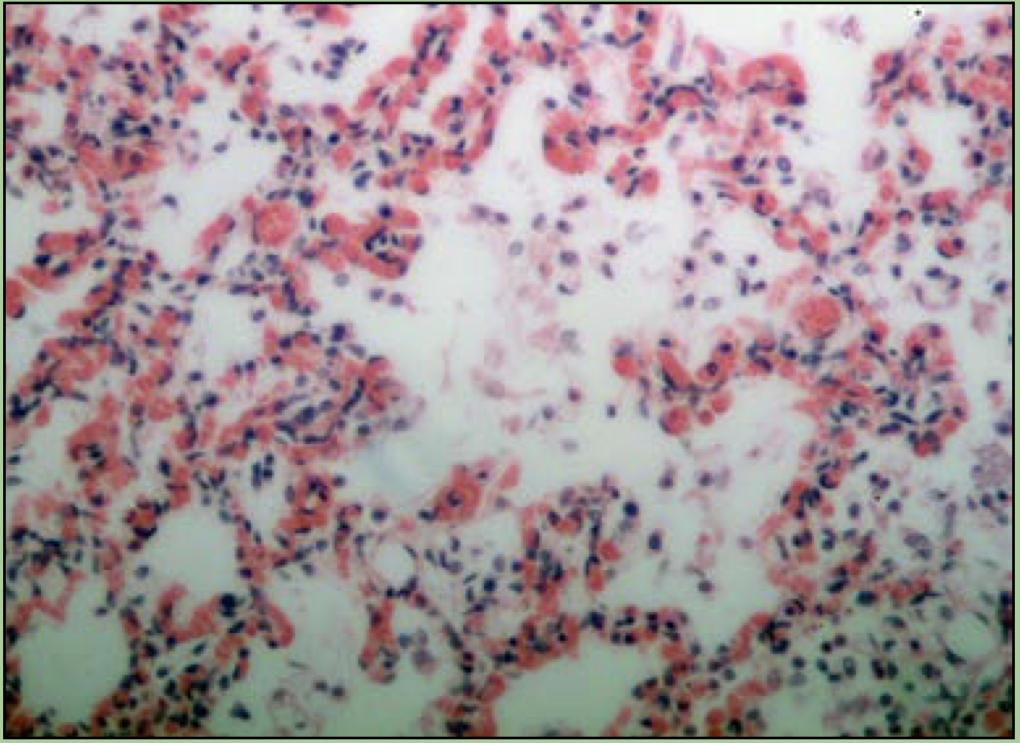
What disorder is this?
Pneumonia
inflammatory disease
inflammatory disease
96
New cards
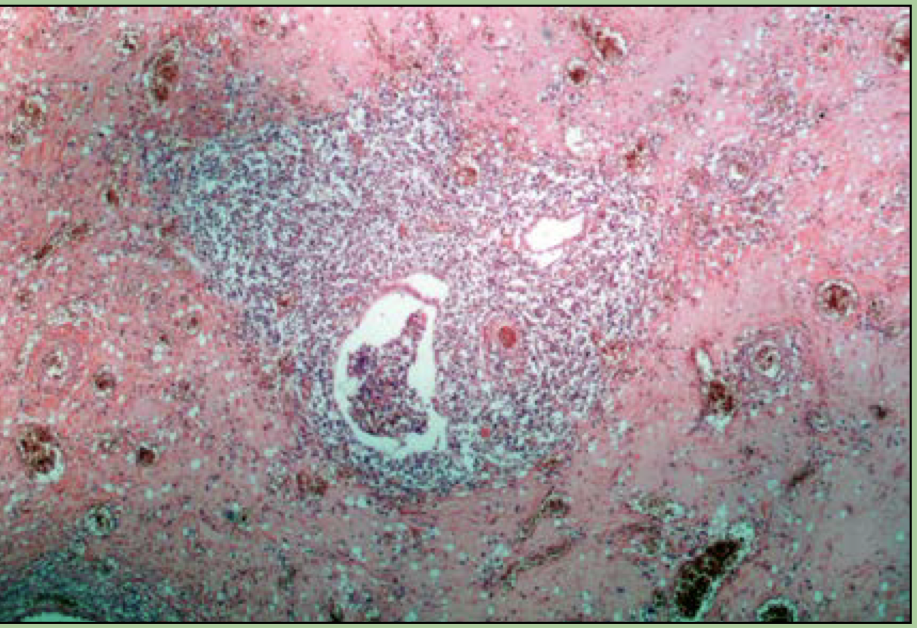
What disorder is this?
Tuberculosis
mycobacterium tuberculosis
mycobacterium tuberculosis
97
New cards
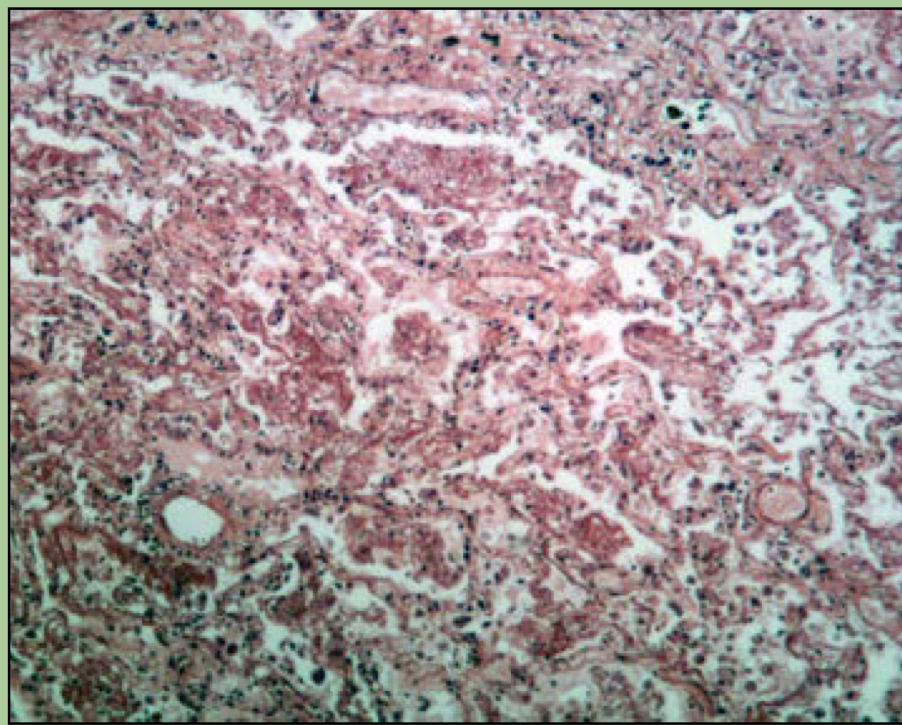
What disorder is this?
Lung carcinoma
primary lung cancer
primary lung cancer
98
New cards
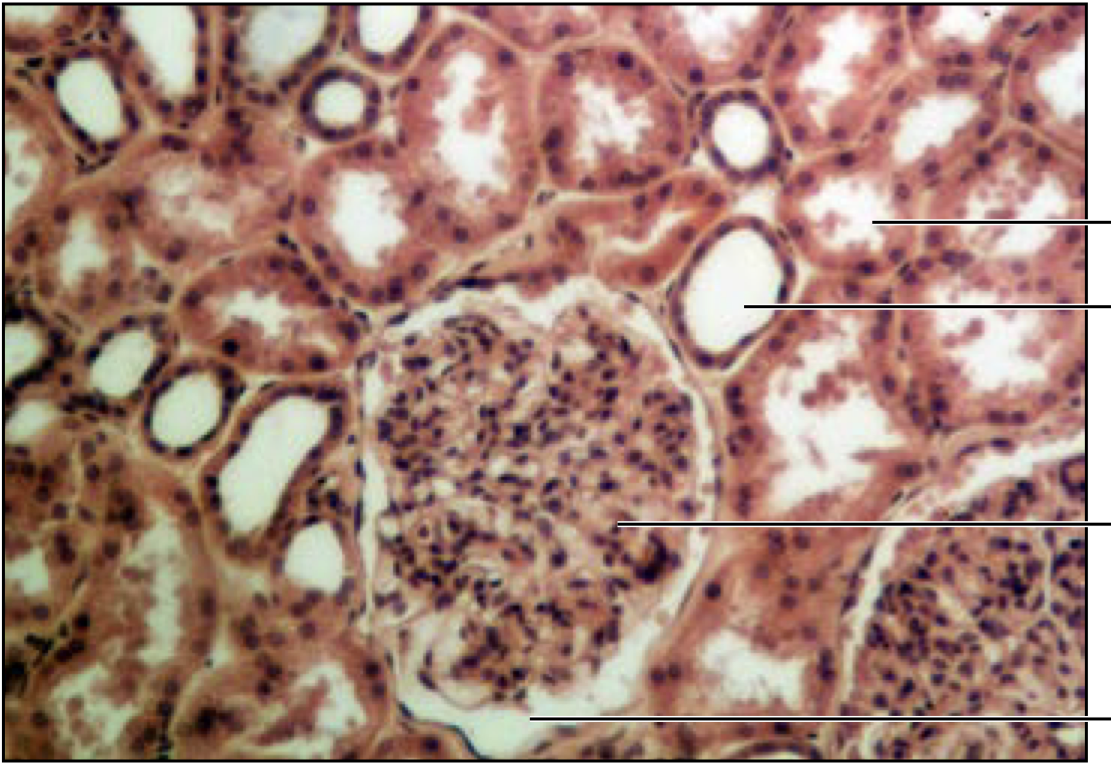
Kidney
Bowmans capsule
Bowmans capsule
99
New cards
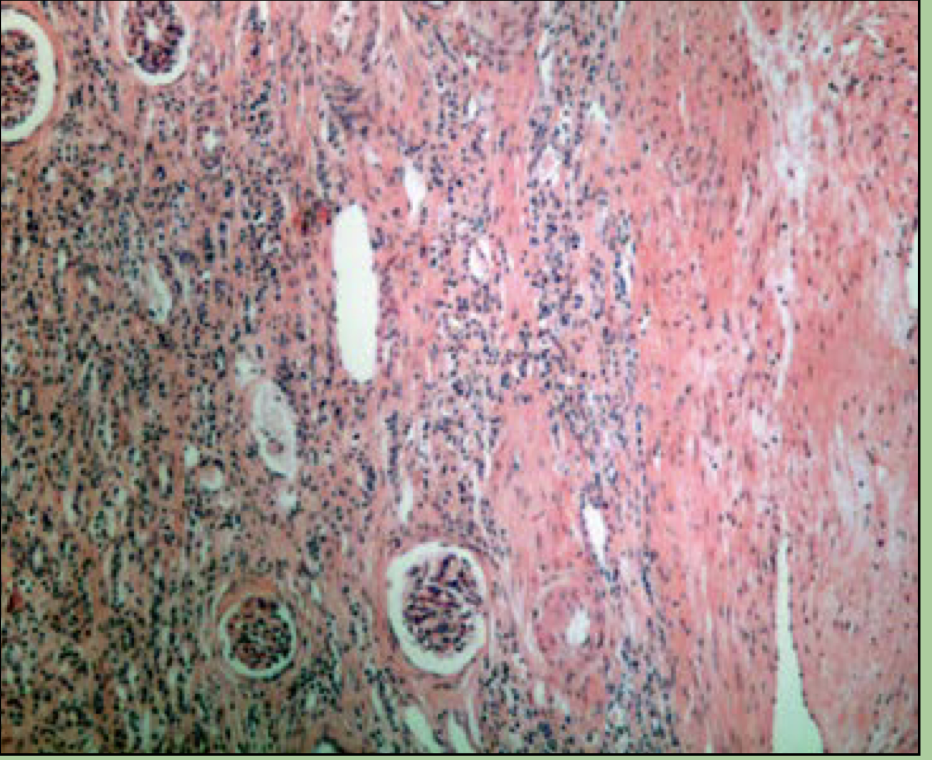
What disorder is this?
Kidney carcinoma
cancer of the kidney that originates in the renal tubules and renal pelvis
cancer of the kidney that originates in the renal tubules and renal pelvis
100
New cards
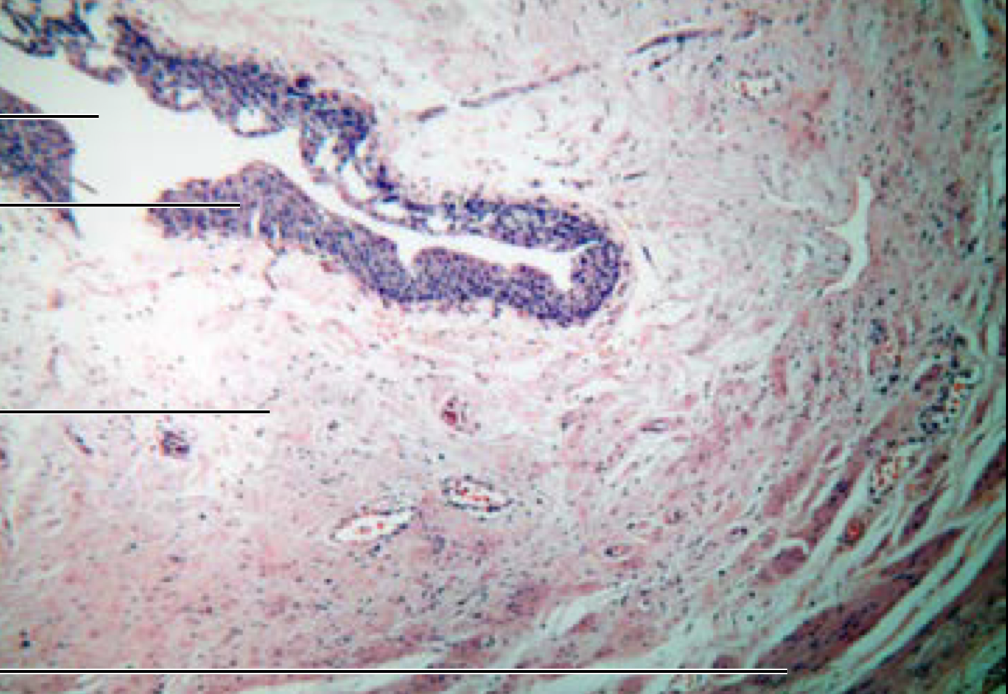
Ureter