3.4 The Brain, Spinal cord, and nerves
1/14
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
15 Terms
What is the brain
The brain is the central organ responsible for info integration
contains 2 hemispheres and 4 lobes (each hemisphere has part of each lobe)
Key roles of the brain
1) process info from multiple inputs
2) Learn
3) Form memory
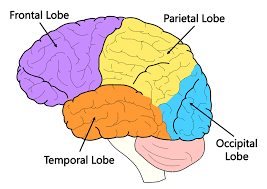
What are the four lobes
frontal
parietal
temporal
occipital
CNS vs PNS
CNS: consists of the brain and spinal cord, acting as the bodys main control centre for information
PNS: Consists of all nerves outside of the brain and spinal cord relaying messages between the body and the CNS
Components of PNS
Somatic: voluntary movement of skeletal muscles
Autonomic: (Sympathetic/Parasympathetic) involuntary movements
what is the spinal cord
integrating centre for unconscious processes
protected by spinal column
key roles of spinal cord
help transmit impulses between brain and body
facilitate reflex actions
What is a neuron and what are the different types
Neuron = excitable cells that conduct signals between tissues
Sensory neurons- (CNS ←→ receptor cells)
Motor neurons - (CNS ←→ muscle fibres)
Neurons can be myelinated or non-myelinated which means they can either be covered in a protective sheath or not
How to draw neuron
See notes*
Nerve fibre vs Nerve
Nerve fibre = a bundle of neurons
Nerve = a bundle of nerve fibres
What are reflexes
The spinal cord is given permission to respond to injury creating a reflex which is a response created involuntarily without brain involvement
Draw a reflex
see notes*
What is the cerebellum
Responsible for muscle coordination and movement
What is neuroplasticity
The brains ability to adapt to disadvantages
what is the eye and how does it work
Organ that focuses light entering through pupils on to photoreceptors that send information to brain to create an image.