Biochem-L14-Microtubule motors, mechanism of movement, regulation and the roles in physiology
1/8
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
9 Terms
what is the structural composition of microtubules?
+ end Beta(55kDa) subunit facing
- end Alpha(53kDa) subunit facing
polar for directionality- grows from the plus end and also MOTOR proteins move in specific directions
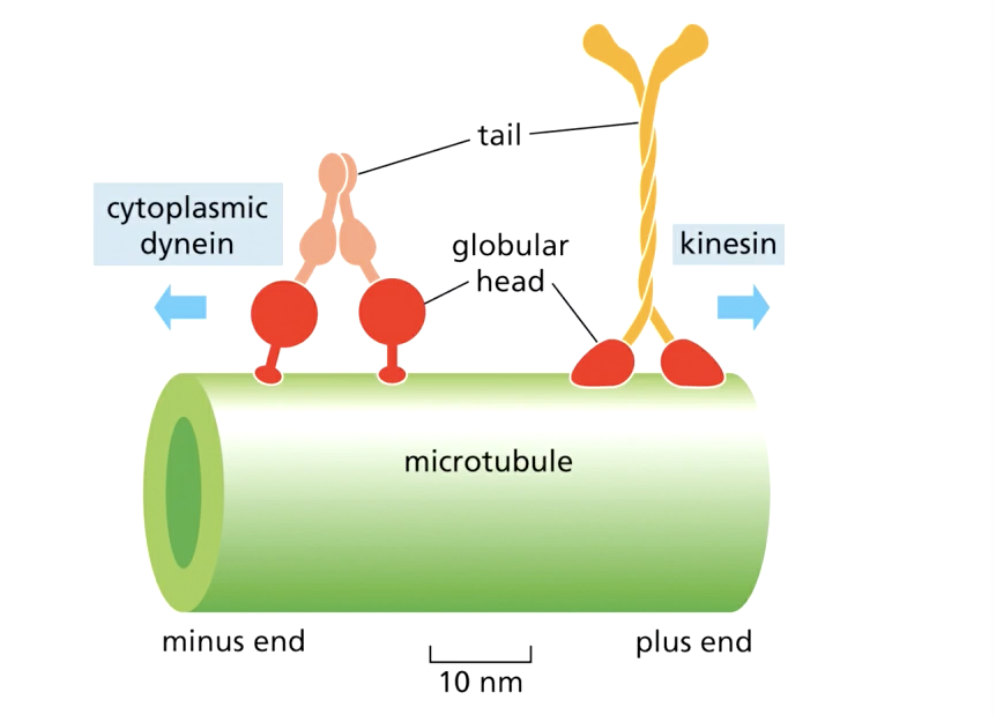
name the 2 motor proteins associated with microtubules and how they move(Direction), and characteristic
kinesins
move cargo from the minus end(alpa) to the plus end(beta
goes from the cell centre to the periphery/axon
600kDa protein with ATPase activity
dyneins
move cargo from the + end(beta) to the- end(alpha)
inward transport- ie from axon to the cell body
1.4 MDa ATPases- large
how do motor proteins move along microtubules?
using their 2 globular head domains- bind to the beta tubulin
each head has ATPase- uses ATP hydrolysis to ADP to change shape- in a stepping motion along the microtubule
kinesin- from - to + end
dynein- + to - end
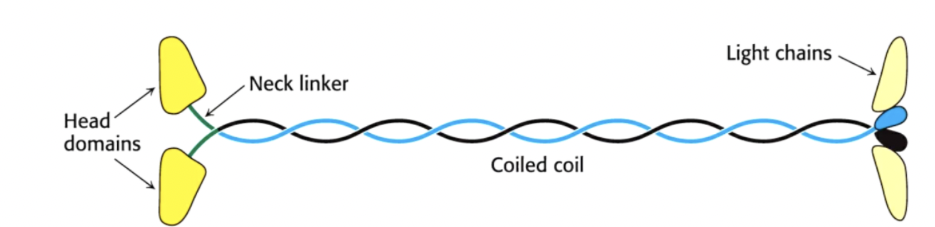
what is the structure of kinesins
kinesin- - to + end
elongated protein with 2 globular head domains and bind microtubule and ATP
long coiled stalk
cargo binding tail
600kDa
composition- heterotetramer
2 × 110kDa- heavy chains- have ATPase motor heads and bind beta-tubulin on microtubules
2 × 60kDa- bind the cargo- ie vesicles
- to + end
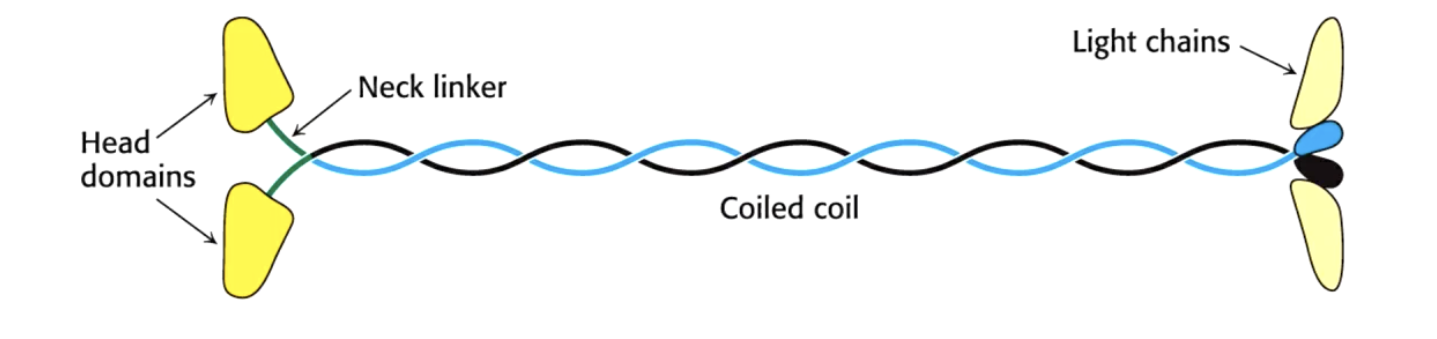
what is the structure of dynein and how is it organised?
more complex that kinesins- dimer of dimers- 12 polypeptides
2 × 520kDa- heavy chains- ATPase motor ring- walk on microtubulin
2 × 74kDa- intermediate chains- bind the cargo by dynactin complex
2 × 53kDa- light intermediate chains
6 × 16.5 kDa light chains
go from + to - end
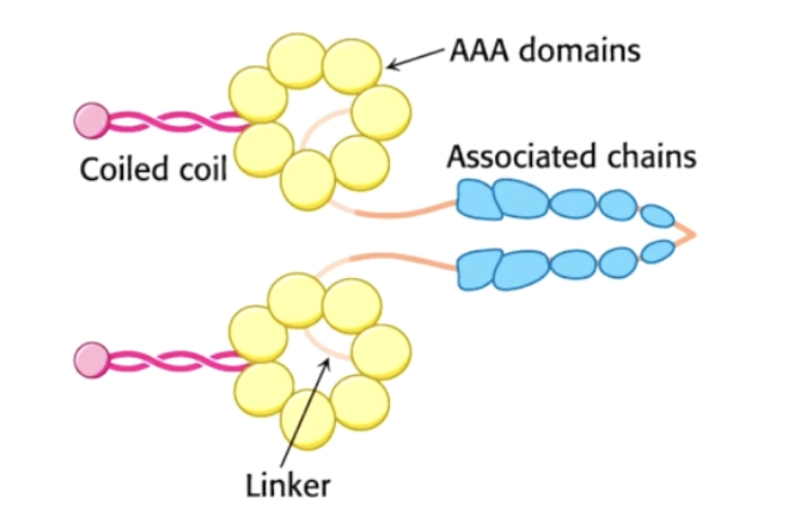
kinesins and dyneins structure and composition
kinesins- 2 × 100kDA- heavy chains have the ATPase motor head and bind to beta tubulin, 2 × 60kDa light chains- bind the cargo
dyneins- 2 × 530kDa(heavy chain-ATPase), 2 × 74kDa(intermediate binds cargo), 2 × 53kDa(light intermediate), 6 × 16.5(light chains)
how do kinesins bind cargo and move things around to position organelles?
tail regions differ which makes it specific to WHAT it transports
kinesins- moves from - to + ER from nucleus to the periphery
motor head domains bind to the beta subunit on the minus end near the nucleus
light chain- cargo/adapter proteins bound
kinesin pushes the ER outward by walking along microtubule towards the cell periphery- out from the nucleus and spread the ER around to cell edges etc- extends ER network
how do dyneins bind cargo and move things around to position organelles?
moves from + periphery to - end:Golgi apparatus positioned near the nucleus
2 × 74kDa intermediate chains- bind cargo by dynactin complex binds to the Golgi
walks along from the periphery to inwards towards the nucleus
Golgi needs to be near the nucleus as it sends vesicles received from the ER and sends it to the nucleus if needed
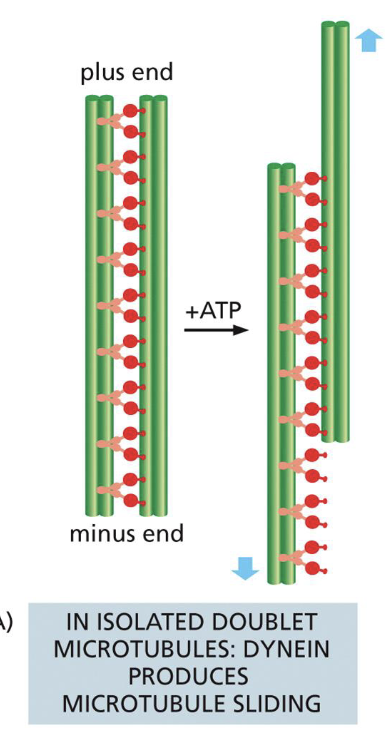
what is the microtubule structure of cilia and flagella? how motor protein is associated with this
both have 9+2 arrangement
9 fused doublet(A/B microtubule) microtubules in a circle around 2 central singlet microtubules
9 doublet is fused by linkin
dynein walks along the adjacent microtubule doublets- and slides along them, converted to bending and produces the beating motion(also properly flagella forward)