Physics chp4
1/10
Earn XP
Description and Tags
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
11 Terms
Explain the difference between mass and weight
Weight measured in Newtons, magnitude is variable, depends on location where as mass is measured in Kg and is constant for a specific object anywhere in the universe
weight = mass x gfs
Define centre of gravity
An imaginary point at which the entire weight of an object seems to act
How can you find the centre of gravity of a 3D shape?
Freely suspend card from clamp stand and hang a plumb line
Draw line along plumb line and repeat for 2 more suspensions
Centre of gravity where lines intersect
What are the two most important factors that affect magnitude of drag?
Speed and cross-sectional area of the object
Describe how the forces on an object change as it falls through a fluid
At the instant it starts to fall: total force = weight of the object and acceleration = g
As the object falls its speed increases which in turn increases the magnitude of the opposing drag force and decreases the instantaneous acceleration
Eventually the object reaches terminal velocity, drag force is equal and opposite to weight, acceleration is zero and speed is constant
Define drag
The frictional force experienced by an object travelling through a fluid
Define a Newton
The force needed to accelerate a body weighing one kilogram by one metre per second per second
What is the principal of moments?
For a body in rotational equilibrium: sum of the clockwise moments = sum of the anticlockwise moments
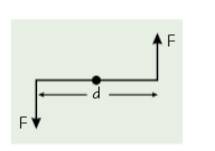
Define couple
Two forces that are equal in magnitude but that act in opposite directions to each other, have different lines of action.
Doesn’t cause any resultant linear force but does produce a turning force (torque)
Define torque
The turning effect due to a couple
How can you calculate torque?
Torque = size of one of the forces x perpendicular distance between forces