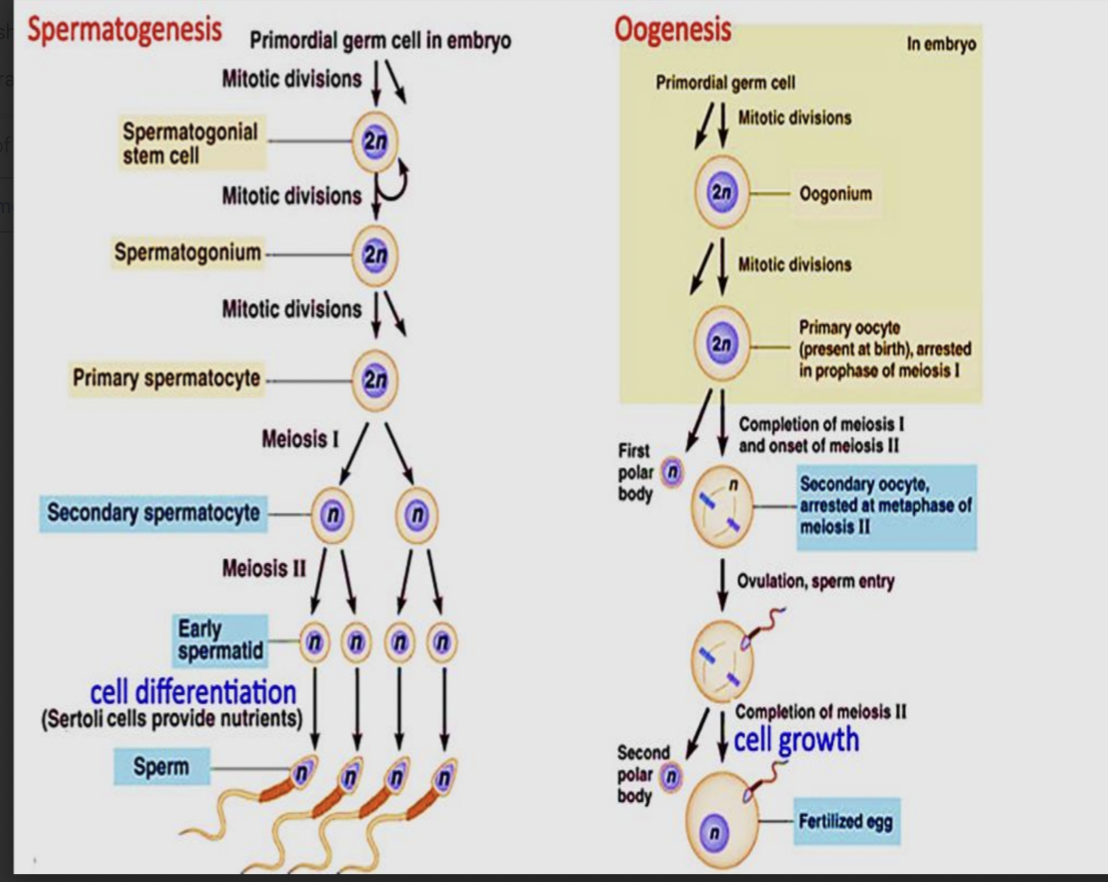
Spermatogenesis
1/8
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
9 Terms
1ry sex organs vs 2ry sex organs of male reproductive system
1ry sex organs:
Testes → Interstitial cells of leydig (Testosterone) , Seminefrous tubules (sertoli cells of spermatogonia (spermatogenesis)
2ry sex organs: External genitalia, seminal vesicles, prostate, duct system
Functions of sertoli cells (Structural, Barrier, Nutrient, Regulation, Phagocytic, Fluid)
Structural (physical) support → surrounds developing germ cells in seminefrous tubules forming nuturing environ
Tight junction form blood-testis barrier → separates basal from liminal compartment to protect germ cells from immune system (prevents autoimmune reaction)
Nutritional (and metabolic support) to developing sperm → transfers glucose, lactate, amino acids, phagocytes residual cytoplasm (spermiogenesis)
Endocrine function by responding to FSH and Testosterone →
ABP (androgen binding protein) concentrates testosterones in tubules for spermatogenesis
Inhibin B inhibits FSH secretion
Anti mullerian hormone (AMH, fetal life) regresses Mullerian ducts in male embryo
Spermatogenesis regulation as coordinates germ cell maturation by release growth factors and cytokines
Phagocytic role by removing apoptotic germ cells and cytoplasmic remnants ensures proper sperm developments
Secretes tubular fluid → helps transport sperm through seminefrous tubules
Serotoli cells produce hormones and their effects
Androgen binding proteins ABP → concentrates testosterones in tubules for spermatogenesis
Mullerian inhibiting factor → regression of mullerian duct prevents forming female genital tract
Estrogen (small amount)
Inhibin → FSH inhibition
Male reproductive physiology
Before birth masculinizes reproduction tract and external genitalia
Testes descent
Ceases at birth
Returns at puberty testicular leydig cells secrete testosterone
Testes descend and pass out of abdominal cavity
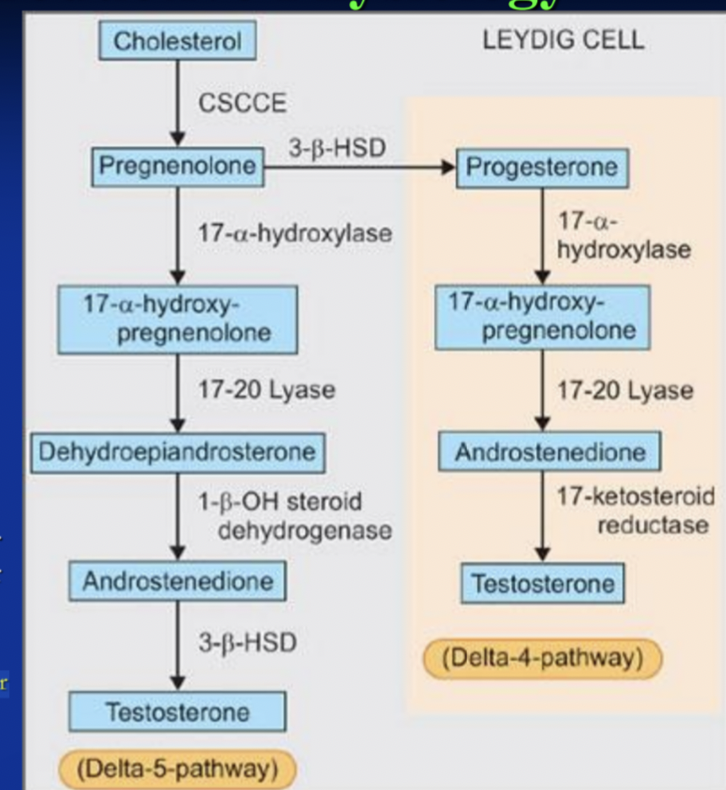
Star protein needed for cholesterol transport into mitochondria rate limiting step (protein in outer mitochondrial membrane of steroid producing cells (Leydig cells, adrenal cortex, ovarian theca/luteal cells))
Puberty in male
Usually 10-14 yrs old
Endocrine, physical and behavioural
Leydig cells awake
Leydig cells stay awake for about 50 years
Leydig cells response to LH decrease by age
Leydig cells help in oxytocin release which allow seminiferous tubules and epididymis motility
Spermatogenesis
Accessory sex glands enlarge and become secretory
Penis and scrotum enlarge
Testosterone 25% decrease in evening