Side A - Electricity
1/45
Earn XP
Description and Tags
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
46 Terms
Define Current
Rate of flow of charge
Carried by electrons in a wire
What is conventional current flow?
Electric current moving from positive to negative
What is electron flow?
Electrons in a circuit moving from negative to positive
Current equation
Current (I) = Change in charge (Q) / Change in time (t)
I = A
Q = C
t = s
Q = I x t
t = Q / I
Define potential difference
Work done/energy transferred per unit charge passing through circuit
Potential difference equation
Voltage (V) = Work done (W) / Charge (Q)
V = V (1 volt = 1 joule per coulomb)
W = J
Q = C
W = V x Q
Q = W / V
Define electromotive force (emf)
Energy supplied per unit charge by power supply
Electromotive force (emf)
Emf (ϵ) = Energy supplied (E) / Charge (C)
ϵ = V
E = J
Q = C
E = ϵ x Q
Q = E / ϵ
Define resistance
Measure of difficulty of making current pass through substance
caused by repeated collisions between charge carriers and positive ions
Resistance formula
Resistance (R) = pd across component (V) / current through component (I)
R = Ω
pd = V
I = A
V = I x R
I = V/R
How are ammeters connected?
In series
So they experience no resistance or as little as possible to impede the current flow
How are voltmeters connected?
In parallel so resistance is as high as possible so ammeter only measures current through resistor
So they have a high resistance
Also allows for them to measure V at 2 points and find the difference between them (pd)
Electrical power formula
Power (P) = Current (I) x Voltage (V)
P = W
C = A
V = V
I = P/V
V = P/I
P = I² x R
P = V² / R
What is Ohms law?
p.d across ohmic conductor is proportional to current through it, if conditions dont change (temp and dimension of conductor)
What does Ohmic mean?
Obeying Ohms law
On a graph you can find resistance using gradient as it is a proportional and straight line
On I-V graph the steeper the gradient, the lower the resistance
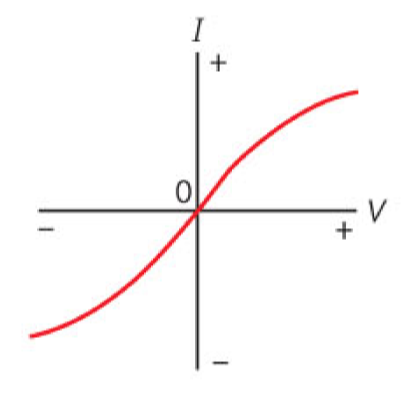
What I-V graph is this, and what are the characteristics of the component?
Filament Bulb
Not Ohmic - current and voltage aren’t proportional so gradient doesn’t equal resistance
The resistance increases as current increases, as when current increases temp increases and temp increases resistance
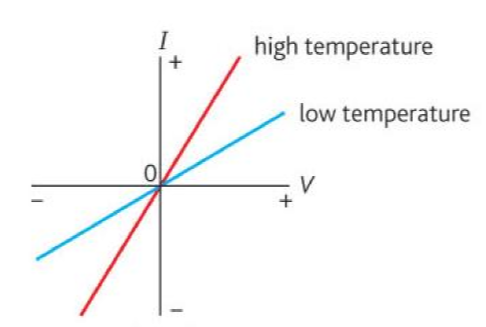
What I-V graph is this, and what are the characteristics of the component?
Thermistor
Ohmic - If temp remains constant
When temp is higher there are more charge carriers and free electrons - so its a better conductor, so there is less resistance
Resistance decreases as temp increases
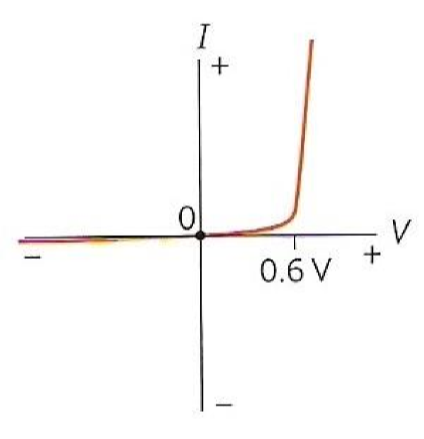
What I-V graph is this, and what are the characteristics of the component?
Silicon Diode
Not Ohmic - as resistance varies depending on direction/bias
High resistance (so little current) until reaching threshold voltage (0.6V), when resistance drops and current rapidly increases
Increase in voltage frees electrons, so there are more charge carriers to carry current
Characteristics of reverse direction/bias diode
Very high resistance
current below 1 μA
Characteristics of forward direction/bias diode
When p.d below 0.6V (threshold voltage) - resistance is high
when p.d above 0.6V resistance falls rapidly - so current increases rapidly
Threshold voltage of LED (light emitting diode) and what is a LED
1.5V
Diode that emits light when conducting
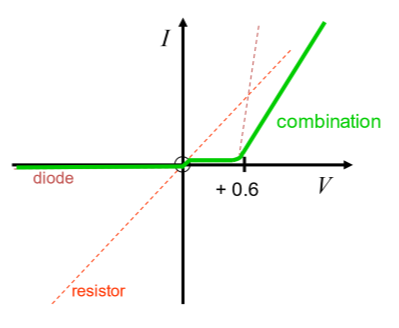
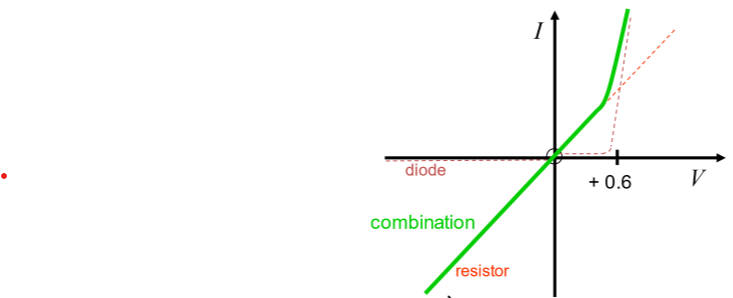
What I-V combination is this?
Diode + Resistor in Series
Current increases at threshold but with less steepness, as current still acted on by fixed resistor
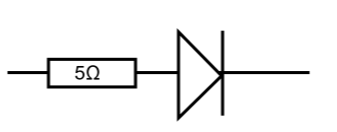
What I-V combination is this?
Diode + Resistor in parallel
resistance of resistor acting on current initially and proportionally
until diode switches on and resistance falls and current increases
Characteristics of metal conductors
Slow resistance increase with temperature increase
Positive temperature coefficient - resistance increases as temp increases
Positive ions in conductor vibrate as temp increases, so charge carriers (electrons) cant pass through conductor easily when p.d applied
Characteristics of Semiconductors
Fast resistance decrease with temperature increase
Negative temperature coefficient - Resistance decreases as temp increases
No. of charge carriers rapidly increases with temp, compared to the impedance (opposition) of the vibrating positive ions
(more charge carriers so resistance becomes smaller)
Resistivity equation
ρ (resistivity) = R (resistance) x A (Cross sectional area) / L (length)
ρ = Ωm
each element has a different resistivity
Cross sectional Area equation
A = πr²
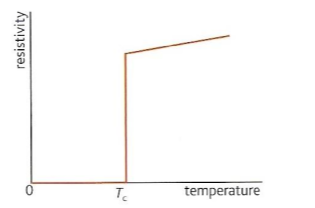
What is superconductivity
State where materials have 0 resistivity
they are man made compounds with no resistivity at a critical temp
critical temp depends on material but is usually below 200C
Used in very strong electromagnets (MRIs) and superconducting magnets (Large hadron collider)
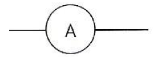
What component is this?
Ammeter
Measures current in Amps
Connected in series
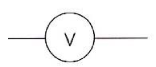
What component is this?
Voltmeter
Measures Voltage across a component at 2 different points
Connected in parallel
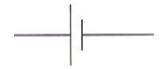
What component is this?
A cell
A singular battery
Source of chemical energy
Short = negative, Long = positive
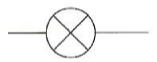
What component is this?
Filament lamp
emits light
as it heats up it converts electrical energy into light energy
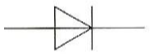
What component is this?
Diode
Arrow is forward direction
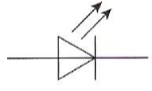
What component is this?
Light Emitting Diode
emits light when diode conducts

What component is this?
Resistor
component designed to have certain resistance
limit current
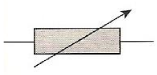
What component is this?
Variable resistor
used to set resistance to specific value
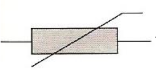
What component is this?
Thermistor
resistance decreases as temp increases

What component is this?
Light dependant resistor
Resistance decreases as light intensity increases
Graph same as thermistor

What component is this?
Heater
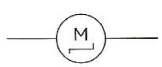
What component is this?
DC (direct current) motor
they convert electrical power into mechanical
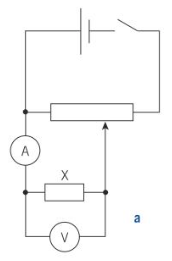
What is the resistance component used to control resistance in a level circuits?
Potential divider
You can move it all they way from 0 to max volts giving you more control over your components
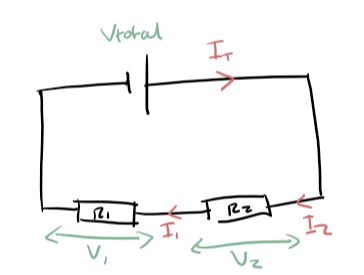
Characteristics of series circuit
All components have same current (It = I1 = I2)
Total resistance is sum of individual resistances (Rt = R1 + R2) greater total R
Total voltage is sum of individual voltage (Vt = V1 + V2)
If one bulb blew all remaining bulbs would turn off
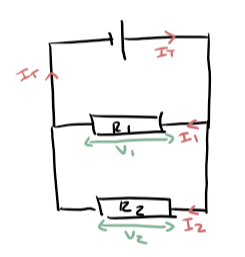
Characteristics of parallel circuits
Total current leaving junction = total current entering it (Kirchoffs’s 1st law) (It = I1 + I2)
1/Rt = 1/R1 + 1/R2 - Smaller total R
All components have same voltage (Vt = V1 = V2)
Kirchoff’s 2nd law
In any complete circuit loop the sum of all emfs i equal to the sum of all potential energy
Power in series
current = same
resistance = greater
pd = greater
greater pd = greater power = brighter lighting bulb
Power in parallel
voltage = same