Advanced Anatomy - Back
1/138
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
139 Terms
seven
How many cervical vertebrae are there?
twelve
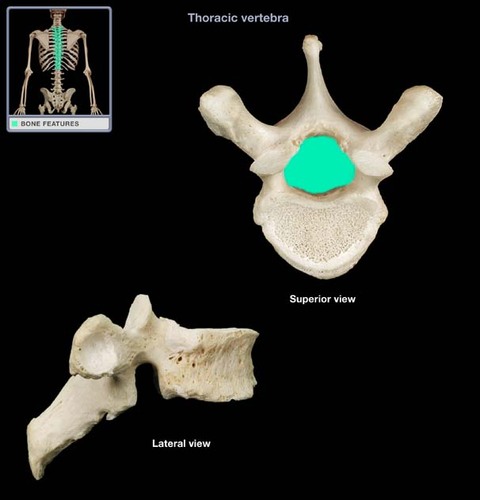
How many thoracic vertebrae are there?
five
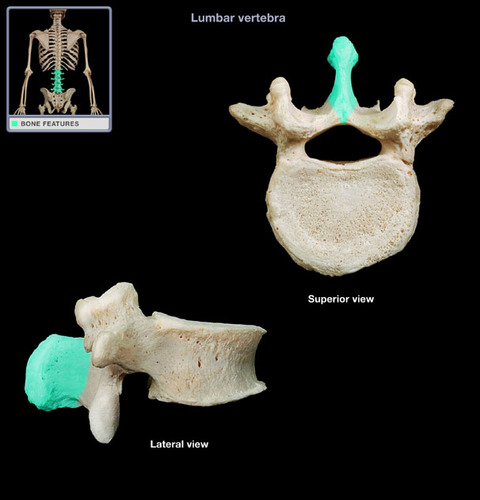
How many lumbar vertebrae are there?
five (fused)
How many sacral vertebrae are there?
four (fused to form the coccyx)
How many coccygeal vertebrae are there?
twenty-four
How many different vertebral elements are moveable?
thoracic and sacral
Which regions of the vertebral column are the primary curvatures?
cervical and lumbar
Which regions of the vertebral column are the secondary curvatures?
kyphosis
The name for the primary curvatures of the vertebral column is…
lordosis
The name for the secondary curvatures of the vertebral column is…
trunk flexion
Name the action
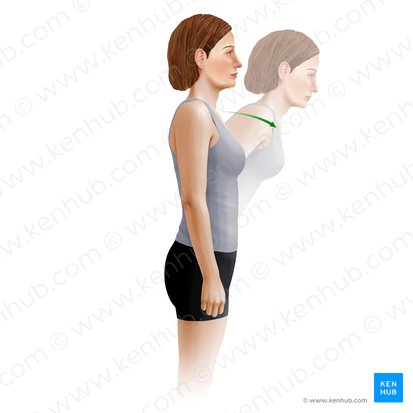

sagittal
What plane does this action happen in?
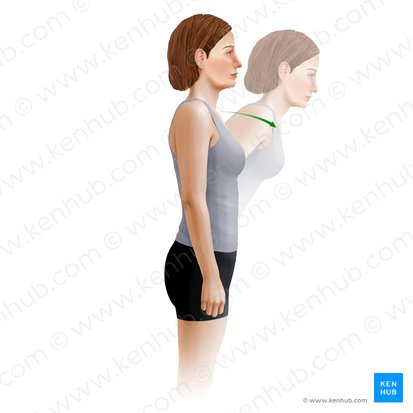

medial-lateral
What axis is this action happening about?
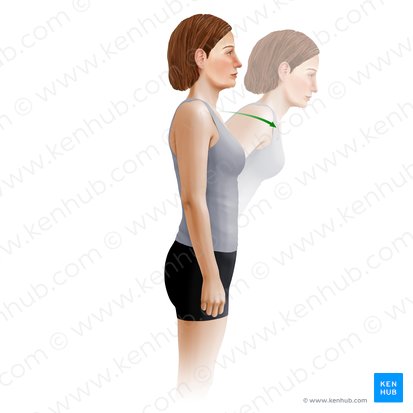

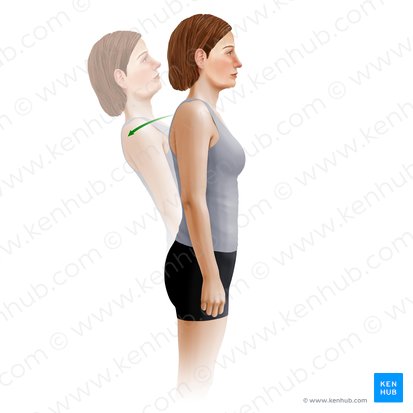
trunk extension
Name the action
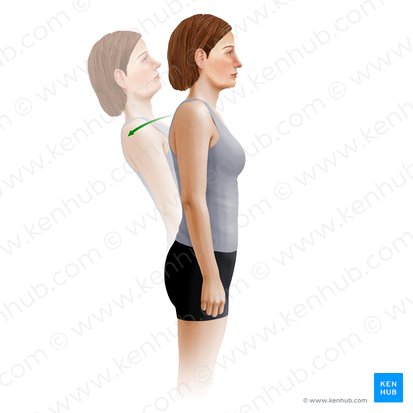

sagittal
Which plane does this action happen in?
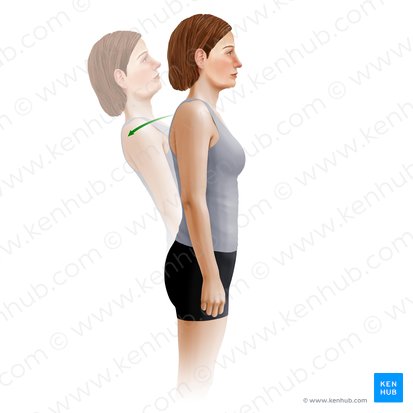

medial-lateral
Which axis is this action happening about?

lateral trunk flexion
Name the action
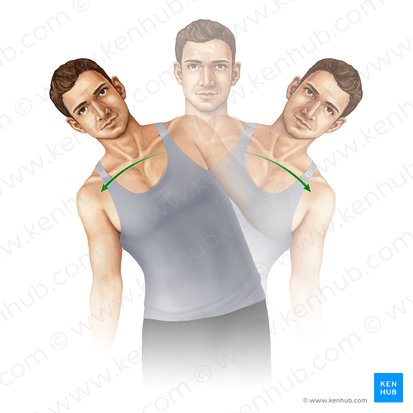
coronal
Which plane does this action happen in?
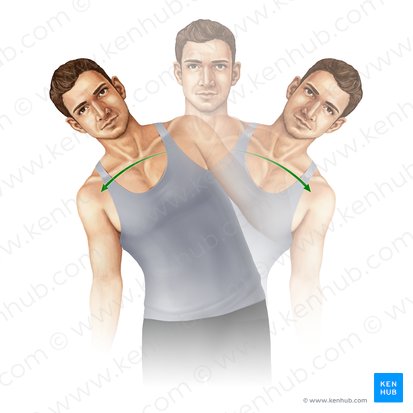
anterior-posterior
Which axis is this action happening about?
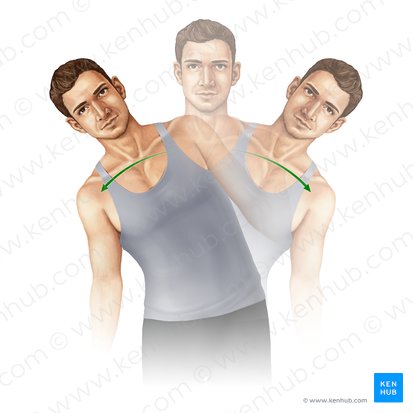
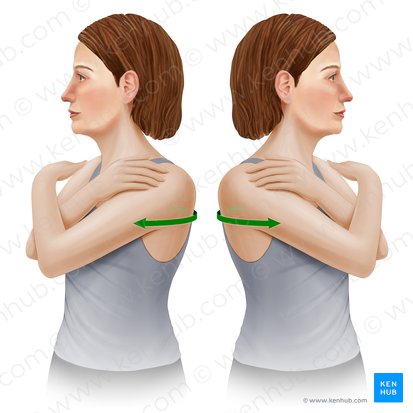
trunk rotation
Name the action
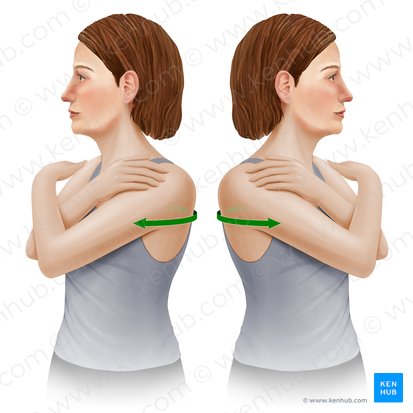
transverse
Which plane does this action happen in?
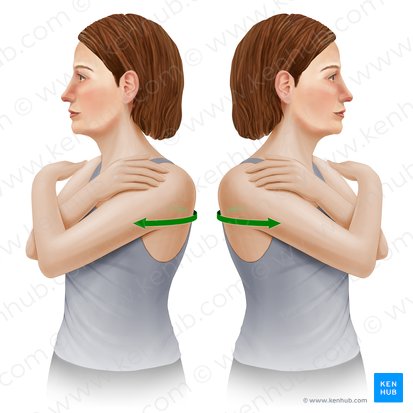
vertical
Which axis is this action happening about?
facet joint
between articular facets of adjacent vertebra
orientation of joint and movement of joint unique to each region
allows for slight amount of gliding motion
movement that occurs in spine, determined by orientation of facets
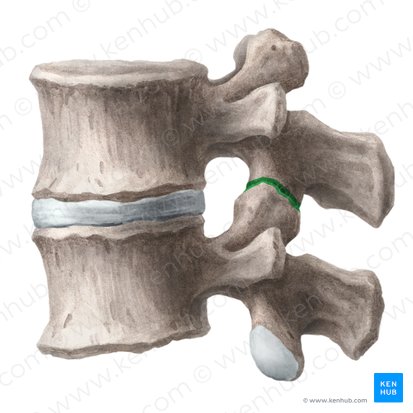
zygapophysial joint
A facet joint is also known as a…
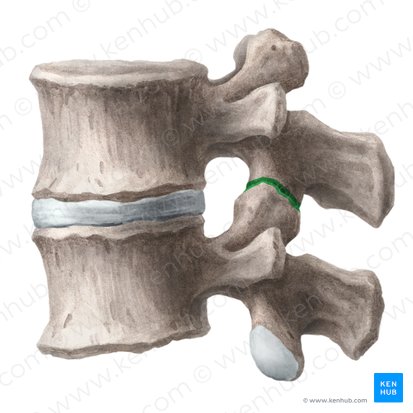
synovial joint
What type of joint is a facet joint structurally?
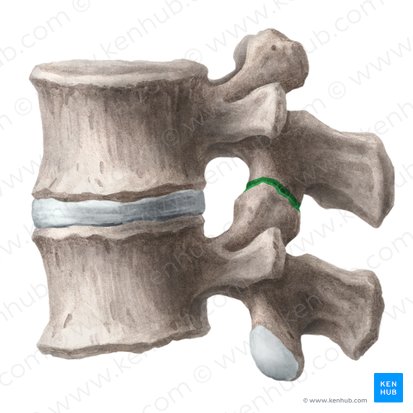
planar
The facet joint is this type of synovial joint
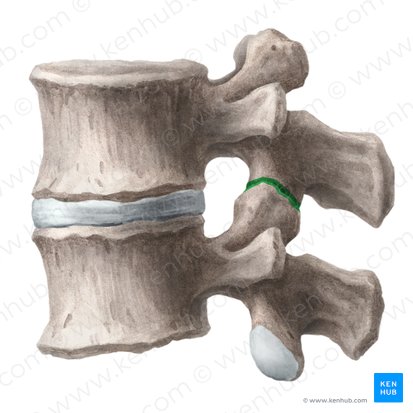
cartilaginous joint
What type of joint is the intervertebral disc joint structurally?
symphysis
The intervertebral disc joint is this type of cartilaginous joint
atlantooccipital joints
where the “yes” movement happens
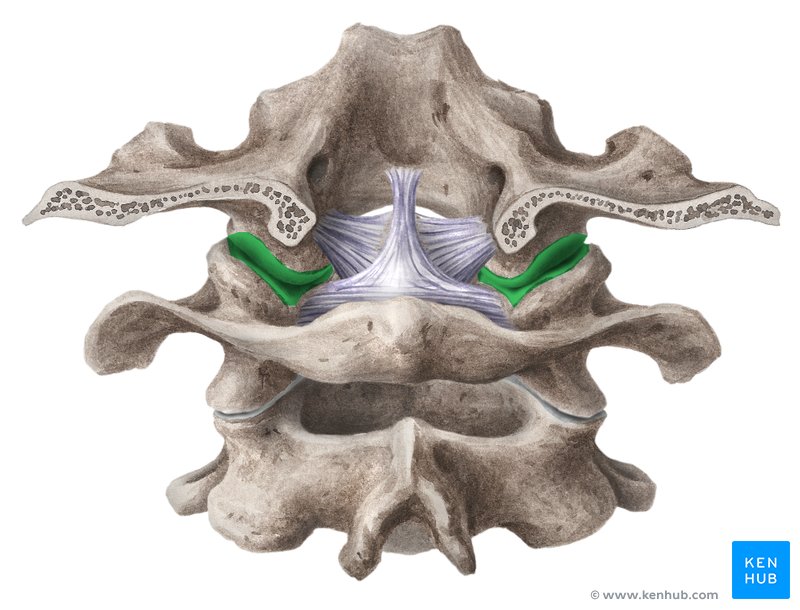
occipital bone and atlas
Which two bones make up the atlantooccipital joints?
synovial joint
What type of joint are the atlantooccipital joints structurally?
condyloid
The atlantooccipital joints are this type of synovial joint
lateral atlantoaxial joints
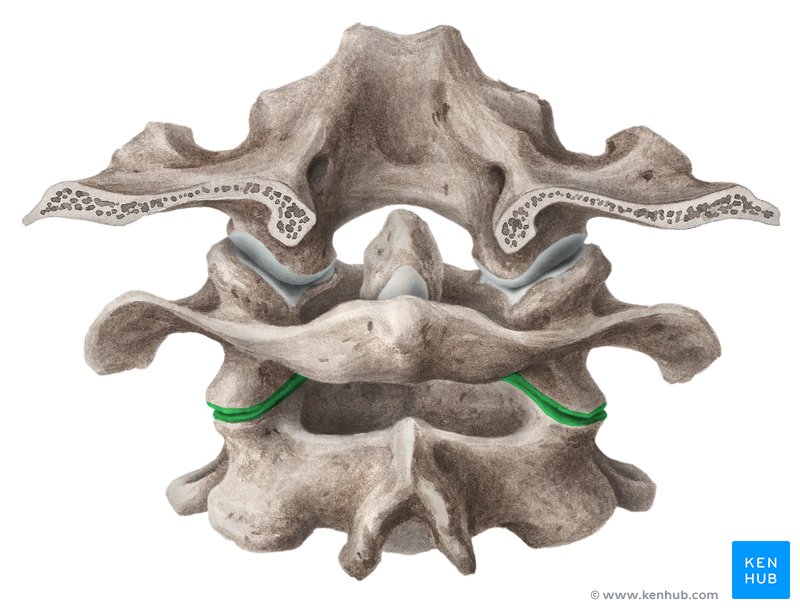
synovial joint
What type of joint are the lateral atlantoaxial joints structurally?
planar
The lateral atlantoaxial joints are this type of synovial joint
median atlantoaxial joint
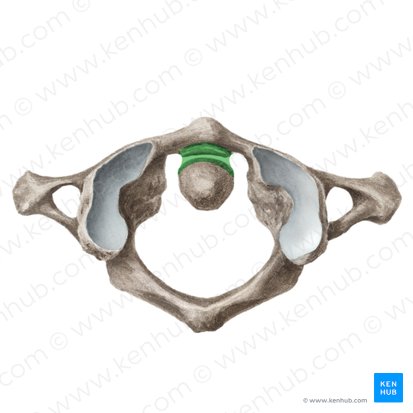
synovial joint
What type of joint is the median atlantoaxial joint structurally?
pivot
The median atlantoaxial joint is this type of synovial joint
uniaxial
Is the median atlantoaxial joint uniaxial, biaxial, or multiaxial?
three
The atlantoaxial joints have this many points of articulation
atlas and axis
Which two bones make up the atlantoaxial joints?
C1 and C2
The atlas and axis are also known as…
atlantoaxial joints
Where does the “no” movement happen?
C2, C3
Dermatomes: The neck is innervated by which spinal nerves
C3/C4 - L2/L3
Dermatomes: The back is innervated by which spinal nerves
lesser occipital nerve and greater auricular nerve
Peripheral Nerve Domains: The main cutaneous nerves that innervate the back of the neck are…
cutaneous branches of cervical and thoracic DPR of spinal nerves
Peripheral Nerve Domains: The main cutaneous nerves that innervate the back are the…
dorsal primary rami
What does DPR stand for?
ventral primary rami
What does VPR stand for?
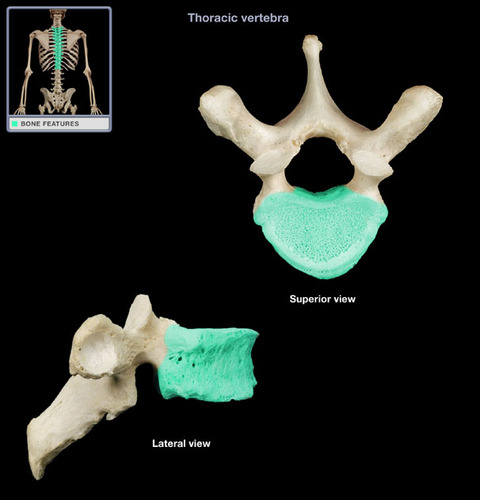
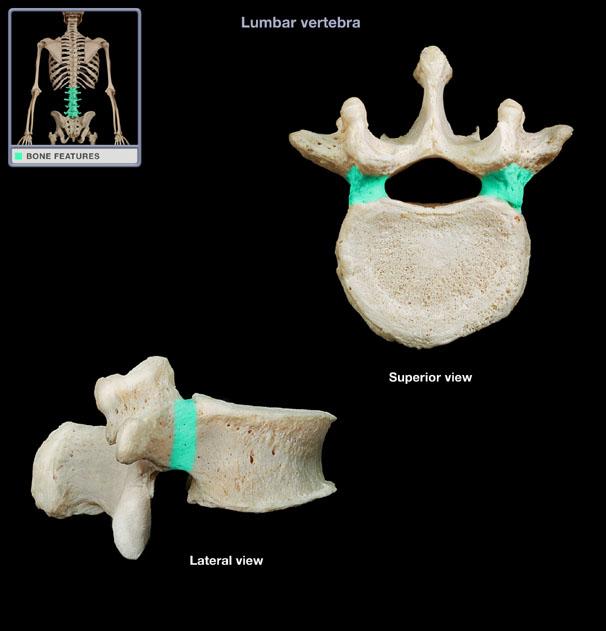
vertebral body
the weight-bearing component
trabecular bone surrounded by a thin layer of cortical or compact bone
vertebral arch
houses and protects the dorsal and lateral surfaces of the spinal cord
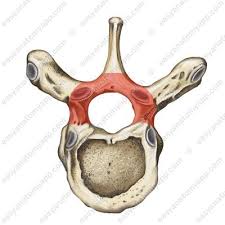
neural arch
What is another name for the vertebral arch?
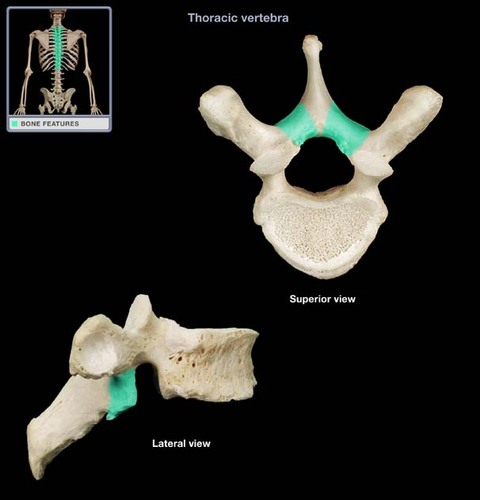
pedicle
lamina
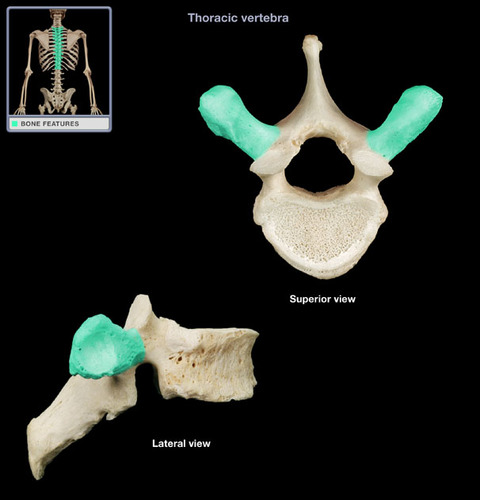
transverse process
superior articular process
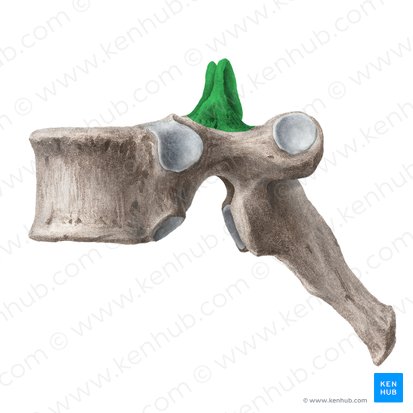
inferior articular process
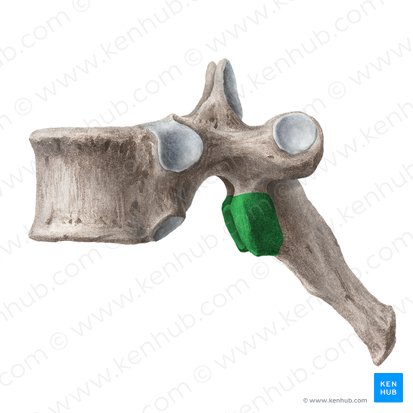
spinous process
pars interarticularis
vertebral foramen
foramina
plural of foramen
spinal canal
What is another name for the vertebral canal?
vertebral canal
The vertebral foramina collectively form the…
ligamentum flavum
a short, but thick ligament that connects the laminae of adjacent vertebrae from C2 to S1
preserves upright posture
assists the vertebral column in resuming its shape after flexion
resists excessive separation of the adjacent vertebral laminae
prevents buckling of the ligament into the spinal canal during extension, preventing canal compression
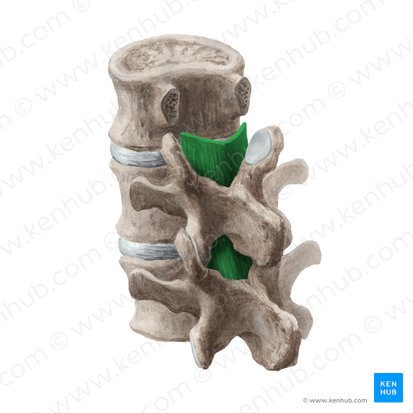
posterior longitudinal ligament
What does PLL stand for?
vertebral body and intervertebral disc
anterior border of vertebral foramen
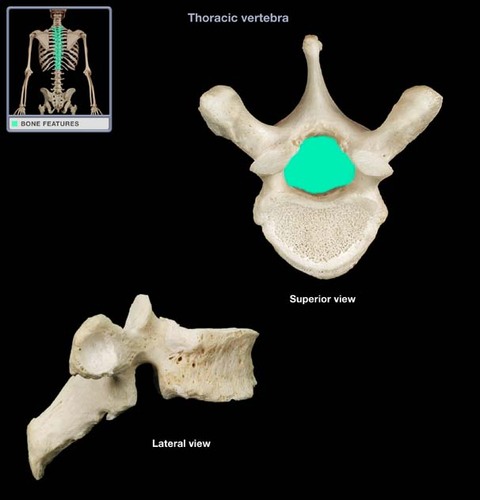
pedicles
lateral border of vertebral foramen
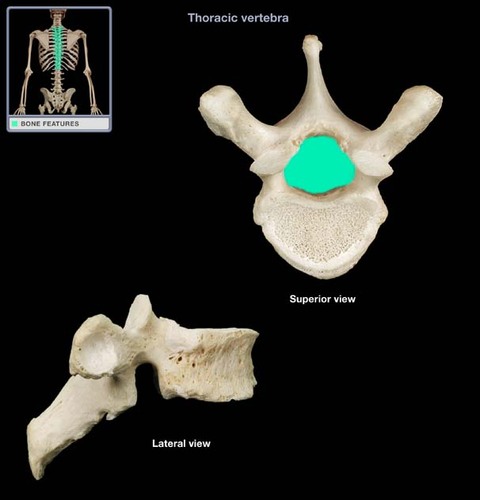
laminae
posterior border of vertebral foramen
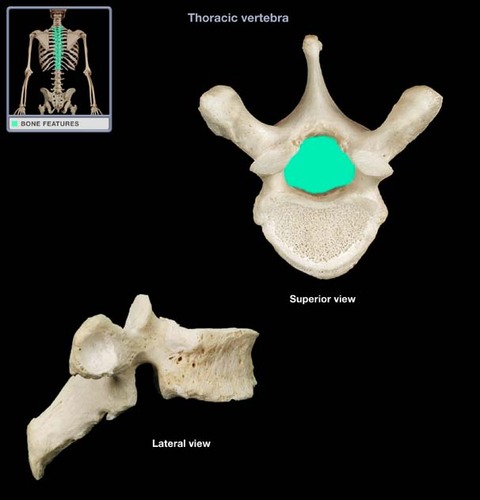
vertebral body, intervertebral disc, PLL
anterior border of the vertebral canal
pedicles
lateral border of vertebral canal
laminae and ligamentum flavum
posterior border of vertebral canal
spinal cord, nerve roots, meninges, and blood vessels
contents of vertebral canal
vertebral body and intervertebral disc
anterior border of intervertebral foramen
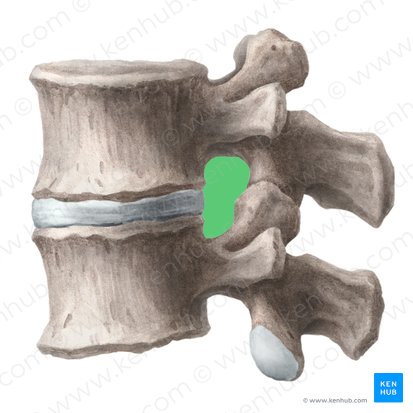
superior and inferior articular processes, facet joint, and associated joint capsule
posterior border of intervertebral foramen
inferior vertebral notch of pedicle of superior vertebrae
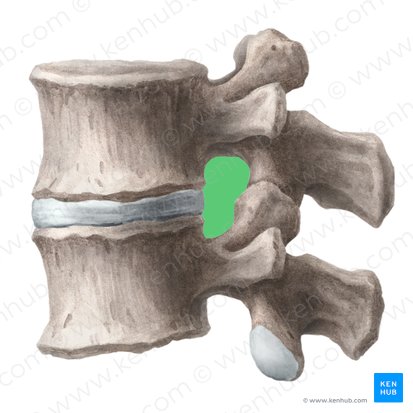
superior border of intervertebral foramen
superior vertebral notch of pedicle of inferior vertebrae
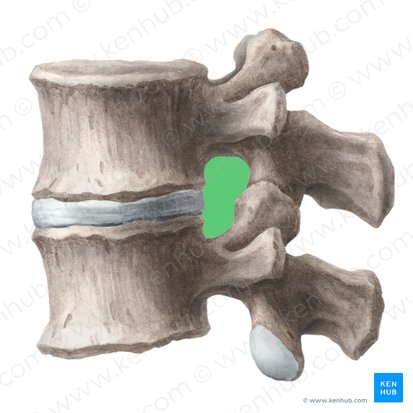
inferior border of intervertebral foramen
dorsal root ganglion, spinal nerve roots, blood vessels, lymphatic vessels, and fat
contents of intervertebral foramen
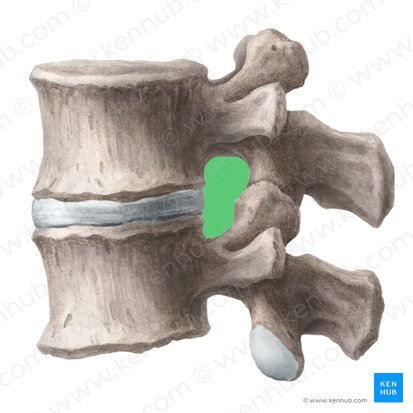
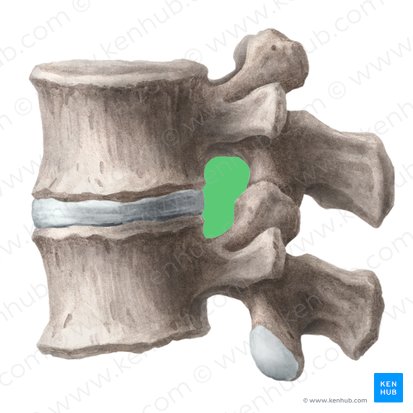
superior vertebral notch
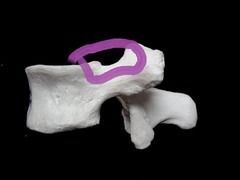
inferior vertebral notch
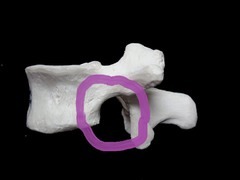
TLF
deep fascial complex that forms the sheath of the erector spinae muscle
important for stabilization and load transfer
acts as a “myofascial girdle”
erector spinae and latissimus dorsi attach here
transversus abdominus (TA) and internal oblique (IO)
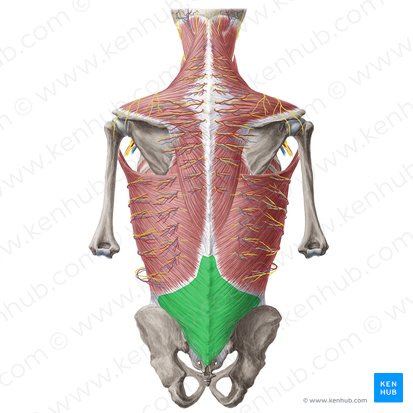
thoracolumbar fascia
What does TLF stand for?
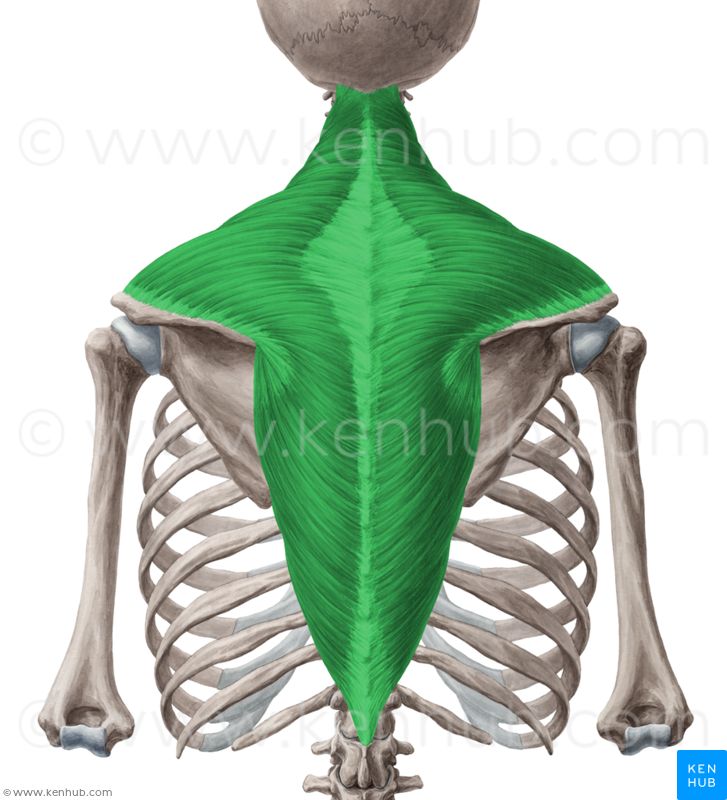
trapezius
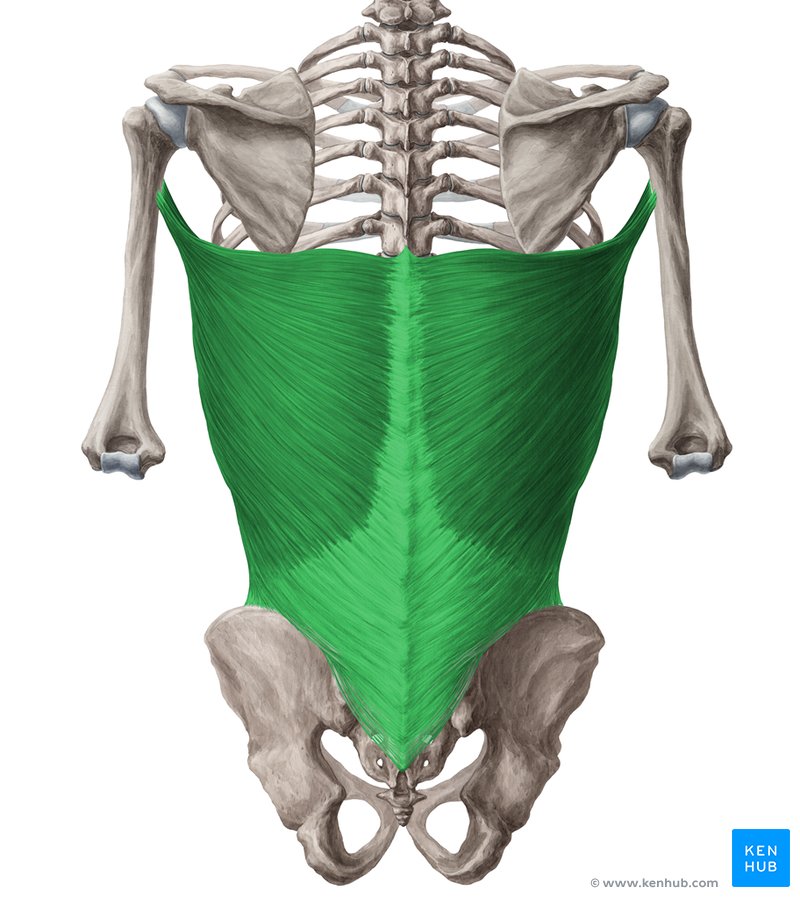
latissimus dorsi
rhomboid major
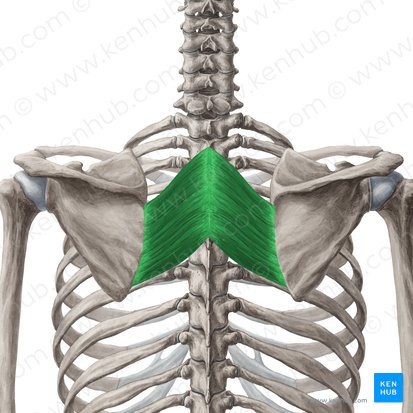
rhomboid minor
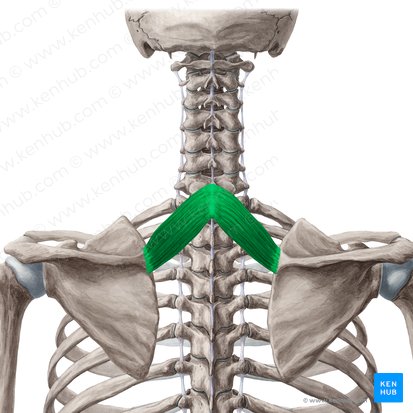
levator scapulae
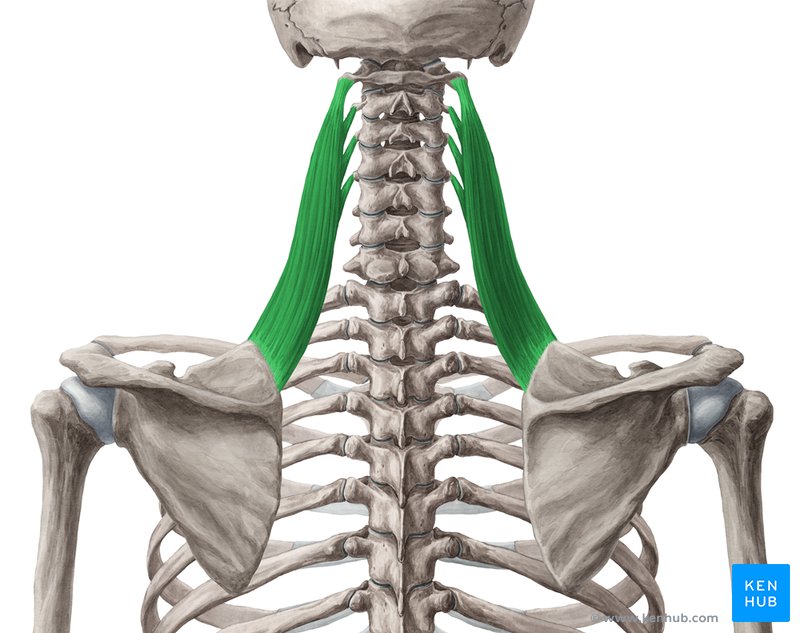
trapezius, latissimus dorsi, rhomboid major, rhomboid minor, levator scapulae
Name all 5 of the extrinsic back muscles: superficial layer
acromion process
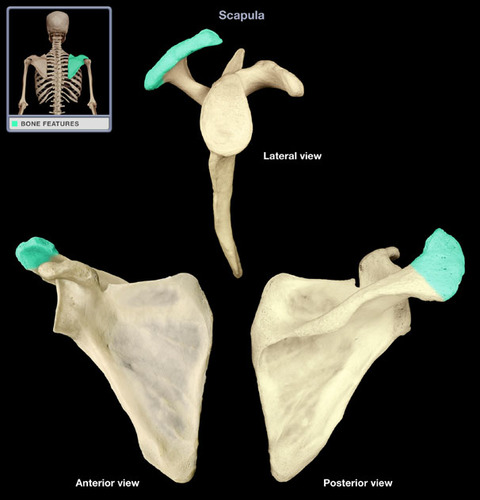
superior angle of scapula
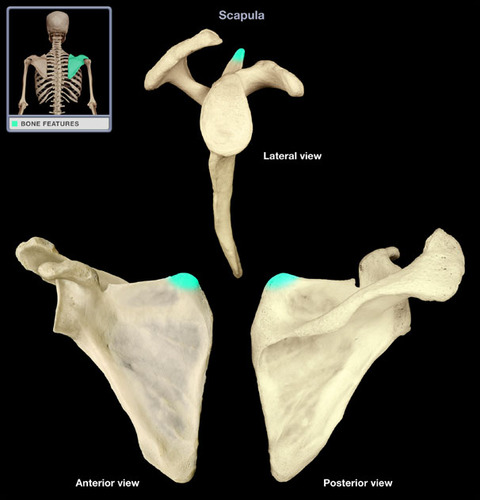
spine of scapula
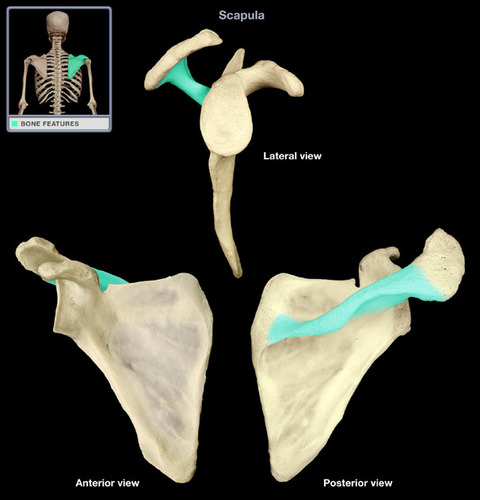
medial border of scapula
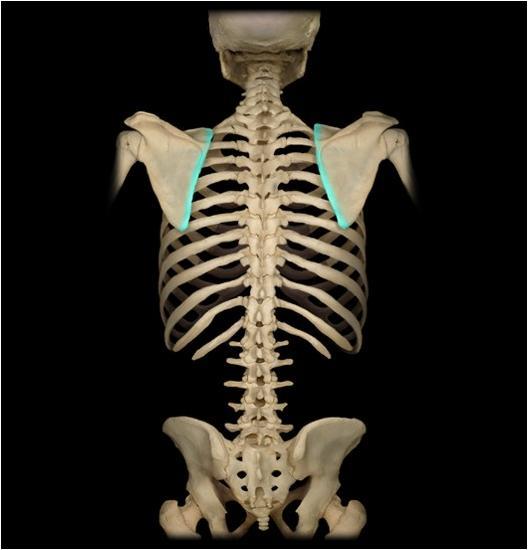
lateral border of scapula
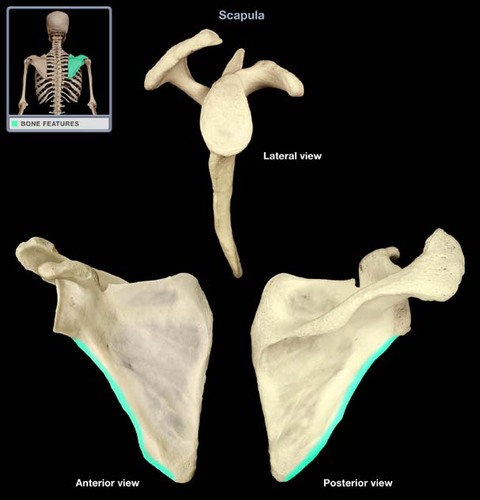
inferior angle of scapula
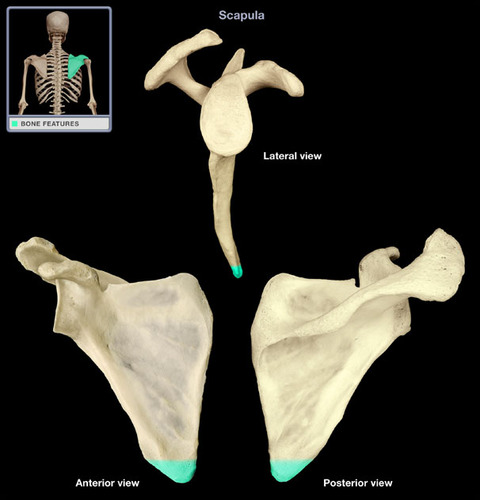
serratus posterior superior, serratus posterior inferior
Name the 2 extrinsic back muscles: intermediate layer
serratus posterior superior
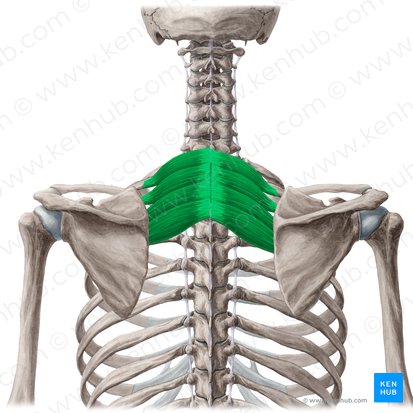
serratus posterior inferior
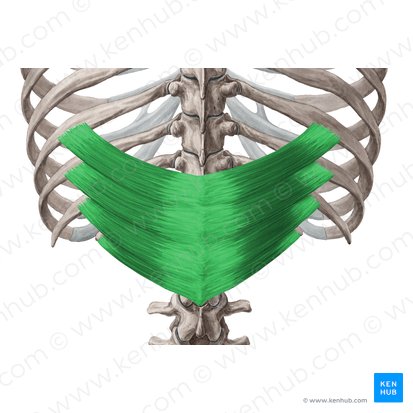
two
How many layers of extrinsic back muscles are there?
splenius capitis, splenius cervicis
Name the 2 intrinsic back muscles: superficial layer
splenius capitis
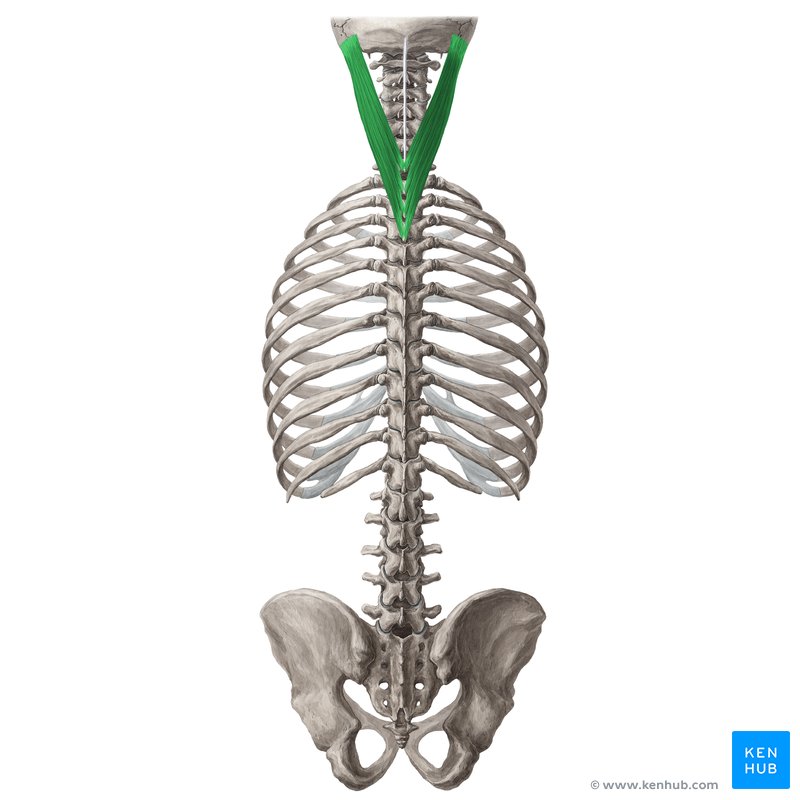
splenius cervicis