Unit 7C - Photoelectron Spectroscopy (PES) - AP Chemistry
1/32
Earn XP
Description and Tags
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
33 Terms
the nature of light
all light is electromagnetic radiation
photons consist of two perpendicular fields: an electric field wave and a magnetic field wave
wavelength
the distance from crest (peak) to crest
typically measured in nanometers (nm) (1m = 109 nm)
frequency (v)
the number of crests (peaks) that pass by a given point per second
measured in units of 1/s or s-1
speed of light (c )
all light waves propagate at the same speed through a vacuum
3.10 × 108 m/s
speed of light equation
c = λ * v
energy of a light wave
E = hv = hc/λ
planck’s constant (h)
6.63 × 10-34 Js
same wavelength emitted/absorbed =
same energy required to move between energy levels
duality of light
light energy exhibits evidence of behaving both as a wave and as a particle
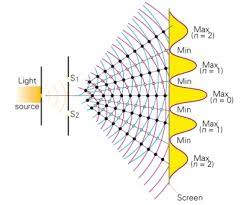
light as a wave
Youngs dual split experiment
when waves are in phase, ______ increases
amplitude/brightness
constructive interference
when the crests of two separates waves line up to increase amplitude
destructive interference
when the crests of two separates waves do not line up to decrease net amplitude
light as a particle
photoelectric effect
photoelectric effect
the observation that photons short-wave (visible or UV) light can cause it to emit electrons
example of ionization, with the photons providing the ionization energy
how the photoelectric effect works
when visible or ultraviolet light is shone on a substance, the energy from the photons of light excites electrons in the substance
if the energy exceeds the ionization energy of an atom in the substance, the electron is emitted (these are called photoelectrons)
requirements for photoelectron emission
light frequency needs to be higher than a certain critical value
amplitudes effect on electron emission
number of electrons emitted
no effect on KE
more e- emitted = more “packets” of light (photons) hitting = increased brightness
increased wavelength frequency =
increased kinetic energy (how much energy e- get kicked out with)
increased amplitude/brightness =
increased number of photons
1 eV =
1.602 × 10-19 J
EB
binding energy of electron to nucleus
Wo
work function, the amount of additional energy it takes to move the delocalized electron to the surface of the material (zero for gases, but nonzero for solids)
Einstein’s equation for the photoelectric effect
EKE = hv - EB - Wo
photoelectron/photoemissions spectroscopy
using the energy from electrons emitted via the photoelectric effect to gain information about the electronic structure of a substance
how photoelectron/photoemission spectroscopy works
a substance is bombarded with photons, which have a given amount of energy based on their frequency
by measuring the KE of the emitted electron, and predetermining the work function of the substance, we can calculate the binding energy of the electron from Einstein’s equation for the photoelectric effect
photoelectron spectroscopy is generally used for
gases
photoemission spectroscopy is generally used for
electrons emitted from solid surfaces
ultraviolet photoelectron spectroscopy (UPS) and extreme ultraviolet photoelectron spectroscopy (EUPS) are used
to study valence electrons and the electrons that participate in chemical bonding
X-ray photoelectron spectroscopy (XPS) is used
to study core electrons, particularly in solids
evidence for electrons as particles
cathode ray experiment
absence of propagation of electrons
ability to reflect cathode beam with a given electrostatic charge —> mass to charge ratio
mass characteristics = particulate behavior
evidence for electrons as waves
Young’s dual slit experiment with electrons
over time, showed pattern of constructive and destructive interference, just like with light
schrodinger’s equation (wave equation)
used to predict the electron positioning in orbitals