AP Macroeconomics Unit 1
1/68
Earn XP
Description and Tags
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
69 Terms
economics
the study of resources that have alternative uses that are used to fulfill nearly unlimited human desires.
utility
satisfaction
scarcity
less than what we want
marginal
additional
trade offs
giving up one thing for another
allocate
to distribute
opportunity cost
the next best use for resources
positive statements
fact; avoids value judgement (what is)
normative statements
opinion; includes value judgement (what ought to be)
microeconomics
study of small economic units such as individuals, firms, and industries (competitive MARKETS, labor markets, personal decision making, etc.)
macroeconomics
study of the large economy as a whole or in its basic subdivisions (NATIONAL ECONOMIC GROWTH, government spending inflation, unemployment, etc.)
adam smith
known for the first comprehensive system of political economy: “An Inquiry into the Nature and Causes of the Wealth of Nations”
Command Economy
a central authority makes most of the what, how, and for whom decisions. Economic decisions are made by the government and the people have little, if any, influence over how the basic economic questions are answered. Ex. North Korea, Soviet Union
Advantages: can change direction drastically in a relatively short time, many health and public services are available to everyone for little cost
Disadvantages: not designed to meet the wants of consumers, does not incentivise people to work hard because everyone is paid the same wages
market economy
an arrangement that allows buyers and sellers to come together in order to exchange goods and services. People’s decisions act as votes and supply/ demand power the economy.
Advantages: can adjust to sudden change, high degree of individual freedom on what and how, small degree of government interference, and decision making is individual choice
Disadvantages: can fail if there isn’t consistent competition, reasonably free resources, and adequate Info for consumers to make wise choices. Doesn't provide for everyone’s basic needs, does not provide enough services that people highly value, high degree of uncertainty for workers and businesses as a result of change
traditional economy
the allocation of scarce resources and nearly all other economic activity stems from ritual, habit, or custom. Habits and custom tend to dictate social behavior.
Advantages: everybody knows which role to play, you know what to produce and how, for whom the products are made is dictated by the traditions of the society.
Disadvantages: discouragement of new ideas, those who break rules are often punished, little growth, distinct lack of progress which equates to a lower living standard
mixed economy
any combination of traditional, market or market economy
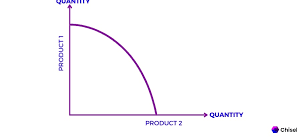
production possibility curve (PPC)
shows opportunity cost and trade offs (how much you must give up of one thing for another)
Increasing opportunity cost
bowed line
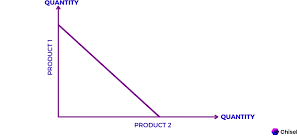
constant opportunity cost
linear fit
full employment
any point on the PPC line
inflation
a sustained rise in the general price level in an economy
recession
a decline in economic activity
right shift
economic growth
left shift
economic decrease
key four things necessary to make more
labor, resources, capital (the machine that makes the product), and technology/ productivity
capital
machine that makes the product
the product market
the place where goods and services produced by businesses are sold to households
the resource (factor) market
the place where resources (land, labor, capital, and ent.) are sold to buisnesses
four factors of production
land, labor, capital, entrepenuership
land
all natural resources that are used to produce goods and services. Anything from nature (water, sun, oil, etc.)
labor
any labor for which a person in paid (manual laborers, teacher, lawyers, doctors, etc.)
three types of capital
physical capital, human capital, and financial capital
physical capital
human made resource used to create other goods/ services (tools, tractors, machines, buildings, factory, etc.)
human capital
skills/ knowledge gained by a worker through education and experience (college, vocational training, etc.)
financial capital
money companies use to buy resources
entrepreneurship
ambitious leaders that combine the other factors of production to create goods and services
the law of demand
quantity demanded of a good is inversely proportional to its price
the demand curve
the demand curve represents the demand for a product at a given price
income effect
when things are more expensive, we buy less. When things are cheaper, we buy more.
substitution effect
when apples are expensive and their substitute (pears) are relatively cheap, I buy fewer apples and more pears
diminishing marginal utility
each additional unit of a product purchased gives less marginal utility (happy points) than the previous unit. Therefore, the only way I will buy more is if the price is lower
shifters of demand
consumer tastes/ preferences, prices of related goods, consumer income, number of consumers, change in expectations of future prices.
consumer tastes/ preferences
advertising
prices of related goods
complements (fries with burger), substitutes
consumer income
normal goods vs inferior goods
normal goods
want to buy and have money
inferior goods
forced to buy and don’t have money
number of consumers
more consumers equals more demand
change in expectations of future prices
expecting lower price= left shift, expecting higher price= right shift
law of supply
quantity supplied of a good is proportional to its price
the law of increasing marginal cost
its more costly to produce two than one. Therefore, I must collect a higher price if I am going to produce more.
supply curve
the supply curve shows the quantity supplied at a specific price.
sifters of supply
price of resources (land, labor, capital), number of suppliers, price of other goods, productivity (ex. technology), government policies, expectation of future prices
government policies which may shift supply
taxes (money taken from businesses), subsidies (money to businesses), and regulations (rules for businesses)
equilibrium
when supply equals demand
surplus
when the supply is greater than the demand
what happens in event of a surplus
companies will lower their prices
shortage
when the demand is greater than the supply
what happens in the event of a shortage
companies will raise prices
demand shifts to the left
price and quantity both go down
demand shifts to the right
price and quantity both go up
supply shifts to the left
Price goes up while quantity goes down. Worst thing to happen to a market
supply shifts to the right
price goes down while quantity goes up. good thing to happen to a market
oil market
price goes down and quality is indeterminate
price ceiling
highest price you’re allowed to charge for an item. If it’s below equilibrium it can create a shortage. Demand is greater than supply
price floor
the lowest price you’re allowed to charge for an item. If it’s above equilibrium it can create a surplus. Demand is less than supply
consumer surplus
the difference between what a customer would have paid and what they actually paid
producer surplus
the difference between what a producer sold their good for and the minimum they would have sold it for
dead weight loss
the lost value/ surplus due to a market interference, usually by the government