A&P II: Chapter 17
1/82
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
83 Terms
transport, regulation, and protection
Three main functions of blood
blood
O2, nutrients, waste, and hormones are transported by ___
blood
Body temperature, pH, and fluid volume are regulated by ___
blood
Prevents blood loss and infection
Color ranges, slightly alkaline, denser than water, and 8% of body mass
Physical characteristics of blood
Plasma (55%), buffy coat (<1%), erythrocytes (45%)
Composition of blood
Albumin (60%), Globulins (36%), and Fibrinogen (8%)
Plasma proteins most abundant by mass
Albumin
Plasma protein that shuttles molecules through circulation
Alpha/beta globulins
Plasma protein that transport proteins that bind to lipids, metal ions, and fatsoluble vitamins
Gamma globulins
Plasma protein that are the antibodies that circulate throughout the body
Fibrogen
Plasma protein that forms the fibrin threads of blood clots
Erythrocytes
Blood cells that bind to and transport oxygen and carbon dioxide (CO2)
Leukocytes
Blood cells involved in the immune response
Platelets
Blood cells that are involved in blood clotting
Erythrocytes
Blood cell that is anucleate and a biconcave disc; Hemoglobin, Antioxidant enzymes, and spectrin
small size/shape, don’t consume oxygen they carry, dry mass >97% hemoglobin
Three characteristics that contribute to erythrocytes ability to transport gases
250 million
An erythrocyte has ___ million hemoglobin molecules
heme groups
A hemoglobin has four ___ groups
four
A heme group can bind to ___ oxygen molecules
Oxyhemoglobin
Partially oxidized by oxygen and changes shape; turns ruby red
Deoxyhemoglobin
Oxygen detaches and hemoglobin resumes former shape; turns dark red
Carbaminohemoglobin
CO2 binds to amino acids instead of the heme group; Binds more readily when hemoglobin is in a reduced state
hematopoiesis
Process of producing new blood cells in the body, primarily the bone marrow
hemocytoblasts
All blood cells in the body arise from these hematopoietic stem cells
erythropoiesis
the process by which erythrocytes are produced in the bone marrow
erythropoietin (EPO)
stimulates formation of erythrocytes
testosterone
enhances kidneys production of erythropoietin (EPO)
100 to 120 days
The life span of an erythrocyte lasts between ___ to ___ days
spleen
Organ known as the red blood cell graveyard
Anemia
A condition in which the blood’s oxygen-carrying capacity is too low to support normal metabolism
Hemorrhagic anemia
A form of anemia which is caused by blood loss
Iron-deficiency anemia
A form of anemia which is caused by hemorrhagic anemia, but also results from inadequate intake of iron-containing foods or impaired iron absorption
Pernicious anemia
A form of anemia which caused by an autoimmune disease that most often affects older adults
Renal anemia
A form of anemia which is caused by the lack of EPO, the hormone that controls red blood cell production
Aplastic anemia
A form of anemia which is caused by the destruction or inhibition of the red marrow by certain drugs, chemicals, ionizing radiation, or viruses
Hemolytic anemia
A form of anemia which is caused when erythrocytes rupture, or lyse, prematurely
Sickle-cell anemia
A form of anemia which is caused by an abnormal shape in the hemoglobin
Thalassemias
An erythrocyte disorder typically occuring in people of mediterranean ancestry where one of the globin chains is absent or faulty and the erythrocytes are thin, delicate, and deficient in hemoglobin
Polycythemia
An erythrocyte disorder where an abnormal excess of erythrocytes increase blood viscosity, causing it to flow sluggishly
Leukocytes
Only formed blood cells that count as complete cells
Diapedesis
Leukocytes can slip out of the capillary blood cessels which is known as ___
Amoeboid motion
Leukocytes move through tissues via ___ motion
positive chemotaxis
Leukocytes move to pinpoint area of tissue damage and infection by ___ ___
Leukocytosis
An increase in the number of leukocytes in the blood, especially during an infection
Granulocytes and agranulocytes
Two major categories of leukocytes
Granulocytes
Leukocytes that are larger and shorter lived than erythrocytes; Has a lobed nuclei and contains membrane-bound cytoplasmic granules
Agranulocytes
Leukocytes that lack granules
Neutrophils → lymphocytes → monocytes → eosinophils → basophils
Most abundant to least abundant granulocytes (Never Let Monkeys Eat Bananas)
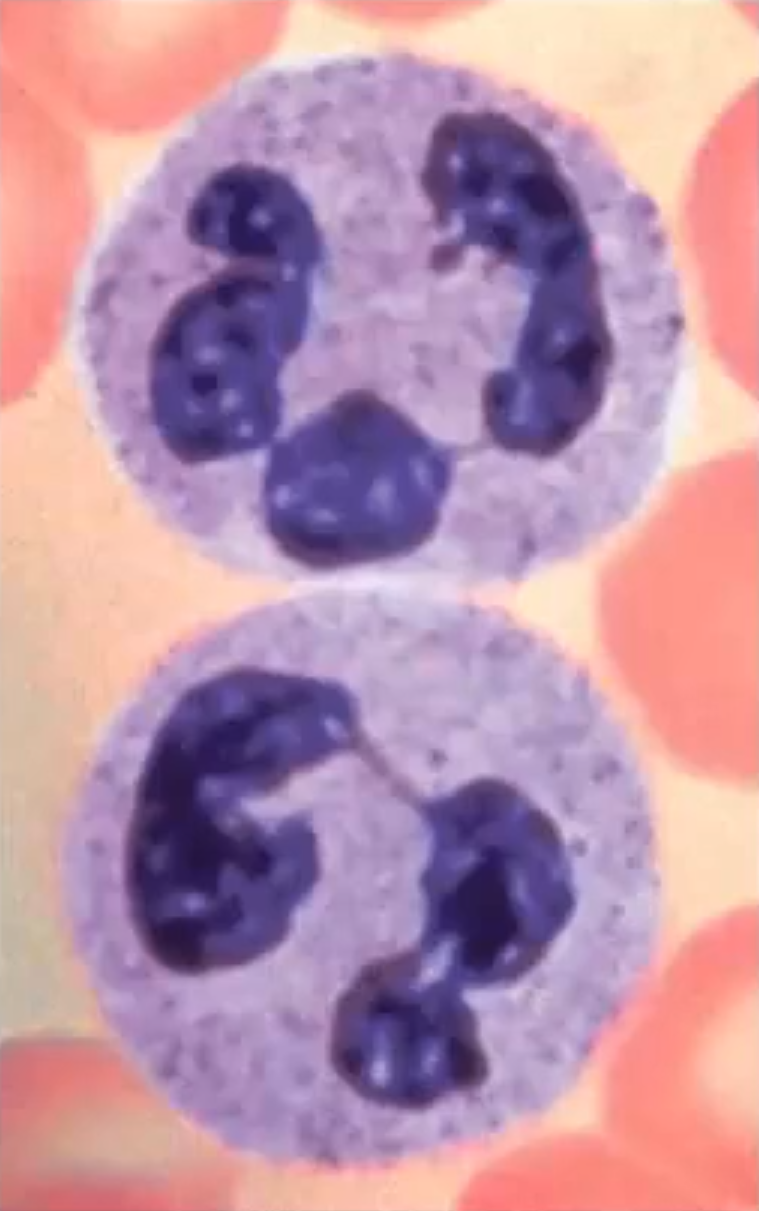
Neutrophils
A granulocyte that is 50-70% of leukocyte population; Twice as large as erythrocytes; Multi-lobed nucleus (6-8)
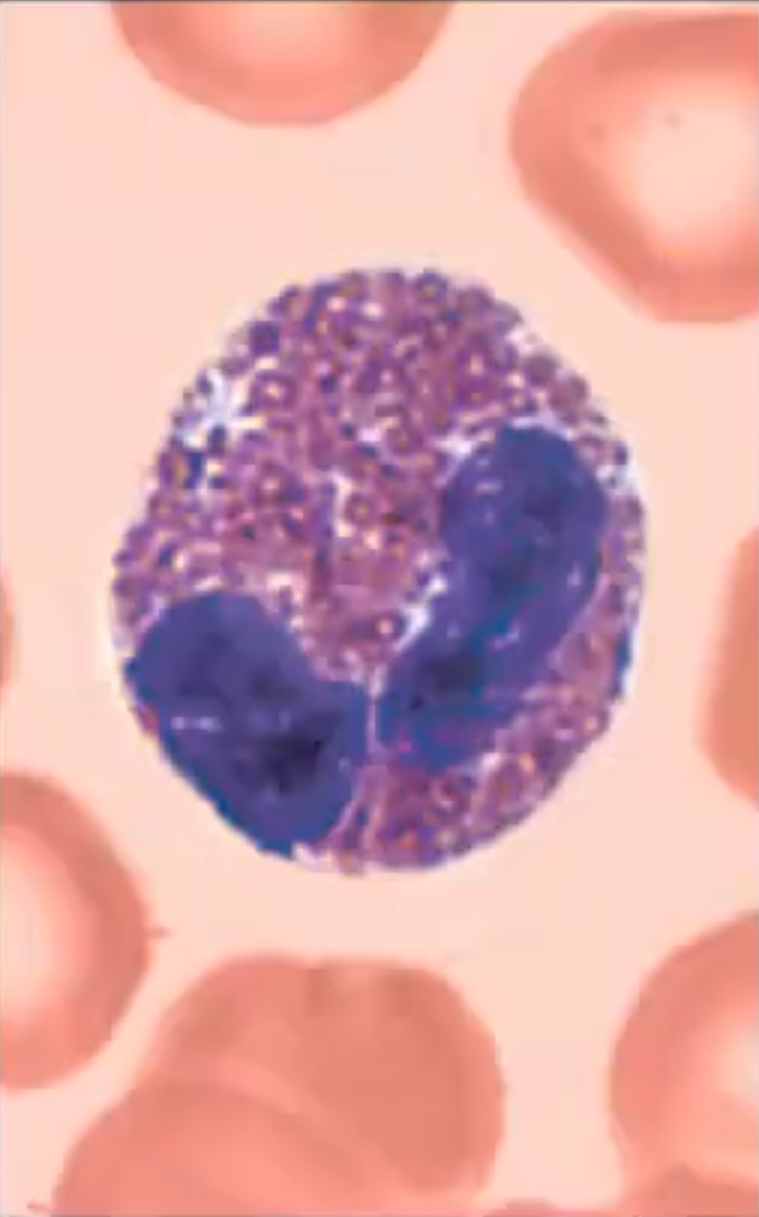
Eosinophils
A granulocyte that is 2-4% of leukocyte population; Defense against parasites, allergies and asthma; Two nuclei lobes connected by a broad band
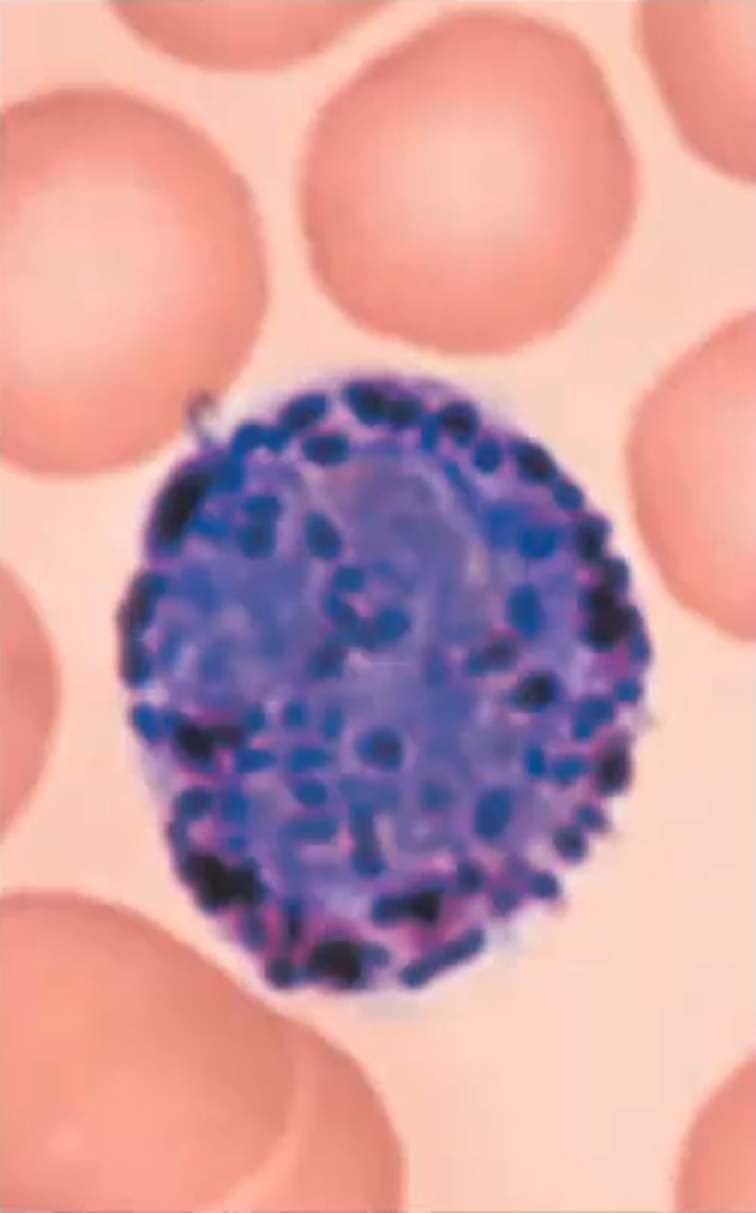
Basophils
A granulocyte that is 0.5-1% of the leukocyte population; Nucleus generally U or S shaped with one or two constrictions
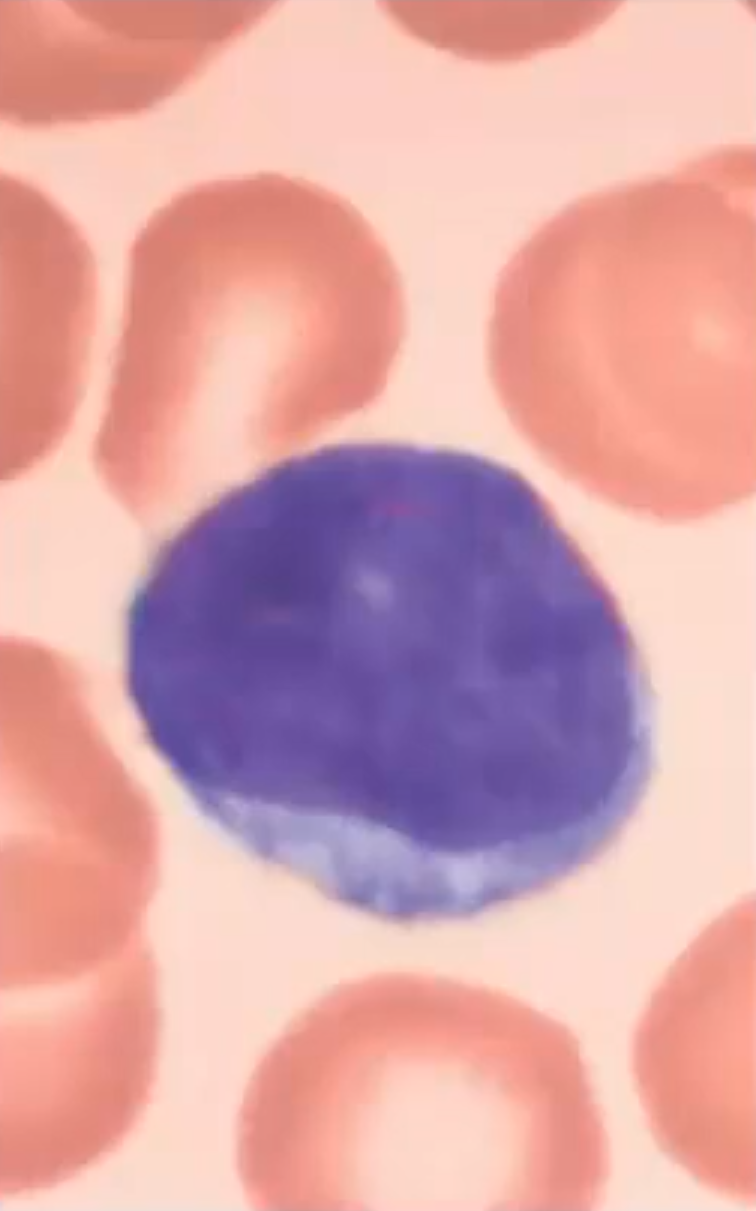
Lymphocytes
A agranulocyte that is +25% of the leukocyte population; Large spherical nucleus that occupies most of the cell
Monocytes
A agranulocyte that is 3-8% of the leukocyte population; Nucleus is U or kidney-shaped
Leukopoiesis
the process of forming leukocytes from pluripotent stem cells in the bone marrow
Leukemia
A type of leukocyte disorder that causes the production of abnormal leukocytes, which can accumulate in the bloodstream and interfere with the normal function of other blood cells
Leukopenia
A type of leukocyte disorder that is commonly induced by drugs which causes an abnormally low white blood cell count
Acute leukemia
A form of leukemia that is quickly advancing because it derives from stem cells
Chronic leukemia
A form of leukemia that is slowly advancing because it involves proliferation of later cell stages
Myeloid leukemia
A form of leukemia that involves myeloblast descendants
Lymphocytic leukemia
A form of leukemia that involves lymphocytes
Infectious mononucleosis
Aka “kissing disease”, a highly contagious viral disease most often seen in young adults caused by the epstein-barr virus; Causes an excessive number of lymphocytes
Platelets
A cell fragment that is derived from megakaryocytes; Degenerates within 10 days if not involved in clotting
Thrombopoietin
A protein hormone that plays a crucial role in the regulation of platelet production
vascular spasm, platelet plug formation, and blood coagulation
Three steps of hemostasis which prevents blood loss
Prothrombin (p2) → thrombin (p2)
Intrinsic and extrinsic pathways both lead to the prothrombin activator during phase 1 at which point it moves to phase 2
fibrinogen (p3) → fibrin (p3)
Intrinsic and extrinsic pathways both lead to the prothrombin activator during phase 1 at which point it moves to phase 2 and then phase 3
tissue factor (TF)
Required in the activation of the extrinsic pathway during phase 1
calcium (Ca2+)
Element required in many steps in both extrinsic and intrinsic pathways
Clot retraction
Platelet-induced when the platelets contain actin and myosin at which point put contract to pull surrounding fibrin strands to stabilize the clot
Platelet-derived growth factor (PDGF)
Released by platelets which stimulate smooth muscle cells and fibroblasts to divide to rebuild vessel wall
Fibrinolysis
A process that removes unneeded clots when healing has occured using plasmin, a fibrin-digesting enzyme, and tissue plasminogen activator (tPA)
Antithrombin III
An inhibiting factor that inactivates any thrombin not bound to fibrin
Protein C
An inhibiting factor that inhibits activity of other intrinsic pathway clotting factors
Heparin
A inhibiting factor contained in basophil and mast cell granules, surface of endothelial cells; Inhibits thrombin and intrinsic pathway
Thrombocytopenia
A clotting disorder characterized by a low number of circulating platelets
Disseminated intravascular Coagulation (DIC)
A disorder that involves both widespread clotting and severe bleeding
Hemophilia
An inherited bleeding disorder that occures when the blood does not clot properly
plasma
The fluid portion of blood is called ___
buffy coat
The ___ ___ portion of blood is made up of white blood cells and platelets
hematocrit
The red blood cell portion of blood is called ___
vascular anastomoses
___ ___ is used to connect two blood vessels together
vascular anastomoses
___ ___ is useful when the body sustains damage because you can use it to reroute blood flow around the damaged area
Venous system
Most of the blood volume in a human body is contained within this system