NCLEX UWorld
1/1321
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
1322 Terms
When do advanced directives go into effect?
when person is unable to speak for him/herself due to either:
1. Mental Incapacity - coma (GCS score ≤ 7)
2. Aphasia
(≠as soon as signed; directives can always be changed later by person)
SBAR Communication Framekwork Components
1. S = Situation - what prompted the communication (eg what changes occurred)
2. B = Background - pertinent information, relevant history, vital signs
3. A = Assessment - nurse's assessment of the situation (when & what changes occurred)
4. R = Recommendation - request for prescription or action from HCP
Appropriate order of actions when client found on floor
1. Assessment of physiological stability ABCs
2. Assessment of injuries
3. Moving client
4. Notifications
5. Documentation
Conditions of being ineligible to leave AMA
1 danger to self or others
2. lack of consciousness
3. Altered consciousness
4. Mental illness
5. Being under chemical influence
6. Court decision
Effective handoff communication components
Nurse should:
1. Provide identifying information (eg client's name and room number)
2. Note care priorities and upcoming or outstanding tasks (eg time to replace medication infusion bag, need to perform delayed wound care and cause of delay)
3. Provide exact, pertinent information (eg medication dose, time, measurable outcomes)
4. Include multidisciplinary plans (eg radiology examinations, family meetings, physical therapy)
5. Relay significant client changes in a clear manner
Risk factors for cervical cancer
1. Infection with high-risk HPV strains
2. History of sexually transmitted diseases
3. Early onset of sexual activity
4. Multiple or high-risk sexual partners
5. Immunosuppression
6. Oral contraceptive use
7. Low SES
8. Tobacco use
what medications interact with grapefruit?
1. calcium channel blockers (diltiazem, nifedipine, verapamil, etc)
2. statins
3. SSRIs
Risk associated with stent placement using the femoral approach
retroperitoneal hemorrhage
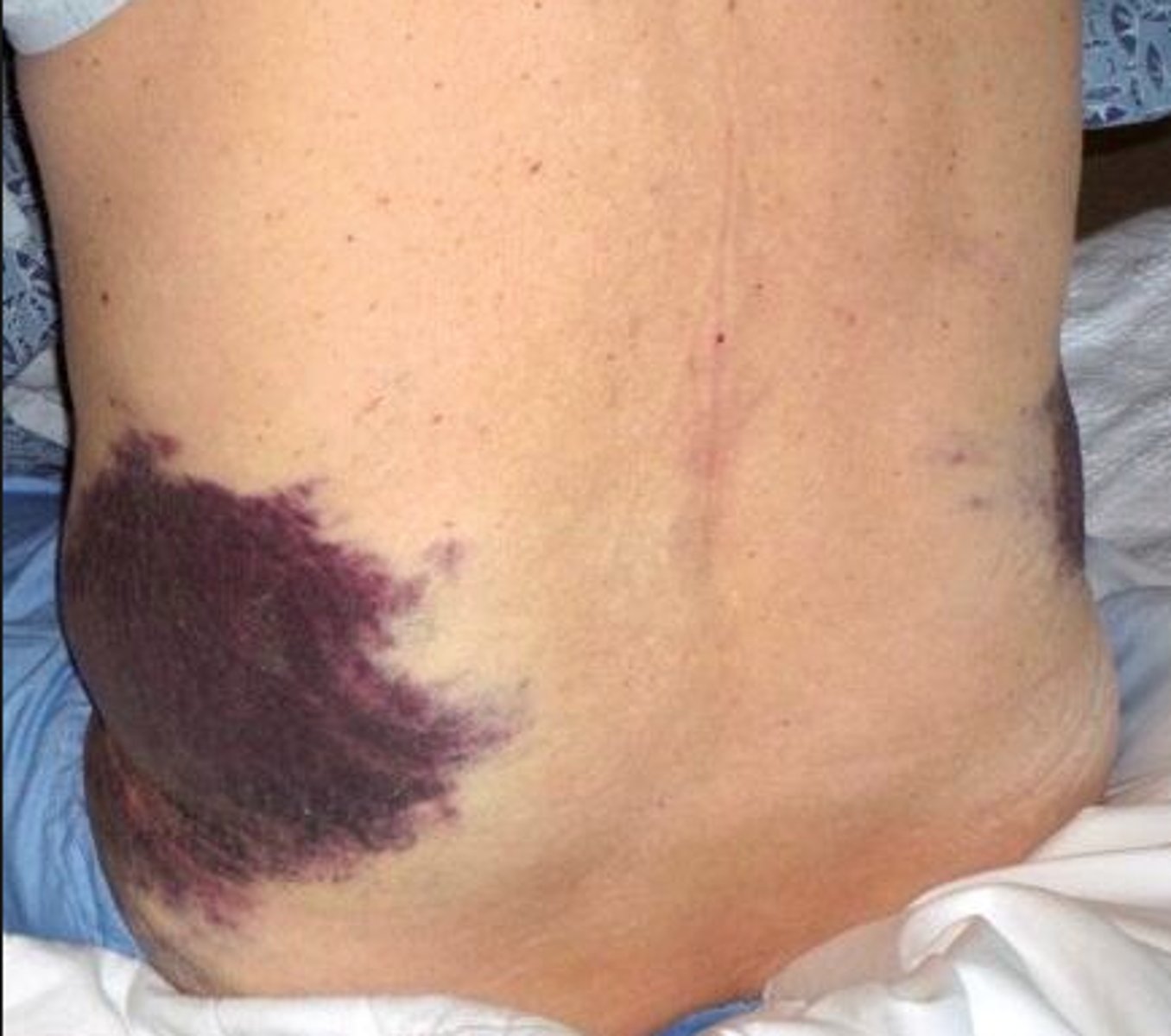
what are early signs of bleeding into the retroperitoneal space?
hypotension, back pain, flank ecchymosis (grey turner sign), hematoma formation, diminshed distal pulses
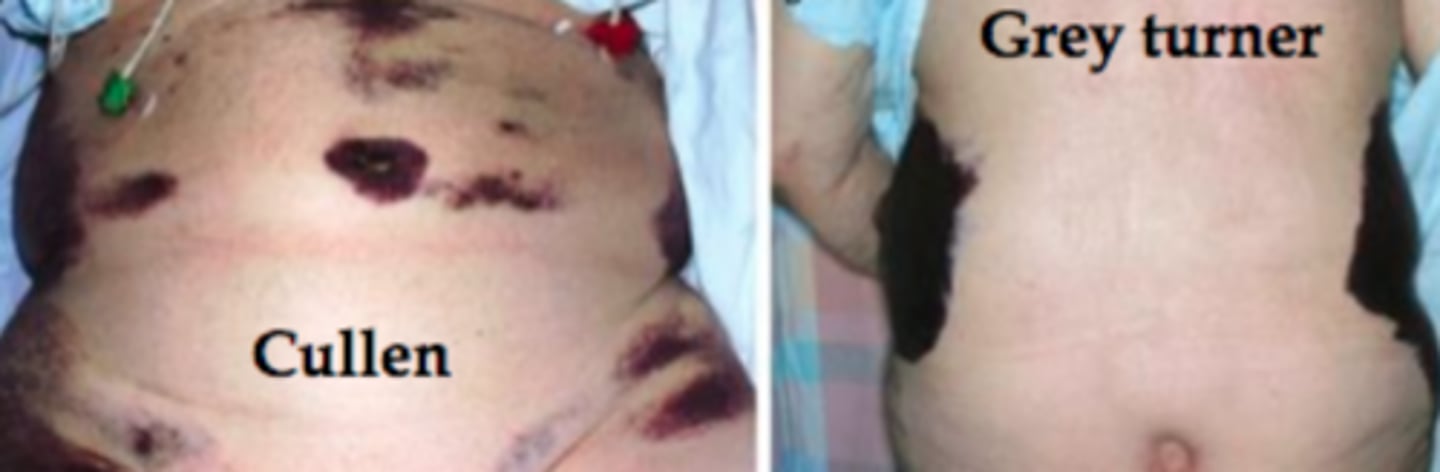
what is the grey-turner sign and what is it a sign of?
bruising of the flanks and retroperitoneal hemorrhage and is a bluish color
what are some physical signs of peripheral arterial disease?
intermittent calf muscle pain?, rest pain, hair loss, decreased peripheral pulses, cool, dry, shiny skin, thick brittle nails, gangrene, ulcers (all of these are in the extremities)
transplanted hearts are expected to be
tachycardic like 90-110
what is the priority intervention for pain with sickle cell crisis and why?
administer IV fluids to reduce blood viscosity and restore perfusion to areas affected by vasoocclusion
what is the purpose of continuous bladder irrigation?
it is prescribed after TURP to prevent obstruction of urine outflow by removing clotted blood from the bladder
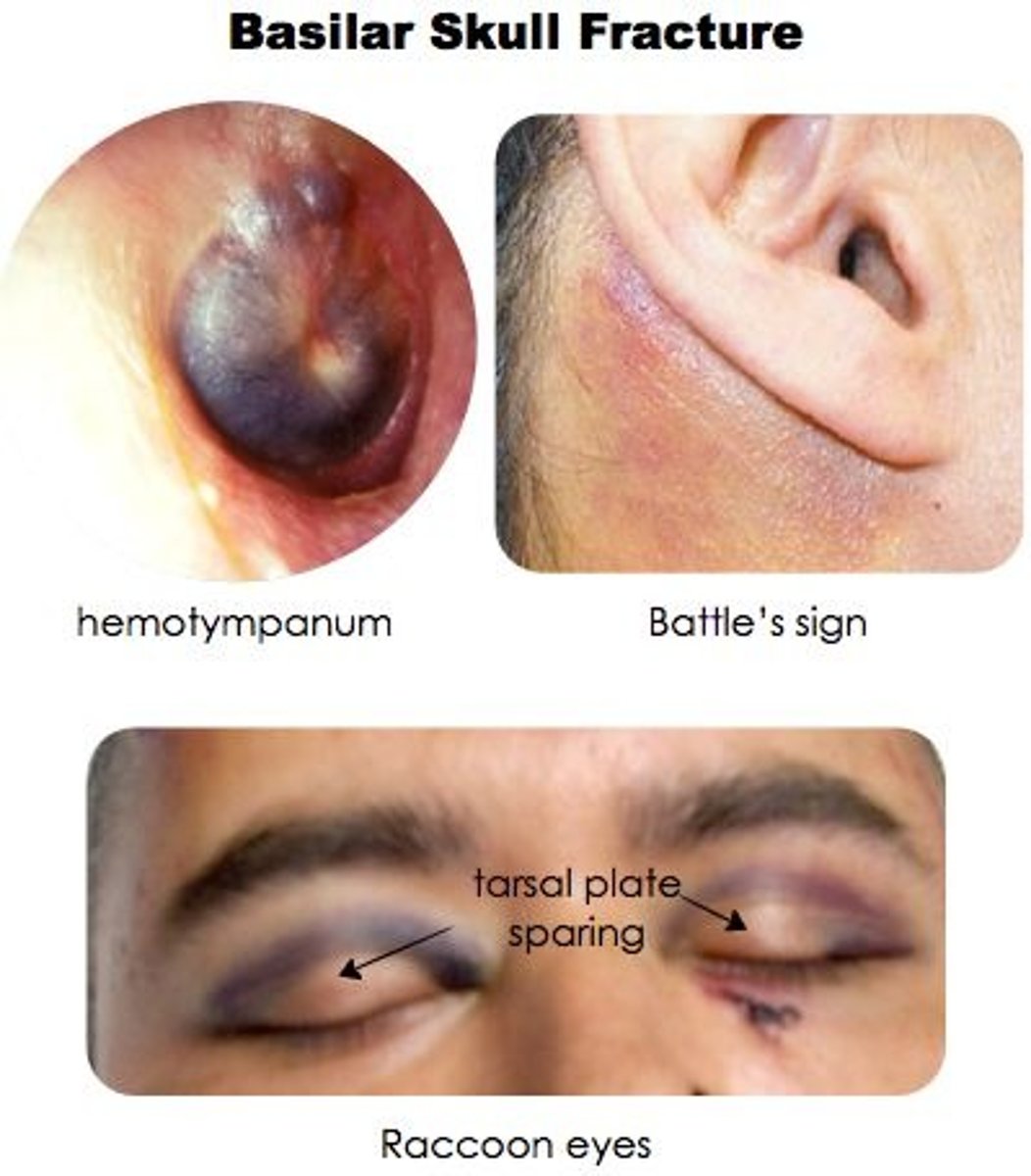
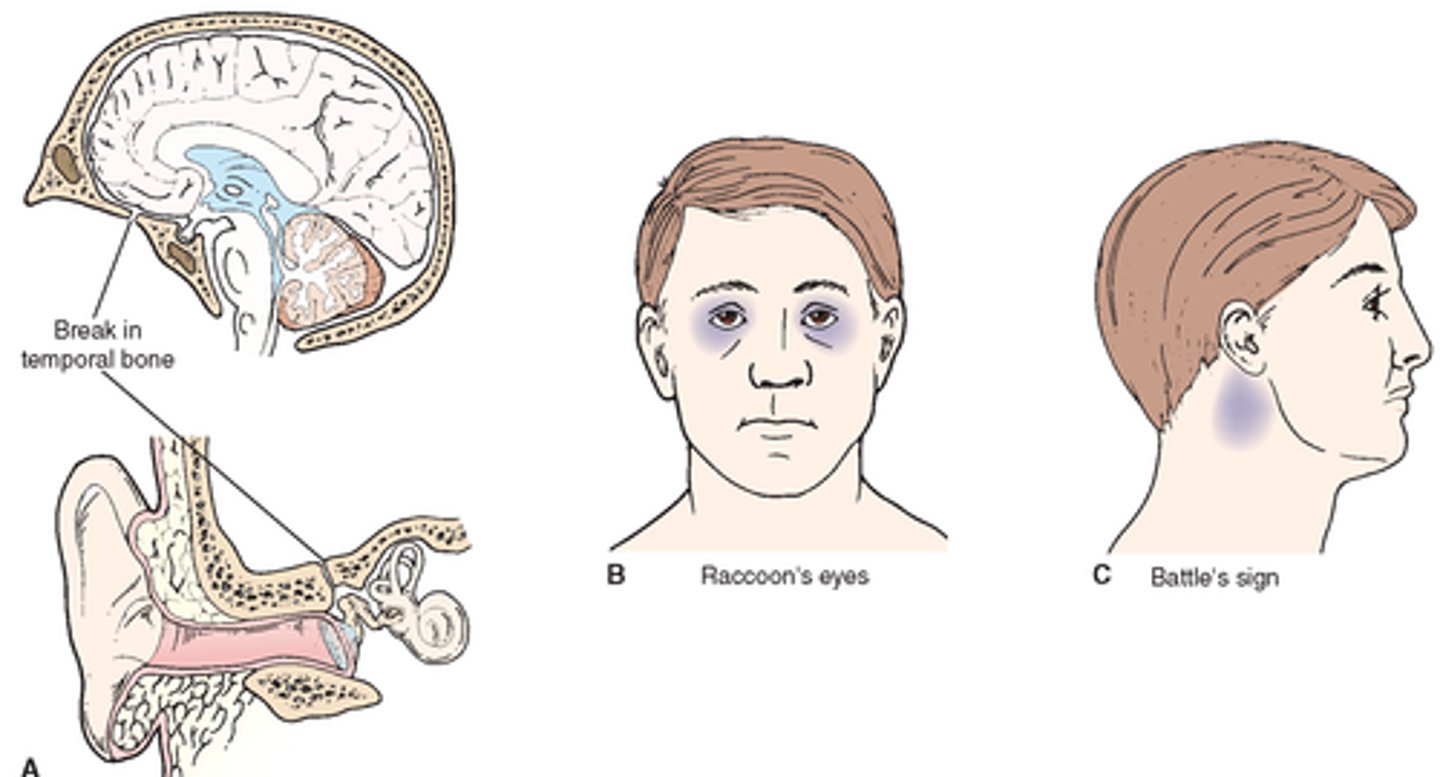
characteristics of a basilar skull fracture
periorbital hematomas (raccoon eyes), csf fluid rhinorrhea, and battle sign (behind the ear bruising)
immediate client care for basilar skull fracture
cervical spine immobilization, close neurologic monitoring, and support of ABCs
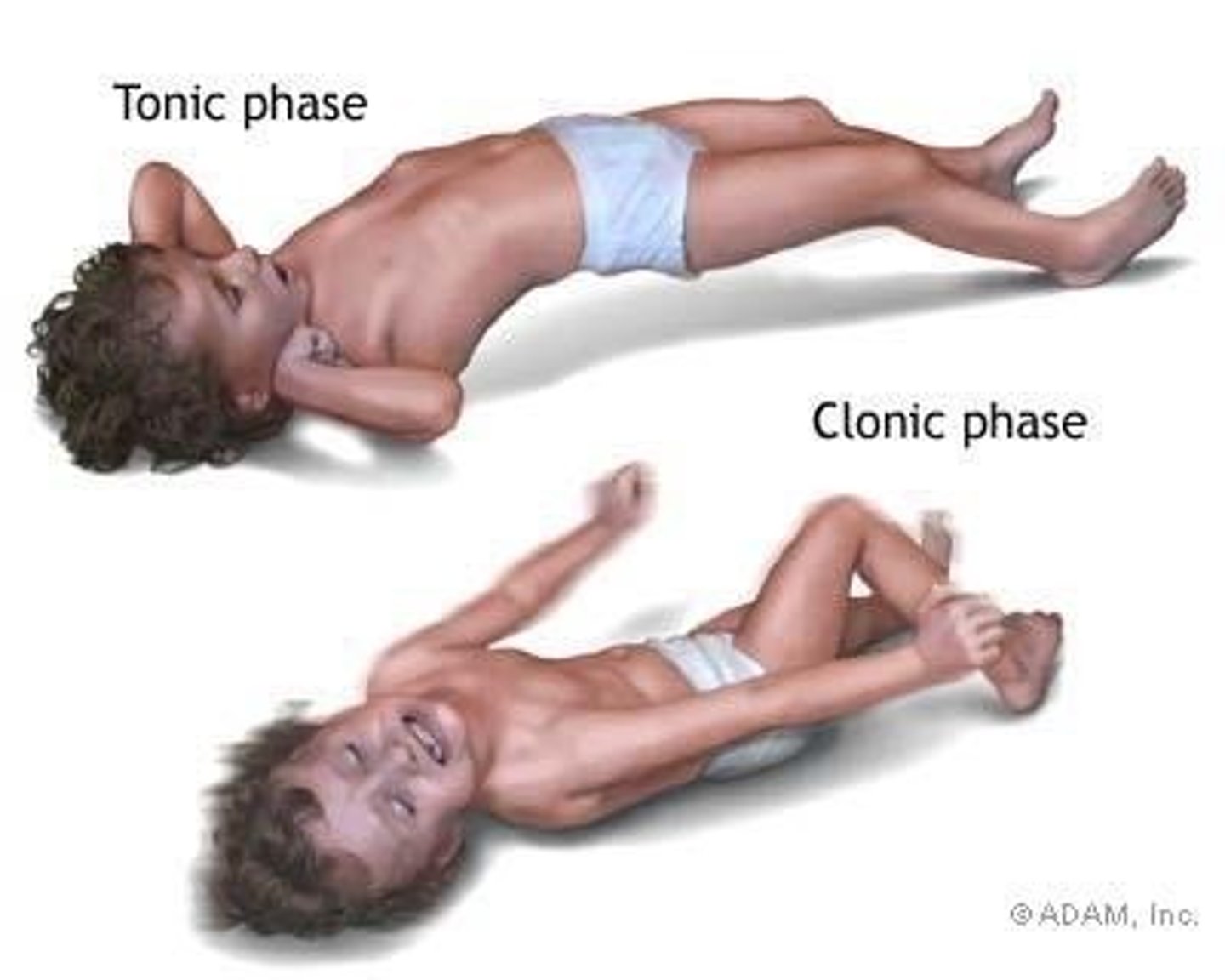
nurse actions during a seizure
assist them to lie down is standing/sitting, put them on side for patent airway, loosen tight clothing, give oxygen as needed, remove objects from immediate area, document time and duration of seizure (for tests are done later to see which type of seizure and maybe what exacerates it)
never put anything in mouth or restrain them since muscle contractions can occur during a seizure
what are some early symptoms of Increased Cranial Pressure?
altered LOC, headache, abnormal breathing, rise in bp, slow pulse, vomiting
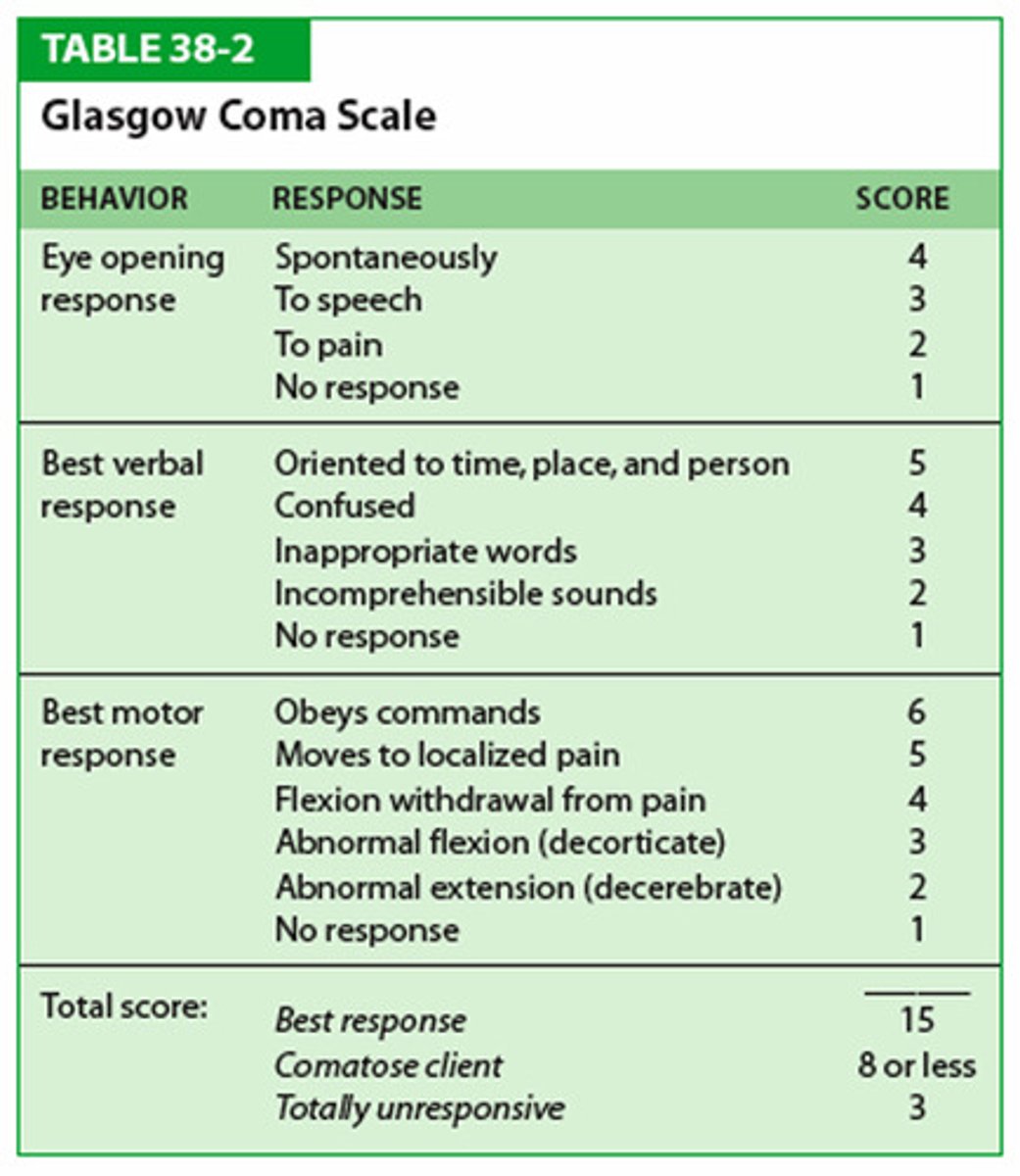
glasgow coma scale ranges from
3-15; 3 being worst 15 being best condition (8 or below in a coma)
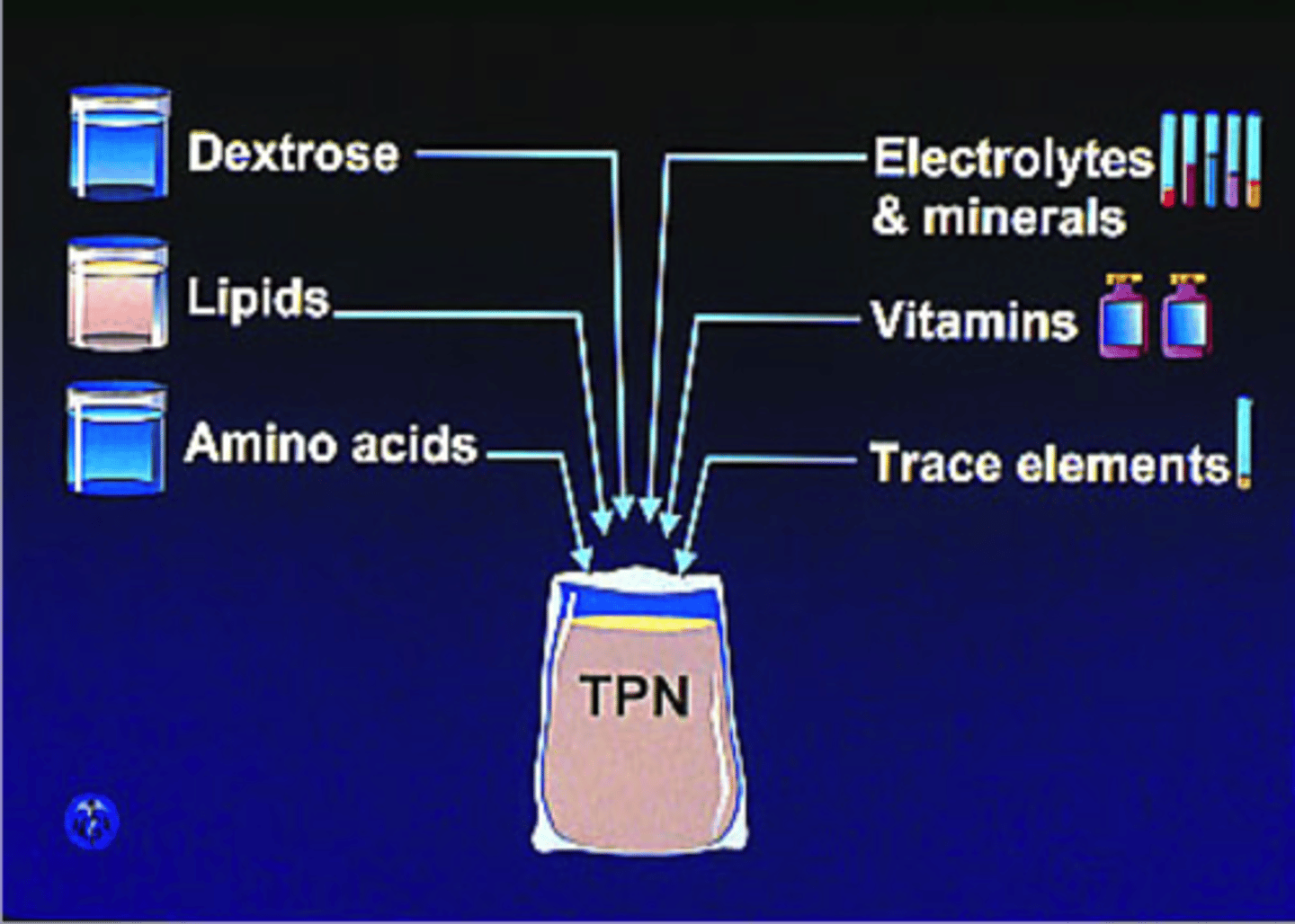
what is a primary component in TPN?
glucose, so the nurse should be monitoring blood glucose and be assessing for signs of hyperglycemia
what are the 4 categories for triaging?
immediate (red tag)- life threatening injuries with good prognosis once treated
delayed (yellow)- injuries requiring treatment within hours
minimal (green tag)- injuries requiring treatment within a few days
expectant (black tag)- extensive injuries, poor prognosis regardless of treatment

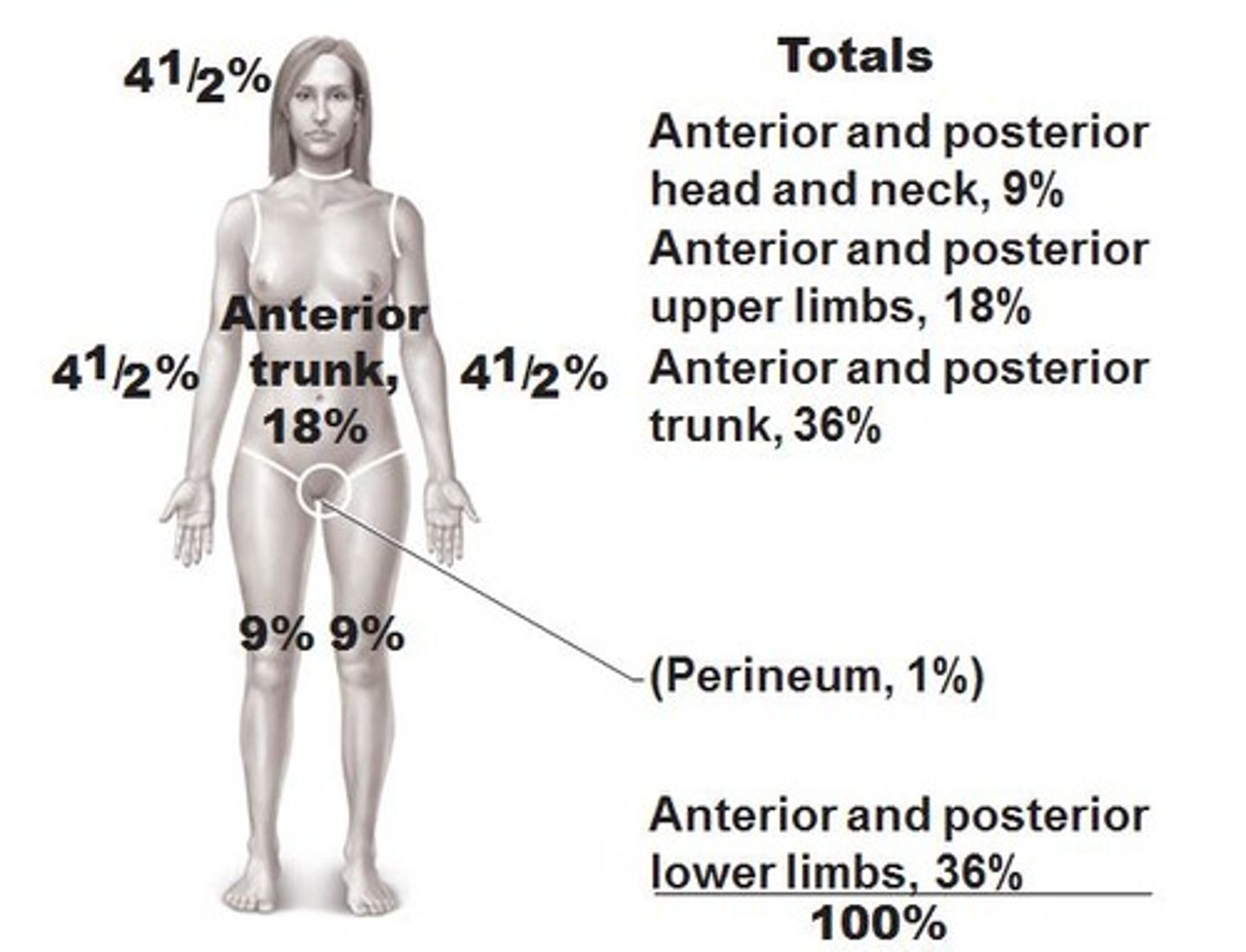
rule of nines
head: 4.5 front 4.5 back
torso: 18 front 18 back
each arm: 4.5 front 4.5 back (each arm is 9 total)
each leg: 9 front 8 back (each is 18 total)
genitals: 1
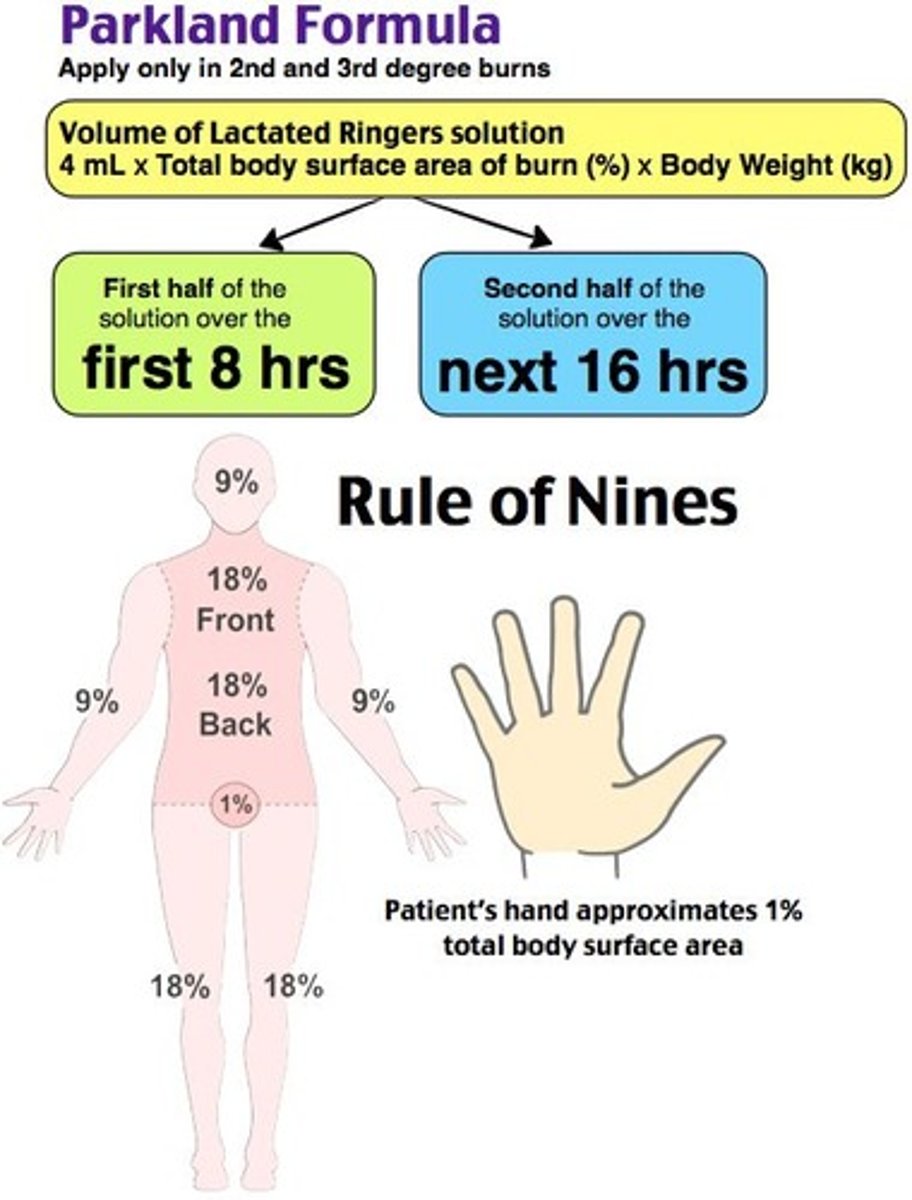
parkland formula for burns
% BSA x weight (kg) x 4
give 1/2 fluids in first 8 hours.
remaining 1/2 in last 16 hours.
airborne precautions
tuberculosis, varicella, and rubeola (measles)
wear N95 respirator (and other as needed like for splashes)
ALSO (neg pressure room and HEPA)
clients suspected are to wear a surgical mask after triage

droplet precautions
spiderman! sepsis, scarlet fever, streptococcal pharyngitis, parvovirus, pneumonia, pertussis,
influenza,
diptheria,
epiglottitis,
rubella,
mumps, meningitis, mycoplasma or meningeal pneumonia, adeNovirus
(Private room and mask)

contact precautions
Methods of infection control that must be used for patients known or suspected to be infected with epidemiological microorganisms that can be transmitted by either direct or indirect contact.

UAP soft wrist restraints can:
do ROM exercises
reapply wrist restraints
report changes in skin to nurse
turn/reposition client in bed
no lasix to what kind of patient
a pneumonia patient with fine crackles bc they dont result from heart failure or edema
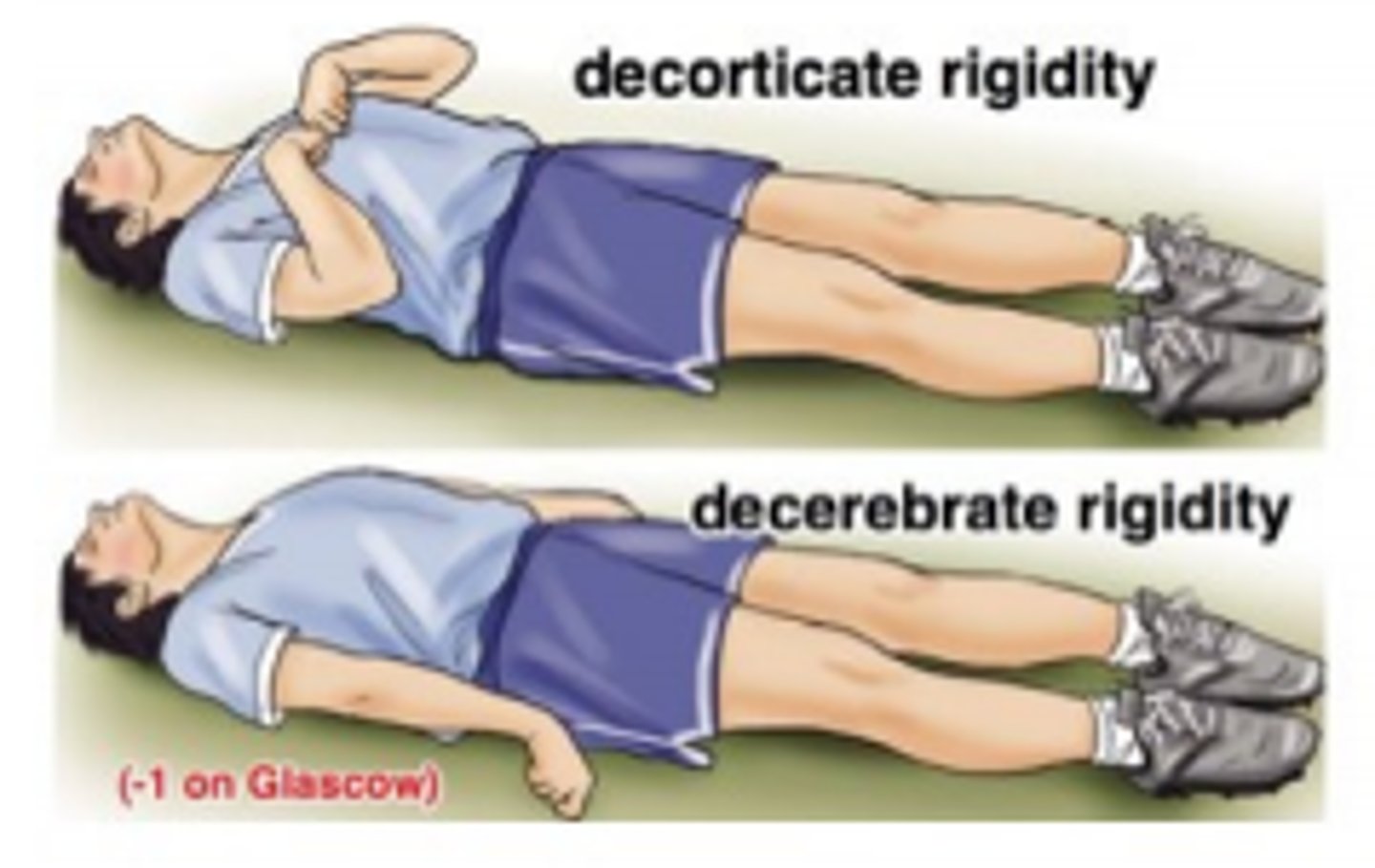
decerebrate posturing (toes point down and amrs/legs straight out) is a sign of
severe brain damage
near drowning hypothermia
warm iv fluids, blankets, and oxygen
also will find weak and thready pulse
intussusception
causes intestinal obstruction
ileum telescopes into cecum, pain obstruction, edema, bowel ischemia, rectal bleeding (CURRANT JELLY stools)
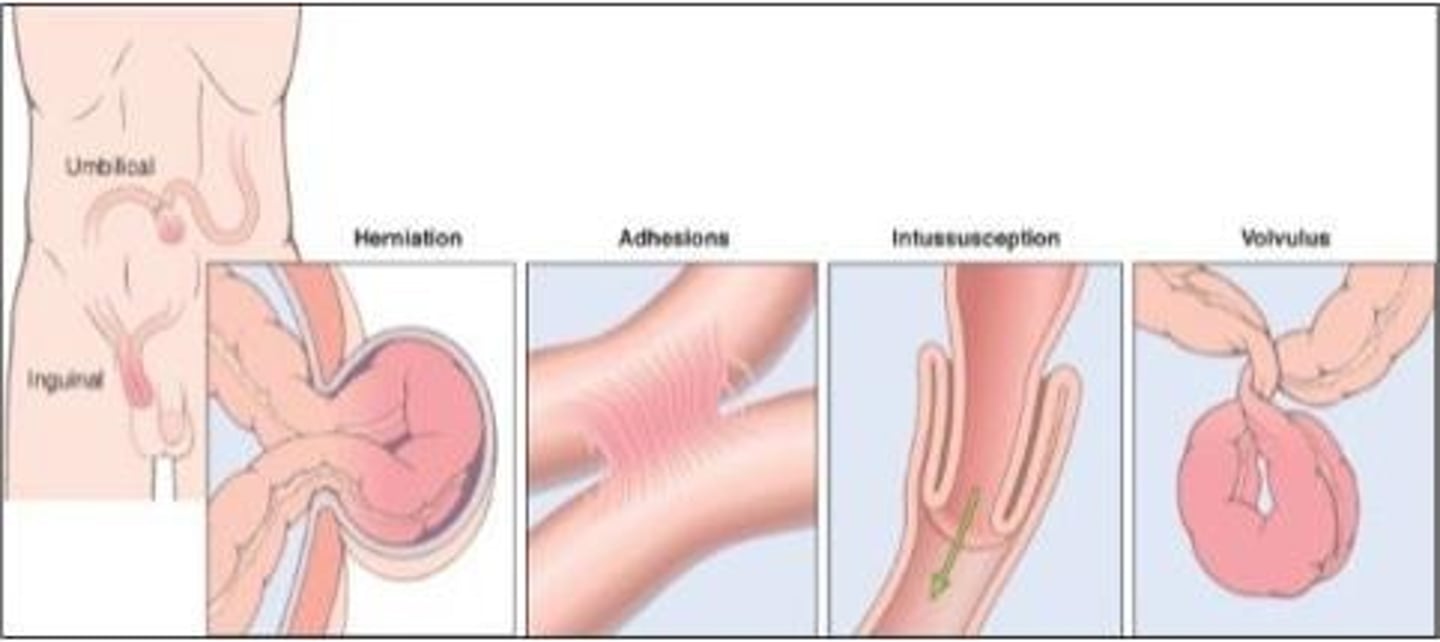
signs of intussusception
initial periodic pain with legs drawn up to abdomen, pain is severe and progressive though, inconsolable crying, blood/mucousy stools "currant jelly"
guaifenesin (Mucinex)
expectorant med that thins secretions to facilitate expectoration
erythropoeitin Epogen
stimulates bone marrow to make RBCs and combats the effects of chemo and used for kidney disease
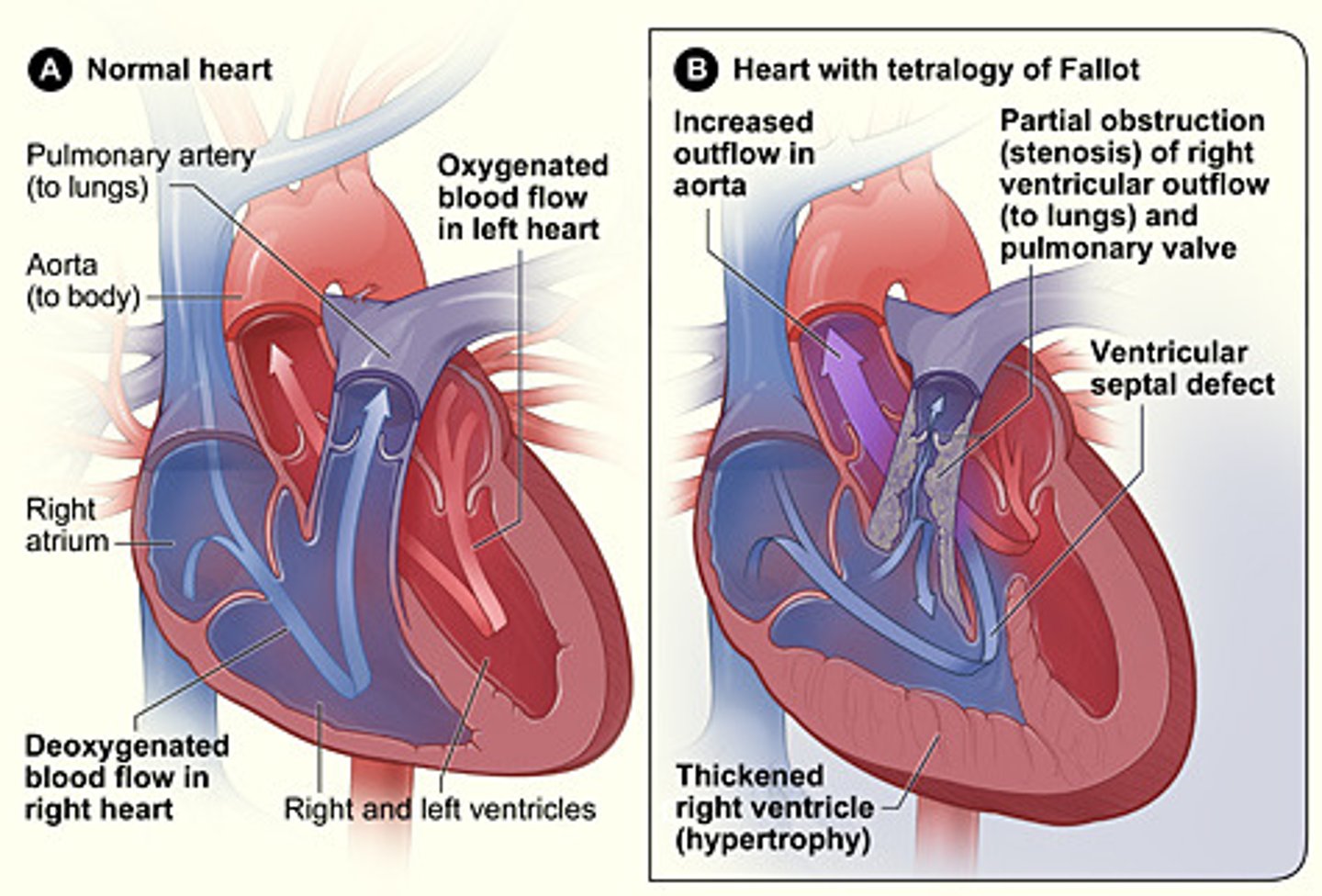
tetraology of fallot
exacerbation can happen when infant or child cries, becomes upset, or is feeding
you immediately place them in KNEE CHEST position
hemolytic uremic syndrome
life threatening complication of e. coli diarrhea

what are the signs?
anemia (pallor), low platelets (petechiae and purpura, and acute kidney injury (low UO)
cognitive behavioral therapy (CBT) 5 basic components
education about pts disorder
self observing and monitoring
relaxation techniques
cognitive restructuring
behavioral strategies
Written consents - Nurse's Role
1. Witness that consent was signed voluntarily
2. That patient was competent at time of signing
3. Documenting in medical records after signature obtained with date/time of signature
how to stop epistaxis
tilt the head forward and apply direct continuous pressure on the alaes (sides) for about 5-20 mins
can also hold a cold washcloth to the bridge of nose for vasoconstriction
keep child calm and quiet
IV iodinated contrast used for ct scan can cause
kidney injury; metformin is discontinued on the day of IV iodine contrast exposure
Gabapentin (Neurontin)
used for neuropathic pain
Phenytoin (Dilantin)
antiseizure
Levofloxacin (Levaquin)
antibiotic
testicular self examination
perform monthly and on same day
perform while taking hot shower bc temps will relax scrotal tissue and make testis hang lower in scrotum
use both hands to feel each testis separately
palpate gently using thumb and first 2 fingers
lactated ringers is often used for
burns

Addison's disease
occurs when the adrenal glands do not produce enough of the hormones cortisol or aldosterone;
hyperpigmentation of the skin
what are some expected symptoms in a TBI?
low grade constant HA, slowness in thinking, memory problems, loss of balance, poor coordination, constant exhaustion, inc sensitivity to light, and heightened irritability
all symptoms that can last up to 6 weeks
Meningitis causes
Infections (viral, bacteria, fungal)
Neurosurgical procedure, basilar-skull fracture
Otitis media, mastoiditis
bacterial meningitis
high fever
change in loc
nuchal rigidity
meningeal signs (positive kernig and brudzinski signs)-- treat with antibiotics
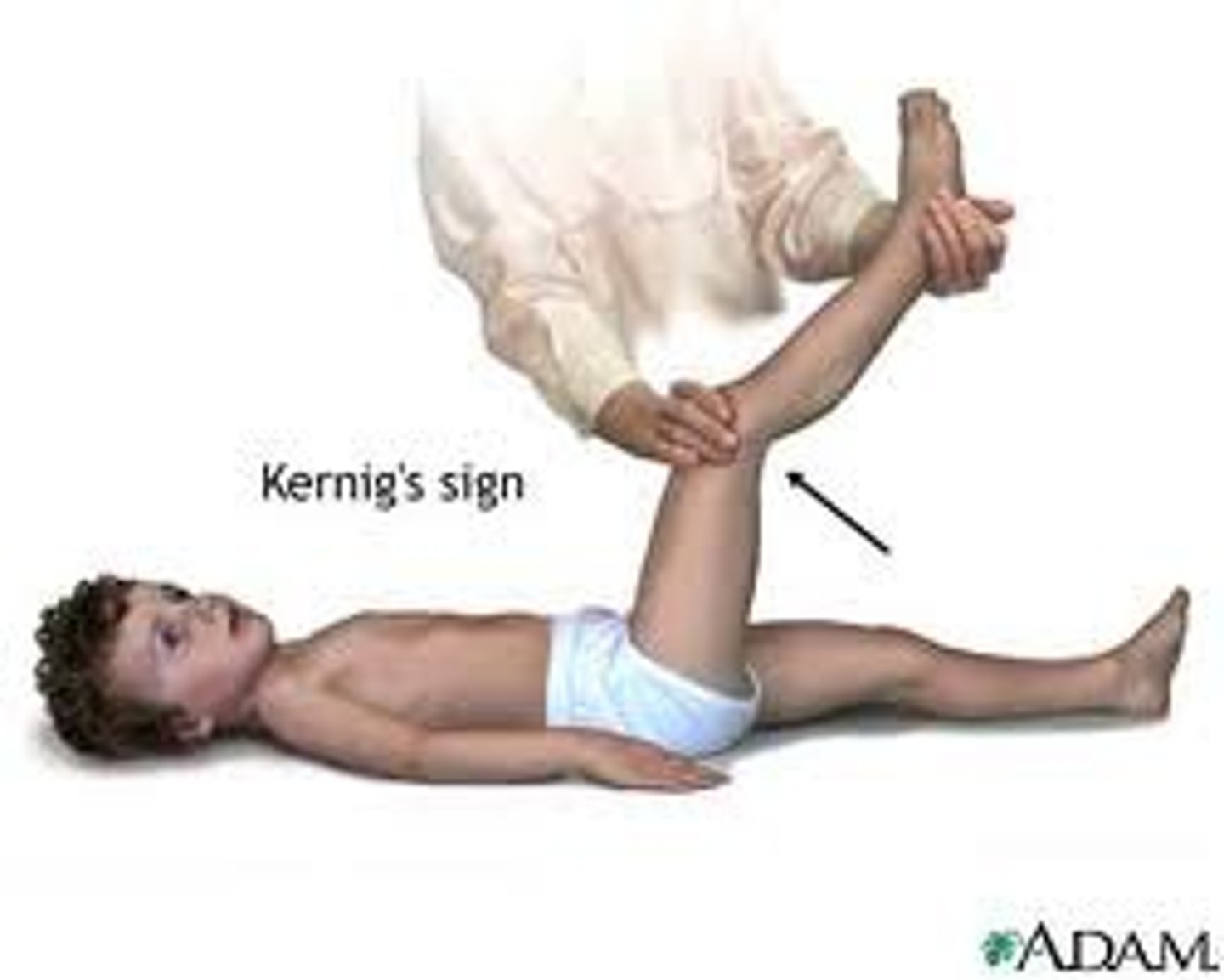
what is the kernig sign?
patient lies supine, thigh is flexed at right angle, and it hurts to extend leg
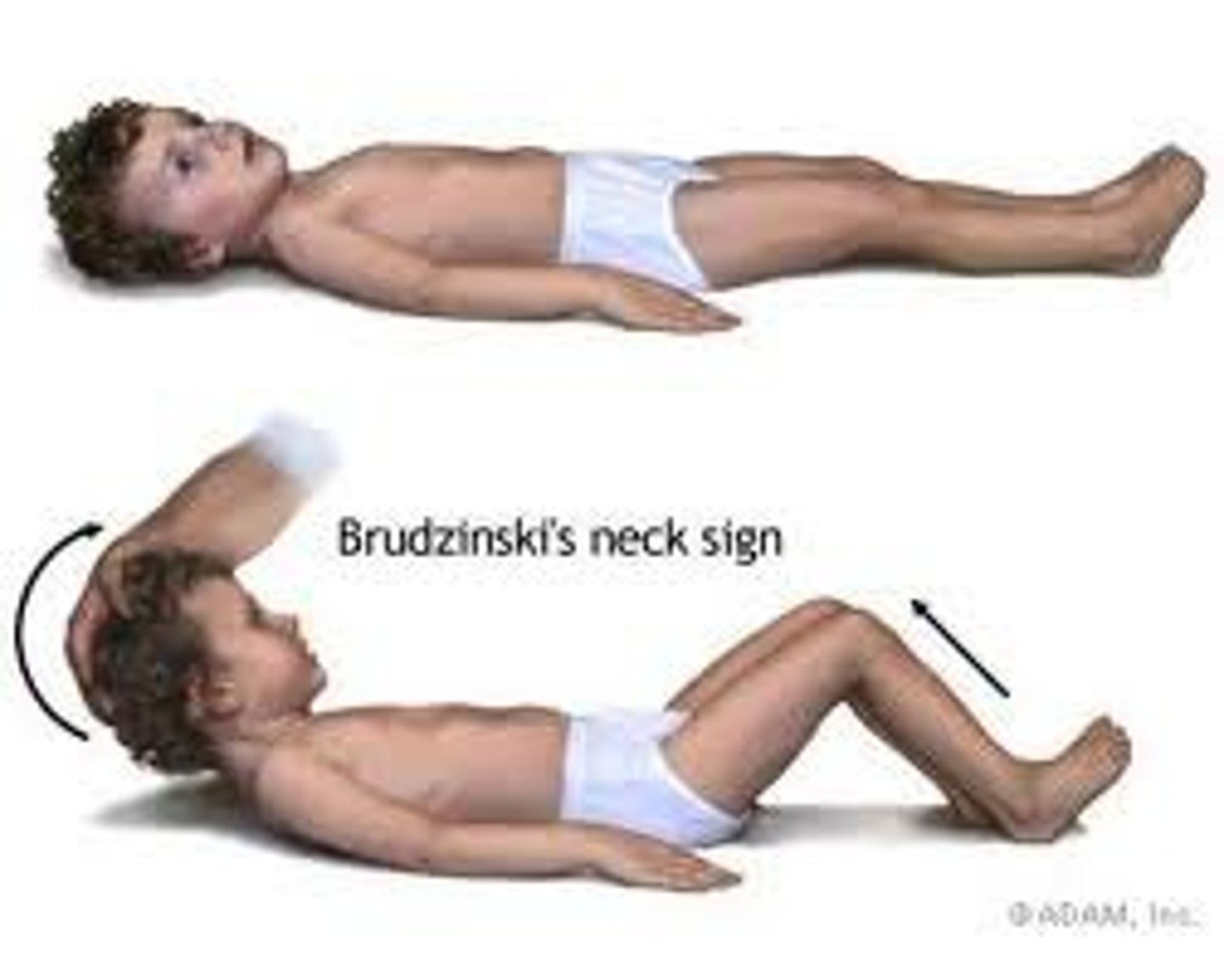
what is the brudzinski sign?
bending of neck causes flexion of knee and hip
client identifiers
first and last name
medical record number
DOB
expected term newborn findings
plantar creases up entire sole
presence of babinski
Epstein's pearls
is the babinski sign present at birth?
yes but it disappears at 1 year
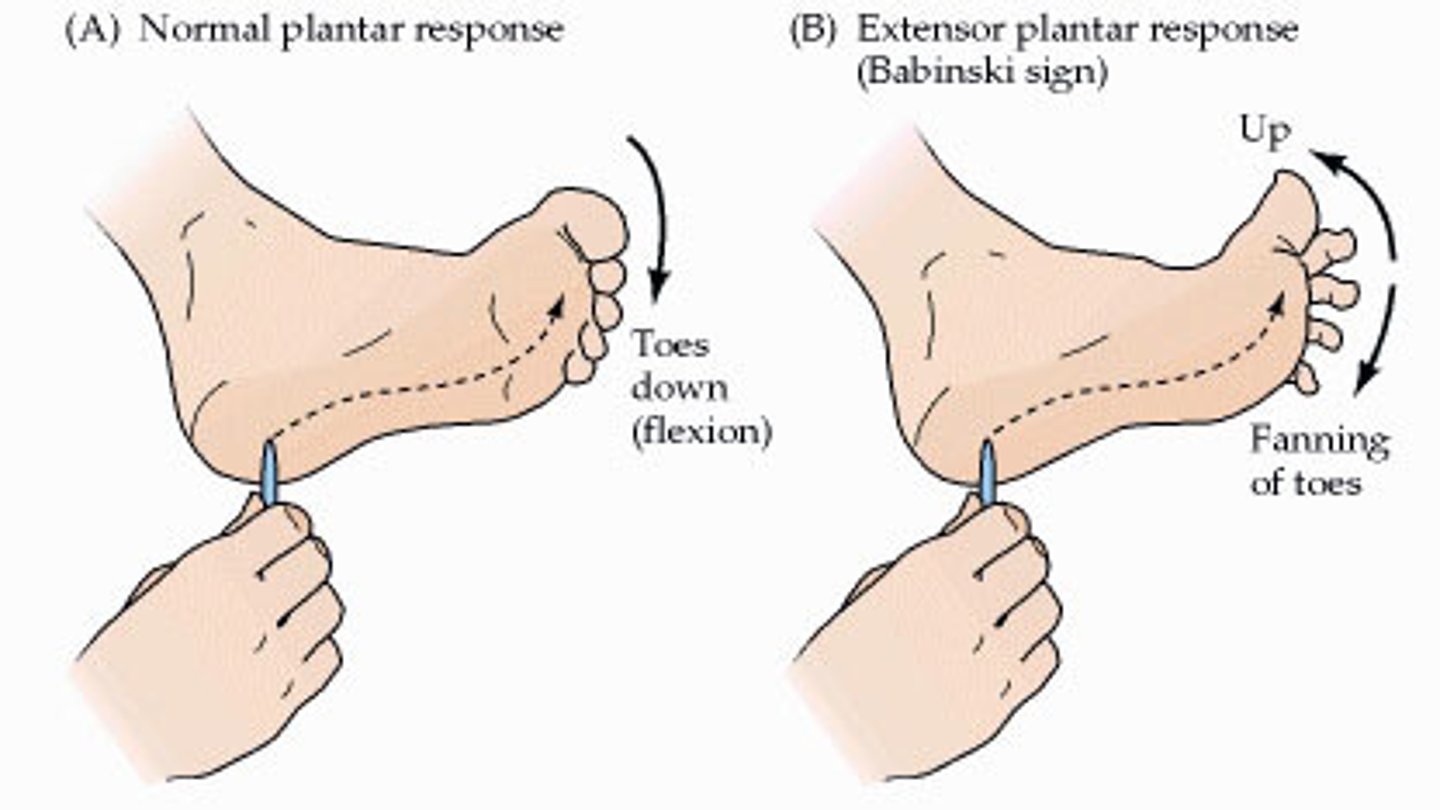
what does an absent babinski or weak reflex indicate?
a neurological deficit
babinski sign for a child less than 1 year
great toe bends upward and smaller toes fan out. this is NORMAL
babinski sign for child more than 1 year and an adult
plantar flexion
normal toe flexion (no babinski)
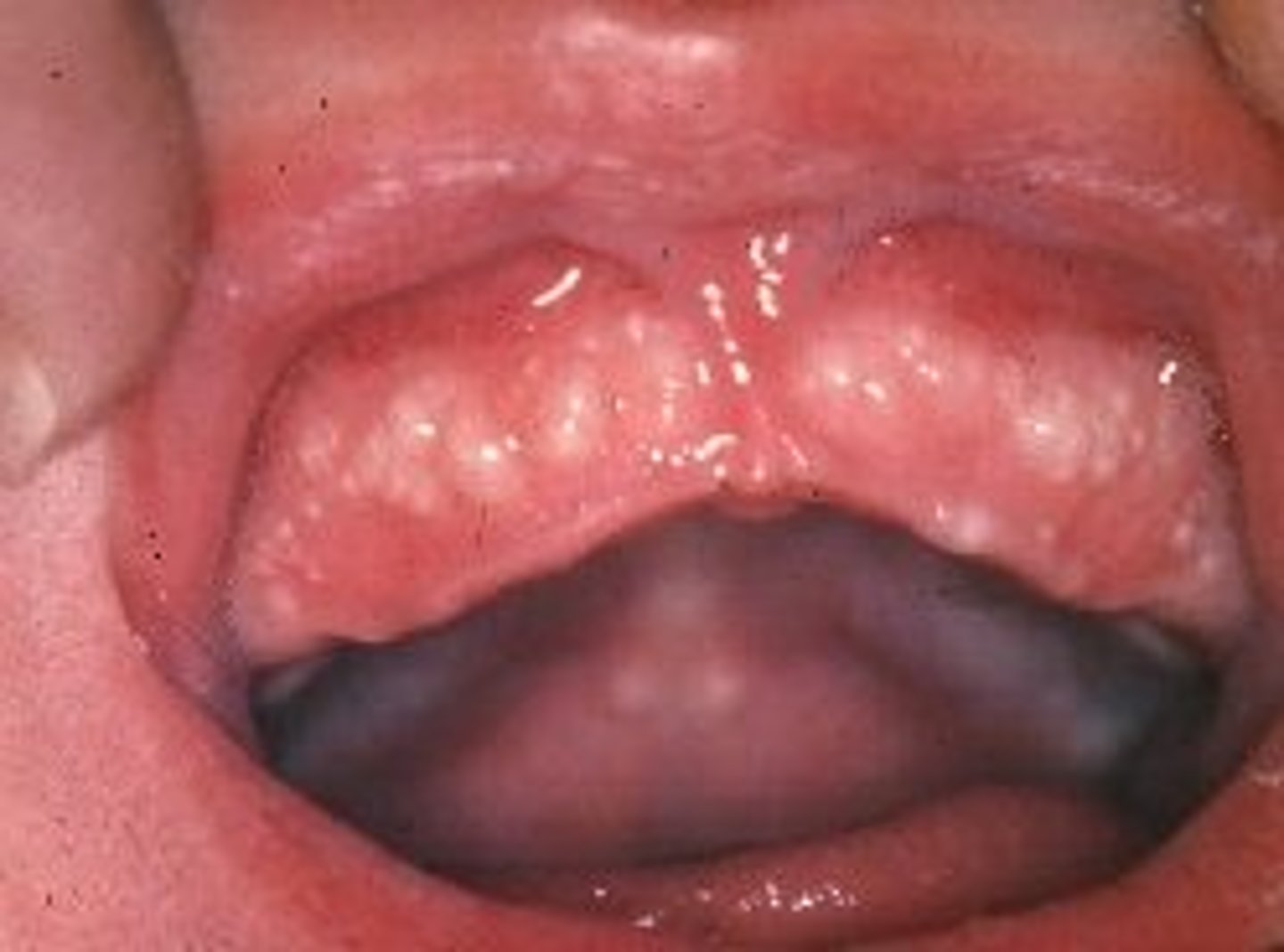
what are epsteins pearls?
white pearl like cysts on gum and palate that are benign and usually go away within a few weeks
when does the umbilical cord detach from body?
within 2 weeks
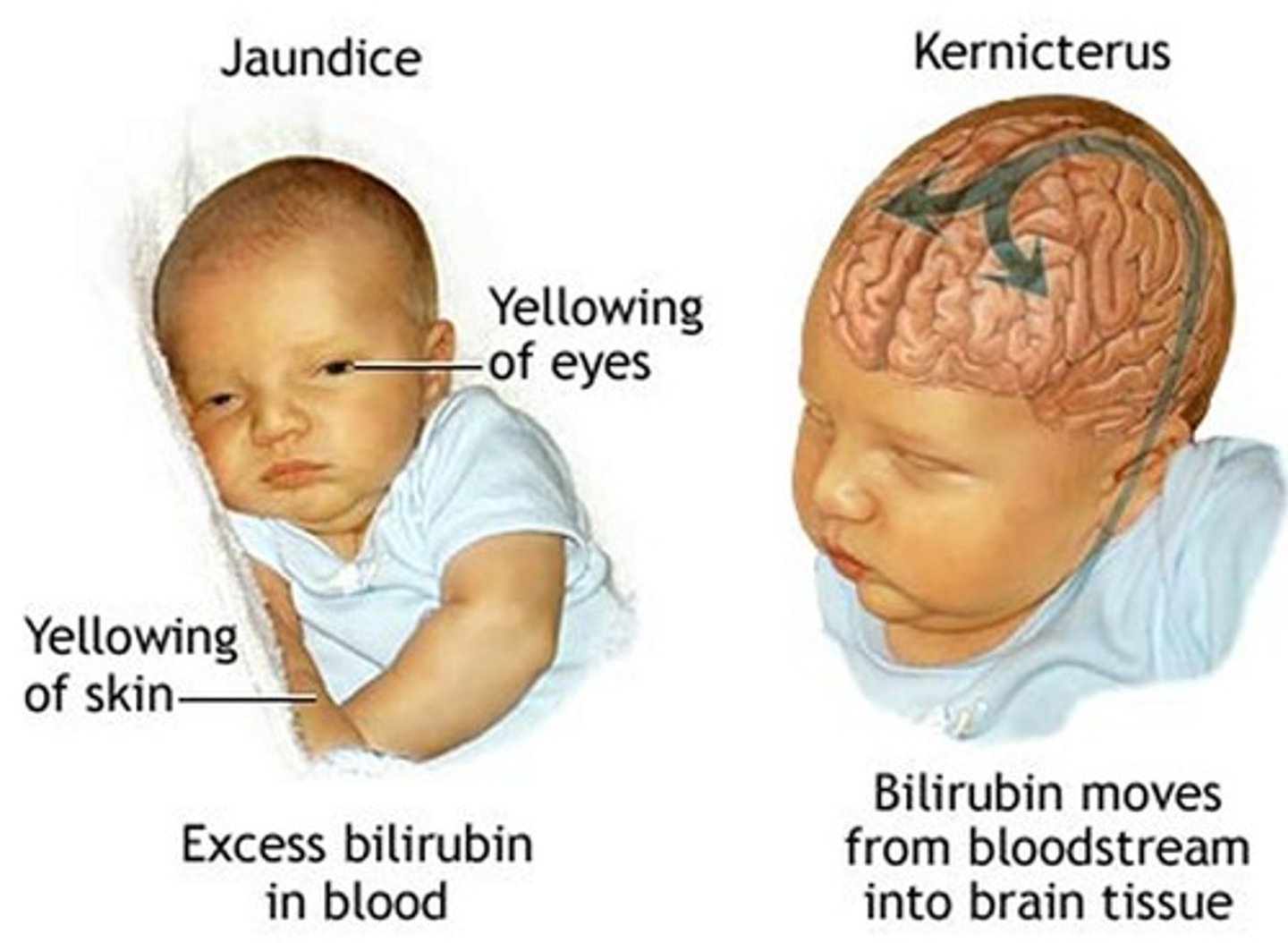
jaundice in a newborn
during first 24 hours: jaundice is pathological (r/t liver problems)
after 24 hours: physiological jaundice r/t inc amount of unconjugated bilirubin in system
infant formula key points
never dilute or concentrate formula
wash tops of forumla cans before opening
unused prepare formula can be used for up tp 48 hours and then discarded after
to warm prepared bottle, place in pan of hot water
never microwave formula
any forumula left over should be thrown out immediately when done
what must be checked before starting statin drugs
liver function tests bc they can cause hepatotoxicity
can cause muscle aches and weakness
take with evening meal or at bedtime
what is a serious complication of statin meds?
rhabdomyolysis
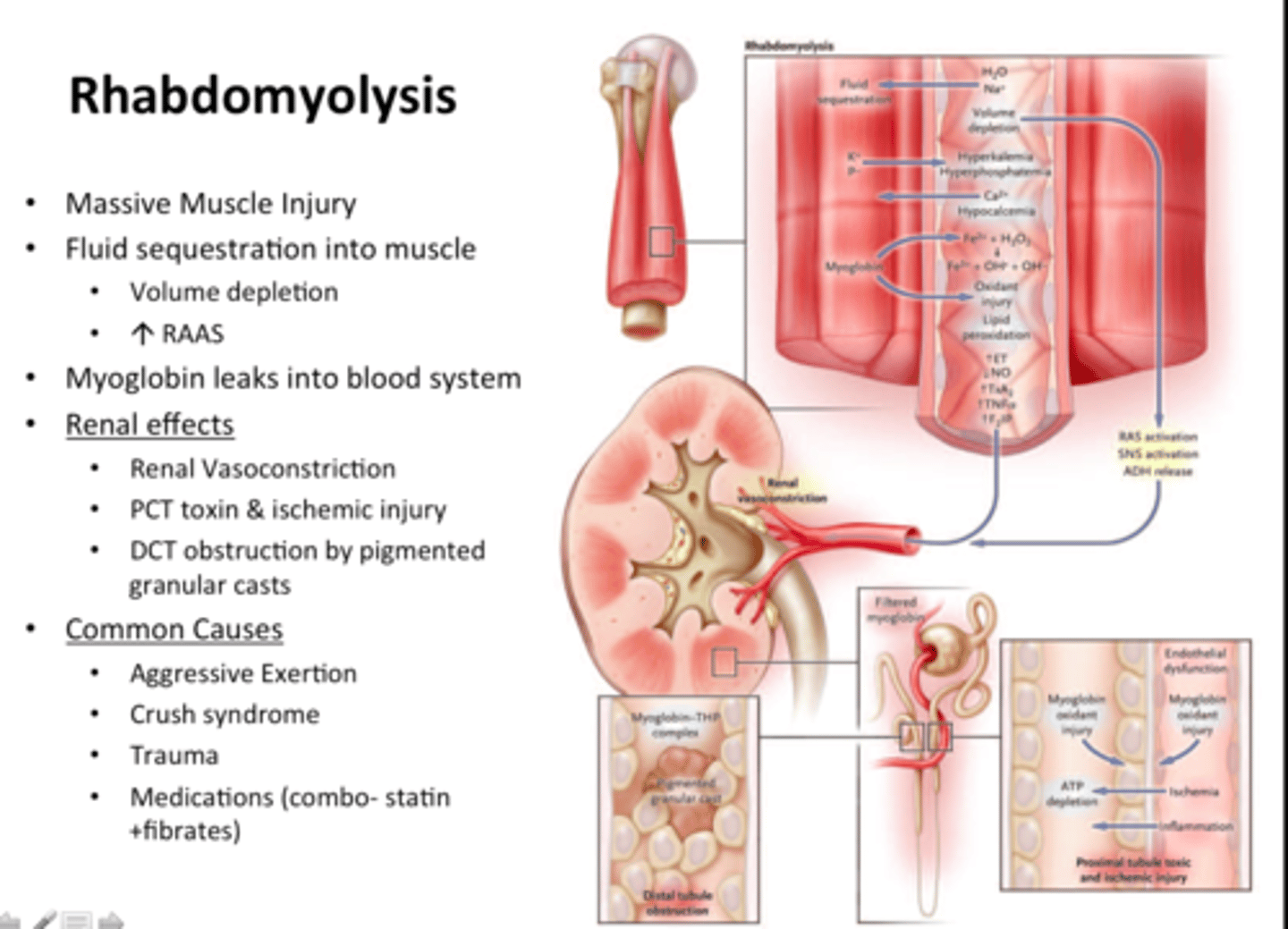
what is rhabdomyolysis?
the breakdown of muscle tissue releases muscle fiber contents into the blood. these substances can cause kidney damage
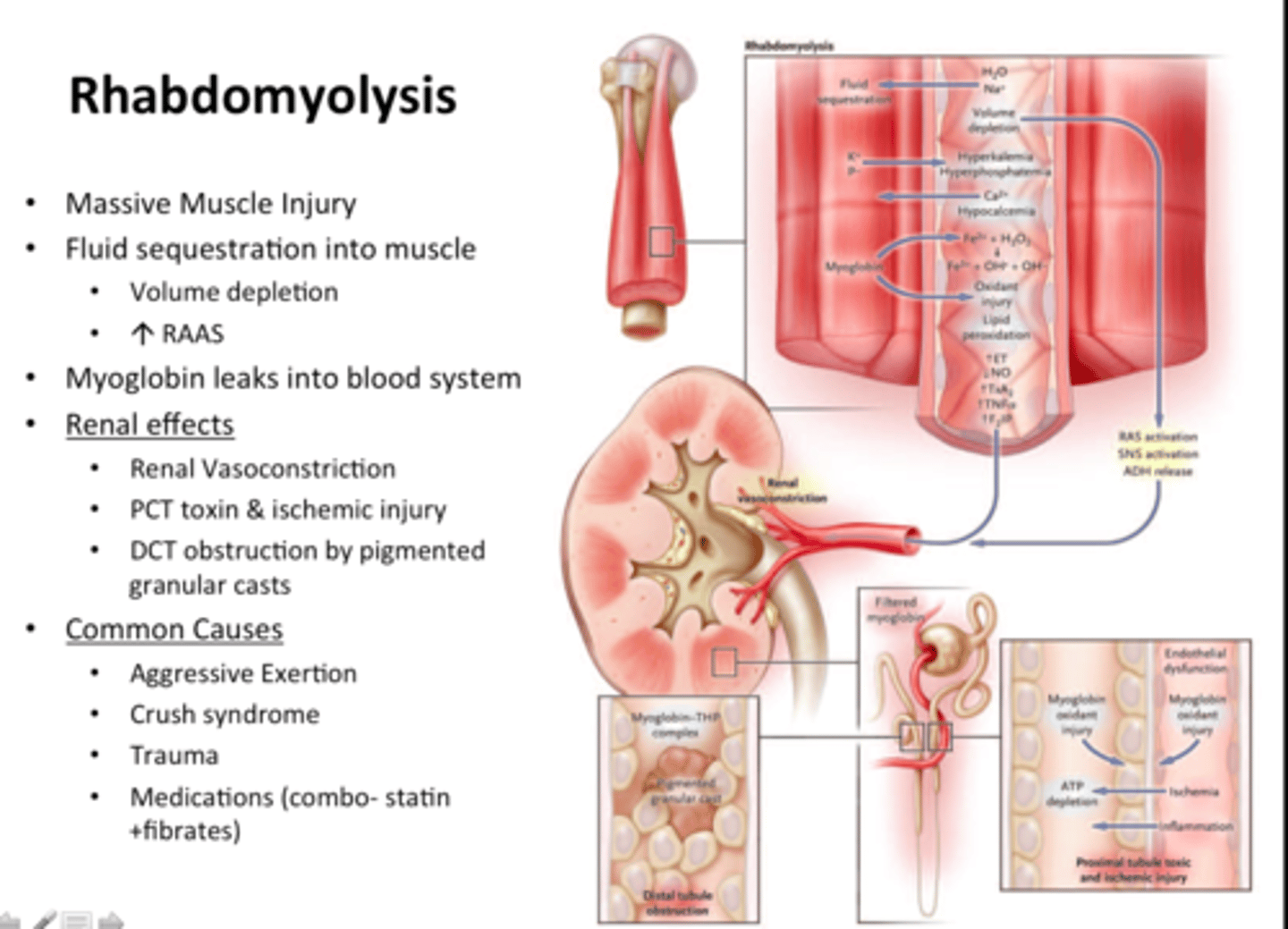
what are some early signs of rhabdomyolysis?
muscle aches or weakness- immediately report to hcp!
behaviors of bulimic person
episodes of binge eating followed by self induced vomiting
using enemas/laxatives
intense frequent exercise
signs of bulimia someone may notice
going to bathroom after meals
large amonts of food disappearing
hidden wrappers/empty food containers like sweets
intense physical exercise
parotid gland enlargement
calluses on hands
preoccupation with weight food and dieting
first thing to do if a pt is in ventricular tachycardia?
assess them for a pulse (bc they can either have a pulse or not)
what is in the lpn scope of practice?
monitor RN findings
reinforce education
routine procedures like catheterization
most medication administrations
ostomy care
tube patency and enteral feeding
specific assessments
notify hcp if child temp is over 100.4 after
immunizations
what are common SE of immunizations?
mild fever and soreness and redness at injection site
anorexia/fussiness in the first 24 hours
thrombocytopenia
low platelet count; so this increases risk for bleeding;<100,000 platelet count
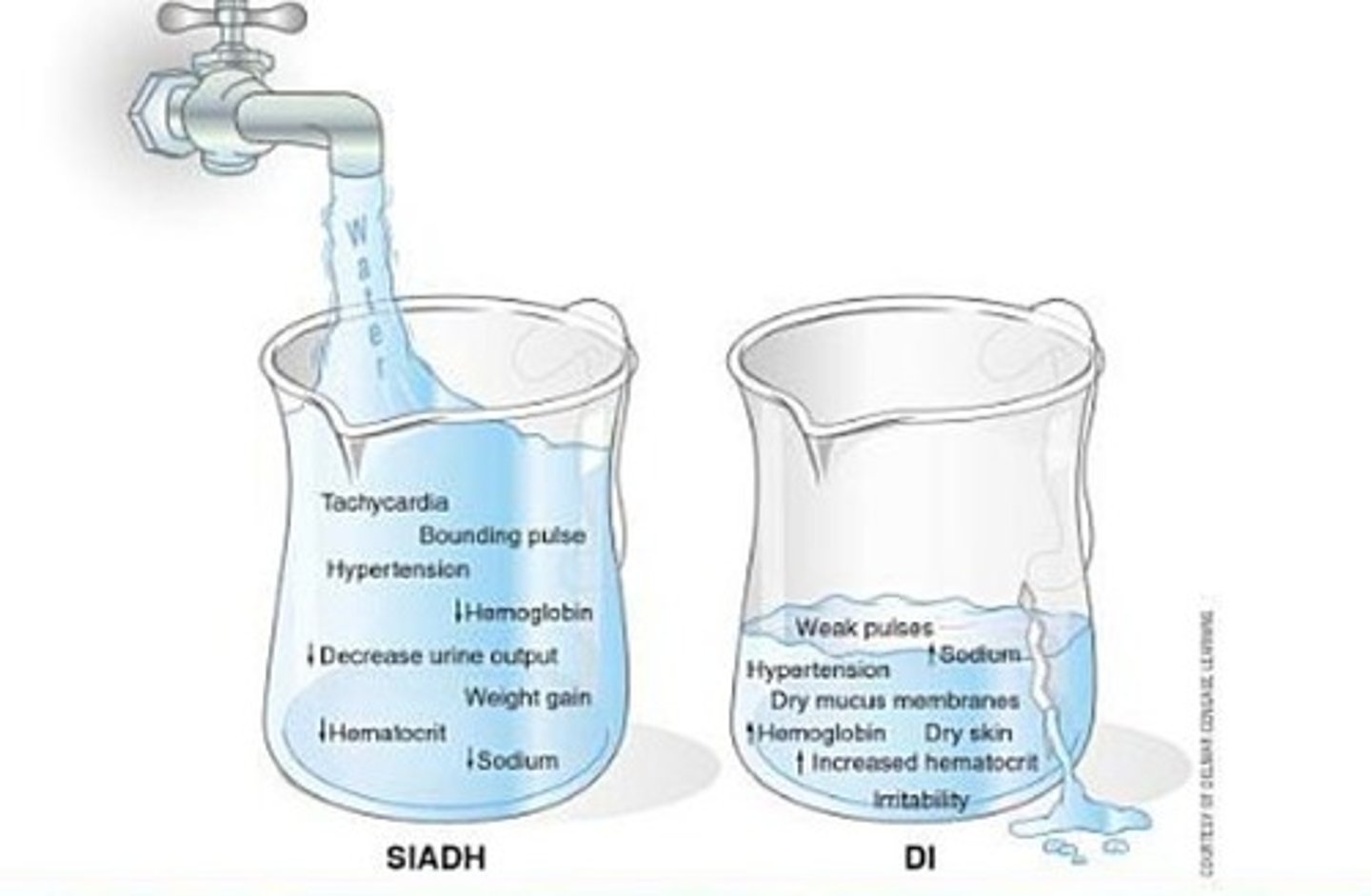
what is SIADH?
high antidiuretic hormone production leads to
water retention
increased total body water
DILUTIONAL HYPONATREMIA
-will see signs of fluid volume overload, changes in loc, weight gain w/o edema, hypertension, tachycardia
-seizure precautions
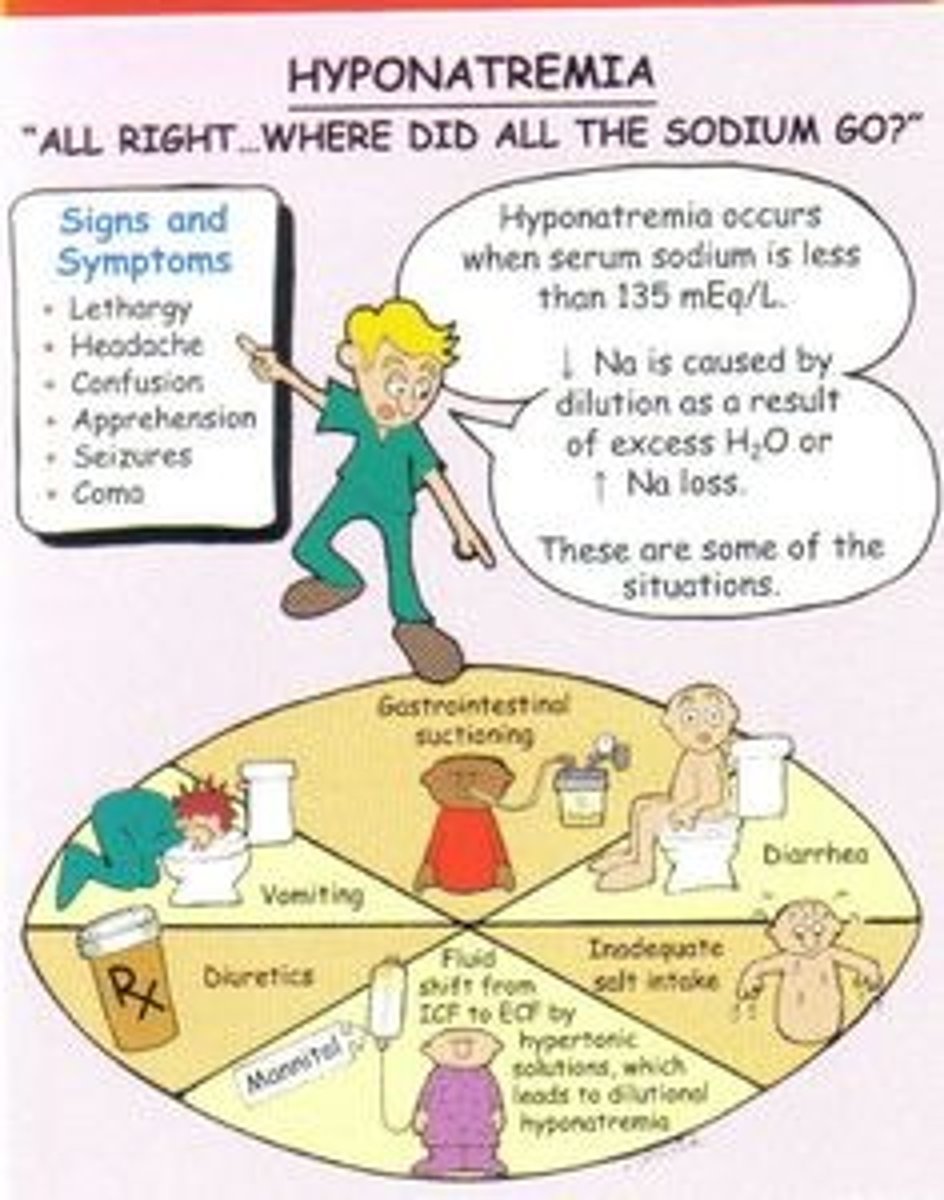
what can hyponatremia cause?
SEIZURES, confusion, neurologic complications
institute seizure precautions
treatment of SIADH
fluid restriction less than 1000 ml per day
oral salt tablets to increase serum sodium
hypertonic saline (3%) or NS IV and/or vasopressin receptor antagonists to decrease renal response to ADH
so a pt with SIADH
does not need extra fluid
needs salt
seizure precautions
strict I/Os
RACE for FIRES in a hospital
R: rescue any pts in immediate danger and move them to safety
A: alarm- sound alarm
C: confine fire by closing all doors to all rooms
E: extinguish fire with extinguisher
what is asystole?
complete absence of ventricular electrical activity in the heart. no ventricular contraction occurs
client is pulseless, apneic, and unresponsive
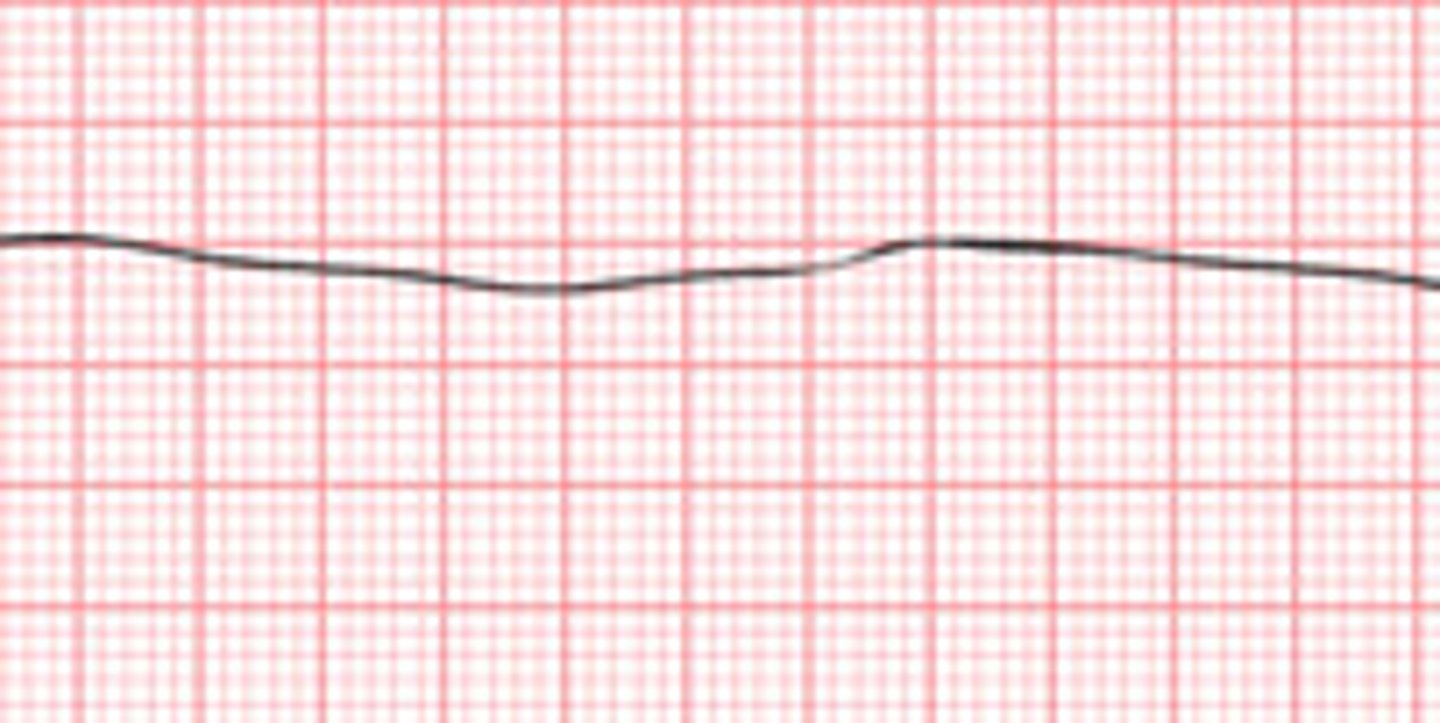
how to treat asystole?
CPR
initiate advanced cardiac life support
give epinephrine and/or vasopressin
place an airway
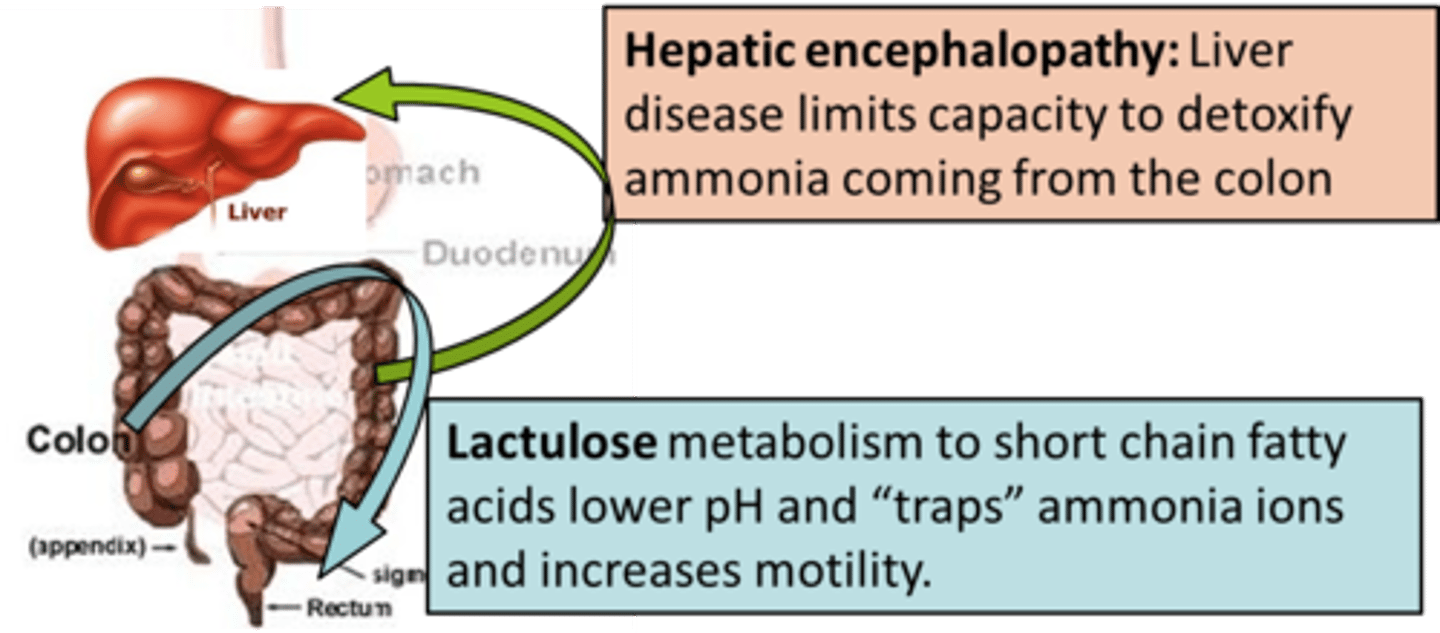
hepatic encephalopathy
impaired ammonia metabolism causes cerebral edema. s/s: change in LOC, memory loss, asterixis (flapping tremor) impaired handwriting, hyperventilation w/ resp alkalosis. treatment: lactulose-traps ammnia and lwoers pH, low protein, safety, rest
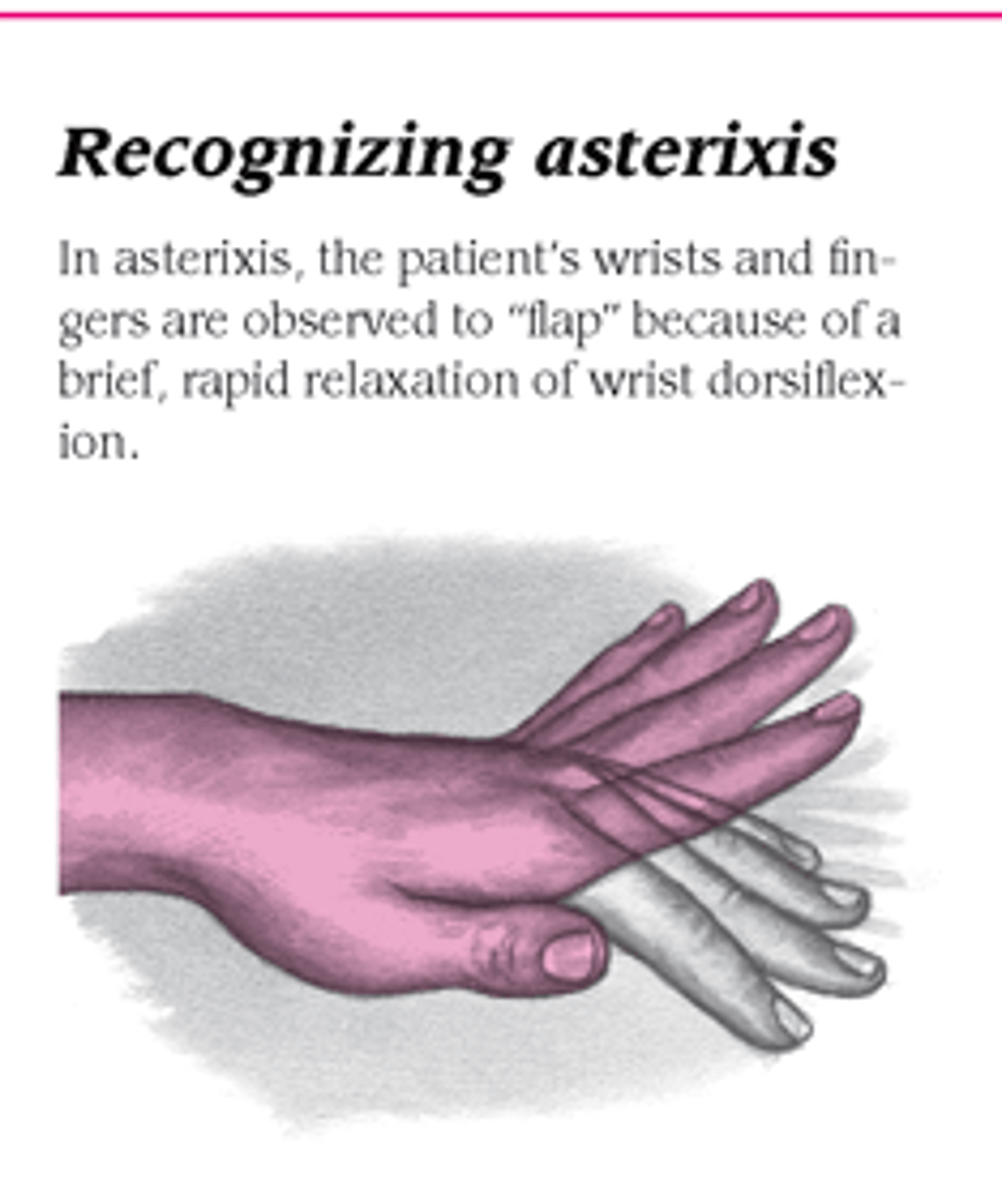
asterixis
flapping tremors of the hands
to assess, have pt extend the arms and dorsiflex the wrist
full weight bearing
independent; no assistance needed unless they are uncooperative or they are a fall risk, which is 1 person standby
partial weight bearing
1 person assist stand & pivot transfer with gait belt or motorized assist device if cooperative
2 person assist with full body sling if uncooperative
no weight bearing
motorized assist device if cooperative and they have upper body strength
2 person assist with full body sling if uncooperative and/or has no upper body strength
how to measure how to safely transfer a pt the first time
assess if they can bear weight
assess whether they are cooperative
how to measure UO in diapers?
subtract the weight of the diaper when dry from its weight when wet
how often and where is growth hormone replacement given to a child?
daily sub q injections
tretment is most successful when it begins early in a child's life, as soon as growth delays are noted; it stops when bone growth finishes or when parents decide
what is the classic sign of a tension pneumothorax?
mediastinal shift and tracheal deviation
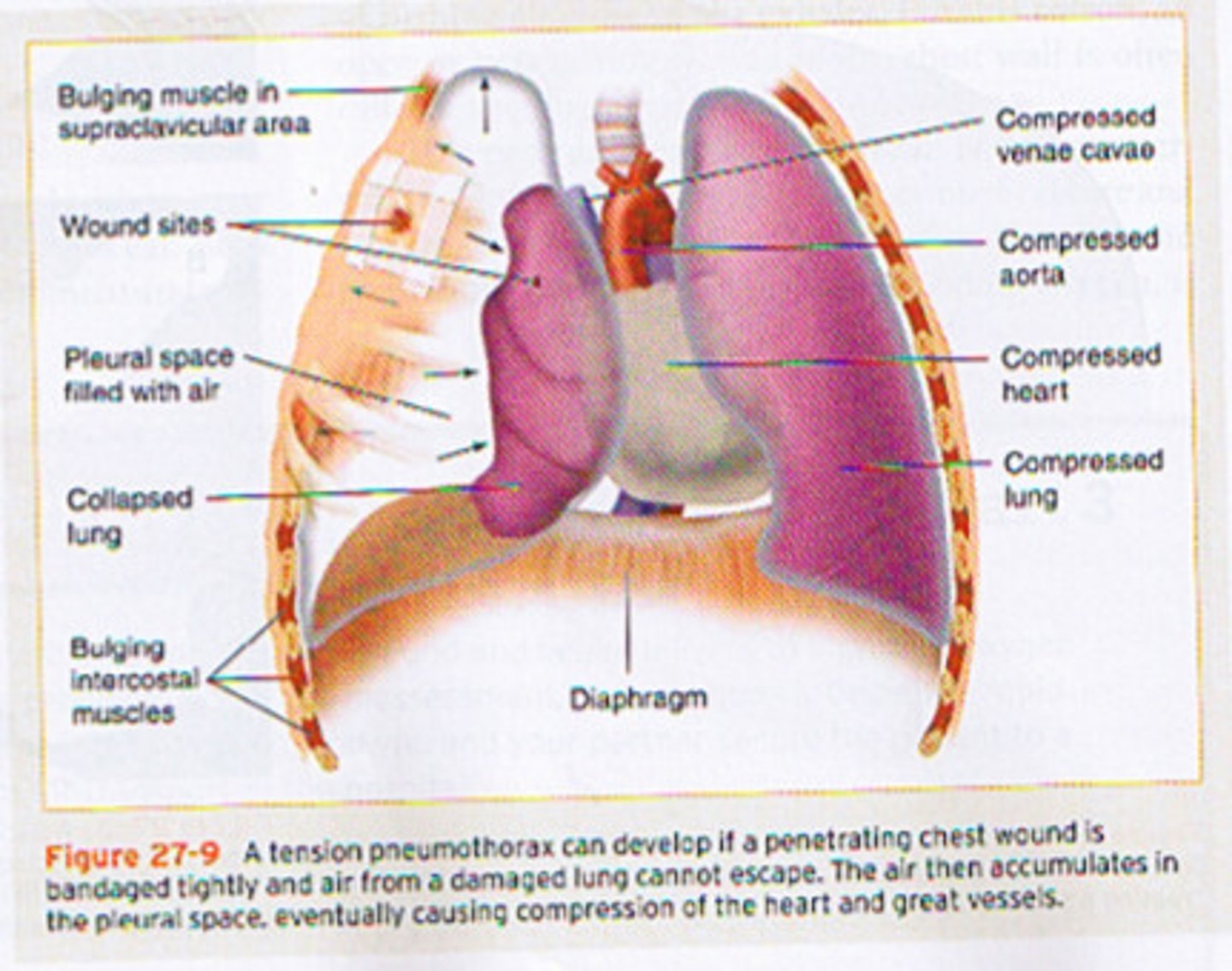
why does tension pneumothorax cause hypotension?
bc the heart and great vessels are compressed/shifted and cardiac output is reduced
it is LIFE THREATENING
what is the treatment for tension pneumothorax?
emergency large bore needle decompression
chest tube
if injury to the spinal cord, what important precaution to take?
hard cervical collar and backboard
major depressive disorder demonstrates
loss of appetite, weight loss, and insomnia or hypersomnia
sleep disturbances
how to help improve sleep
dont nap during day
physical activity at least 5 hours before bed 20 mins of natural sunlight
avoid caffeine after noon
avoid alcohol or smoking at bedtime
relaxing activity before bed
decrease environmental stimuli
avoid heavy meals or large amounts of fluid at bedtime
warm milk or small carbs before bed
what can a baby born to an opioid dependent mom have?
neonatal abstinence syndrome. the baby experiences opiod withdrawal 24-48 hrs after birth
wht are symptoms of withdrawal from opioid in infants?
the baby is HYPERSENSITIVE
irritability
high pitched cry
jitteriness
sneezing
diarrhea
vomiting
poor feeding
tx: opioid therapy like methadone or morphine
what is the nursing care focus opioid dependent newborns?
reduce stimulation
promote nutrition and comfort
after feeding an infant, what does placing it in the side lying position do
promotes gastric emptying and reduces the risk of vomiting
Acceptable methods of blood collection in neonate
- heel stick
- venipuncture (drawing blood from vein) - considered less painful and often requires fewer punctures to obtain sample, especially if larger volume is needed
Neonatal heel stick
- used to collect a blood sample to assess capillary glucose and perform newborn screening for inherited disorders (eg congenital hypothyroidism, phenylketonuria)