Human A&P1, Chapter 12
1/89
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
90 Terms
4 major parts of the brain
Cerebrum, Diencephalon, Brainstem, Cerebellum
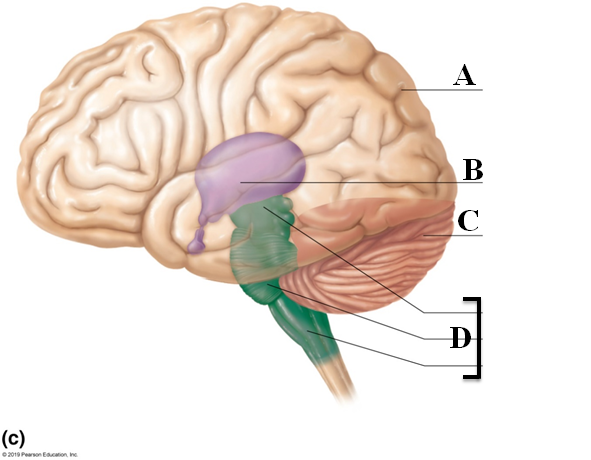
Cerebrum
- All voluntary activities of the body
- Two cerebral hemispheres, 83% of brain
- Cerebral cortex, Grey and White matter (Letter A)
Cerebral cortex
40% of brain mass (in cerebrum), a layer of gray matter covering the cerebral hemispheres
Divided into frontal, parietal, occipital, and temporal
Gray matter
Nonmyelinated axons, has neuron cell bodies
Part of the outside of cerebrum
White matter
Myelinated axons bundled into tracts
Part of inside of cerebrum
Functional regions of the cerebrum
- Contralateral function
- Premotor cortex
- Central sulcus
Contralateral function
A functional region of the cerebrum; left brain to right body
Premotor Cortex
A functional region of the cerebrum in precentral gyrus; think of moving; making things move
Central Sulcus
A functional region of the cerebrum; divides brain into motor (precentral gyrus) and sensory (postcentral gyrus)
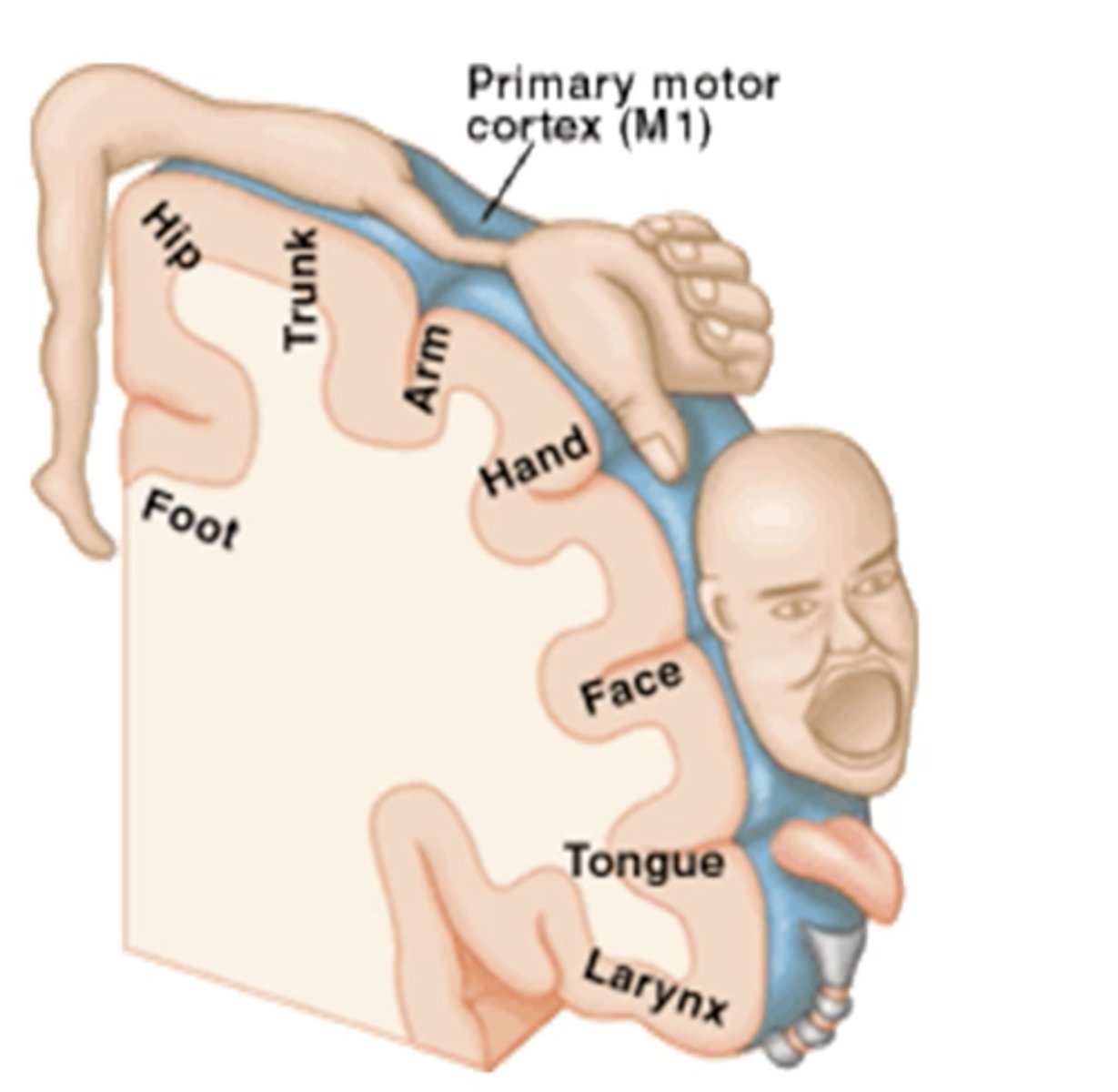
Precentral gyrus
Contains the premotor cortex
Receives impulse from premotor cortex
Postcentral gyrus
Primary sensory area, receives sensory information from proprioceptors
Spatial discrimination
Homunculus
A map like representation of regions of the body in the brain
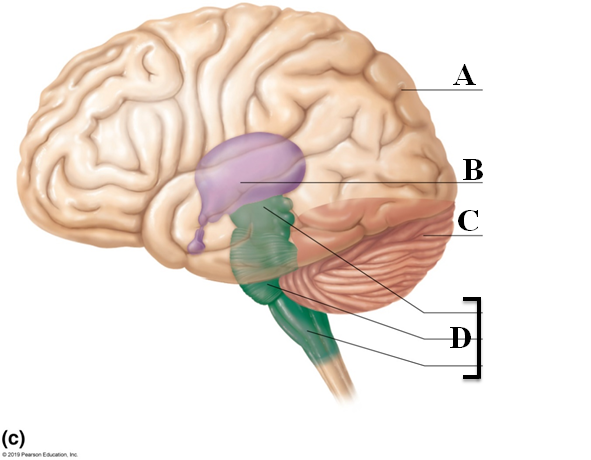
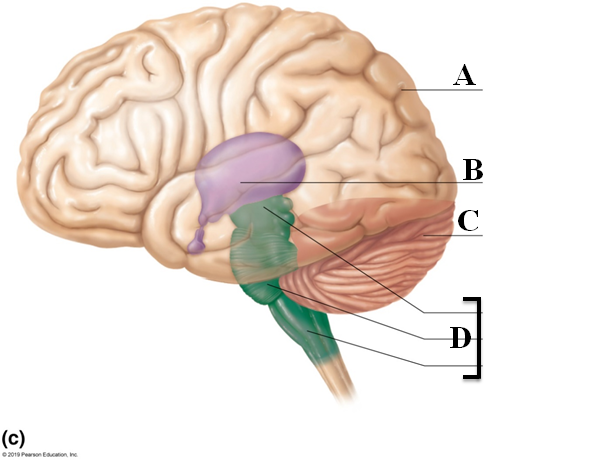
Cerebellum
- Right and left hemispheres connected by vermis (Letter C)
- Three paired cerebellar peduncles connect the cerebellum to the brainstem
- Fine-tunes and coordinates voluntary movement of the limbs
- Alarm clock analogy
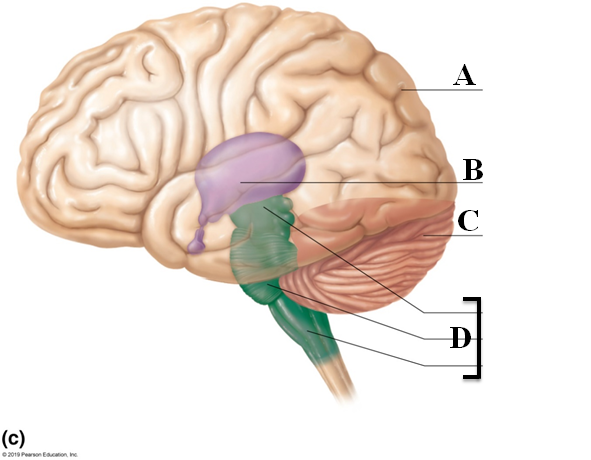
Diencephalon
Contains thalamus, hypothalamus, and epithalamus
Letter B
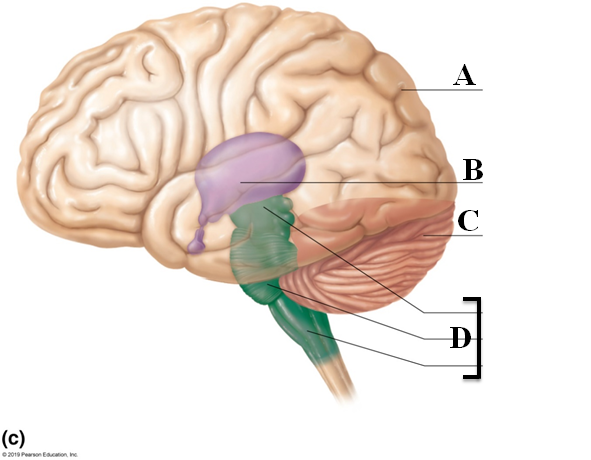
Cerebral lateralization
Assignment of different tasks to hemispheres, correlated with handedness
- Males show more lateralization than females
- Usually right hemisphere is associated with visual, spatial, intuition, emotion, and artistic skills
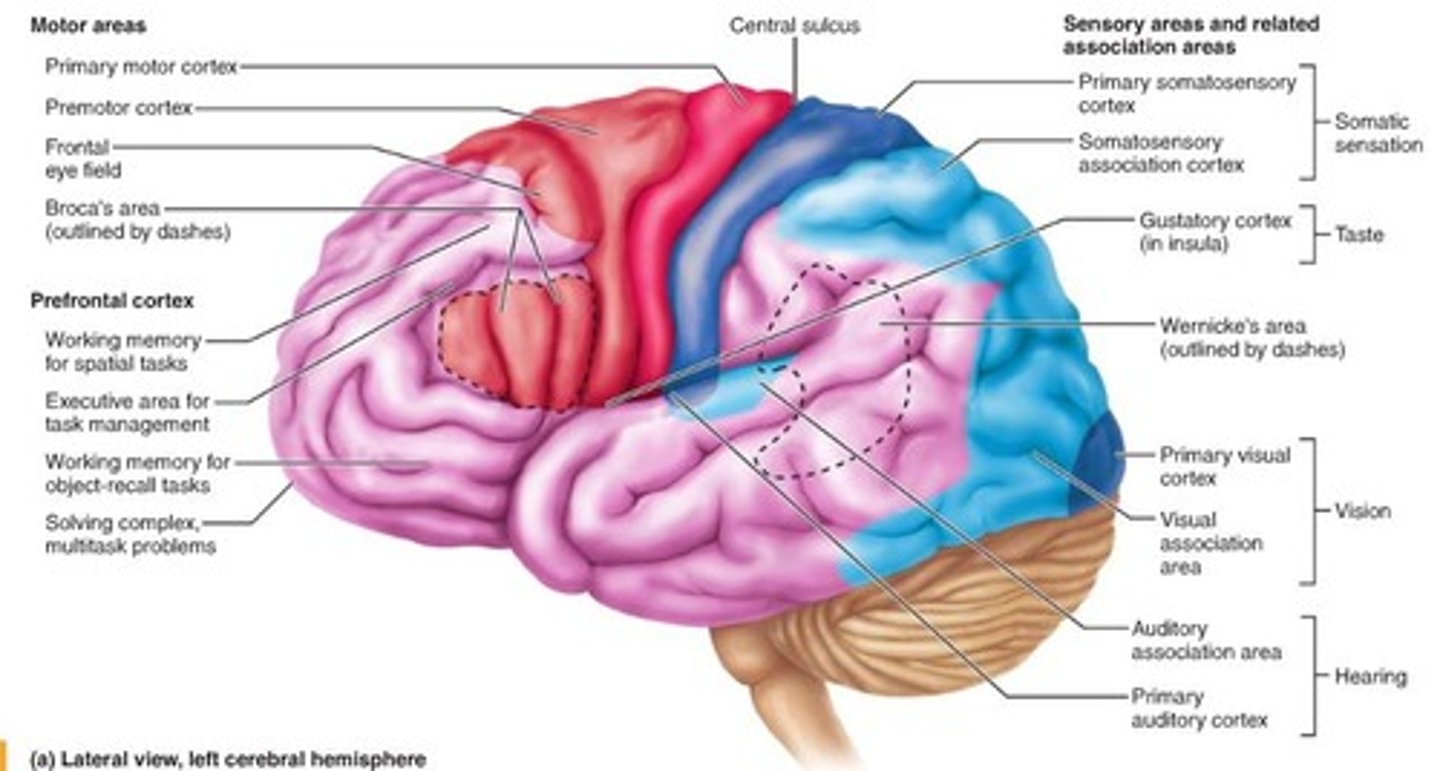
Somatic sensation
Primary somatosensory cortex, somatosensory association cortex
Taste
Gustatory cortex
Equilibrium
Vestibular cortex
Vision
Primary visual cortex, visual association area
Hearing
Auditory association area, primary auditory cortex
Language
- Broca's area
- Wernicke's area
- Angular gyrus
Broca’s Area
Sending speech to mouth, typically left area of brain
Wernicke’s Area
Comprehending speech, typically right area of brain
Angular gyrus
Attention, self-processing, semantic information processing, emotion regulation, and mentalizing
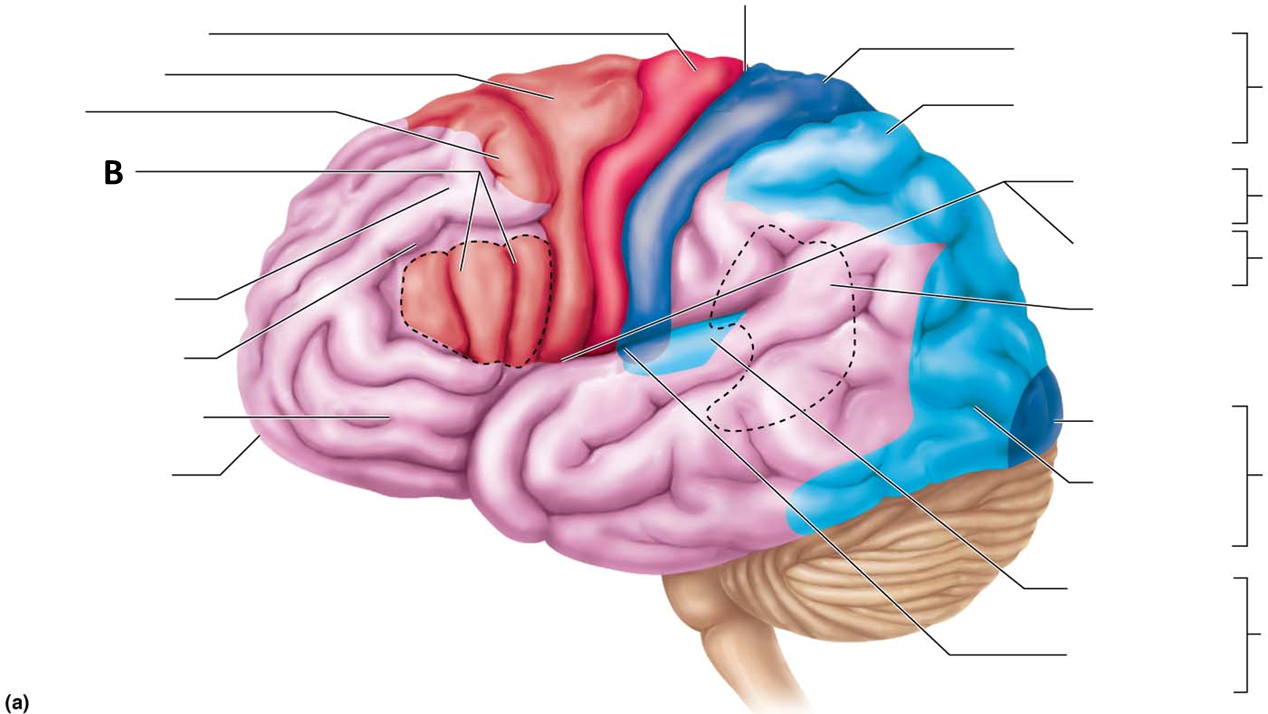
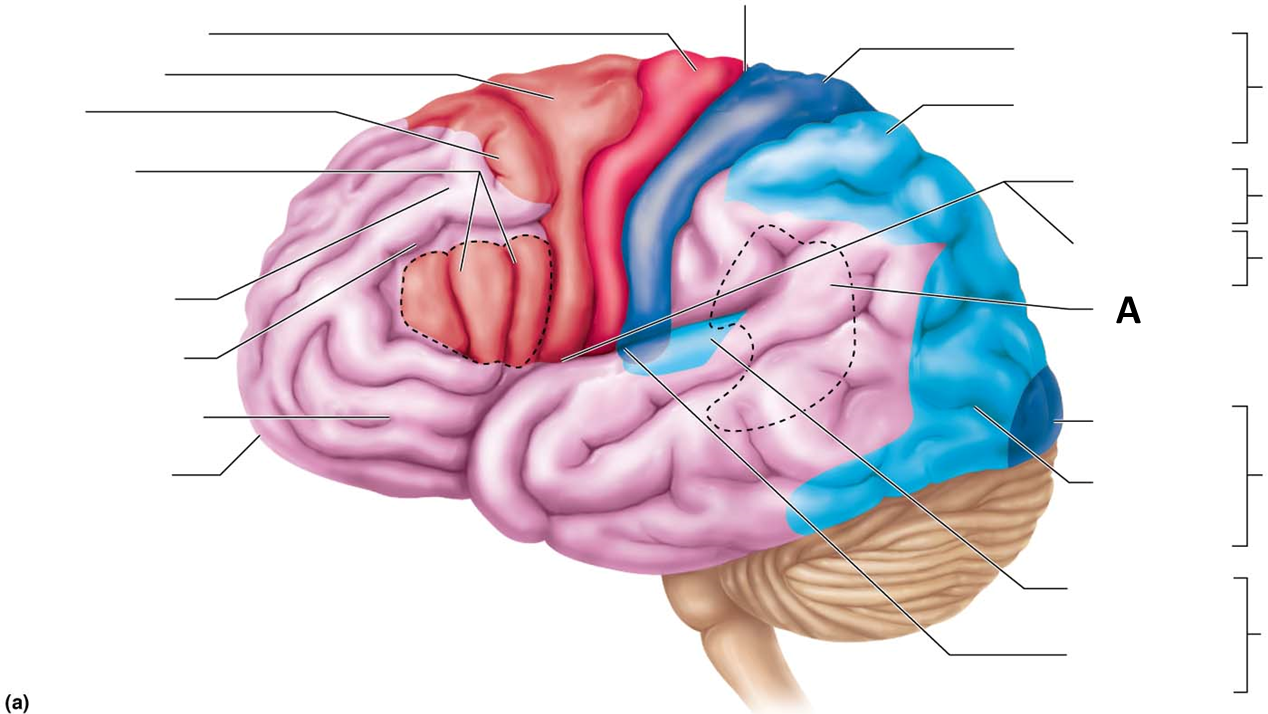
Association tracts
Connect different regions of the cerebral cortex within the same hemisphere
Letter A
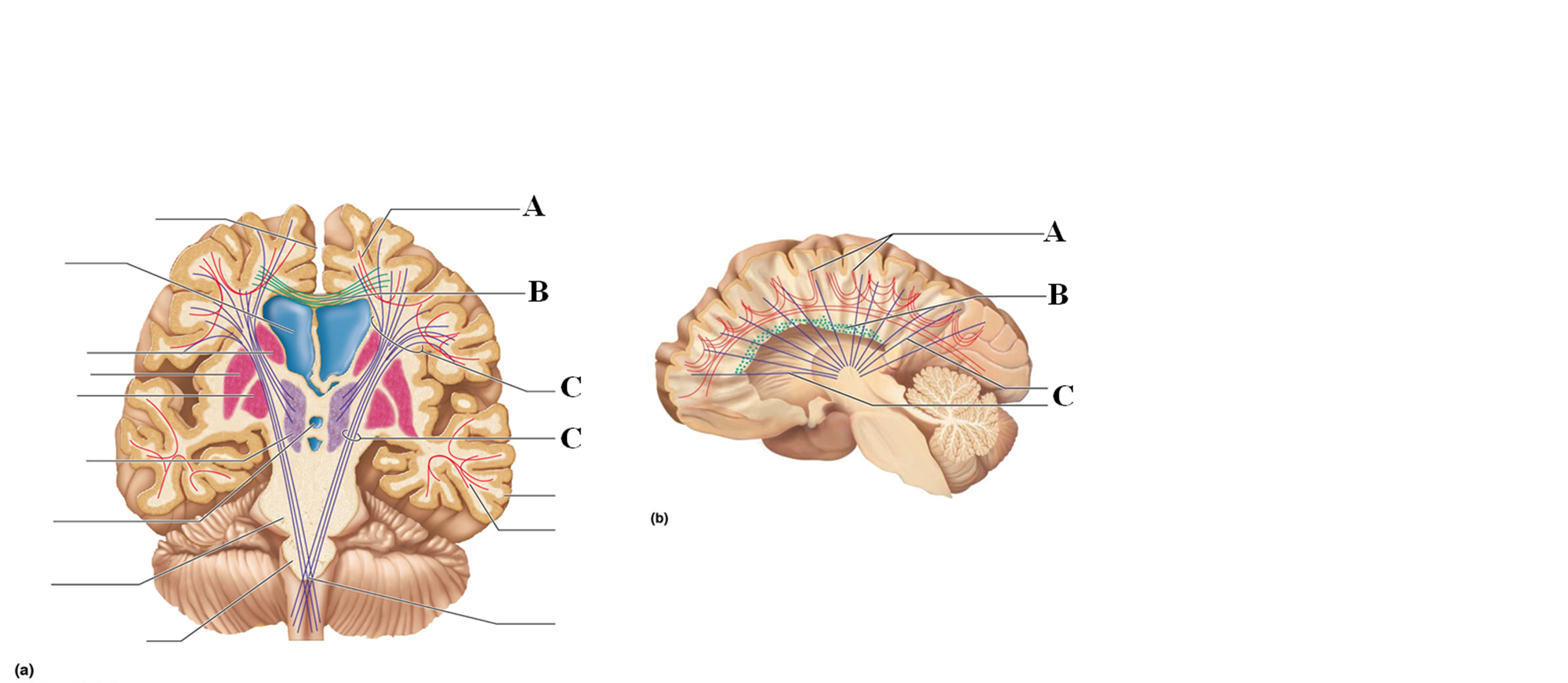
Commissural tracts
Conduct nerve impulses between corresponding gyri from one hemisphere to another
Letter B
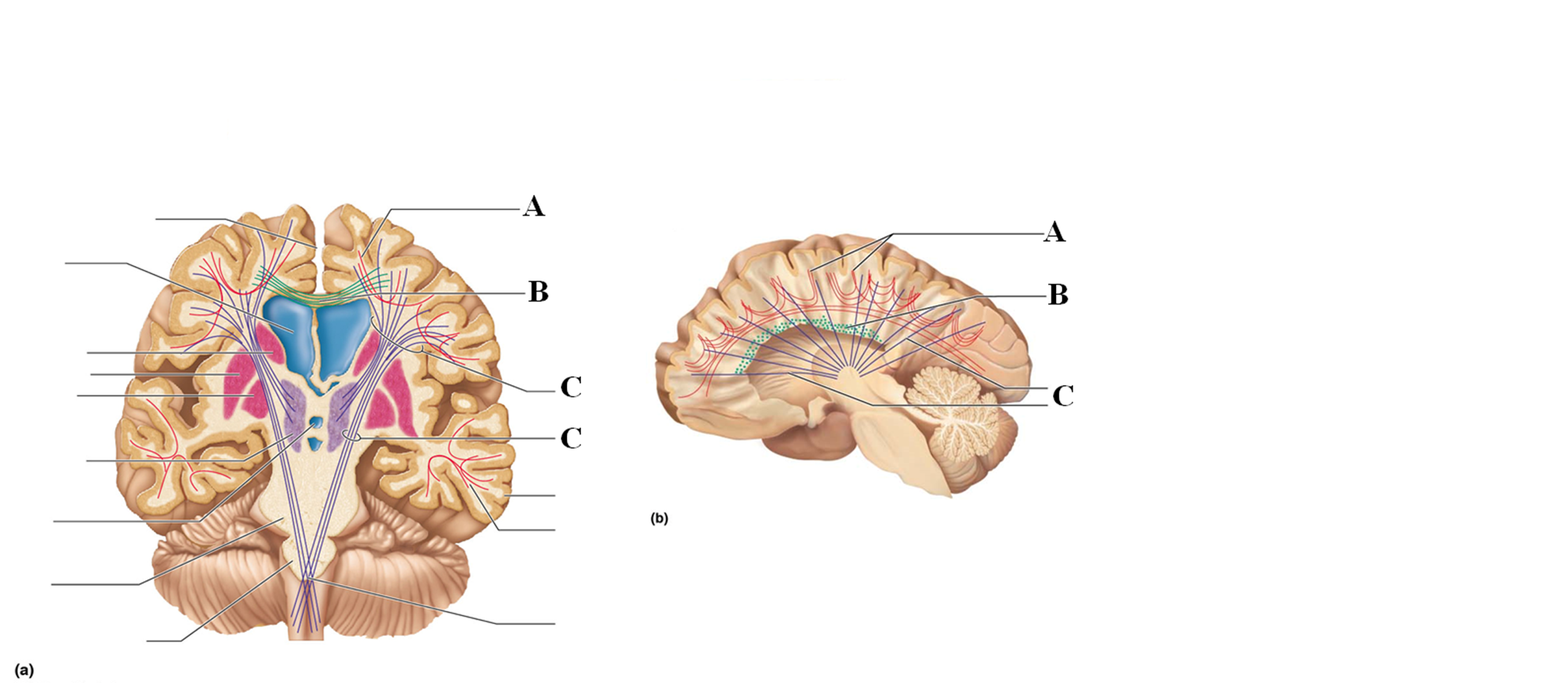
Projection tracts
Link the cerebral cortex to the inferior brain regions and the spinal cord, either ascend or descend from cerebral cortex from lower brain or cord centers
Letter C
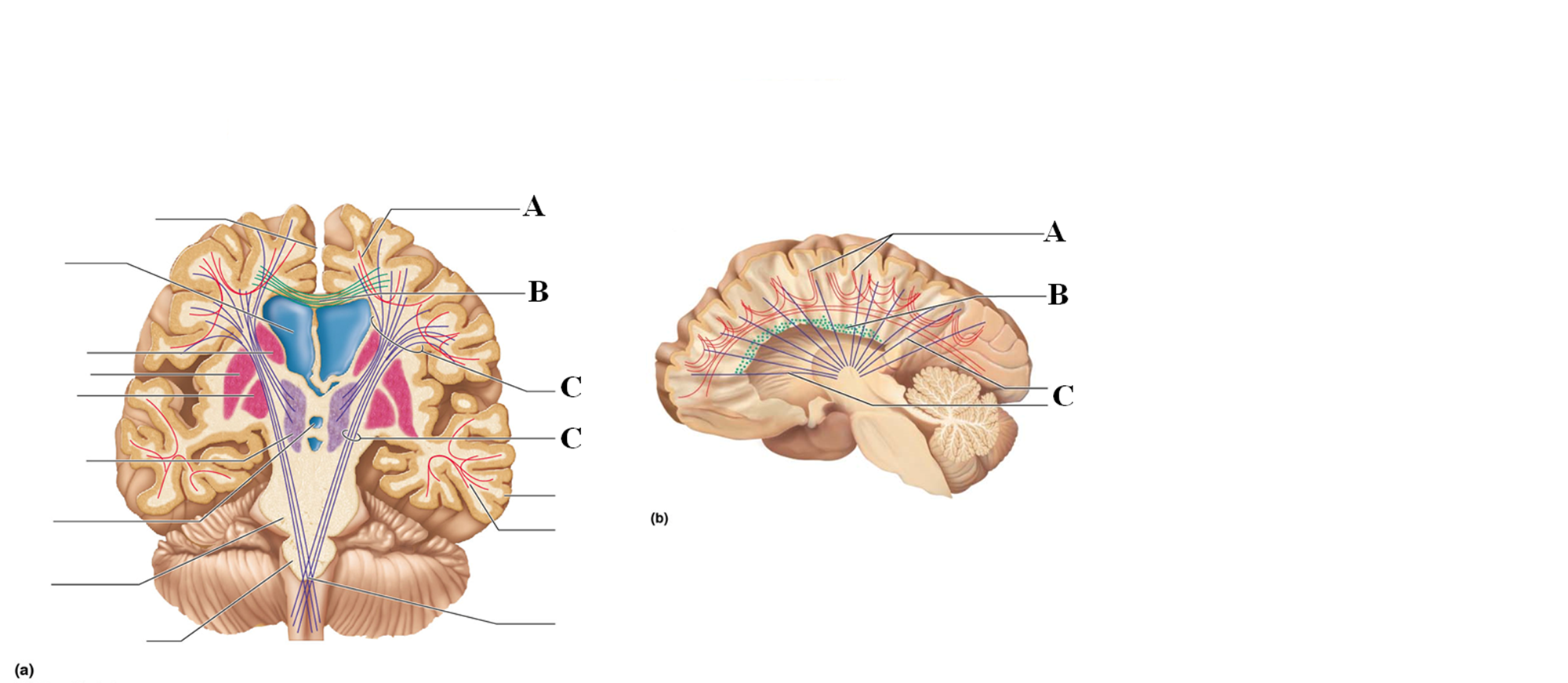
Basal nuclei
- Masses of gray matter buried within the white matter of cerebral hemispheres
- Motor control and thought process
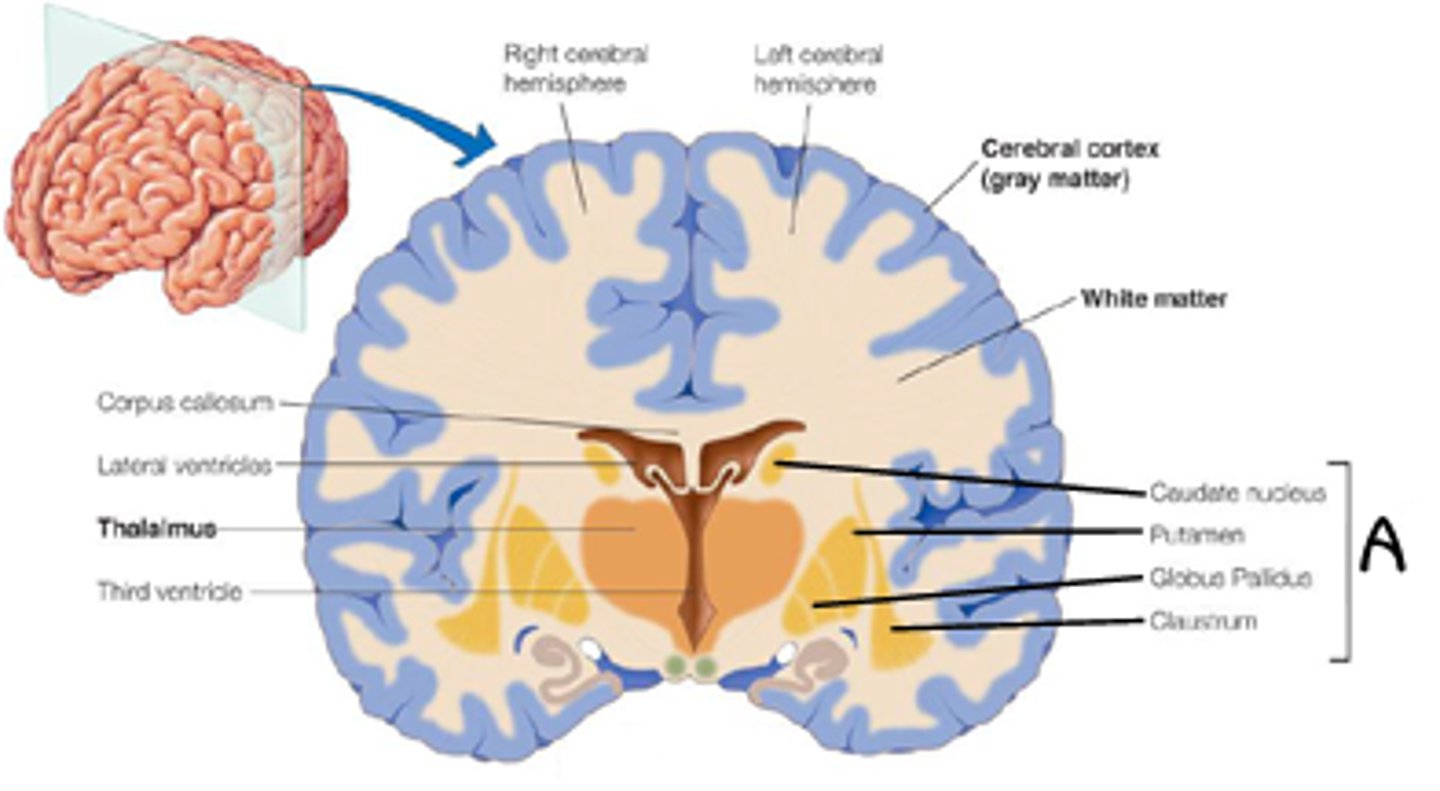
Thalamus
- 2 oval masses of grey matter, narrow intermediate mass in diencephalon
- Encloses the third ventricle
- “Gateway to the cerebral cortex,” nearly all sensory info passes through except for smell (olfaction)
Hypothalamus
- Neural structure lying below the thalamus in diencephalon
- Has many nuclei that manage eating, drinking, body temperature, sleeping/waking; homeostatic mechanisms, and emotion
- Helps govern the endocrine and nervous system via the pituitary gland
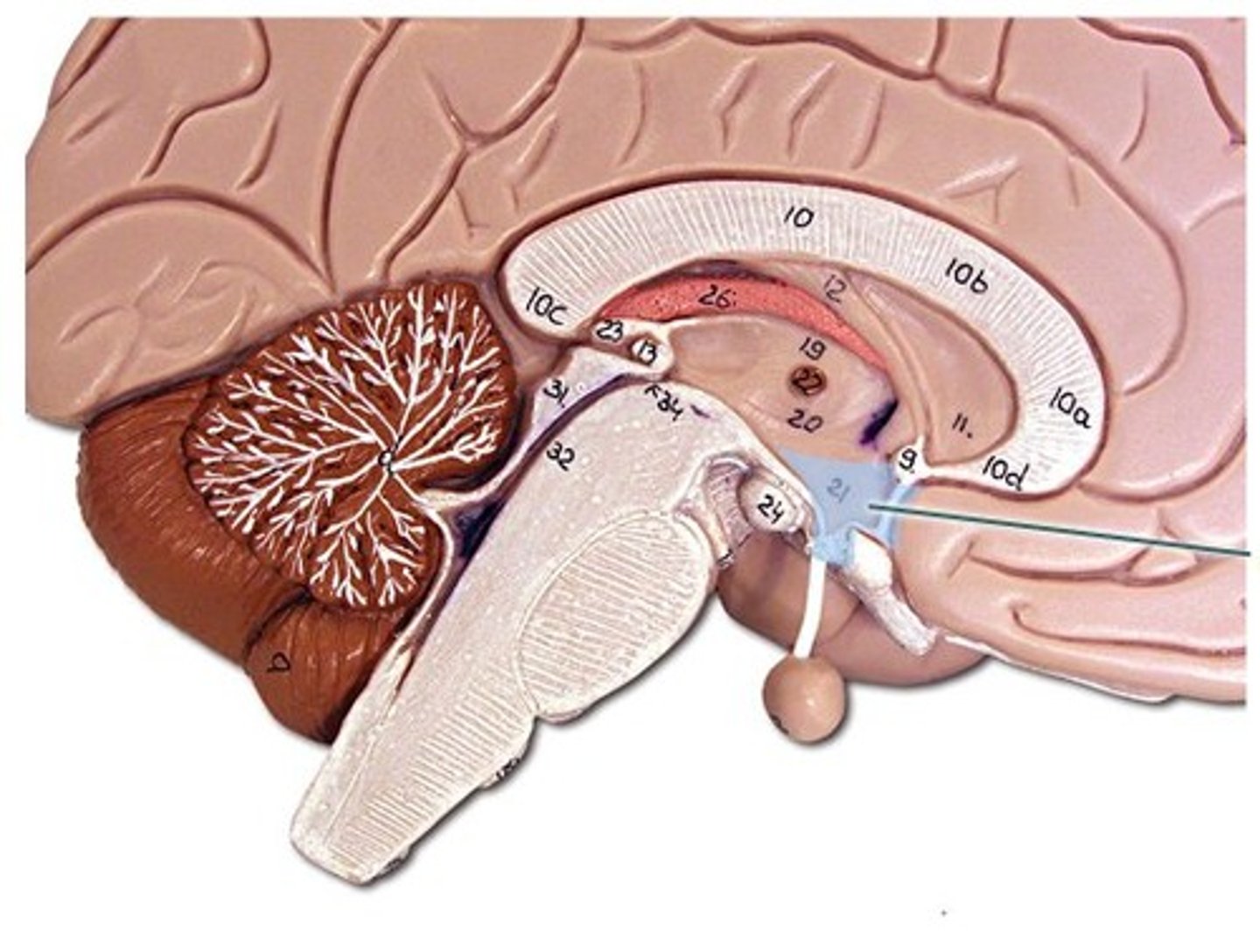
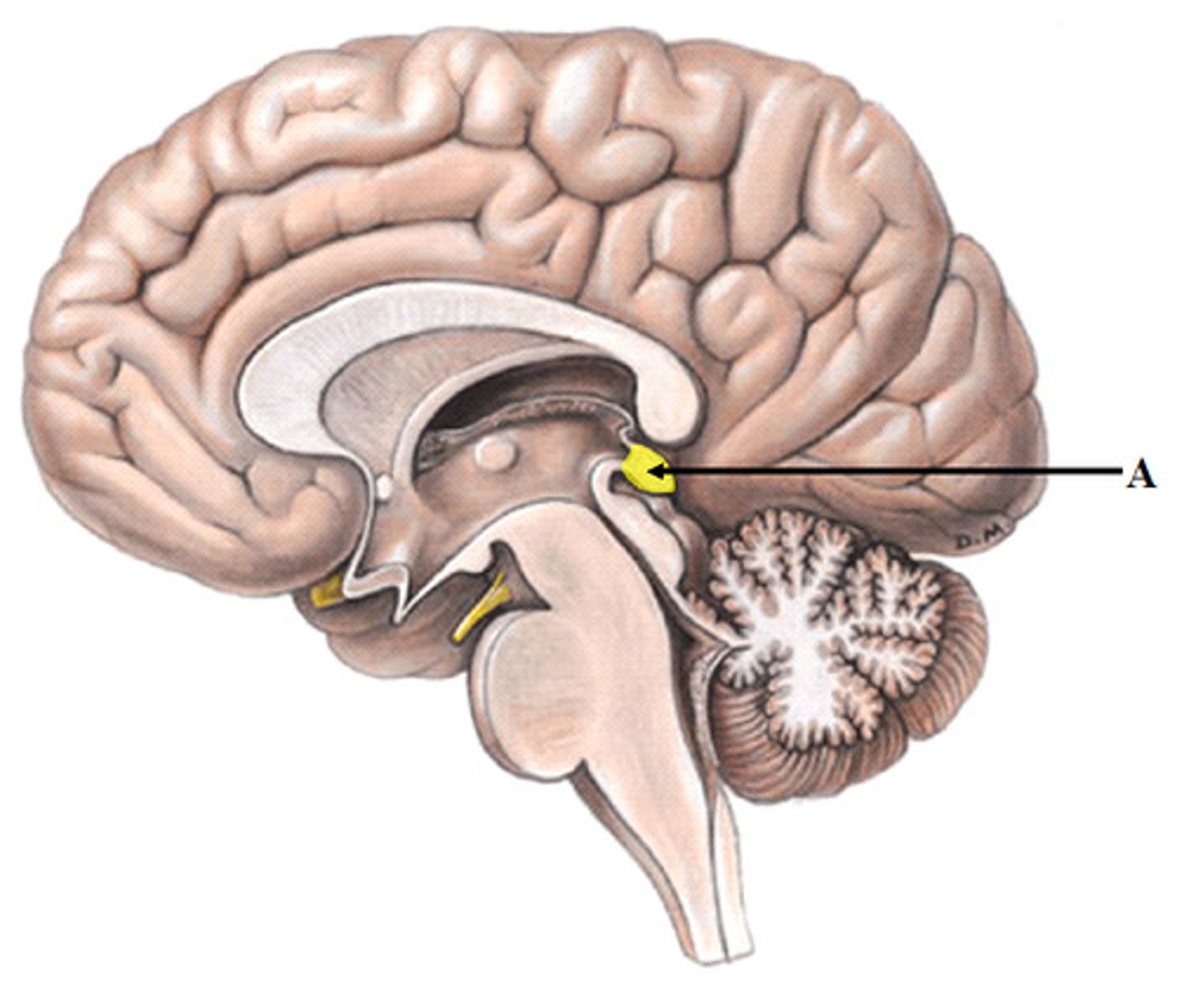
Epithalamus
- Pineal body in diencephalon: melatonin, regulates sleep cycles
- Choroid process: made of ependymal cells that produce CSF
The Brain Stem
Midbrain (1), Pons (2), Medulla Oblongata (3)
Letter D
Midbrain
- Pathways for fear/fight or flight responses + startle (visual) reflex
- Colliculi and Substancia nigra-
- Descending motor pathways
Colliculi
In midbrain, visual and audio reflexes
Substancia nigra
In midbrain, contains melanin, precursor of dopamine (Parkinson's Disease)
Pons
- Contain nuclei that concern posture, sleep, respiration, swallowing, and bladder control
- Signals from cerebrum to the cerebellum pass through tracts in the pons
Medulla oblongata
Control of coughing, sneezing, hiccupping, sweating, vomiting (cardiac, vasomotor, respiratory center)
Connects brain to spinal cord
Choroid Plexus
Functions of Cerebellum
- Modulates and coordinates voluntary movement of limbs
- Maintains tone and posture, eye movements
- Learning motor skills
Input to cerebellum
Vestibular, auditory, and visual go through the pons
- Muscle and joints, reticular, sight, hearing
Functional brain systems
Limbic System, reticular formation
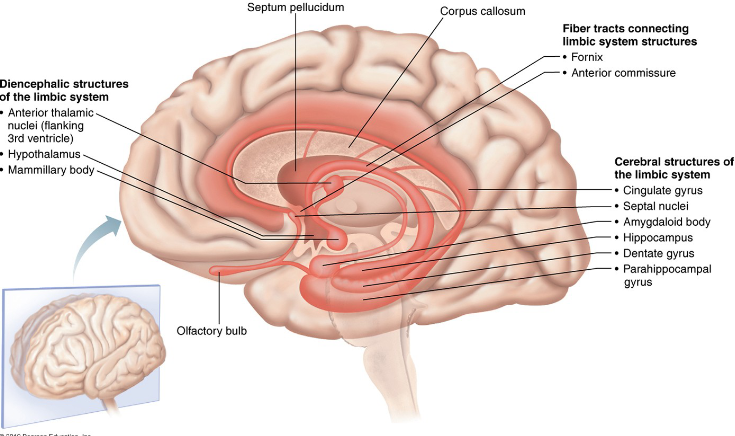
Limbic system
- Loops of cortical tissue surrounding the corpus callous and thalamus
- Many important facts of a person's personality depend on an intact limbic system
- Deals with emotions such as fear, anger, love, etc.
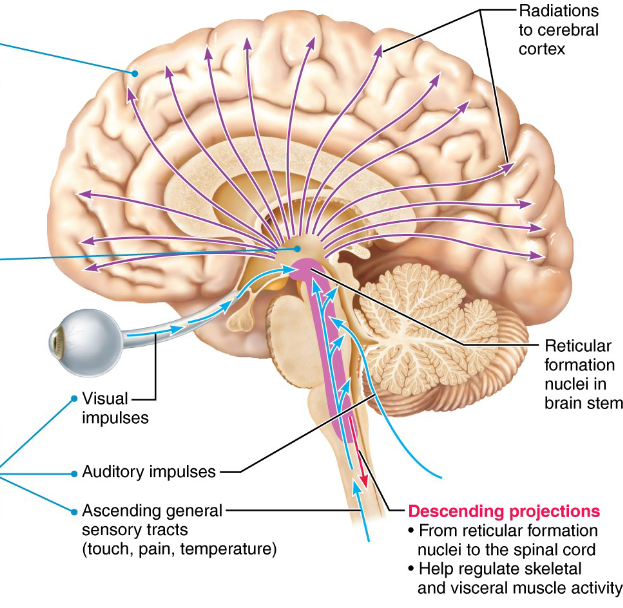
Reticular formation
- Group of 100 nuclei scattered throughout the medulla, midbrain, and pons that function in somatic motor control, autonomic control, arousal, and pain modulation
- Reticular Activating System (RAS) filters out the unwanted stimuli
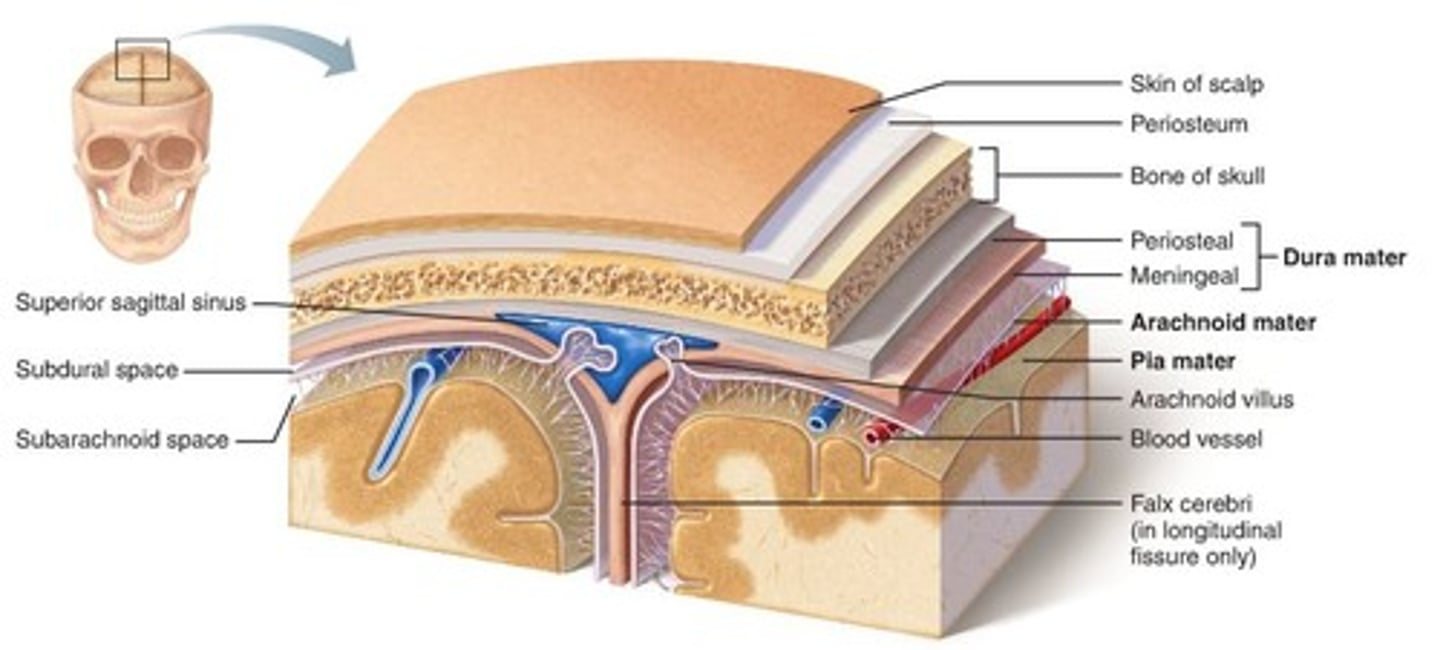
Meninges
Protective membranes that surround the brain and spinal cord
(3) Dura mater
(2) Arachnoid mater
(3) Pia mater
Dura Mater
Tough outer protective layer, lots of collagen, “tough mother”
Arachnoid Mater
Mesh like network between the outer and inner layers of the meninges, contains CSF, “spider mother”
Pia Mater
Highly vascular, closely contours the brain, “soft mother”
cerebrospinal fluid
- Fluid in the space between the meninges
- Produced by the choroid plexus within each ventricle
- It consists of capillaries covered in simple cuboidal epithelium
Functions of CSF
- Acts as a shock absorber that protects
- Helps remove wastes
- Provides a stable chemical environment for the brain
CSF Circulation
Choroid Plexus produces CSF
CSF flows through ventricles and into subarachnoid space via median and lateral apetures
CSF flows through subarachnoid space
CSF absorbed into dural venous sinuses via arachnoid granulations
Blood supply
- Brain is very metabolically active
- 4 minutes of no O2 or Glucose supply can cause irreversible damage
Blood-Brain Barrier
Protects CNS by regulating substances that enter the brain
- Tight junctions within capillaries and astrocytes make up this barrier
Strokes (cerebrovascular accidents)
- Circulation to the brain is blocked
- Can be transient ischemic attacks (TIA)
Causes of Strokes
- Commonly a blockage of a cerebral artery
- Compression of the brain by hemorrhage or edema, and atherosclerosis
Transient Ischemic Attacks (TIA)
Temporary episodes of reversible cerebral ischemia
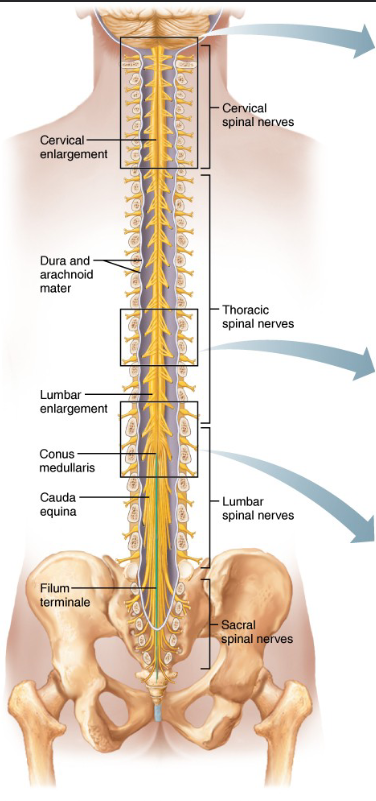
Spinal cord anatomy
- Begins at foramen magnum and ends at 1st lumbar vertebra
- Divided into cervical, thoracic, lumbar, and sacral regions
- Gives rise to 31 pairs of spinal nerves
Spinal Cord functions
Conduct action potentials up and down, conduction, locomotion, and reflex activity
Spinal Cord Diagram
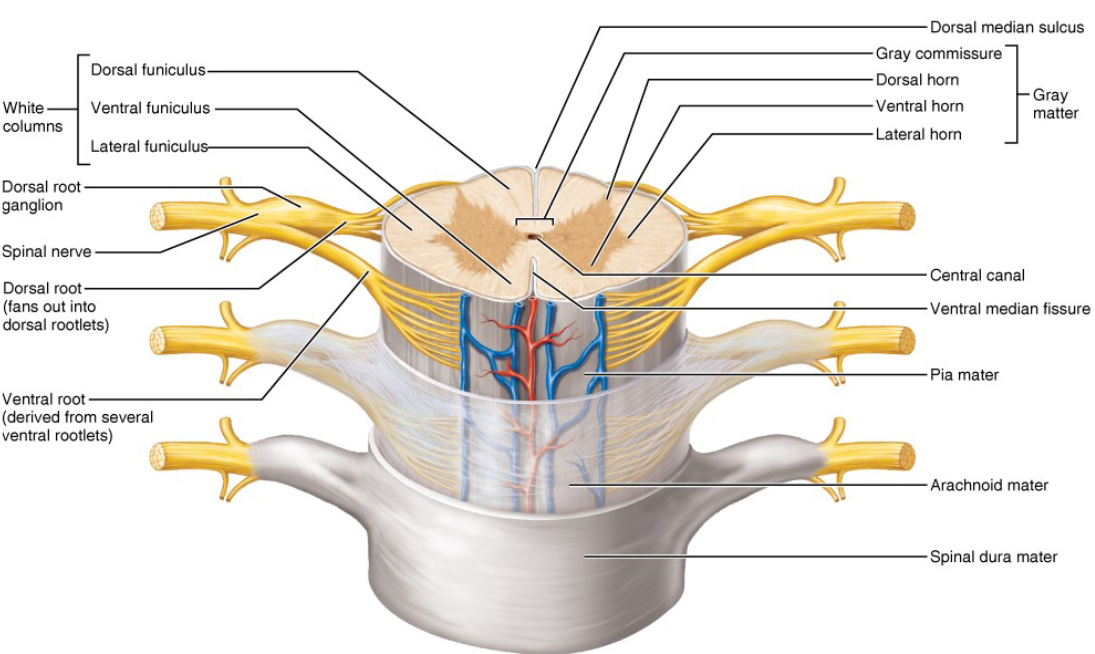
Gray matter on the outside, white matter on the inside
White Matter Columns
Myelinated and nonmyelinated nerve fibers, three funiculi
- Communication within spinal cord and between spinal cord and brain
- Ascending, descending, and transverse fibers
Dorsal Root Ganglion
Sensory (afferent) neurons transmit sensory information from PNS to CNS
- Signals from skin, muscles, and internal organs.
Ventral Root
Motor (efferent) fibers that extend to and innervate skeletal muscles, facilitating voluntary movements.
- From spinal cord to muscles
Central Canal
Plays role in circulating cerebrospinal fluid (CSF)
- Nutrient transport and waste removal
Dorsal Horn of gray matter
Receives input from somatic and visceral sensory neurons
- Interneurons carry sensory information (touch, pressure, paint, temp.) from body to spinal cord via the dorsal roots
Ventral Horn of gray matter
Sending motor commands to skeletal muscles, enabling voluntary movements
- Somatic neurons, motor function, innervates the limbs, has cell bodies
Lateral Horn of gray matter
Innervating visceral organs, both somatic and autonomic efferent fibers
- Autonomic neurons, mostly involuntary organs (smooth, cardiac, glands
Gray commissure
Encloses the central canal, allowing communication between two sides of spinal cord
- Integrating sensory and motor information
Tracts of the spinal cord
- Ascending tracts; not nerves!! They send sensory impulses TO brain
- Descending tracts. They send motor impulses FROM brain to motor neurons
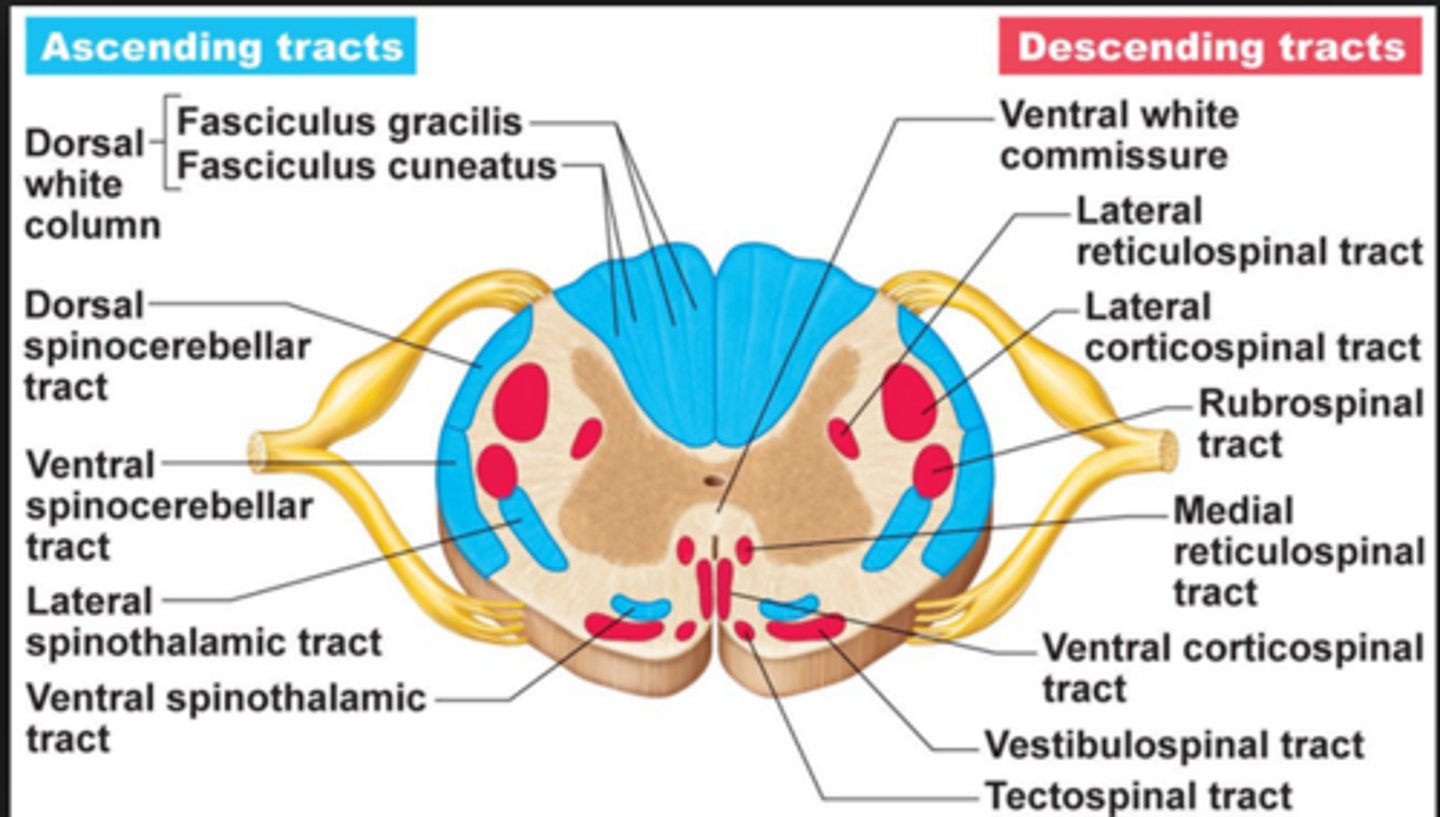
Spinal cord trauma
- Paralysis
- Flaccid paralysis
- Spastic paralysis
Paralysis
Loss of motor function; tracts are severed and cannot send messages
Flaccid Paralysis
Severe damage to the ventral root or anterior horn cells, lower motor neurons are damaged and impulses don't reach muscles, no voluntary or involuntary movement
Spastic Paralysis
Only upper motor neurons of the primary motor cortex, involuntary movement, not complete severance
Transection
Cross-sectioning of the spinal cord at any level results in total motor and sensroy loss in regions inferior to the cut
- Paraplegia
-Quadriplegia
Paraplegia
- Transection between T1 and L1
- Cannot move legs
Quadriplegia
- transection in cervical region
- paralysis of all four limbs
Poliomyelitis
- Destruction of the anterior horn motor neurons by the poliovirus
- Symptoms: fever, headache, muscle pain, and weakness; loss of somatic reflexes
- Vaccines: Salk and Sabin
Amyotrophic lateral sclerosis (ALS)
- Lou Gehrig's disease: Neuromuscular condition involving destruction of anterior horn motor neurons and fibers of pyramidal tract
- Symptoms: loss of ability to speak, breathe, and swallow
- Death occurs within 5 years
- Linked with malfunctioning genes for glutamate transporter and/or superoxide dismutase
Brain waves
Continuous electrical activity
- An (EEG) records this activity
- Patterns of neuronal electrical activity recorded are called brain waves
Electroencephalogran (ECG)
Can be used to diagnose lesions, tumors, Infracts, etc.
Alpha waves
Low-amplitude, slow, asynchronous
- Occipital lobe, calmness
- A relaxed, awake state
Beta waves
Rhythmic, more irregular waves;
- Concentration and stress
- Awake and alert state
Theta waves
More irregular than alpha waves; common in children
- Mediation, drifting off
- Light sleep state
Delta waves
High-amplitude, slow brain waves
- Stage 3 or 4 of non-REM sleep
- Deep sleep state
brain waves change...
over time
two types of sleep
- REM and non-REM
- 4 stages of NREM during first 30-45 minutes
- REM occurs after the fourth stage
sleep patterns
- Alternating cycles of sleep and wakefulness reflect natural circadian (24-hour) rhythm
- RAS activity inhibited during, but RAS also mediates sleep stages
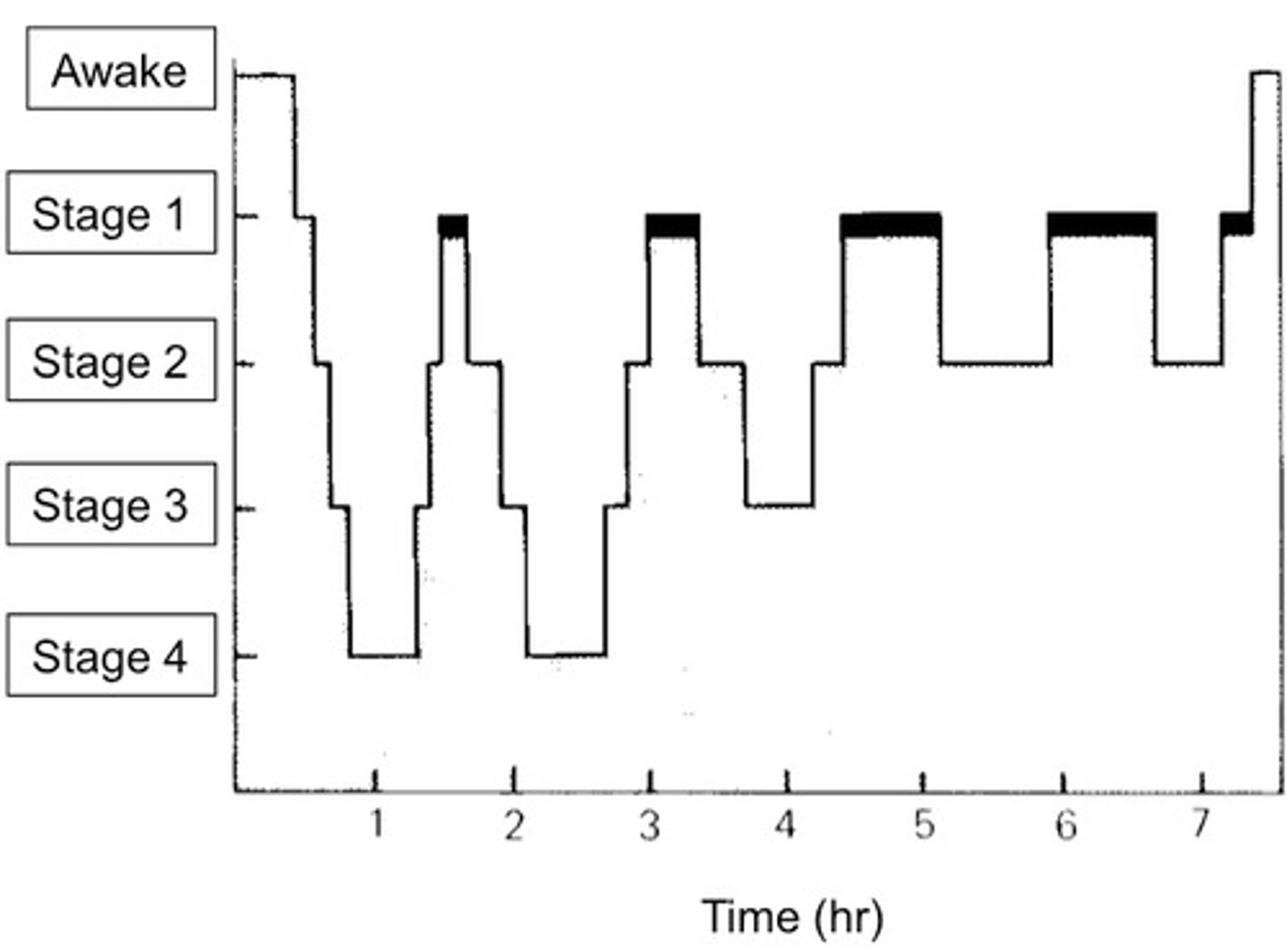
sleep disorders
- narcolepsy: fully conscious and then deep sleep
- insomnia: chronic inability to obtain amount of sleep needed
- sleep apnea: temporary stoppage of breathing during sleep
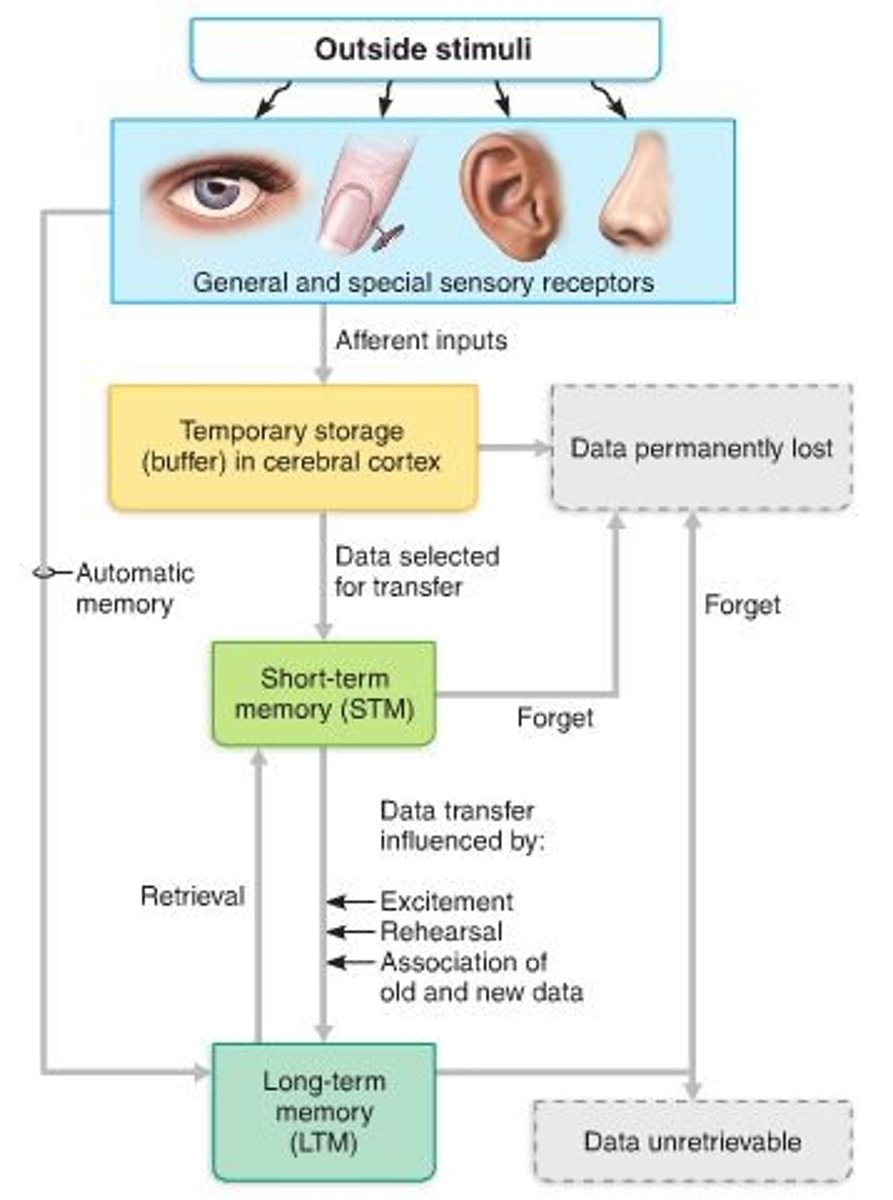
stages of memory
- short-term (STM or working memory): a fleeting memory of events that continually happen, lasts seconds to hours and limited to 7-8 pieces of info
- long-term (LTM): limitless capacity
Transfer from STM to LTM
Factors affecting transfer from STM to LTM
- Emotional state—best if alert, motivated, surprised, and aroused
- Rehearsal—repetition and practice
- Association—tying new information with old memories
- Automatic memory—subconscious information stored in LTM
skill memory
performing skilled motor activities, acquired from practice, don't contain the context to which the thing is learned
fact memory
-learning explicit information
-hippocampus
-related to conscious thoughts and our language stability
-stored with the context in which it was learned