Maths AA DP1-2 (SL & HL)
1/203
Earn XP
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
204 Terms
Arithmetic Sequence
Increases or decreases by the addition of a numerical factor.

Arithmetic Sum
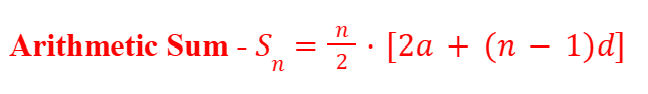
Geometric Sequence
Increases or decreases by the multiplication of a numerical factor.

Geometric Sum
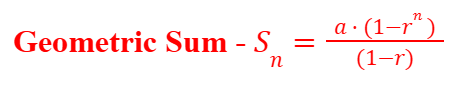
Convergent Series
Keeps decreasing until it converges at one value e.g. geometric sequences.
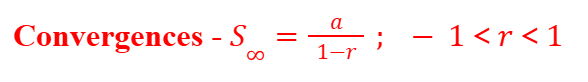
Divergent Series
Keeps increasing till infinity e.g. arithmetic sequences.
Combinatorics
The number of way you choose r objects from n choices.

Permutations

Binomial Expansion
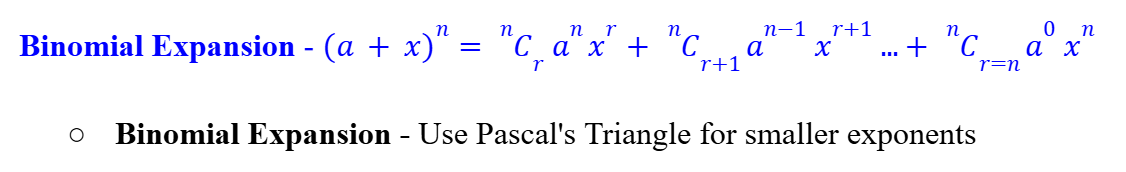
Binomial Expansion for Fractional Powers
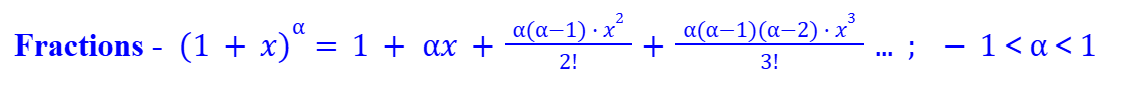
Binomial Expansion for Negative Powers
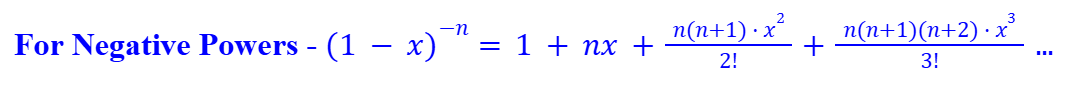
Proof by Mathematical Induction
Zero and One Power Rules (Indices)
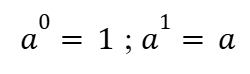
Product and Greater Exponent Rules (Indices)
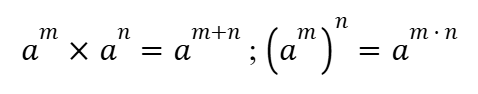
Quotient and Negative Exponent Rules (Indices)
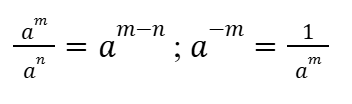
Fractional and Same Exponent Rules (Indices)
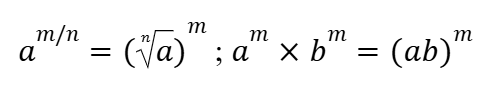
Inverse Function Rule (Logarithms)
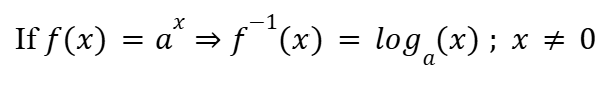
Basic Logarithms
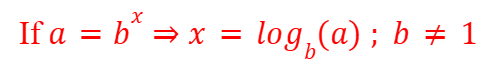
Addition Rule (Logarithms)
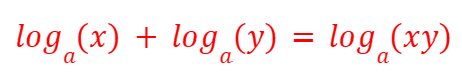
Subtraction Rule (Logarithms)
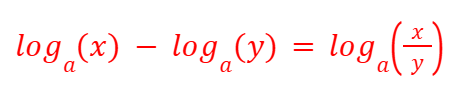
Power Rule (Logarithms)
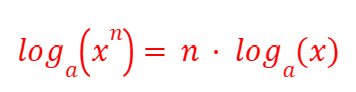
Log of Base and 1 (Logarithms)
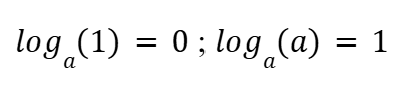
Quotient Rule (Logarithms)
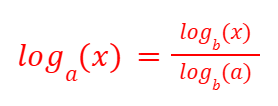
Negative and Fractional Rules (Logarithms)
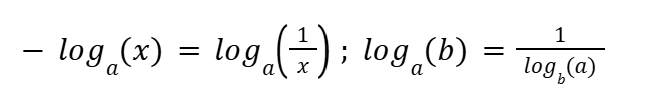
Natural Logs and Greater Exponent Rules (Logarithms)
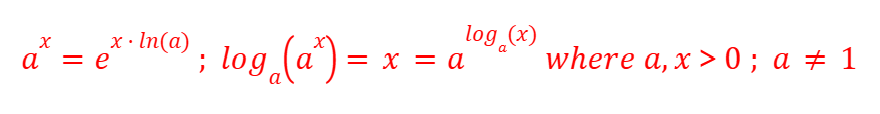
Concept of ‘i’
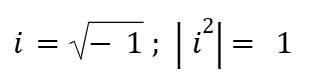
Imaginary/Complex Numbers
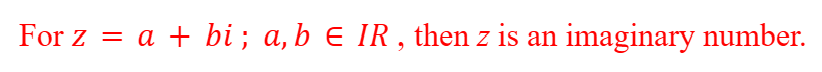
Absolute Value (Complex Numbers)
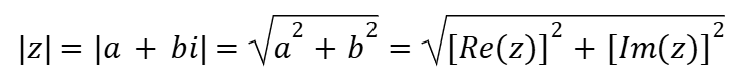
Addition Rule (Complex Numbers)
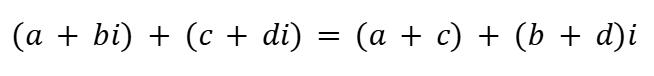
Multiplication by a Scalar (Complex Numbers)
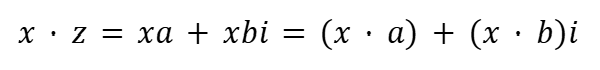
Complementary Imaginary Numbers
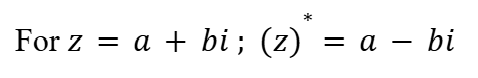
Magnitude of Complex Numbers
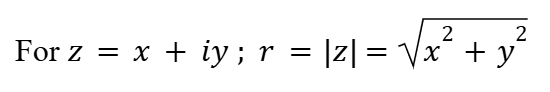
Polar Form (Complex Numbers)
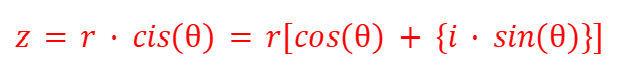
Angle of a Complex Number
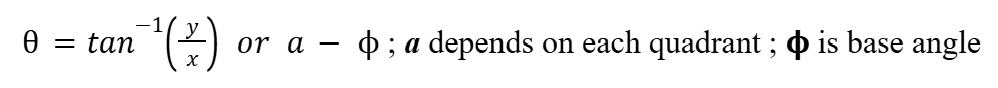
Angles in each Quadrant (Complex Numbers)
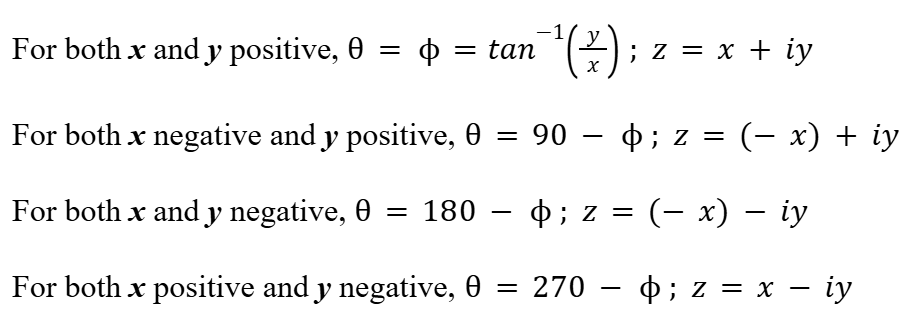
Euler’s Form (Complex Numbers)
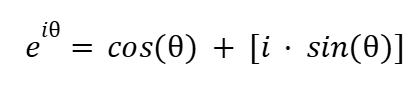
Representation of Complex Numbers
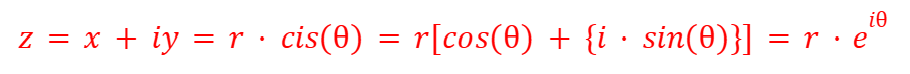
Symmetry of Complex Numbers
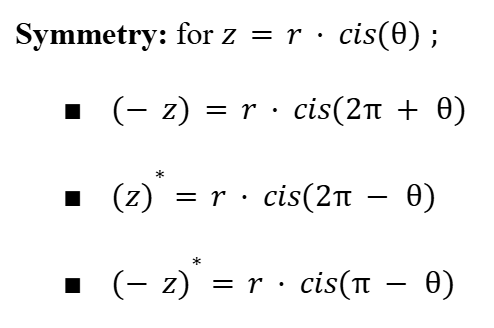
Product Rule (Complex Numbers)
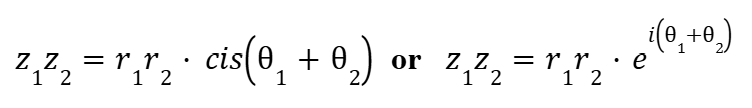
Quotient Rule (Complex Numbers)
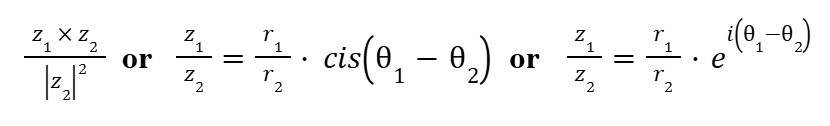
De Moivre’s Theorem
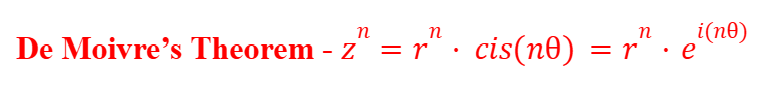
Roots of Complex Numbers
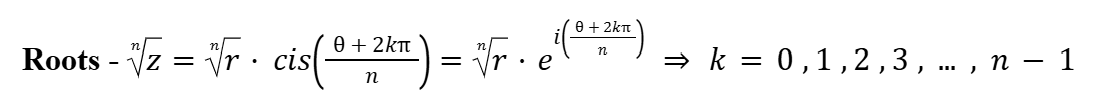
Vertex Form of a Function
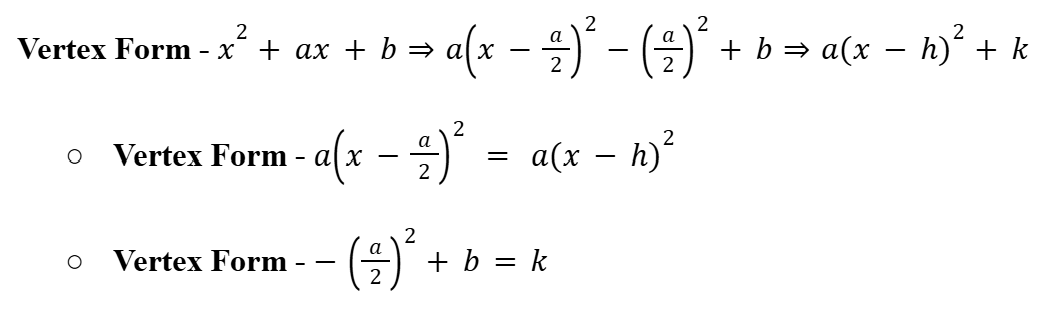
Inverse Form of a Function

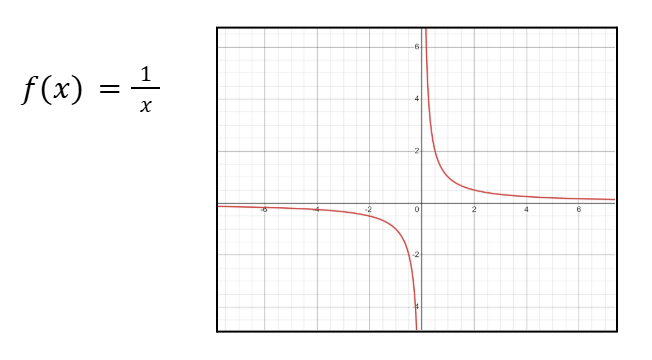
Graph of 1/x
Graph of x2
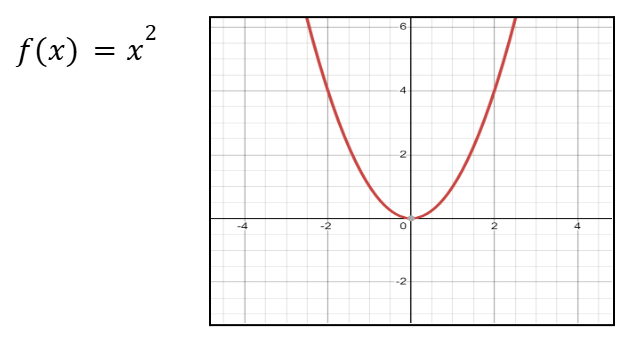
Graph of x3
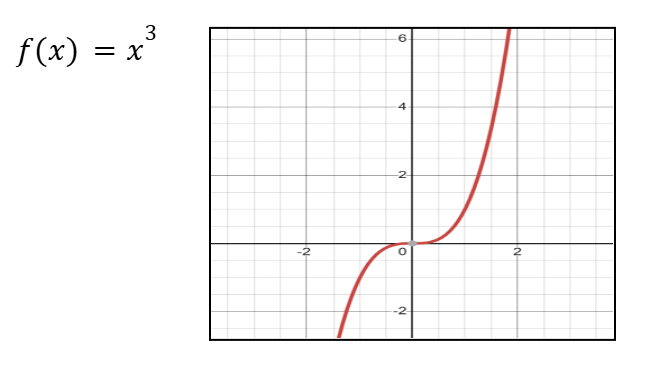
Graph of ax
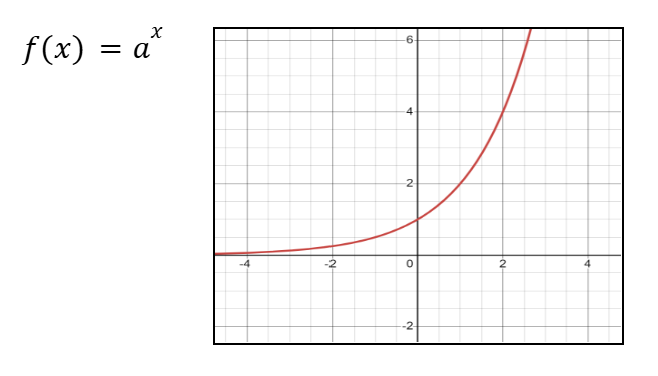
Graph of a-x
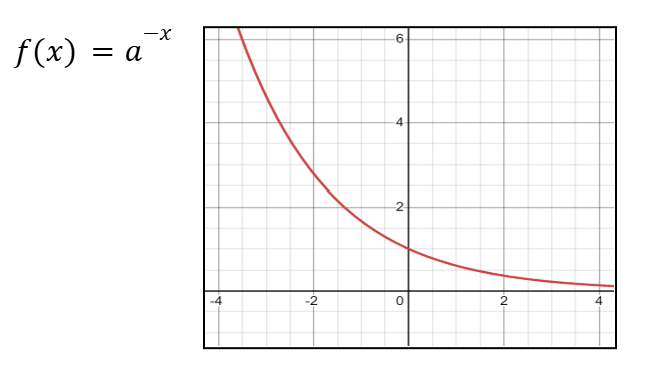
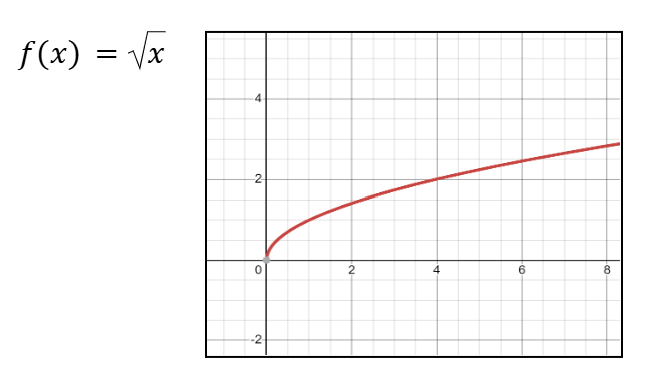
Graph of x1/2 (Square Root of x)
Quadratic Formula
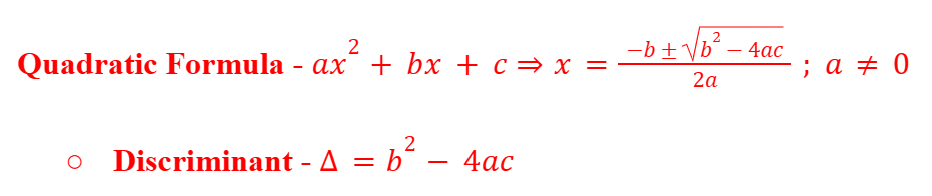
Translations of Functions
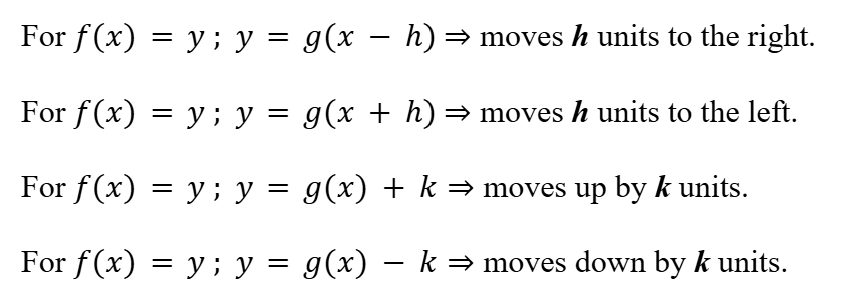
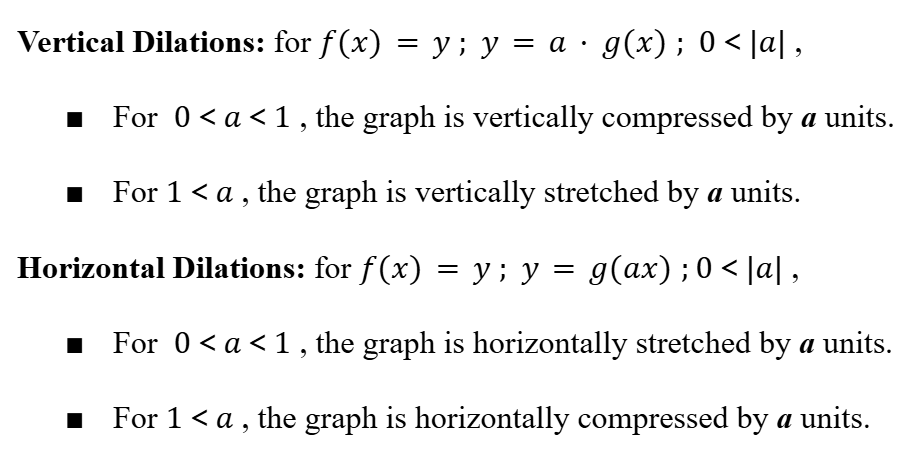
Dilations of Functions
Exponential Growth (Functions)
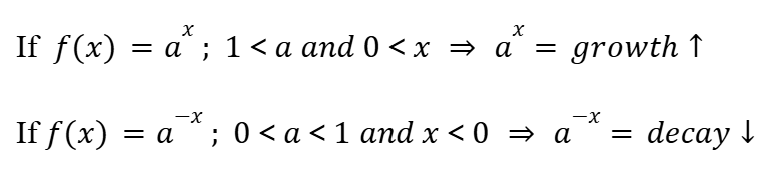
Rational Functions
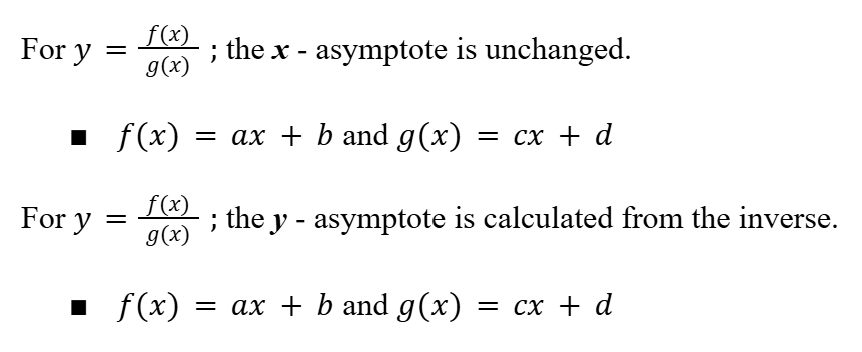
Partial Fractions
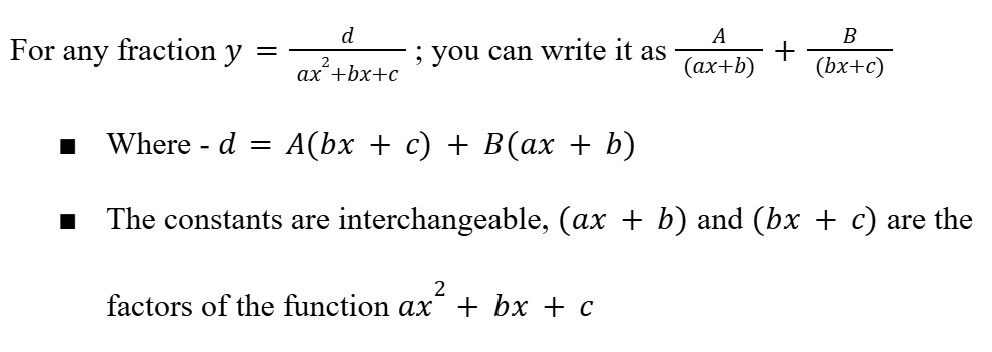
Absolute Value (Functions)
The absolute value of any number a is the ‘real’ value of a, i.e. it is always greater than zero.
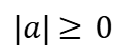
Graph of Absolute Value Functions
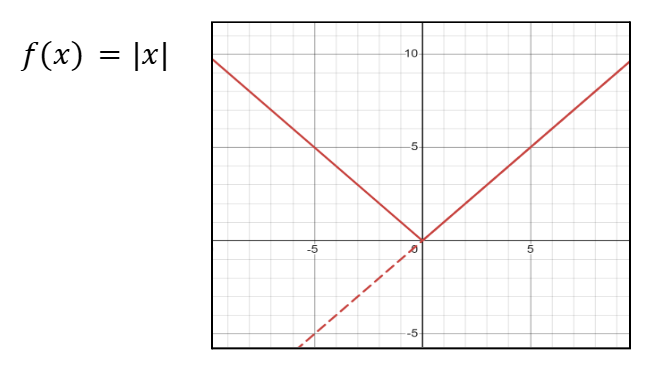
Absolute Value of Negative Numbers
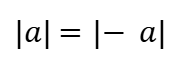
Absolute Value of Zero
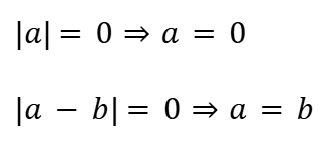
Product Rule (Absolute Value)
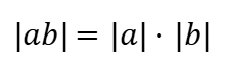
Quotient Rule (Absolute Value)
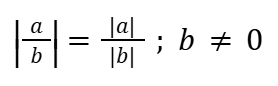
Addition Rule (Absolute Value)
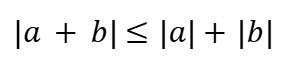
Subtraction Rule (Absolute Value)
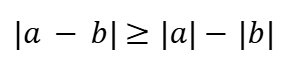
Comparison of Absolute Numbers
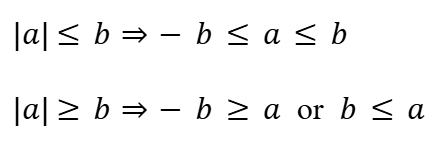
Distance Formula (2D)
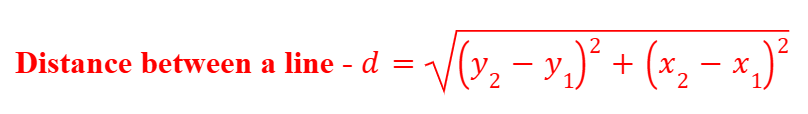
Coordinates of Midpoints (2D)

Parallel and Perpendicular Lines
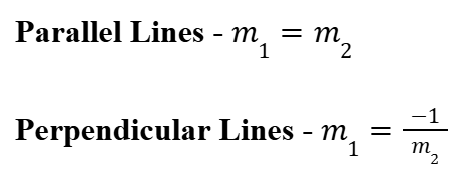
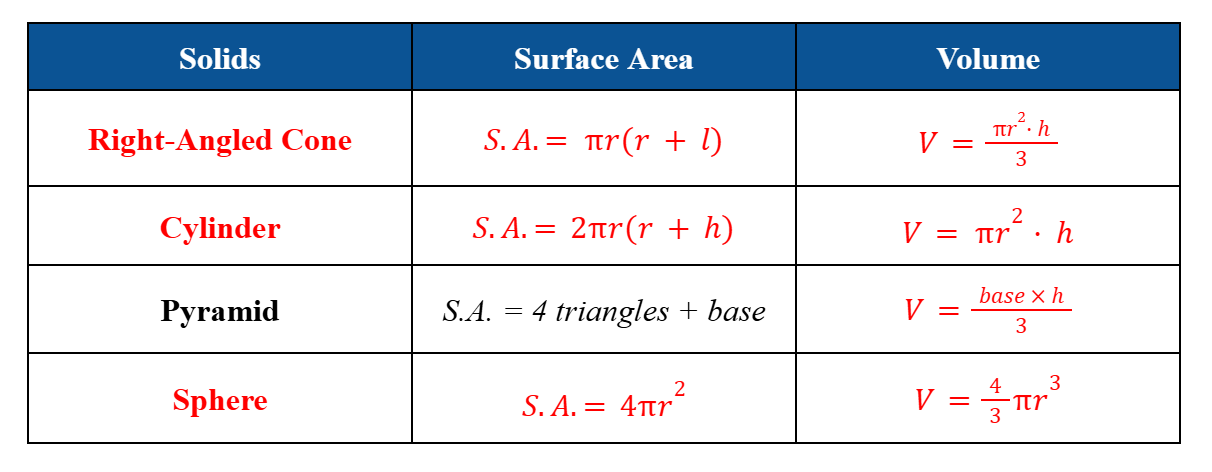
Surface Area and Volumes of Common Solids
Distance Formula (3D)
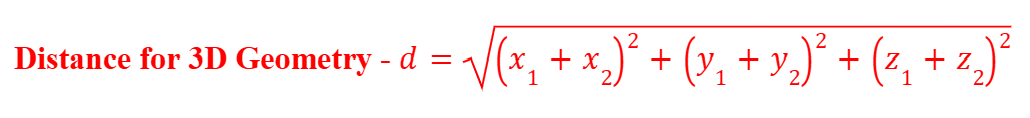
Coordinates of Midpoints (3D)
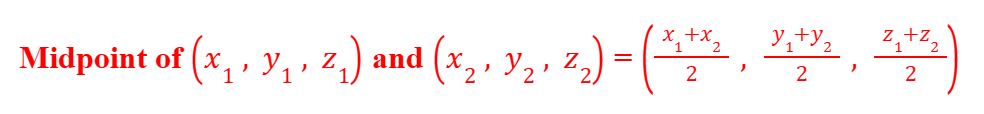
Radians
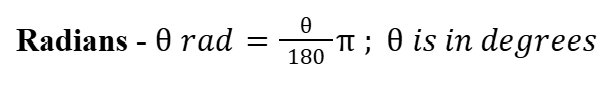
Common Angles in Radians
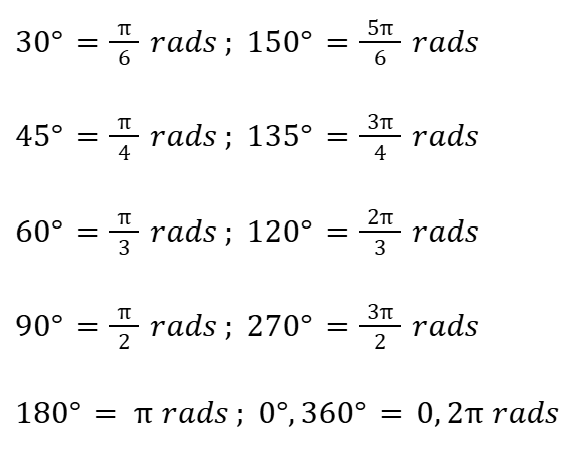
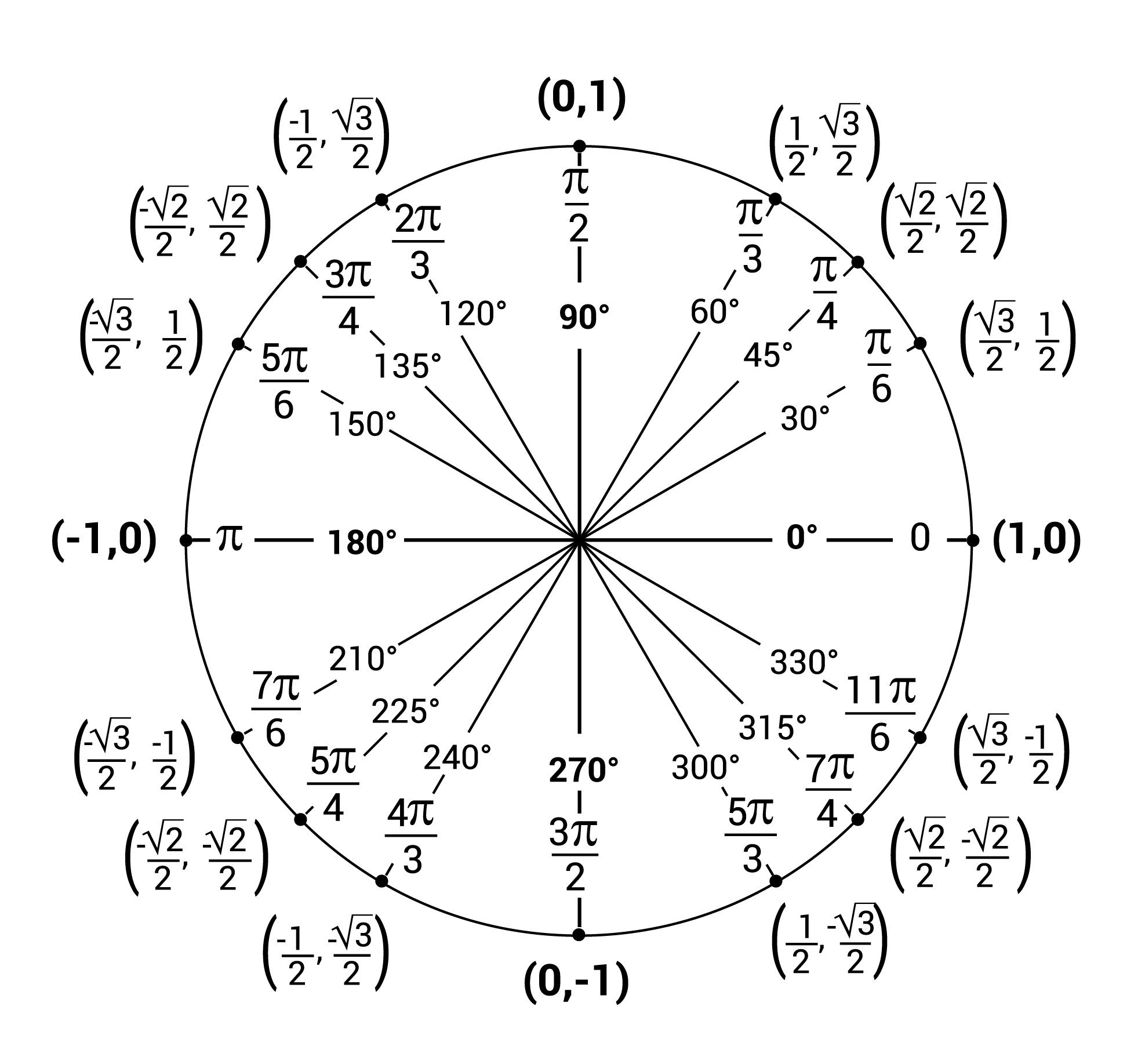
Sine and Cosine in the Unit Circle
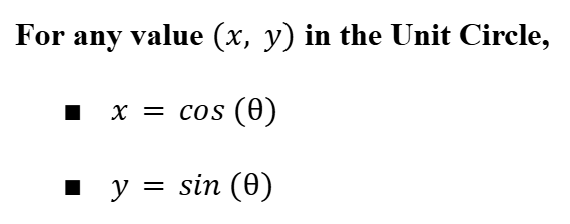
Unit Circle
Arc Length
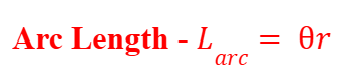
Area of a Sector

Sine Rule
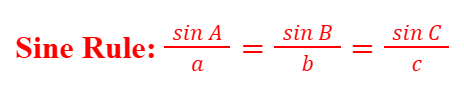
Cosine Rule
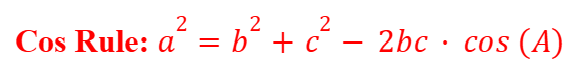
Area of any Triangle

tan (θ)
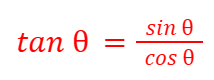
cosec (θ)
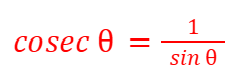
sec (θ)
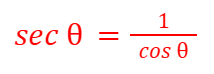
cot (θ)
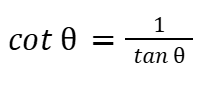
Pythagorean Identity (Trigonometry)
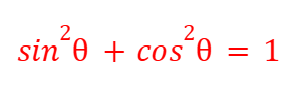
sin(2θ) - Double Angles
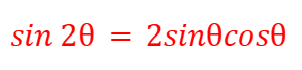
cos(2θ) - Double Angles
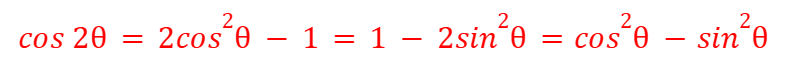
tan(2θ) - Double Angles
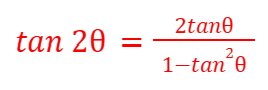
sec2(θ)
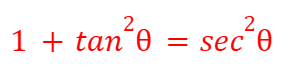
cosec2(θ)
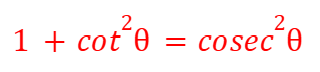
sin (A±B) - Compound Angles
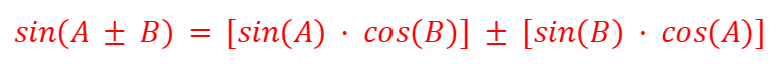
cos (A±B) - Compound Angles
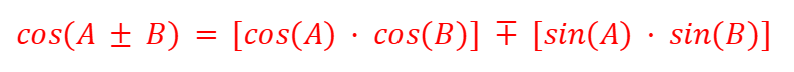
tan (A±B) - Compound Angles
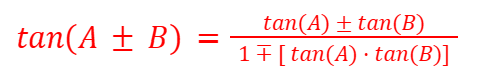
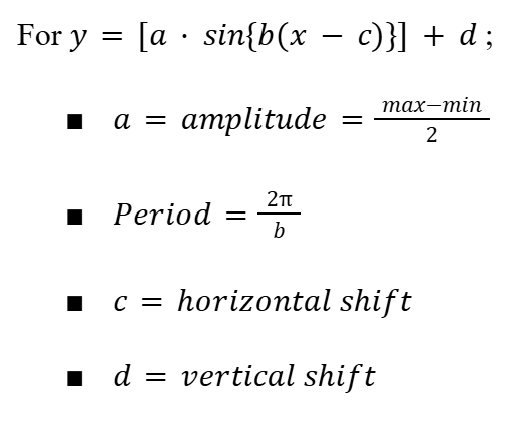
Transformations (Trigonometry)
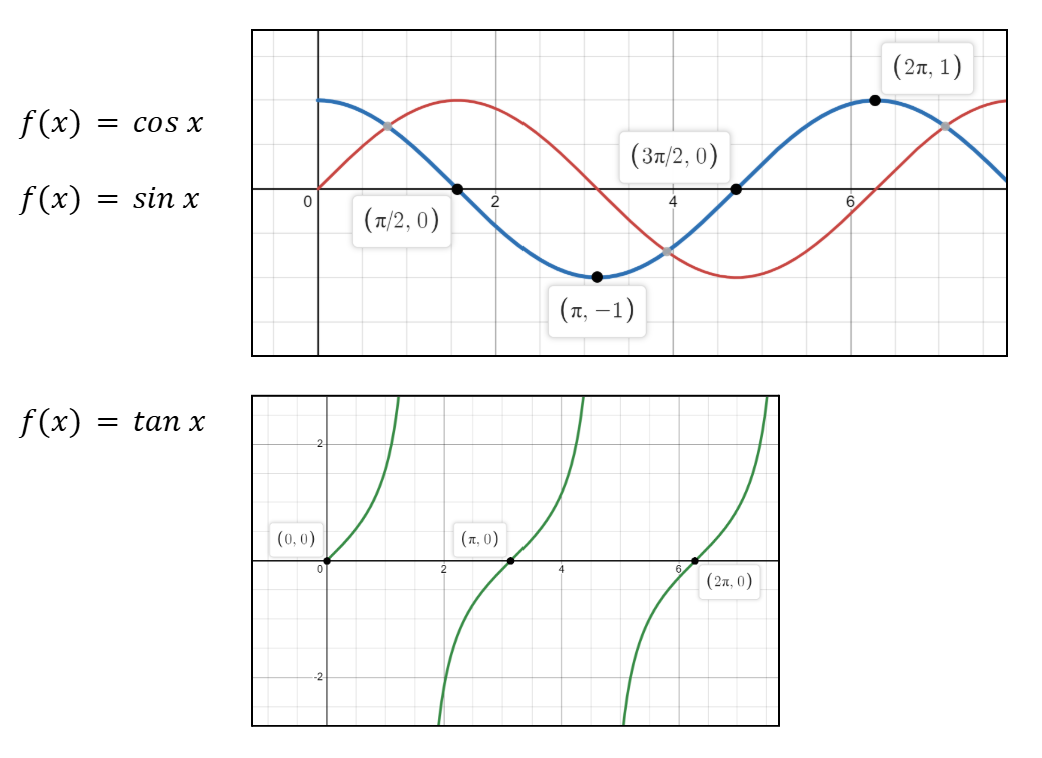
Graphs of sin(x), cos(x) and tan(x)
Periodicity of Angles in Radians
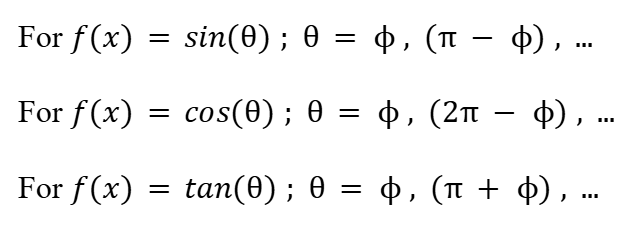
Directed Line Segment

Vectors

Properties of Vectors
Collinearity - Two points are colinear if they lie on the same line.
Coplanarity - Two points or lines are coplanar if they lie in the same plane.
Parallelogram Rule (Vectors)