Organic Chemistry IUPAC Names And Other Stuff For the Exam
1/29
Earn XP
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
30 Terms
An alcohol
is an organic compound containing one or more hydroxyl (-OH) groups attached to a carbon atom. Alcohols are typically characterized by their ability to engage in hydrogen bonding (N O F), which affects their boiling points and solubility.
An ether
is an organic compound in which an oxygen atom is bonded to two alkyl or aryl groups. generally characterized by their low reactivity and distinctive odors.
basicaly when something-o-something
-oxy to the shorter side
An alk/ane/ene/yne
is a class of hydrocarbons characterized by the types of bonds between carbon atoms: alkanes have single bonds, alkenes have double bonds, and alkynes have triple bonds.
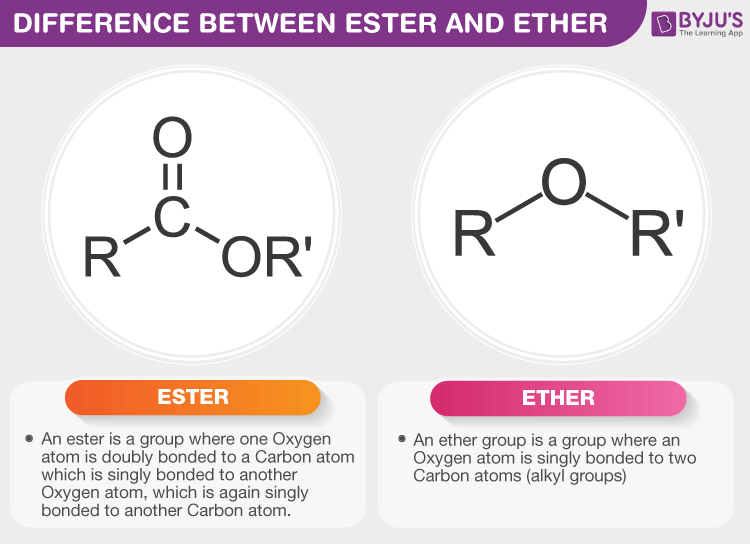
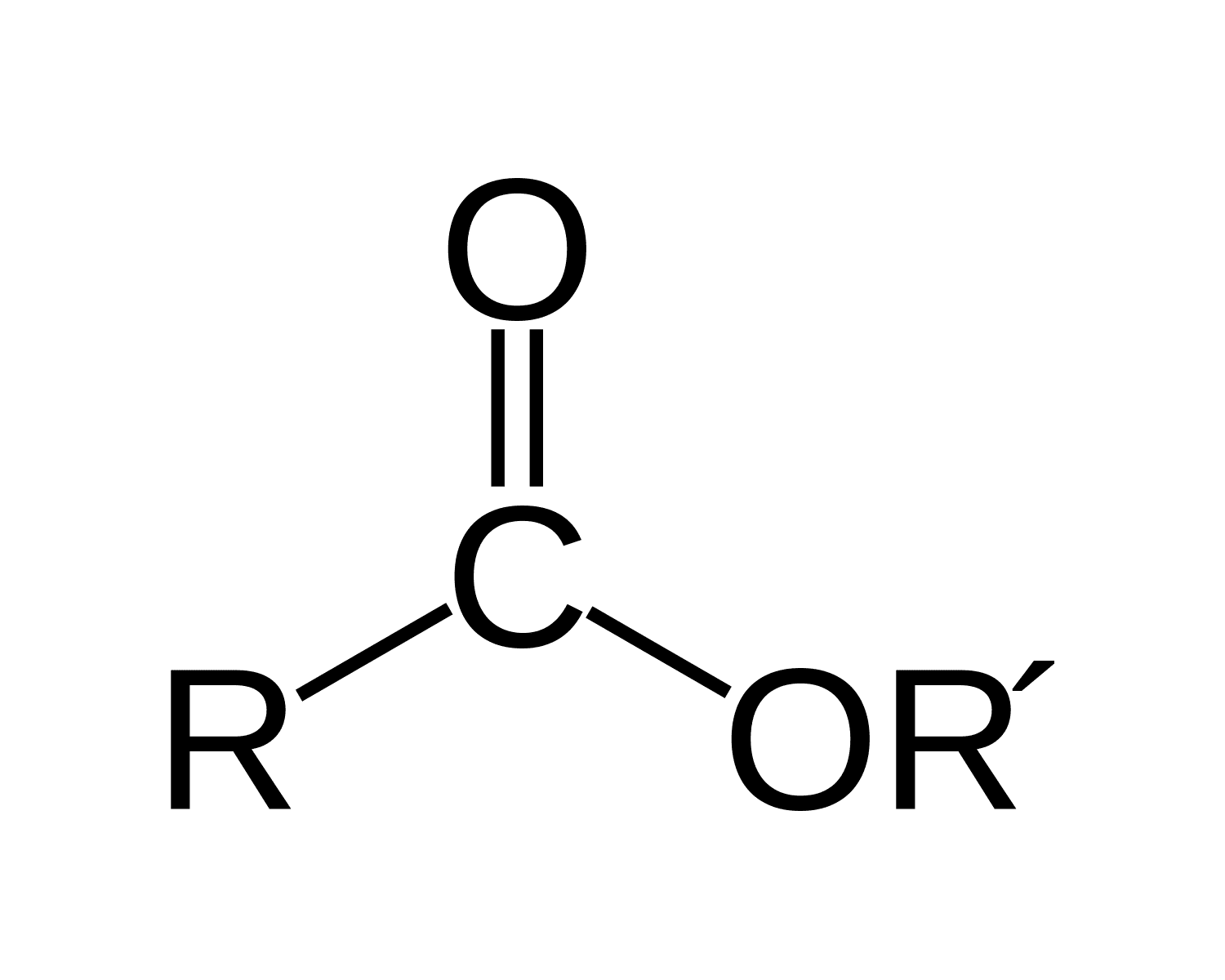
An ester
is an organic compound formed from the reaction of an alcohol and a carboxylic acid, characterized by the presence of a carbonyl group (C=O) adjacent to an ether link (–O–). known for their pleasant fruity odors and are commonly used in flavorings and fragrances.
RCOOR
-ate
fat
Isomerism
Same formula, different structure; can lead to differences in chemical properties and reactivity.
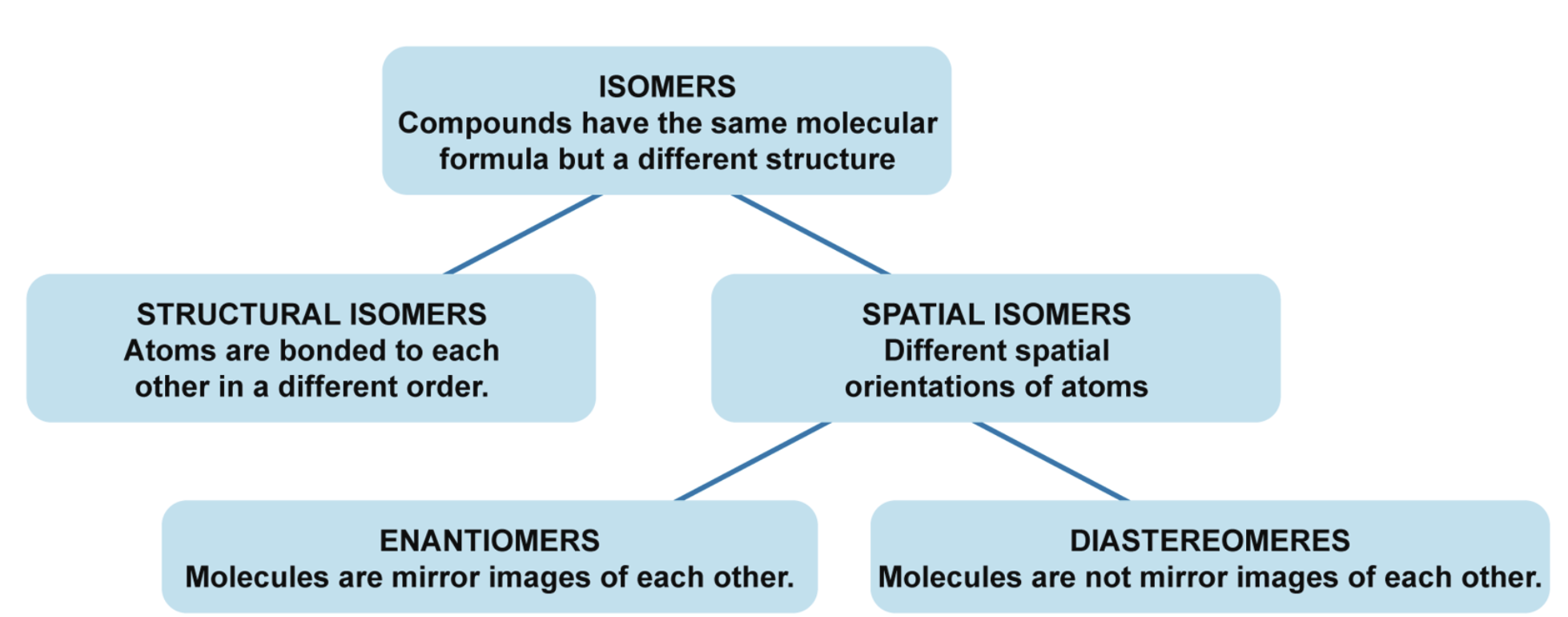
Structural/constitutional isomerism
Includes skeletal, positional and functional isomerism
Stereoisomerism
Includes cis/transisomerism, conformational isomerism and optical isomerism
Diastereomers
stereoisomers that do not mirror each other, one side being a cis and one side being a trans or one being S or R, not all diastereomers are cis/trans isomers tho
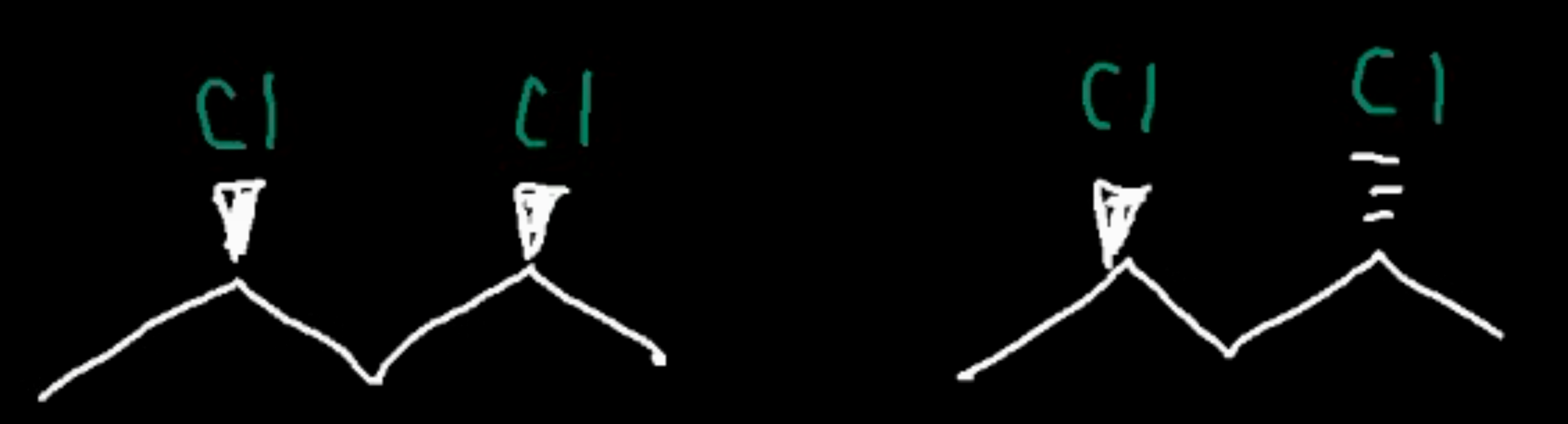
Positional isomers
a func group or other atom in a different spot, affects reactivity if alcohol (primary secondary tertiary)

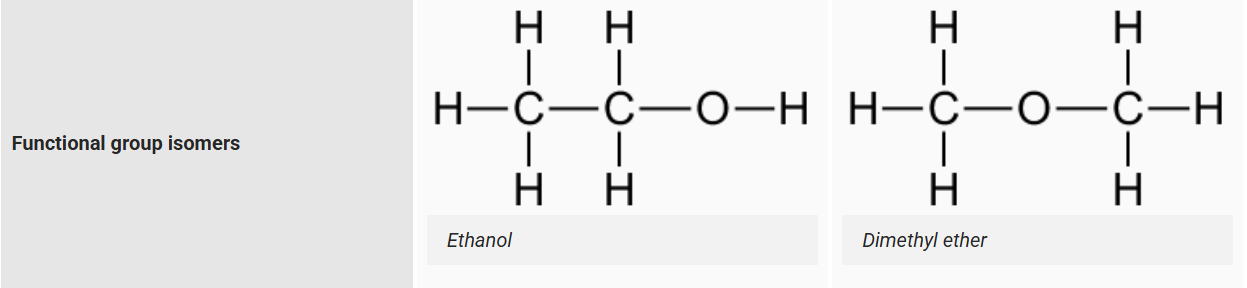
Functional group isomers
same atoms, different func group
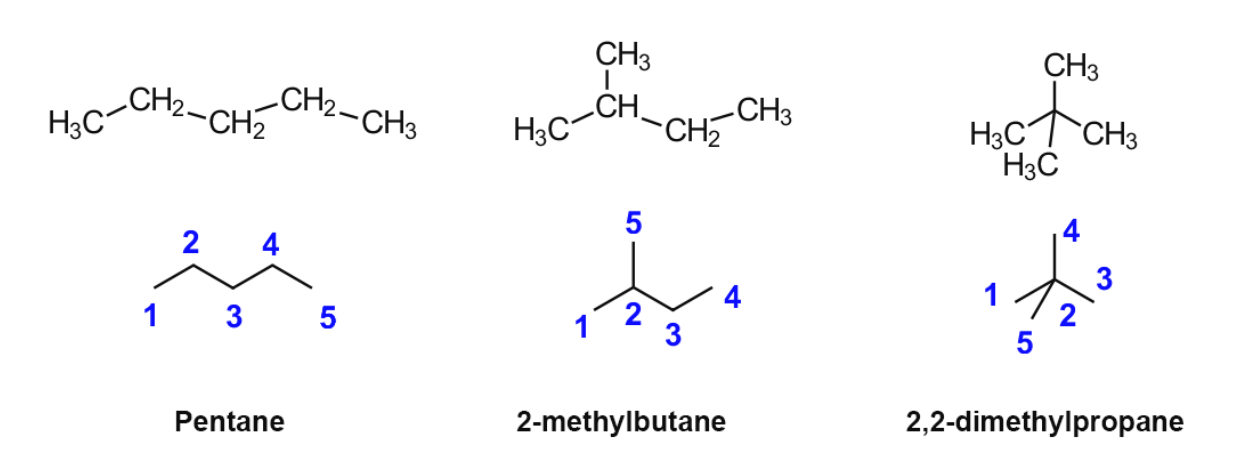
Chain isomers
the carbon chain branches out in a different way
Primary alcohol
OH carbon attached to one carbon only, oxidizes to aldehyde
Secondary alcohol
OH carbon attached to two carbons, oxidizes to ketone
Tertiary alcohol
OH carbon attached to three carbons, needs to turn to secondary or primary to oxidize
Aldehyde
Oxygen with a double bond to C

Ketone
Double bonded oxygen which is kinda like secondary

Carboxylic acid
COOH, -oic acid suffix, polar
Enantiomer
(R/S)molecules that mirror each other, in skeletal structures the wedges are reversed when changing R or S to S or R
if incmplete mirror, is diastereomer

Cis-trans or Entgegen/Zusammen isomerism
Cis (Z): two groups on same side of a plane, polar, higher bp
Trans(E): two groups on opposite sides, nonpolar, lower bp
can also happen in cyclical molecules
different phys propertie
E/Z works by ranking elements by atomic number and basically doing the same

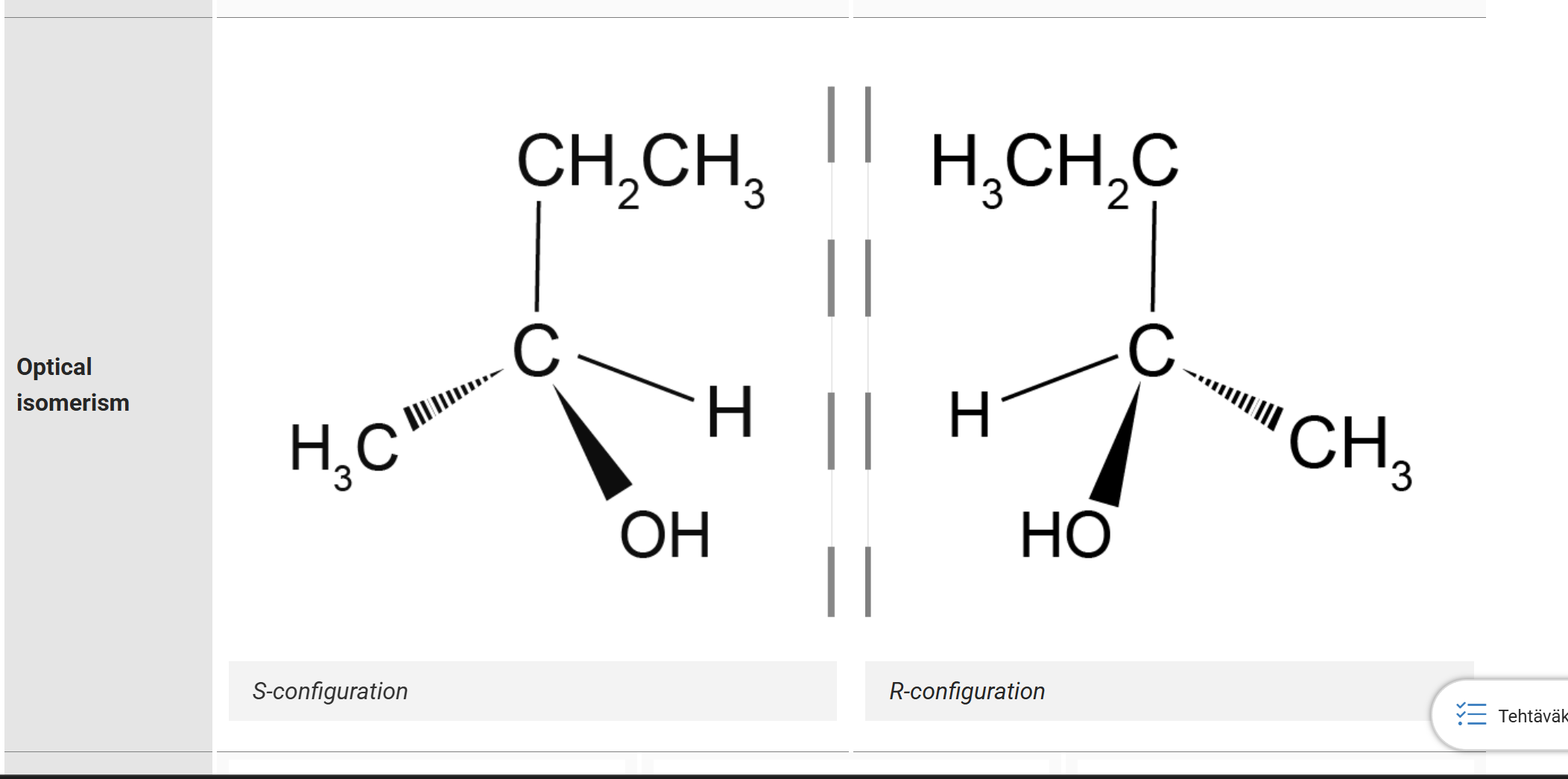
Optical isomerism
when molecules are optically mirrored, aka R/S
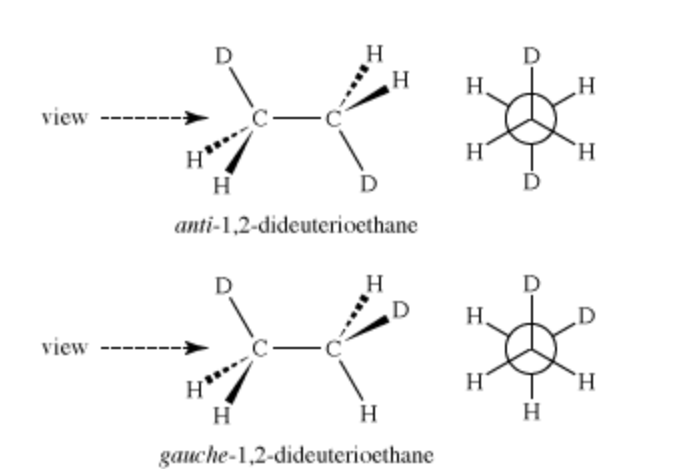
Conformational isomerism
when the atoms are differently arranged around sigma bonds, no bonds are broken aka they twist around their bonds. can be anti, gauche or eclipsed.
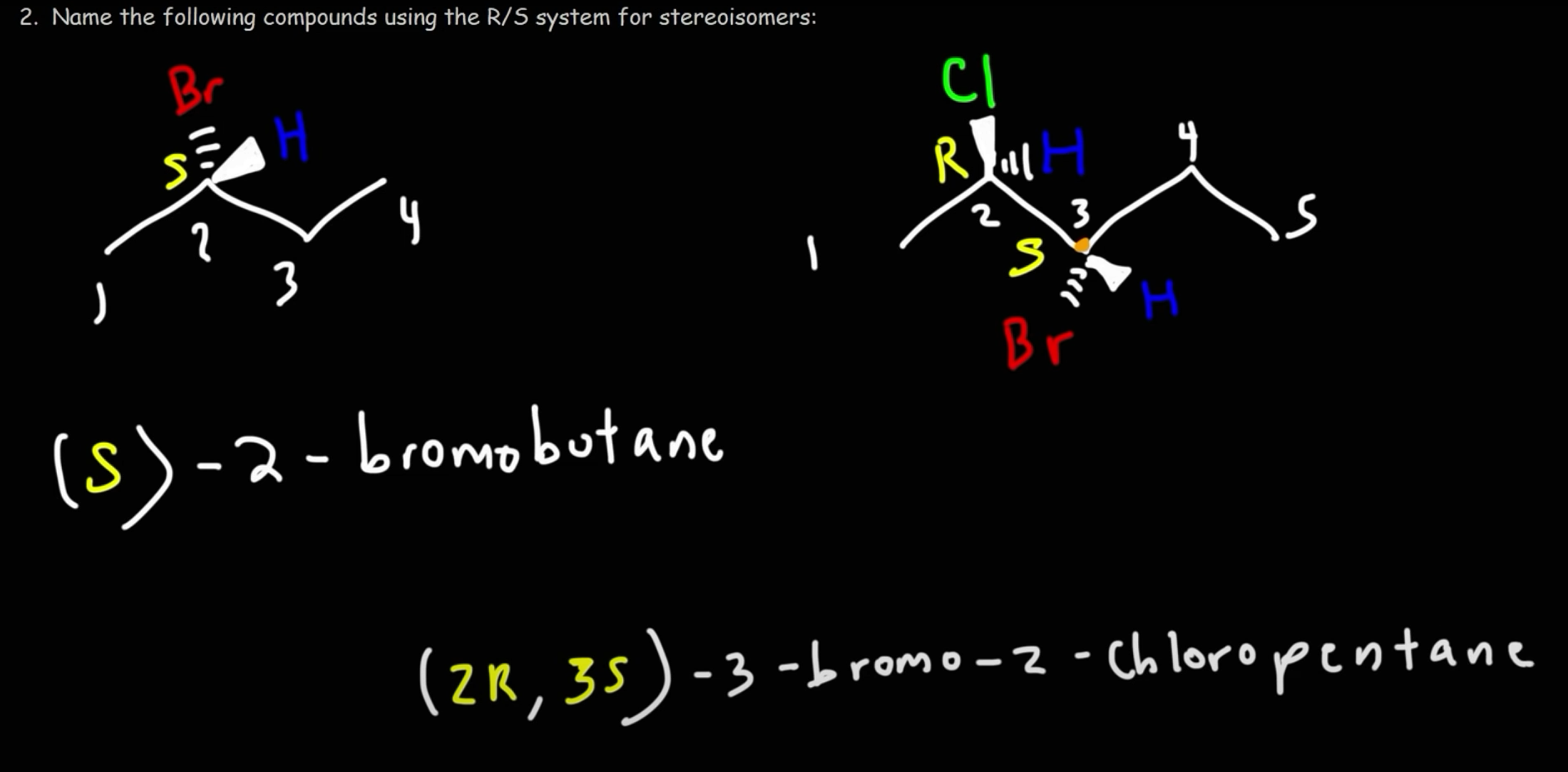
R/S system
S: groups 1-3 (determined by atomic number of the atoms bonded to chiral carbon) go CCW with group 4 in the back
R: groups 1-3 go CW with group 4 in the back
If group 4 is in the front, it has to be switched to the back by reversing the clockwiseness (R->S or S->R)
If group 4 is neutral, put it to the back by doing the triangle thing
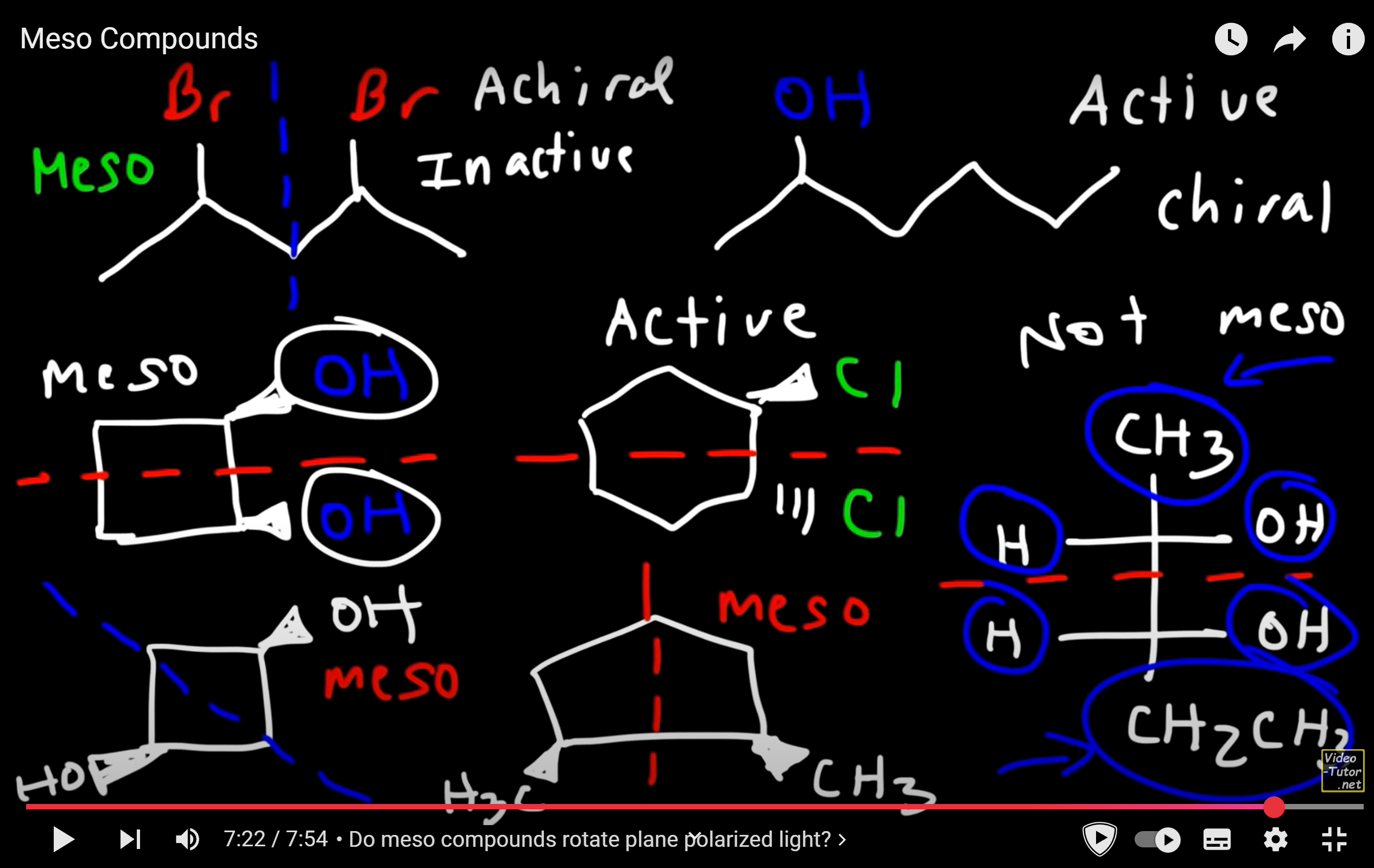
meso compounds
optically inactive, achiral despite having chiral centers, has an internal line of symmetry
aromatic compound
hydrocarbon with benzene ring
durable
benzene ring
cyclic alkane with double bonds in every other bond basically idk
turns to phenyl when anything bonded to it’
electrons delocalized so is durable
hydrocarbon
org compound with h and c
saturated/unsaturated hydrocarbons
unsaturated if double/triple bonds
benzyl group
benzene with methyl
-amine
NH2 or NH or N group, primary=1carbon bonded secondary = 2 tertiary = 3 quaternary = 4 cyclic = more
if for example 1 hydrgen from nitrogen was replace with butane it would be butanamine BUT if nitrogen not at END of butane it will be like any other func group as in “2-butanamine”
when something is attached to N while it is bonded to carbon chain and you wanna name it by the chain its gonna be N-[insert thing here]
when not priority group is [number]-amino somethingsomething
![<p>NH2 or NH or N group, primary=1carbon bonded secondary = 2 tertiary = 3 quaternary = 4 cyclic = more</p><p>if for example 1 hydrgen from nitrogen was replace with butane it would be butanamine BUT if nitrogen not at END of butane it will be like any other func group as in “2-butanamine”</p><p>when something is attached to N while it is bonded to carbon chain and you wanna name it by the chain its gonna be N-[insert thing here]</p><p>when not priority group is [number]-amino somethingsomething</p>](https://knowt-user-attachments.s3.amazonaws.com/d8f9e10e-4bd0-425c-964e-353d1a72b898.png)
-amide
carboxylic acid but OH is an amine lol
CO-NH
solid at room temp except methylamide
mp & bp high has polarity and hbonds
