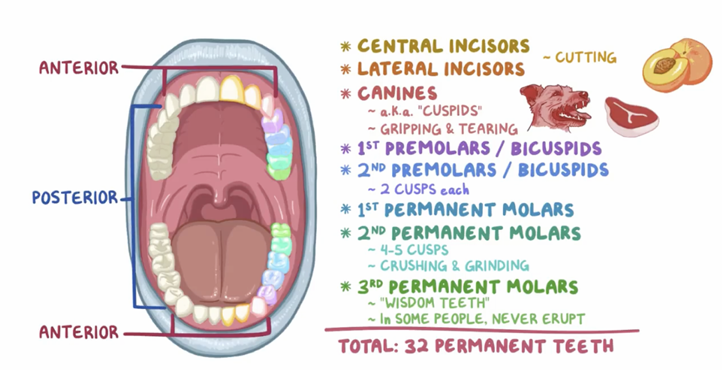
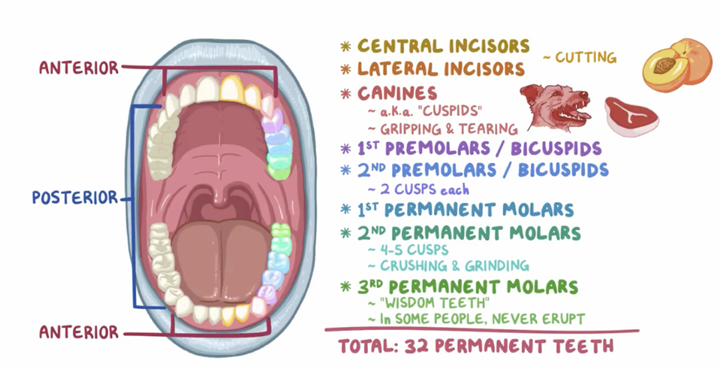
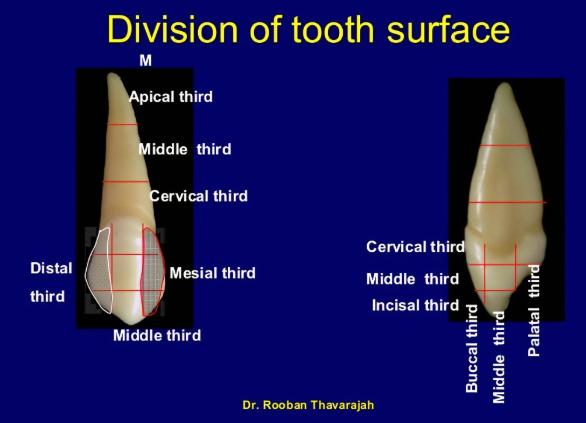
2.2 Morphology of incisors, canines and premolars
1/153
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
154 Terms
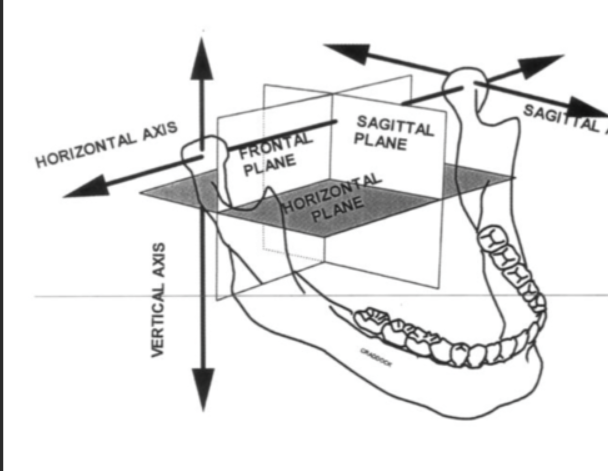
what are the planes of orientations?
sagittal
medial
horizontal
frontal
What are the 4 types of ways to divide teeth into according to shape and function?
Incisors - cutting/tearing food, lip+tongue support, provides incisal guidance, enables speech
Canine - cutting food, corner of dental arch, canine guidance, labial contour, part of aesthetic quadrant, lip support
Premolars - mixed function, cutting+grinding , known as transition teeth, initial mastication, maintain vertical dimensions, canine assistance in cutting food
Molars - grinding food, main mastication, maintain vertical dimensions, less aesthetic influence.
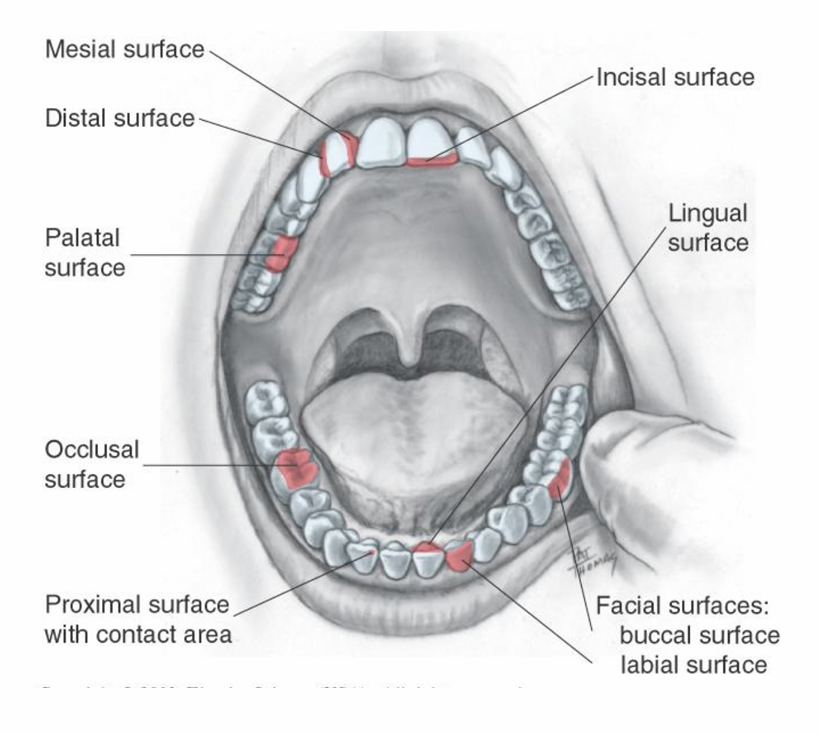
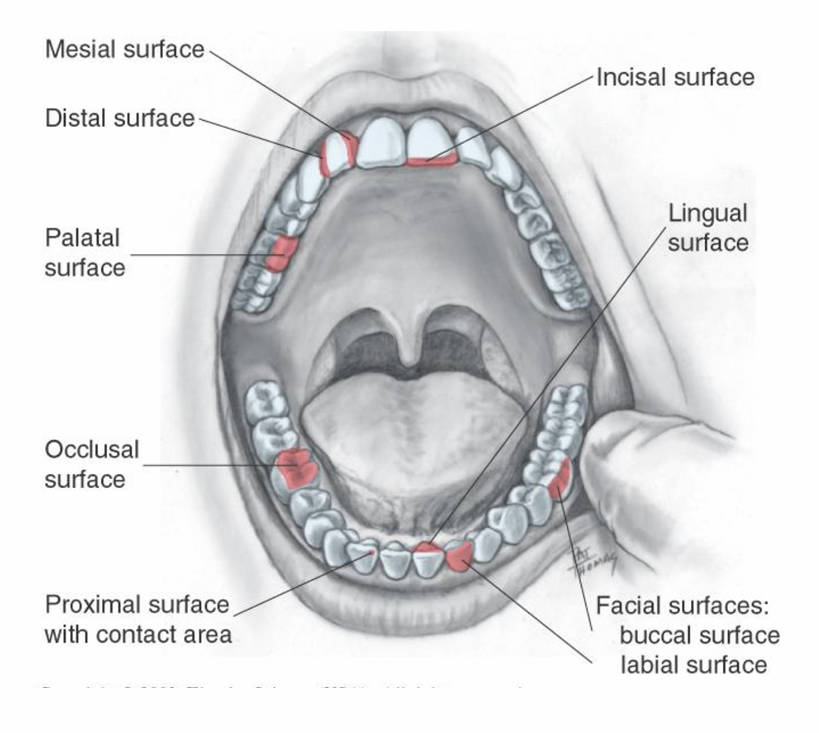
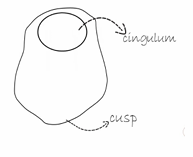
List the cusps of teeth
Mesial cusp ridge
Distal cusp ridge
Buccal cusp ridge
Triangular ridge
The Cusps - Mesial cusp ridge
slope that faces towards the front of the mouth
The Cusps - Distal cusp ridge
slope that faces towards back of the mouth
The Cusps - Buccal cusp ridge
slope on cheek side for most teeth, but for canines, it’s called the labia; ridge since it’s more towards the lips
The Cusps - Triangular Ridge
Slope you’ll find on posterior teeth (like molars), on the tongue side. For canines, this is known as the lingual ridge
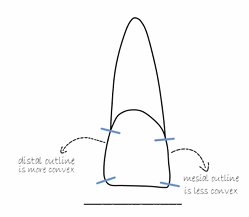
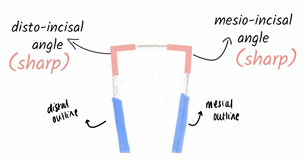
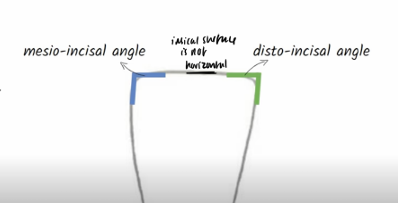
Describe morphology of Incisors (central/lateral, maxillary/mandibular)
slightly more rounded on distal side of incisal ridge
more angled on mesial side
apex of root usually curves distally
Describe morphology of maxillary lateral incisors
smaller than maxillary central incisor
crown and root are narrower mesiodistally (about 2mm narrower) in facial view compared to the central incisor
What is the contact points of maxillary lateral incisors?
mesially at the junction of the middle third and incisal third
distally, at the centre of the middle third
Describe morphology of maxillary central incisor
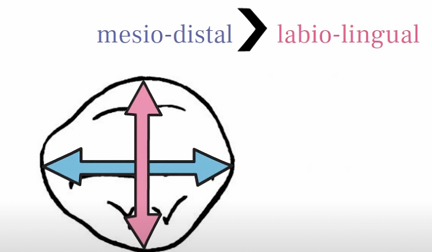
Generally wider labiolingually from the proximal view than the maxillary lateral incisor
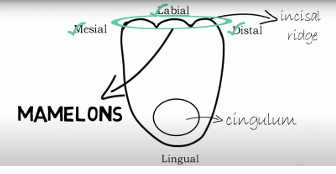
What are the 4 developmental lobes of maxillary central incisors?
facial aspect
lingual aspect
proximal aspect
incisal aspect
maxillary central incisors: facial aspect
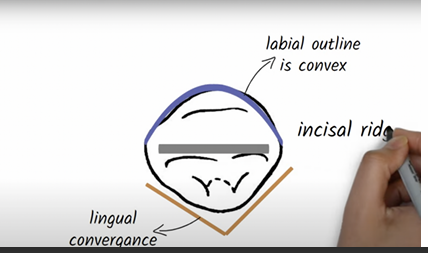
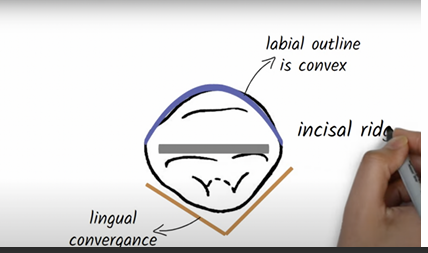
nearly straight incisal edge, mesially straight and while distally rounded
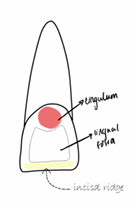
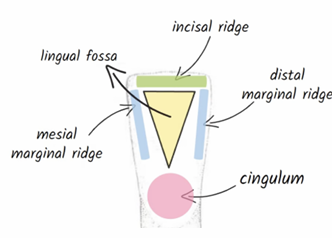
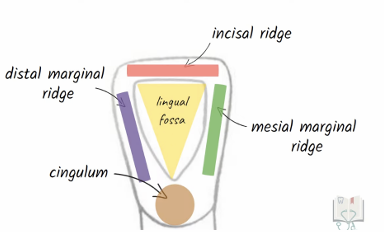
Development lobe of maxillary central incisors: lingual aspect
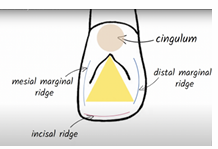
lingual fossa, cingulum and incisal edge
Development lobe of maxillary central incisors: Proximal aspect
mesial and distal aspect present a triangular outline
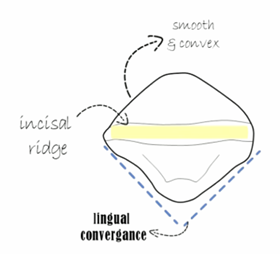
developmental lobes maxillary central incisors: incisal aspect
developmental lobes are the primary growth centers from which teeth form. Each tooth develops from multiple lobes that eventually fuse
Anterior Teeth (Incisors & Canines) – Typically develop from four lobes: three facial lobes and one lingual lobe (which forms the cingulum).
what are the 4 developmental lobes of maxillary lateral incisors?
mesial
labial
distal
lingual
developmental lobe of maxillary central incisor - lingual aspect
prominent marginal ridges and cingulum
developmental lobe of maxillary central incisor - proximal aspect
same as the central but the roots are longer
developmental lobe of lateral central incisor - Incisal aspect
narrower mesiodistally than the central but same thickness labiolingually, shaped more like a diamond
developmental lobe of maxillary lateral incisor - facial aspect
narrower mesiodistally than central and has more rounded incisal edge
what are 4 developmental lobes of mandibular central incisor?
3 facial and 1 lingual (form cingulum)
Development lobe of mandibular central incisor - facial aspect
smallest tooth in dental arch, long and narrow with straight incisal edge
Development lobe of mandibular central incisor - Lingual aspect
concave surface with small cingulum
mandibular central incisor - Proximal aspect
mesial and distal surface present a triangular outline
Development lobe of mandibular central incisor - Distal aspect
incisal edge is at right angle
Developmental lobe of mandibular lateral incisor - facial aspect
develops from four developmental lobes—three facial lobes and one lingual lobe (which forms the cingulum)
Developmental lobe of mandibular lateral incisor - lingual aspect
same as the central but has no symmetry
Developmental lobe of mandibular lateral incisor - proximal aspect
has a triangular outline
Developmental lobe of mandibular lateral incisor - incisal aspect
the edge is twisted from 90 degree angle
What are the 4 developmental lobes of canines?
3 facial one lingual (forms cingulam)
what are the functions of a canine?
cut food
lip support
canine guidance
labial contour
part of aesthetic quadrant
Discuss the size of roots and crowns of canines
Canines have particularly long and thick roots (labiolingually) that help to anchor them securely in the alveolar process
Mandibular canine CROWN is longer than maxillary canine crown
what is the longest tooth in each arch?
canines
……have the longest root and is the longest tooth in the mouth
maxillary canines have the longest root
What do canines have instead of a straight incisal ridge and what do they usually not have?
Rather than being straight, incisal ridge of canines is divided into two inclines: mesial and distal cusp ridge (also called cusp slopes or arms)
Don’t usually have mamelons but may have notch on either cusp ridge
From the facial view, what does the crown of canines resemble?
five-sided pentagon
which cusp ridge is shorter in canines?
mesial cusp ridge is shorter than distal cusp ridge
what is cusp slopes or cusp arms?
it is the incisal ridge of canines made by mesial and distal cusp ridges
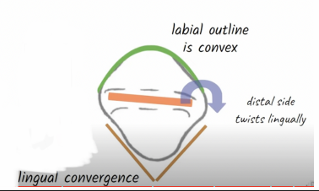
Talk about labial contour of maxillary and mandibular canines
Labial surface is convex with vertical labial ridge
Which teeth has buccal ridge?
premolars
which teeth are the only ones to have a labial ridge?
Canines
in which way is the measurement of the canine crown greater?
What shape are root cervix measurements labiolingually?
measurement of maxillary+mandibular canine crowns is greater (this applies to mandibular incisors as well) labiolingually than mesiodistally
Root cervix measurements are even more oblong labiolingually
what other teeth share the quality of having crowns that are greater in size labiolingually than mesiodistally?
Mandibular incisors
what are some canine traits that are similar to incisors?
similar contact points to most incisors a (except mandibular central incisor)
location of incisal edge wear, similar to incisors
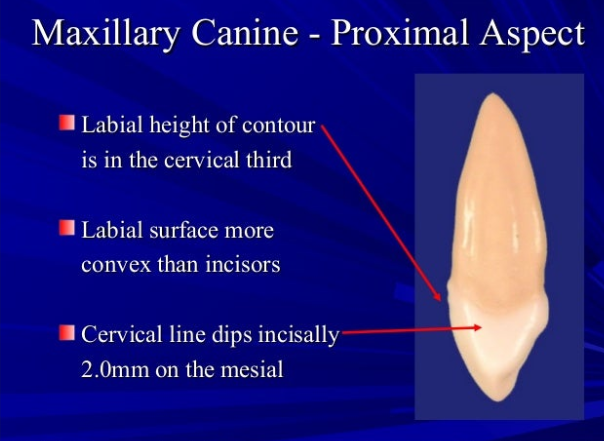
Where is the height of contour on facial and lingual surface of canines?
Both have height of contour at cervical third with the lingual having the contour end on the cingulum
From proximal view what is the shape of canine crowns?
wedge or triangular shaped
The crown outline is more…..on distal than on the mesial surface
convex
For canines the distal contact point is more…..than mesial contact area?
cervical
Where does tooth wear occur on canines?
location of incisal edge wear, similar to incisors
Where does facets form on mandibular canines, compared to maxillary canines?
Facets on mandibular canine cusp tip and cusp ridge usually form more on the labial border, not on lingual border as seen in maxillary canines.
Development lobe of maxillary canine: Facial aspect
1mm narrower than central incisor
distal cusp ridge is longer than mesial
smooth labial surface
maxillary canine: Lingual aspect
well developed cingulum with distinct distal and mesial marginal ridges
Development lobe of maxillary canine: Proximal aspect
mesial and distal aspect present triangular outline
Development lobe of maxillary canine: Incisal aspect
thicker labiolingually than mesiodistally
Development lobe of mandibular canine: facial aspect
narrower and shorter than upper but wider mesiodistally
Development lobe of mandibular canine: lingual aspect
less prominent marginal ridge and cingulum
Development lobe of mandibular canine: proximal aspect
mesial and distal aspect give a triangualr outline with less developed cingulum
Development lobe of mandibular canine: incisal aspect
mesiodistally shorter than labiolingually
function of upper premolars
initial mastication
maintain vertical dimensions of face (between nose and chin)
canine assistance in cutting food
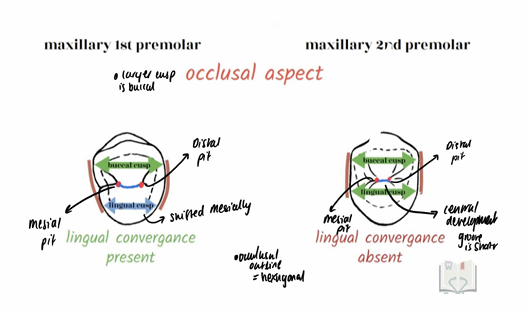
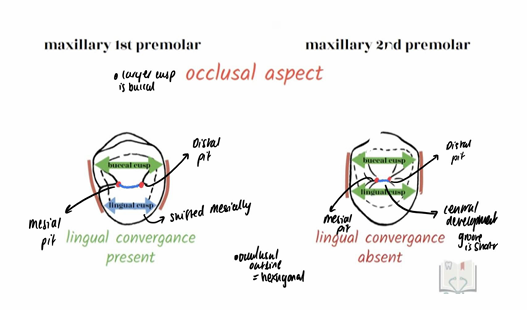
What separates buccal/labial (same as vestibular) cusp and lingual cusp in upper premolars?
two vertical ridges on sides (separating vestibular and lingual cusps)
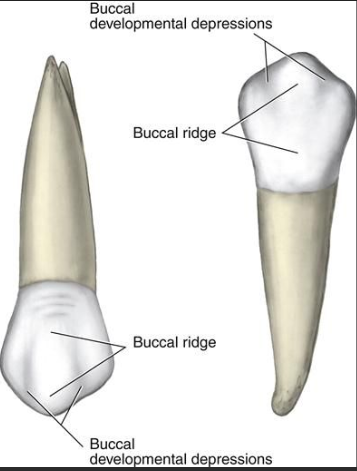
Describe the buccal cusp and buccal ridge of upper premolars?
Buccal cusp is long and buccal ridge extends down to base of tooth
Where is the highest points of upper premolars located on front and back surface?
On front - in cervical third
On back - in cervical third
What is the shape of the buccal surface of upper premolars and which does it resemble?
Rounds buccal surface and resembles canines
what is the widest part of upper premolars?
the middle cervical thirds
From which side is the crown narrower in upper premolars?
Crown narrower towards bottom from buccal/labial side (same as vestibular side)
where is upper premolars located?
between molars and canines
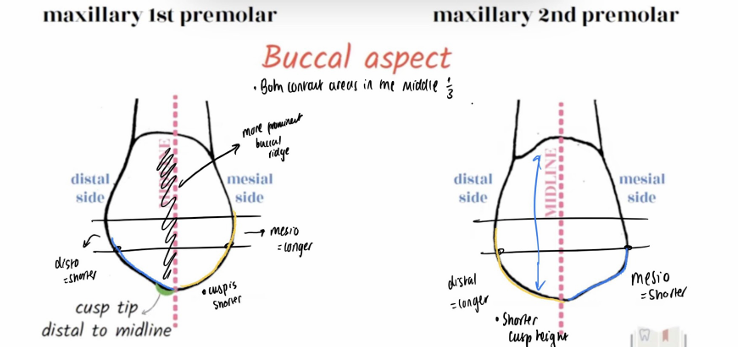
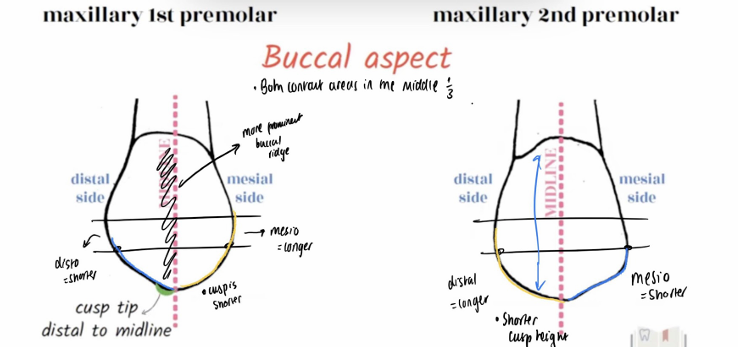
In which of the upper premolars is the buccal ridge more prominent in?
Buccal ridge more prominent on first premolar
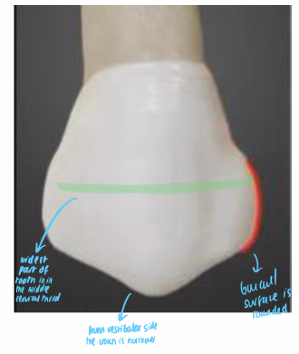
In which of the upper premolars is the buccal cusp longer?
First upper premolars have a longer and sharper buccal cusp
in second upper premolar it is more obtuse and less pointed
Which cusp ridge is shorter and longer in second upper premolars?
Shorter mesial cusp ridge than distal cusp ridge
Which cusp ridge is shorter and longer in first upper premolars?
Longer mesial cusp ridge than distal cusp ridge
What are the contact points of upper premolars?
Mesial contact in middle third
Distal contact, slightly more cervical, still middle third
In which of the upper premolars is the crown larger and in in which is the roots longer?
Crown is larger in first premolar
Root is longer in second premolar
Which way do the roots of upper premolars bend and at what end?
Can bend distally at apical end, but can also be straight
Which tooth has the greatest root-to-crown ratio among maxillary teeth?
second upper premolar (1.8/1)
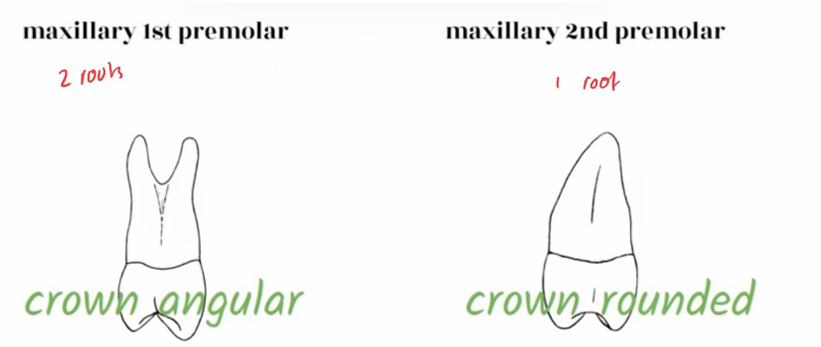
How many roots does second upper premolar have?
one root
How many roots does first upper premolar have?
two roots
What do both the type of upper premolars have in common in terms of their roots?
Both first and second premolar roots taper narrower to the lingual
Which one of the upper first premolars roots is shorter?
Lingual root of the first upper premolar is shorter than the buccal root
Which marginal ridge is more cervical in both types of upper premolars?
Distal marginal ridge
Towards the mesial of whats axis line is the peaks of the lingual cusps of both types of upper premolars facing?
The peaks of both premolar’s lingual cusps are consistently positioned to the mesial of the mid-root axis line
What is the difference in how the mesial and distal ridges of lingual cusp meet in first and second upper premolars?
Mesial and distal ridges of lingual cusp of first premolar meet at somewhat rounded angle
On second premolar the tip of lingual cusp is relatively sharp
Is the lingual cusp longer or shorter than buccal in upper premolars?
lingual cusp shorter than buccal cusp (especially on first premolar)
Lingual cusp and buccal cusp nearly same length on second premolar
Is there a difference in the average length between buccal and lingual cusp peaks of first and second premolar?
Average distance between buccal and lingual cusp peaks of first and second premolar is about the same
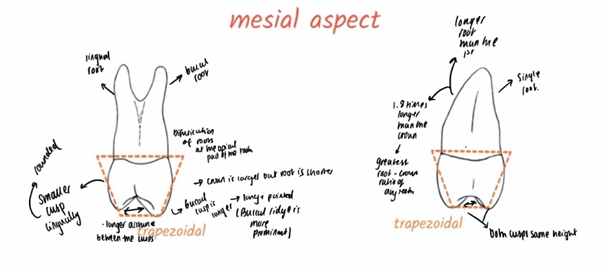
From proximal and lingual aspect, is the buccal or lingual cusp longer in first upper premolar?
what about in second upper premolar?
The buccal cusp is longer than lingual
In second upper premolar, both cusps are nearly equal in length
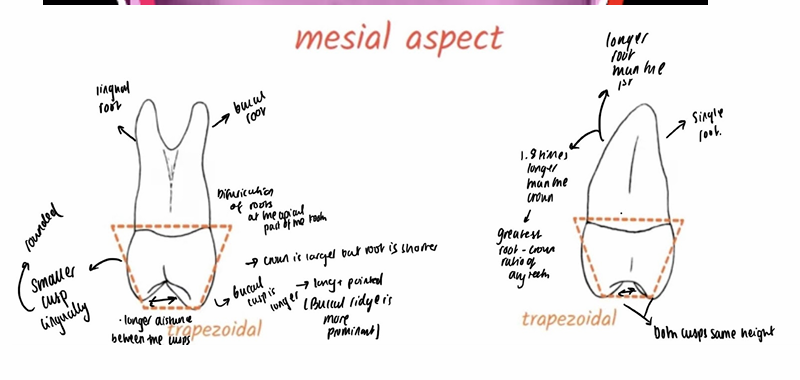
When viewed from proximal aspect what is the shape of the upper premolars?
What does the shape consist of?
both upper premolars resemble trapezoid when viewed from proximal angle
Trapezoid features two parallel sides and two nonparallel sides
In what aspect do upper premolars show distinctive concavity and where does it extend to?
Mesial aspect has distinctive concavity in cervical third that extends onto root
Is it the first or second upper premolar that has developmental depression on the distal aspect?
First upper premolar
What is a distinctive feature of upper premolars?
mesial marginal developmental grooves
Do upper premolars have well defined buccal and lingual cusps?
yes
What are the contact points of the upper premolars?
Mesial contact - near junction of buccal and middle third
Distal contact - middle third
Compare the difference in sizes of cusp ridges of upper second and first premolars
Second premolar has symmetrical occlusal outline so most mesial and distal cusp ridge is even
First premolar the mesial cusp ridge is longer than distal cusp ridge
Describe the shape of the buccal outline of first upper premolars?
Rounded and almost V-shaped
Mesiodistally is the lingual half of upper premolars (especially seen in first premolars) wider or narrower?
Lingual half is narrower mesiodistally
What is the outline of the crowns of both the upper premolars?
oblong