Comprehensive Guide to Meiosis, Genetics, and Cell Division
1/44
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
45 Terms
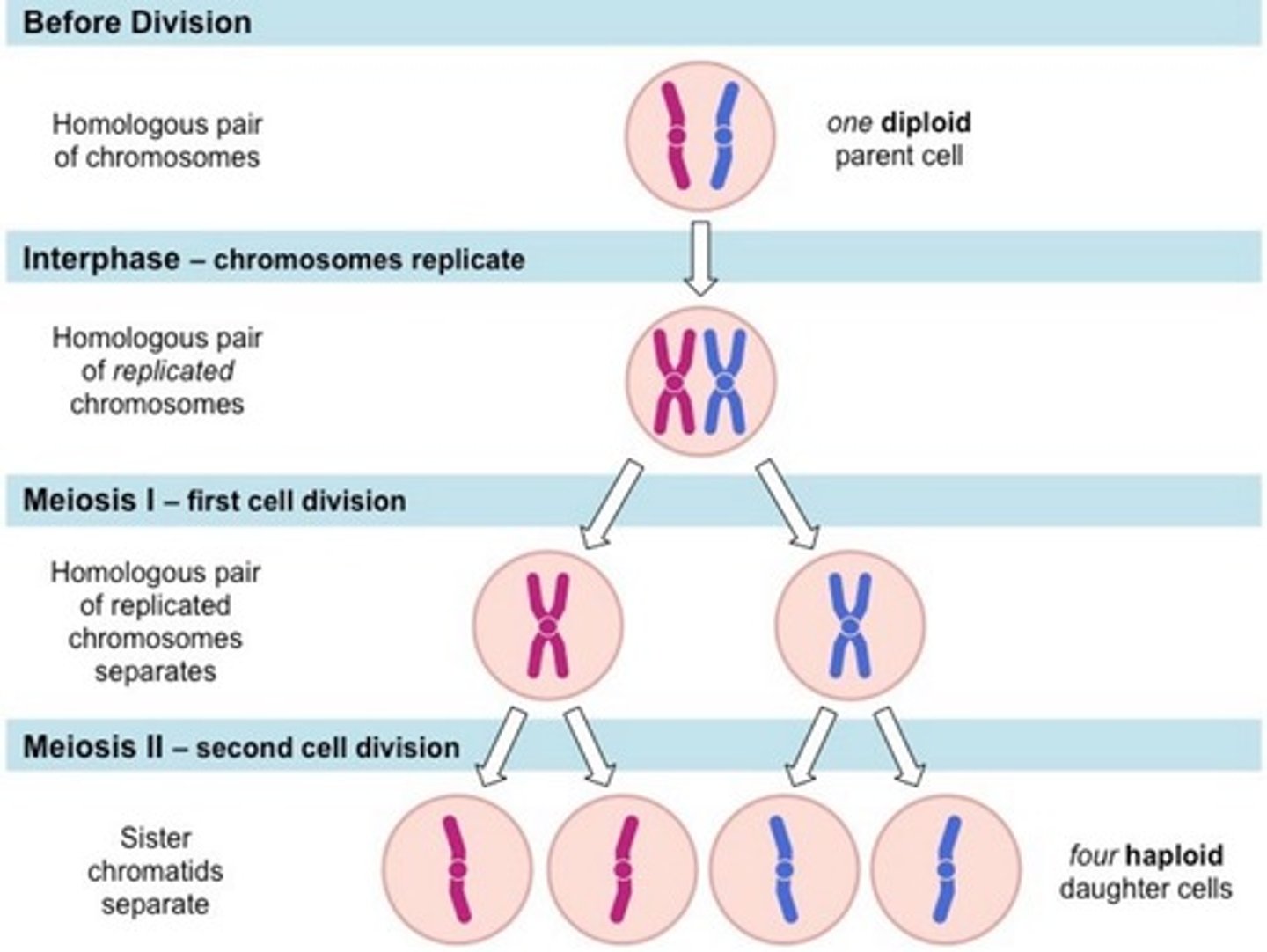
Meiotic division
Conversion of diploid (2N) to haploid (N) gametes.
Heredity
Transmission of hereditary units (genes) from one generation to next.
Variation
Inherited differences among individuals of the same species.
Chromosomes
Functional units of heredity located in the eukaryotic nucleus, comprised of strands of DNA.
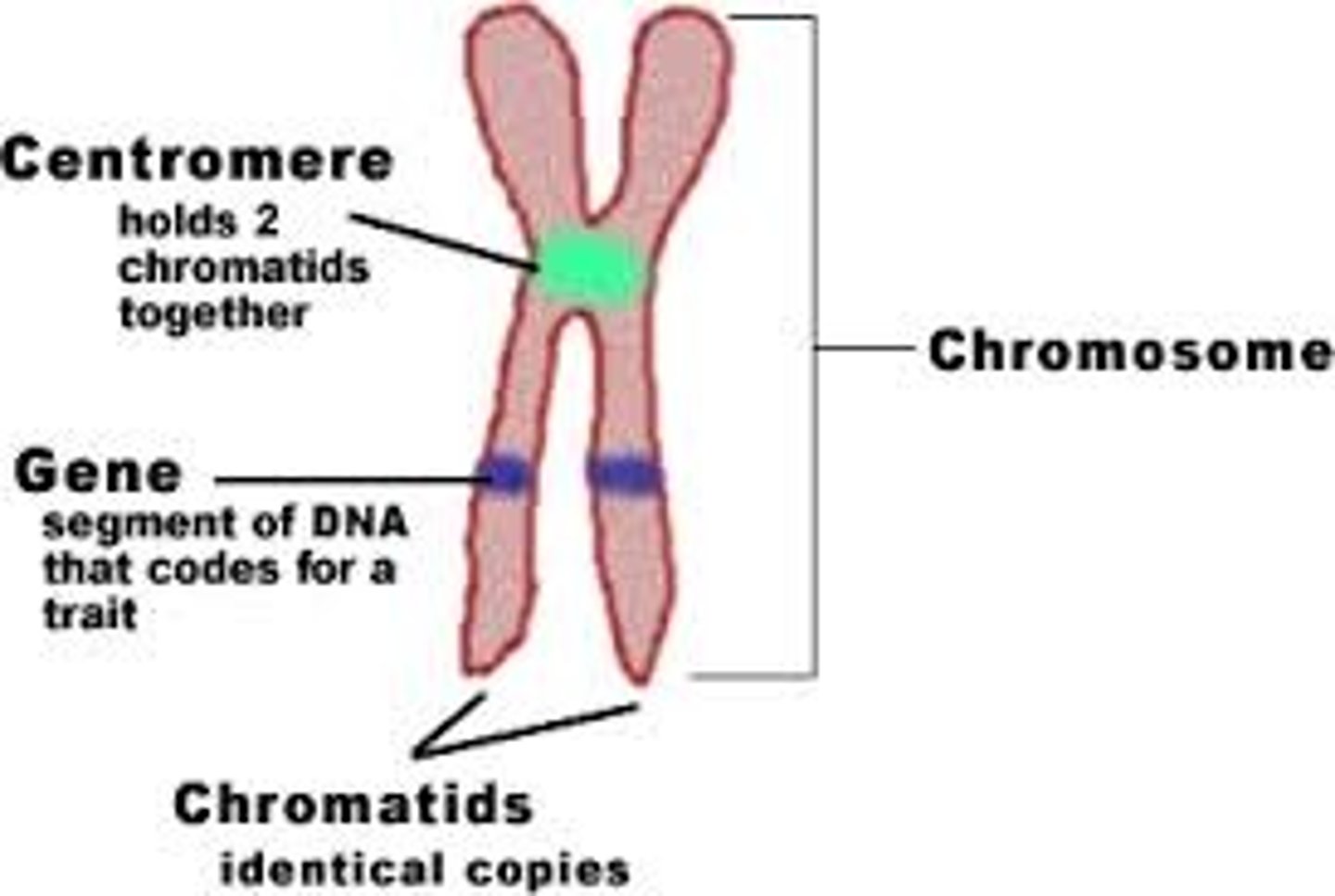
Gene
A sequence (series) of nucleotides that may include hundreds of thousands of nucleotides and associated proteins.
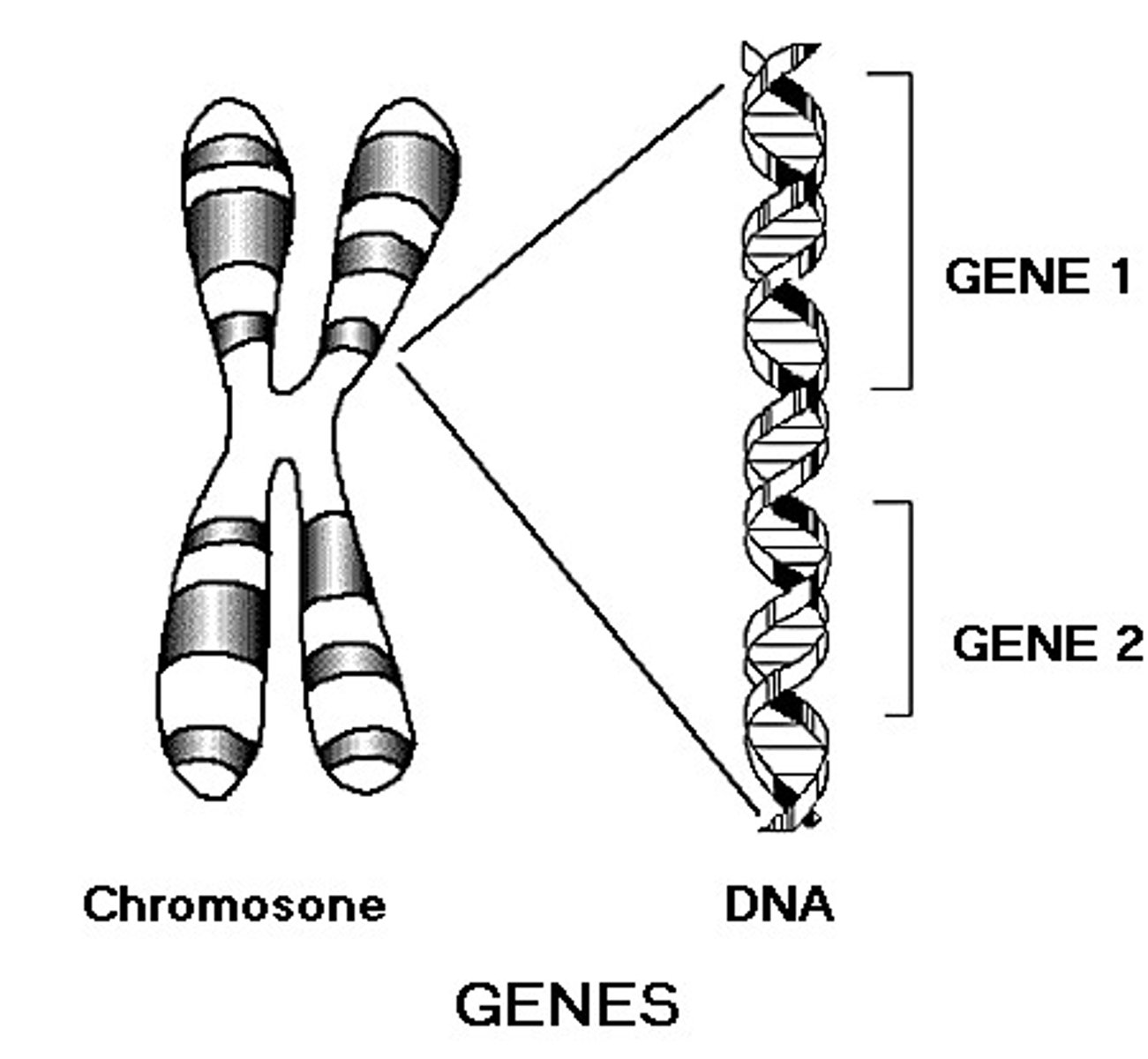
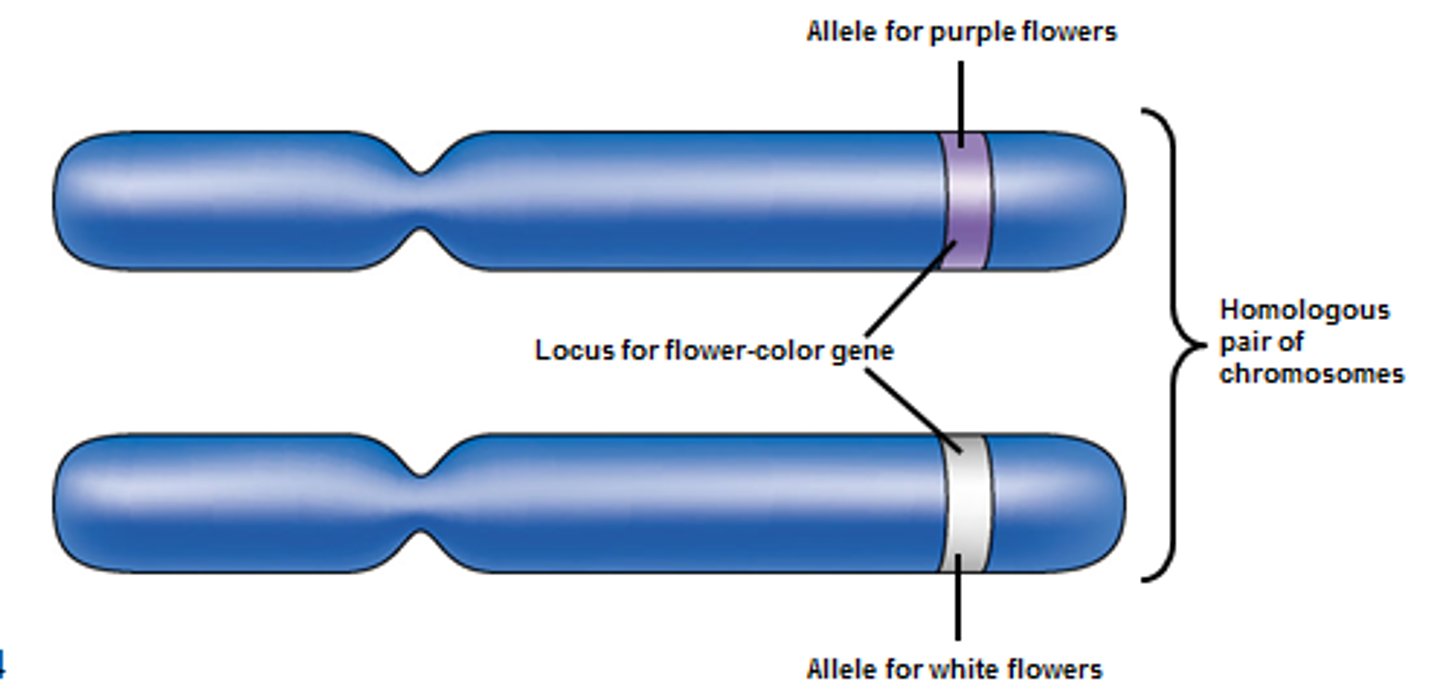
Locus
Exact position of the gene along the strand of DNA.
Asexual Reproduction
Reproduction involving one parent, resulting in genetically identical offspring (except mutations).
Sexual Reproduction
Reproduction involving two parents, resulting in large genetic variability among offspring.
Genetic Variation
Caused during sexual reproduction by meiosis, which is the specific division resulting in haploid gametes.
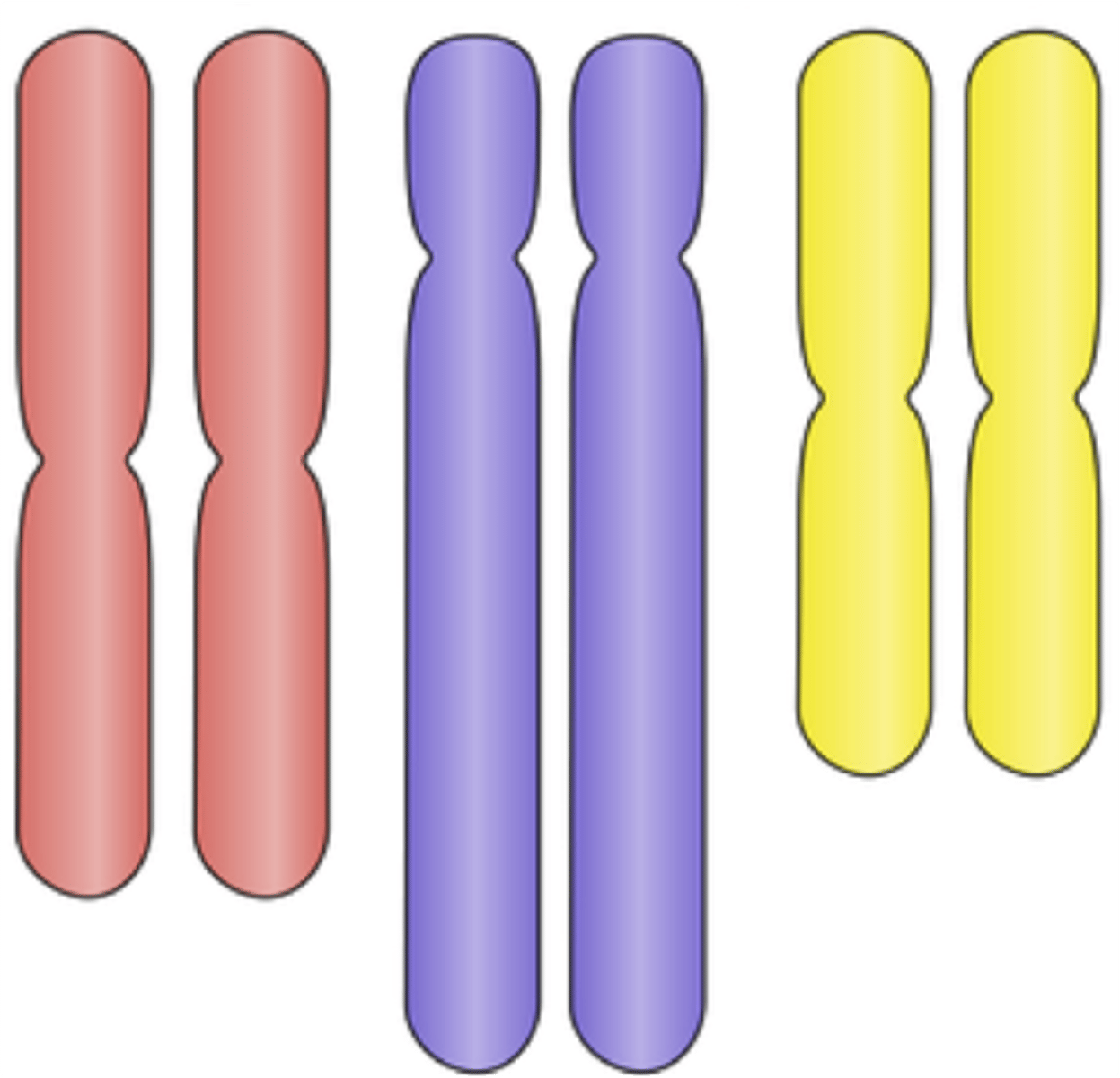
Diploid (2N)
Cells that contain two complete sets of chromosomes, one from each parent.
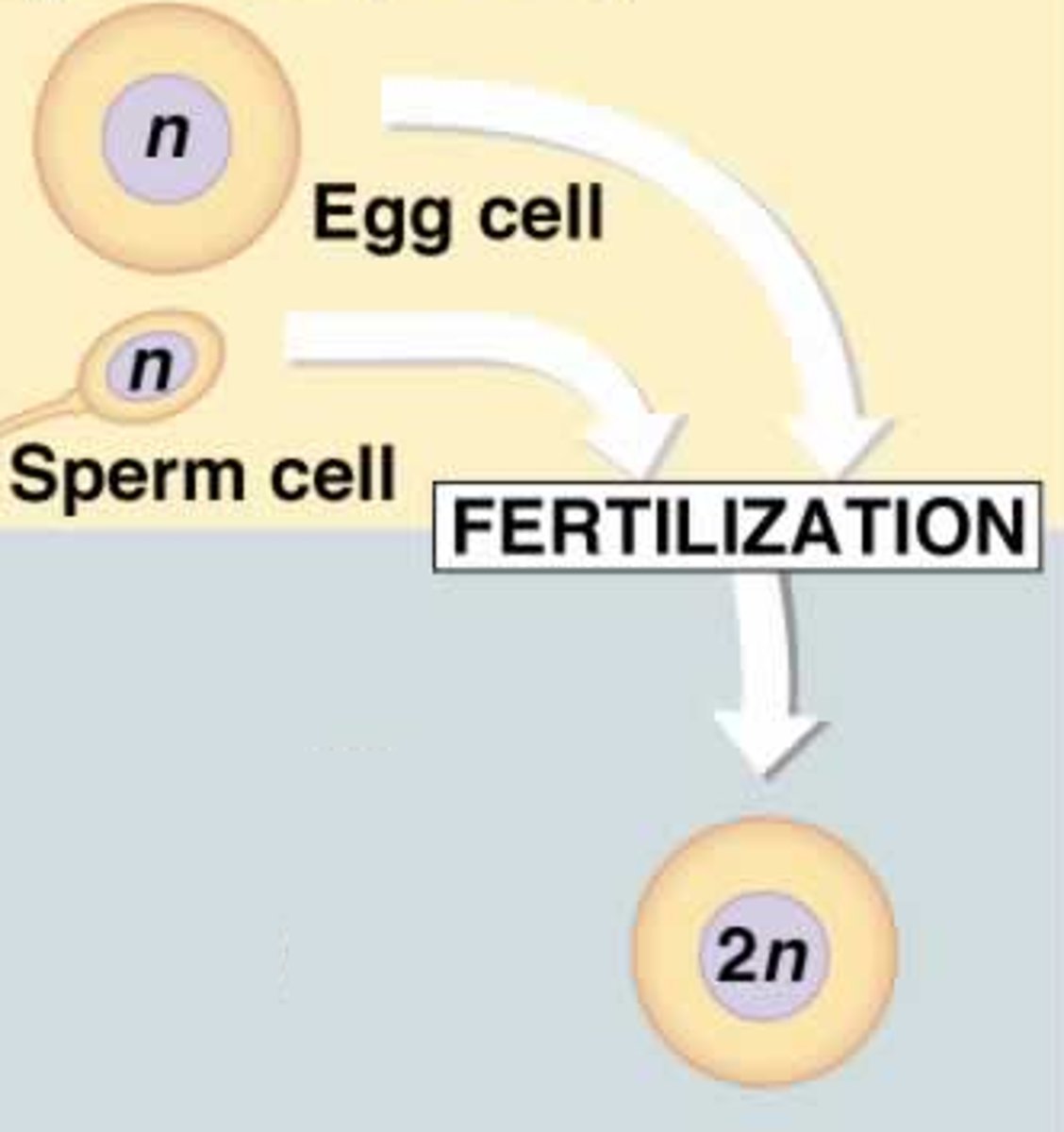
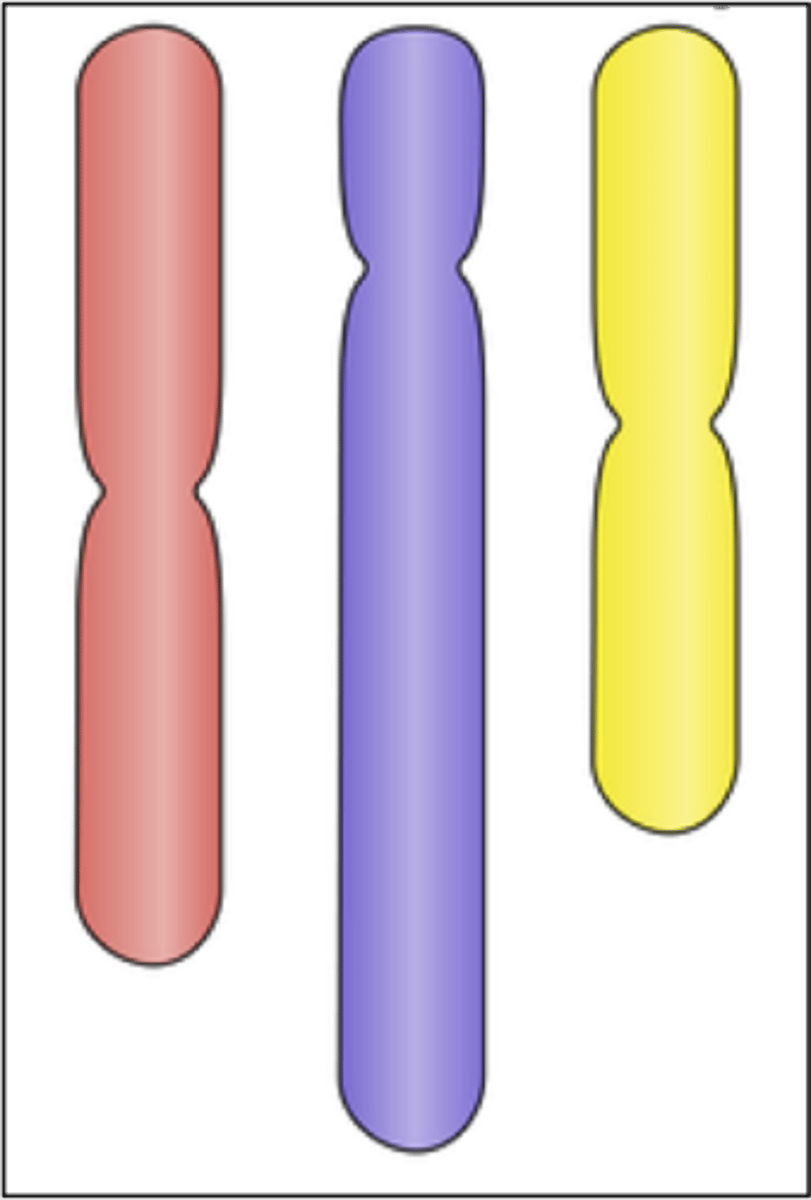
Haploid (N)
Cells that contain one complete set of chromosomes.
Fertilization
Restores diploid (2N) number of chromosomes by fusing haploid (1N) gametes to form a diploid (2N) zygote.
Zygote
The diploid cell formed by the fusion of haploid gametes during fertilization.
Mitosis
The process by which a cell divides to produce genetically identical diploid cells.
Cytokinesis
The process that follows mitosis, resulting in the division of the cytoplasm and formation of two daughter cells.
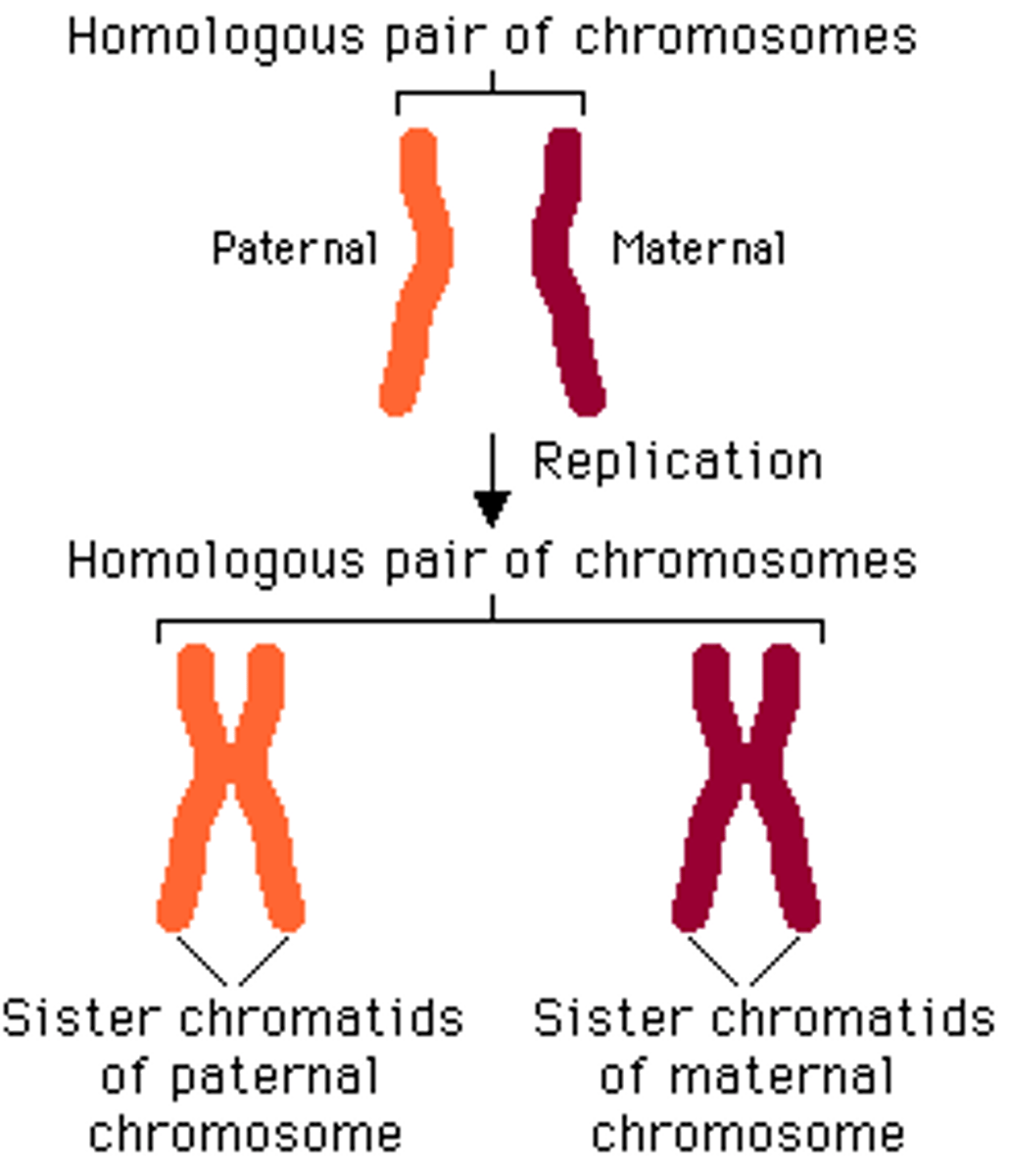
Homologous DNA
Molecules of DNA that are comparable in size and form, containing genes for the same trait at the same locus.
Maternal Origin
Refers to one member of a homologous chromosome pair that is inherited from the mother.
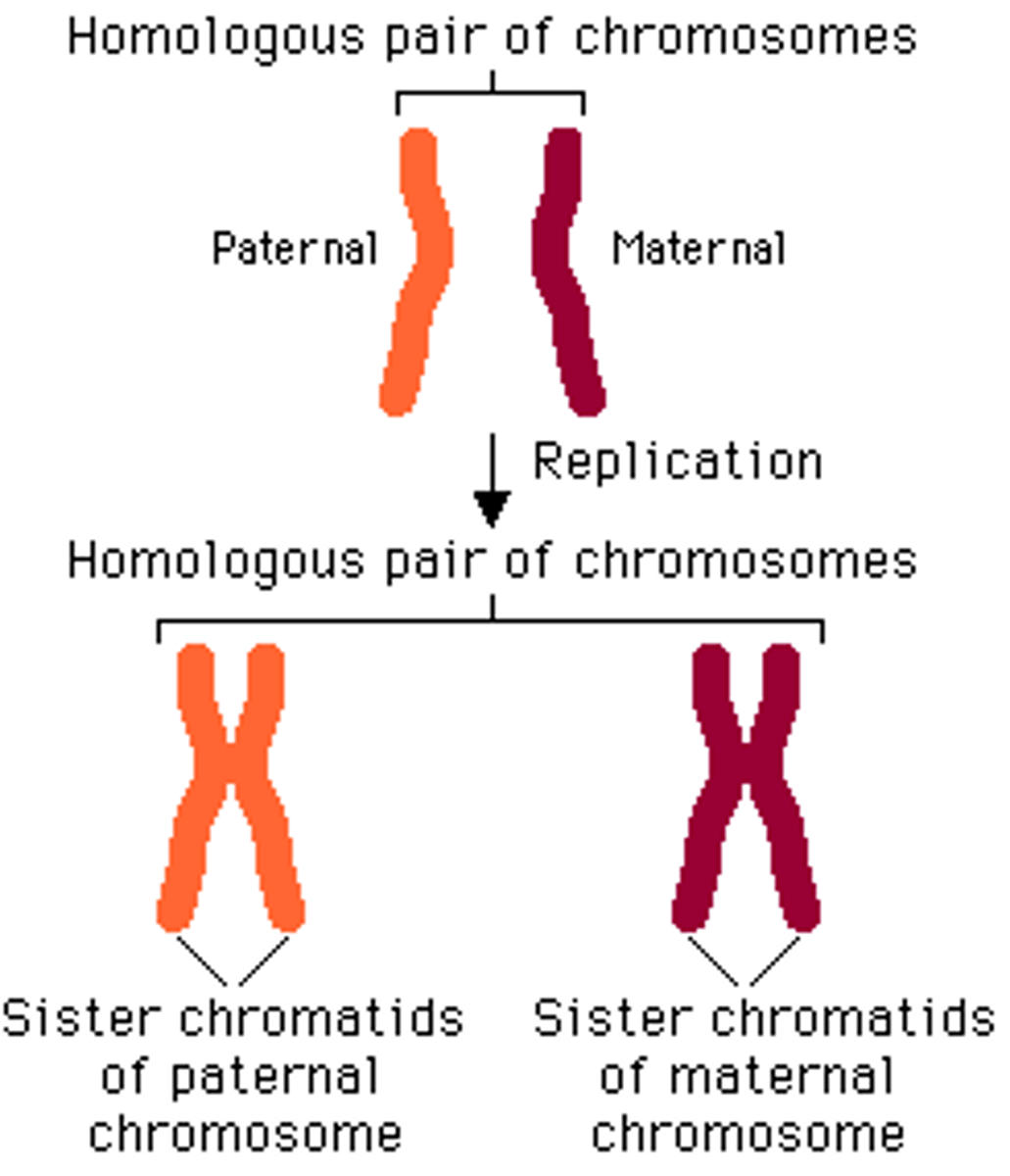
Paternal Origin
Refers to one member of a homologous chromosome pair that is inherited from the father.
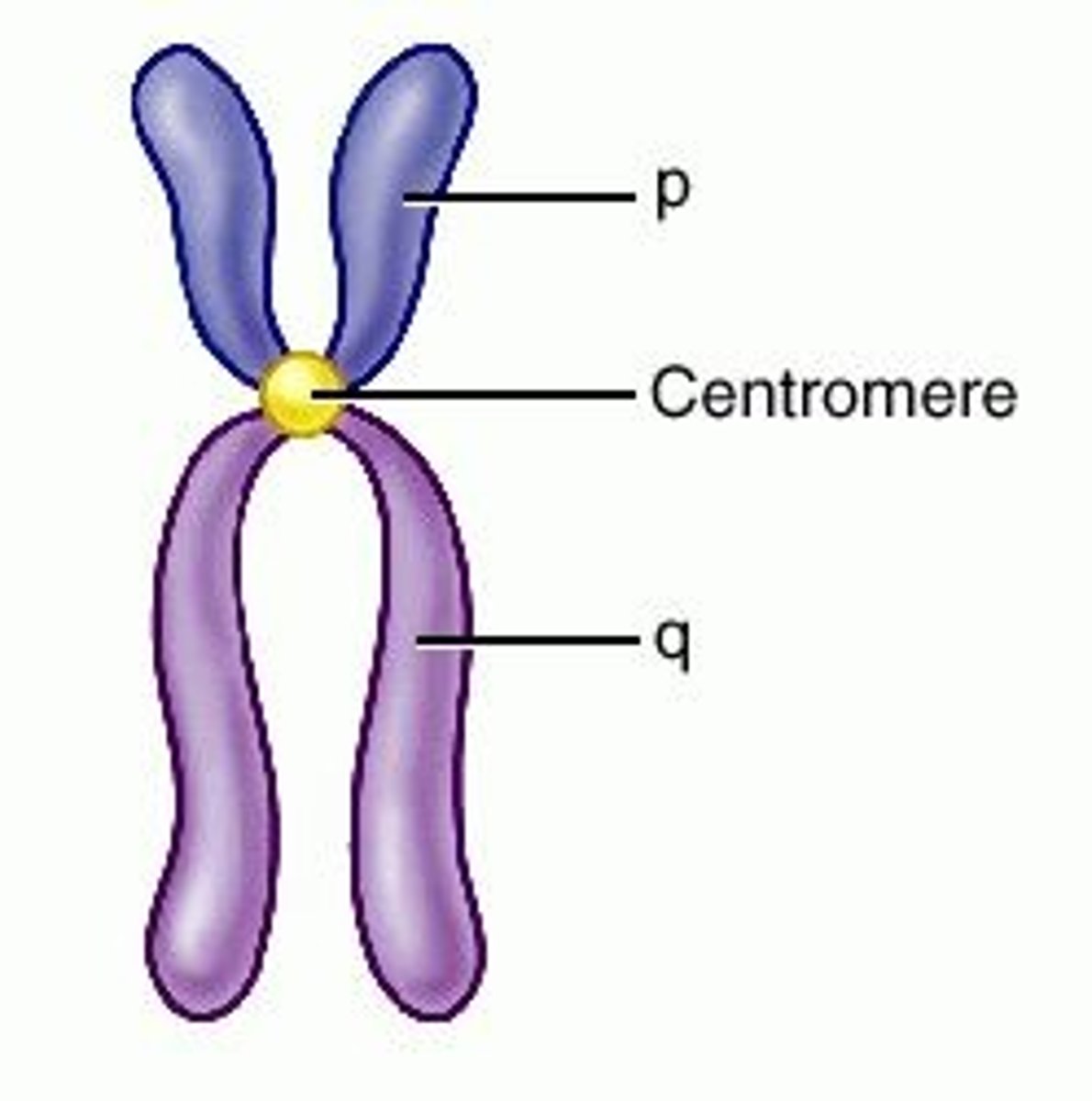
Centromere
The region of a chromosome where two sister chromatids are joined.
Color-stain banding pattern
A characteristic pattern observed in chromosomes that helps identify homologous pairs.
Interphase
Exact same conditions as the starting point of Mitosis.
Nuclear membrane
Complete during Interphase.
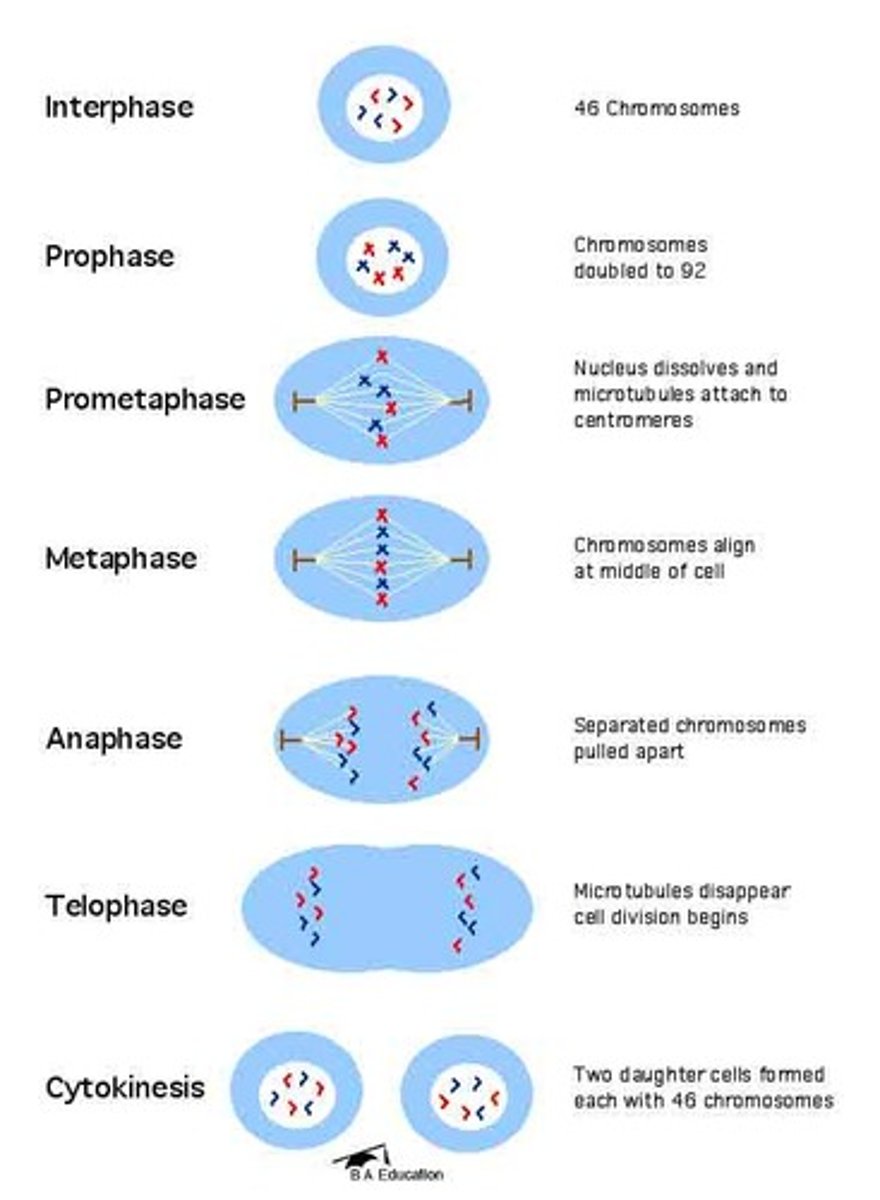
DNA
In chromatin form during Interphase.
Centrioles
Begin to appear in cytoplasm during Interphase.
Meiosis I
The first division in meiosis, consisting of Prophase I, Metaphase I, Anaphase I, and Telophase I.
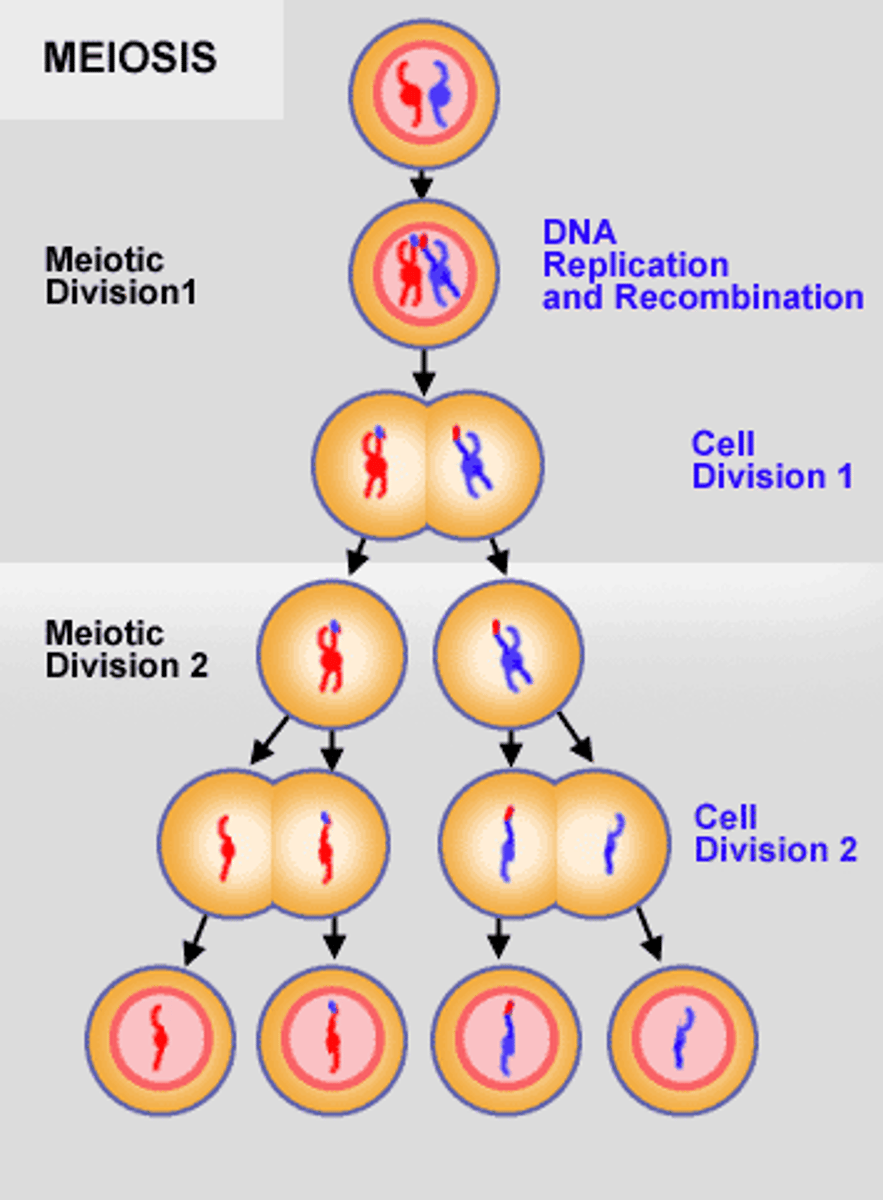
Prophase I
Nuclear membrane begins to dissociate; centrioles migrate toward poles; DNA undergoes duplication and condensation into chromatids.
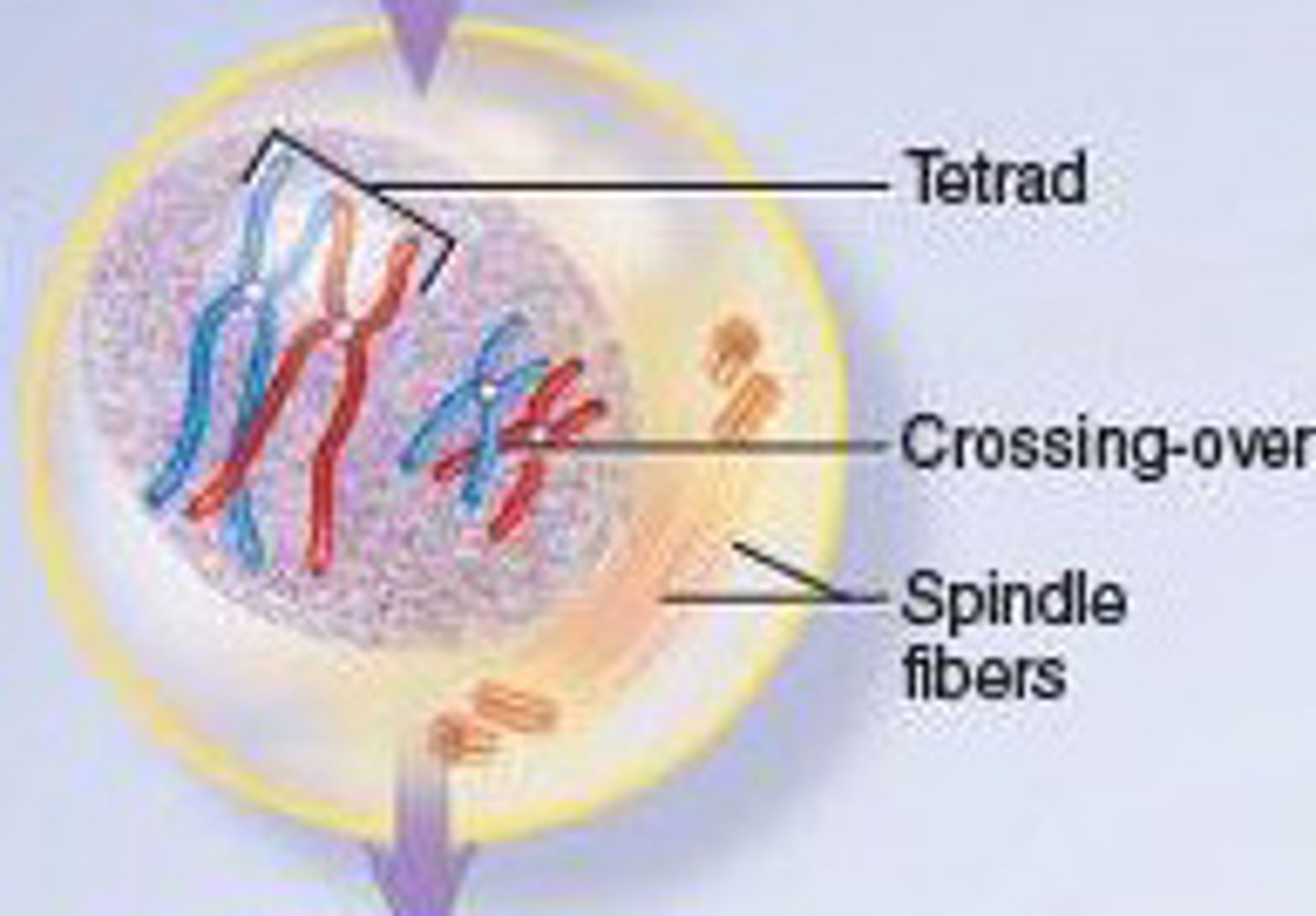
Synapsis
Opposite homologues, in chromatids form, closely wound together, each unit known as a tetrad.
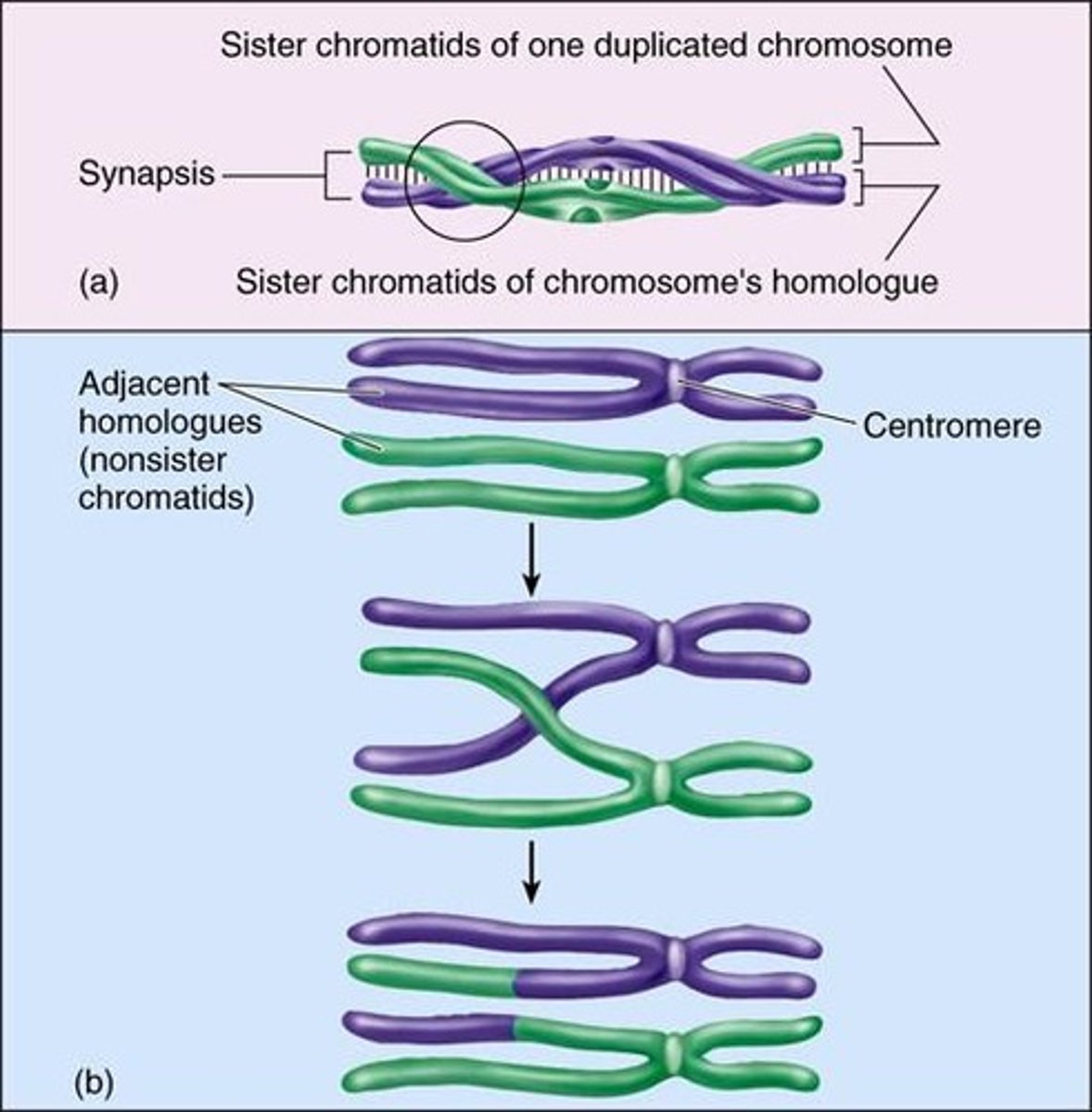
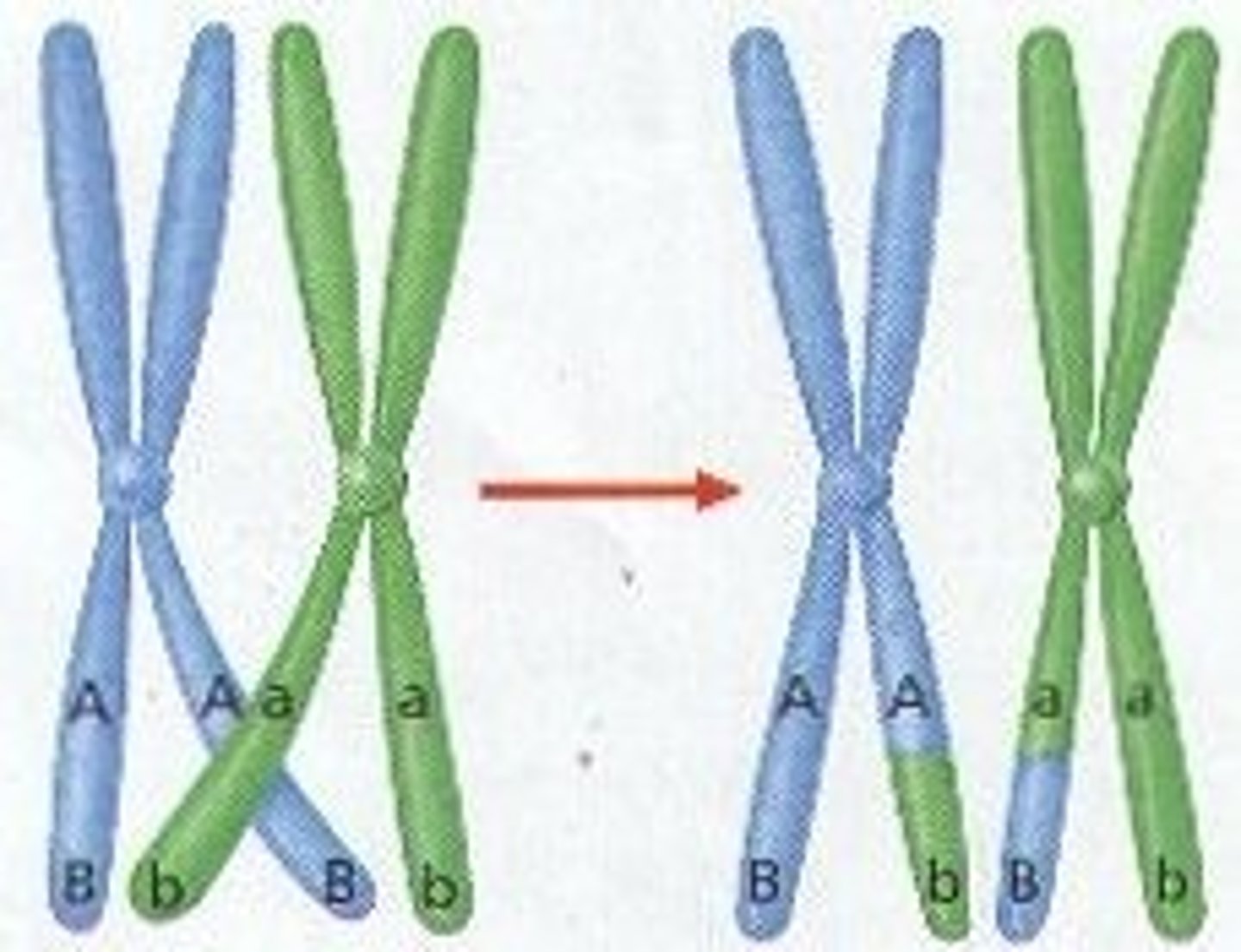
Crossing over
Bonds among nucleotides de-stabilize, allowing tips of chromatids to break off and exchange positions.
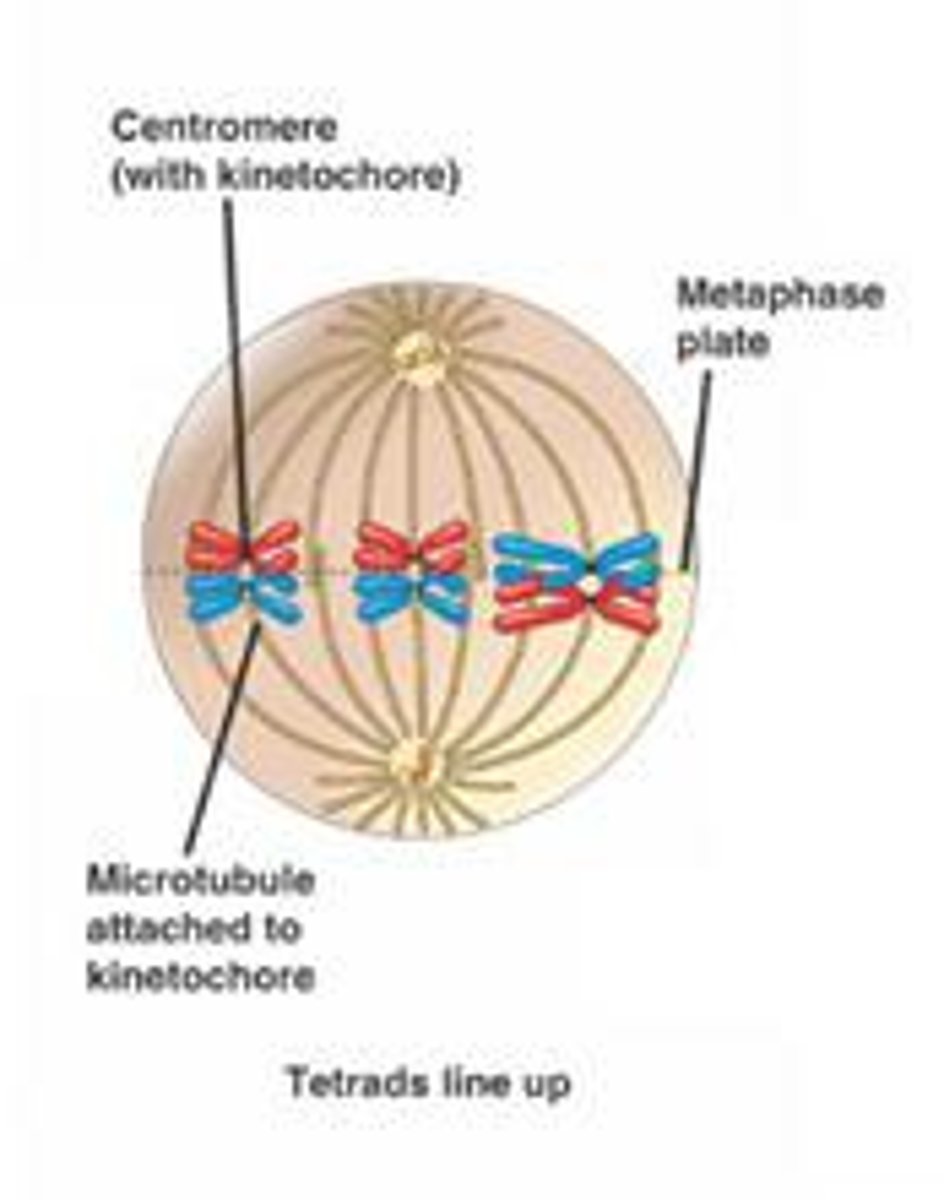
Metaphase I
Nuclear membrane is fully dispersed; DNA is in chromatid form; tetrads are suspended by spindle fibers.
Anaphase I
Contraction of spindle fibers separates homologues; synapsis is lost.
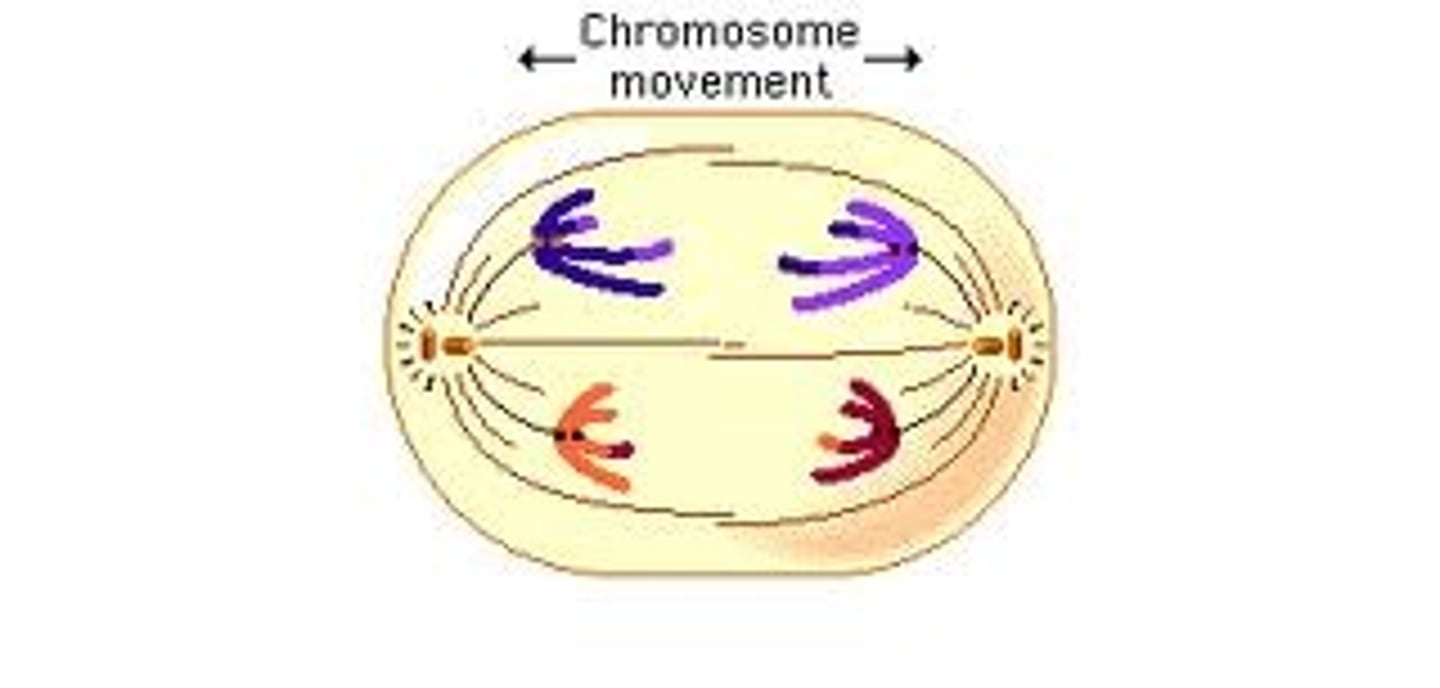
Telophase I
Cytokinesis occurs; nuclear membranes re-form in 2 new cells.
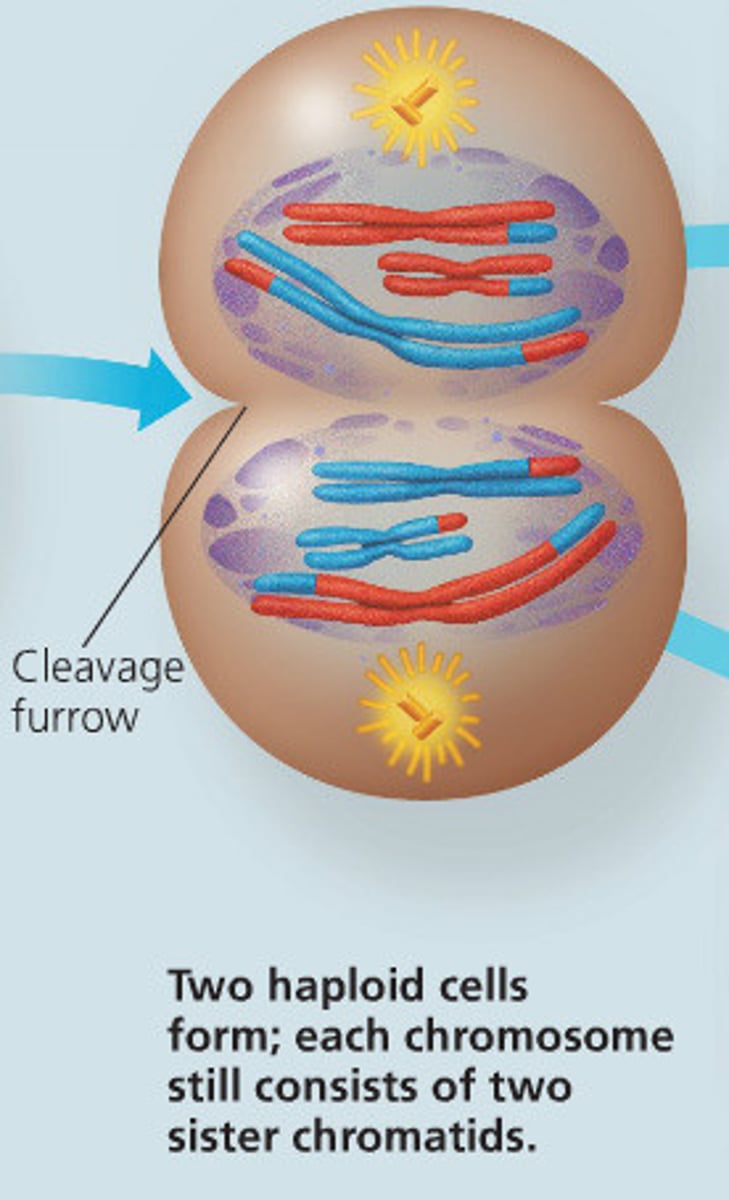
End results of Meiosis I
Homologues are separated; cells are haploid.
Meiosis II
There is no interphase between Meiosis I and Meiosis II; it is a mitotic-type of division.
Prophase II
Cleavage furrow pinches off, producing 2 new cells containing chromatids that have undergone crossing over.
Metaphase II
Chromatids migrate to the equatorial plane.
Anaphase II
Contraction of spindle fibers separates chromatids; first appearance of chromosomes.
Telophase II
Cleavage furrow separates development of 2 new cells; each new cell is now haploid.
Unique events in meiosis
Include synapsis, crossing over, and random separation of homologues during Anaphase I.
Possible orientations
223 possible orientations during random separation of homologues.
Meiotic events contributing to variation
Crossing over and random separation of homologues at Anaphase I.
Comparison of Mitosis & Meiosis
Mitosis is for growth and regeneration; Meiosis is for reduction division.
Resulting Cells in Mitosis
2 genetically identical 2N somatic cells.
Resulting Cells in Meiosis
4 haploid gametes.
Type of Cells in Mitosis
Somatic daughter cells.
Type of Cells in Meiosis
Germ cells or gametes.