Genetics E1- Congenital Abnormalities
1/28
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
29 Terms
What term refers to the formation of a human being?
Morphogenesis
What stage of embryotic development is from fertilization to implantation?
Pre-embryonic
What stage of embryonic development is from implantation through gestational week 8?
Embryonic
What stage of embryonic development is from week 8 through birth (parturition)?
Fetal
What is a morula?
Solid ball of cells (16-32 cells) formed after zygote undergoes rapid cellular division (cleavage) 3-4 days after fertilization
What is a blastocyst?
Hollow sphere in the morula from fluid accumulation that consists of a clump of cells (inner cell mass or ICM) & a ring of flattened cells (trophoblast)
What part of the blastocyst eventually becomes the embryo?
ICM
What part of the blastocyst further develops into the embryonic portion of the placenta that supplies nutrients to & removes wastes from the embryo?
Trophoblast
When does implantation of the blastocyst to the uterine wall occur?
6-7 days after fertilization
What prevents implantation from occurring?
*unimplanted blastocysts are absorbed by endometrium or expelled during menstruation
Endometrial infx, IUD, morning after pill, certain genetic mutations
What occurs by day 14 after fertilization if implantation does occur?
Endometrium grows over blastocyst → endometrial cells produce paracrines such as PGs to promote local changes in endometrial tissue
After the amnion is formed from a layer of separated cells from the ICM, what do the cells of the ICM then differentiate into?
*marks the beginning of organogenesis
3 distinct germ layers: ectoderm, mesoderm, & endoderm
What is the study of abnormal development?
Teratology
What are teratogens?
Anything capable of disrupting embryonic or fetal development & producing malformations
What is the critical period for teratogenic effects?
3-16 weeks of gestation
What teratogen was used to treat morning sickness in the 1950s but was removed from the market due to causing phocomelia?
Thalidomide
What is phocomelia?
Shortened limbs resembling flippers of a seal due to lack of some or all of the long bones in a fetus
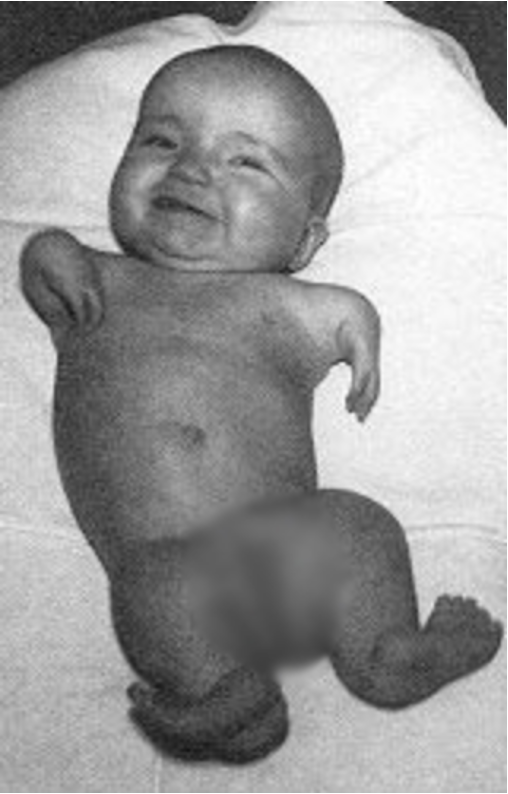
What teratogen is used for the treatment of cystic acne but can cause fetal malformations involving the cranium, face, heart, CNS, and thymus?
Isotretinoin
What is required when a patient is starting Isotretinoin (Accutane)?
hCG before initiation & periodically, and must use 2 forms of birth control
What 5 congenital infections have similar presentations, including rashes, ocular findings, microcephaly, hydrocephalus, and abnormally shaped gyri & sulci?
TORCH: Toxoplasmosis, Other (syphilis), Rubella, CMV, HSV
What virus is an arthropod-borne flavivirus that is transmitted sexually & by mosquitoes and causes miscarriage, microcephaly, developmental delays, myelitis, meningoencephalitis, & GBS?
Zika virus
What abnormalities are seen with fetal alcohol syndrome?
Growth retardation, CNS dysfunction, mental deficiency, emotional disorders, & characteristic facial dysmorphology such as short palpebral fissure length, smooth philtrum, & thin upper lip

Why is the term fetal alcohol effect also used to describe fetal alcohol syndrome?
Not all children adversely affected by maternal alcohol abuse exhibit the entire spectrum of abnormalities
What risks are associated with smoking while pregnant?
Low birth weight (2x risk), SGA newborn (2.5 fold), subfertility, spontaneous abortion, placenta previa & abruption, and preterm delivery
What causes most of the adverse effects to the offspring with maternal cocaine use?
Vasoconstrictive & hypertensive effects of the drug
What is the MC cocaine-related pregnancy complication?
Placental abruption
What causes an isolated limb-reduction defect (ex- absence of a hand)?
Disruption of vascular supply at a critical time during the development of the limb bud
What are 3 factors known to affect the likelihood and extent of teratogenesis?
Dosage, time of exposure, & genotype of the embryo
What is the leading preventable cause of acquired intellectual disability?
Fetal alcohol syndrome