practical 3
1/11
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
12 Terms
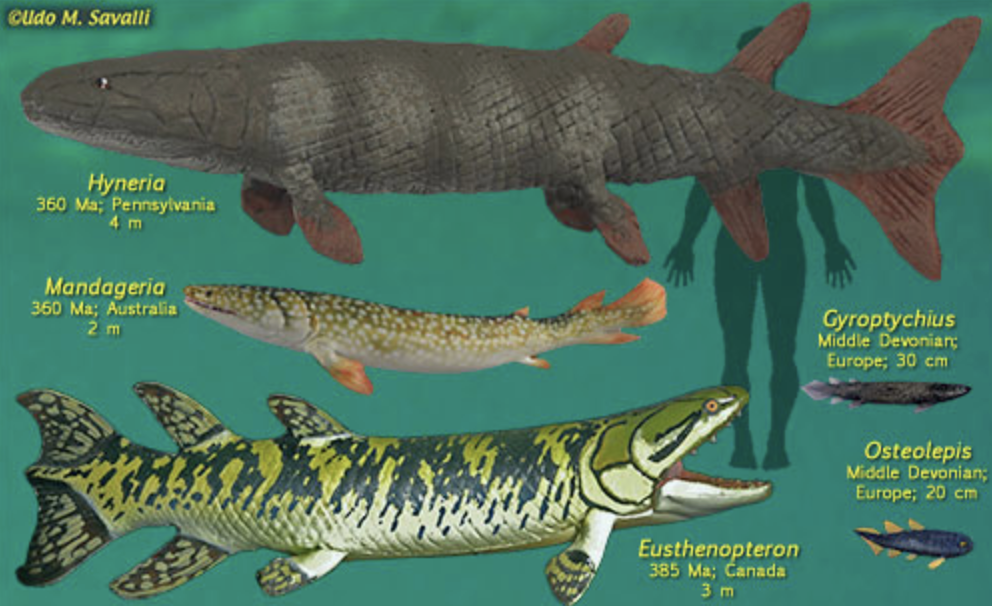

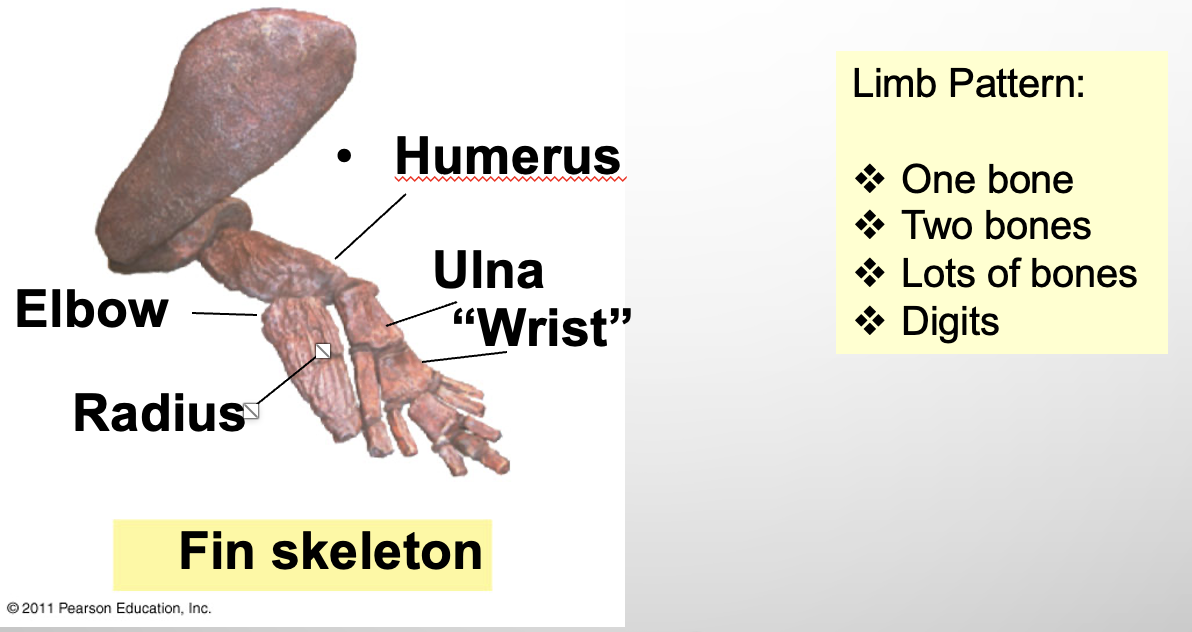
Lungfishes (in lobed finned fish category)
SYNAPOMORPHY= LOBED FINS ??
humans and tetrapods share a common ancestor
humans share a similar limb pattern as lungfishes
one long bone, two bones, wrist, digits
lungfishes are more closely related to humans than other animals
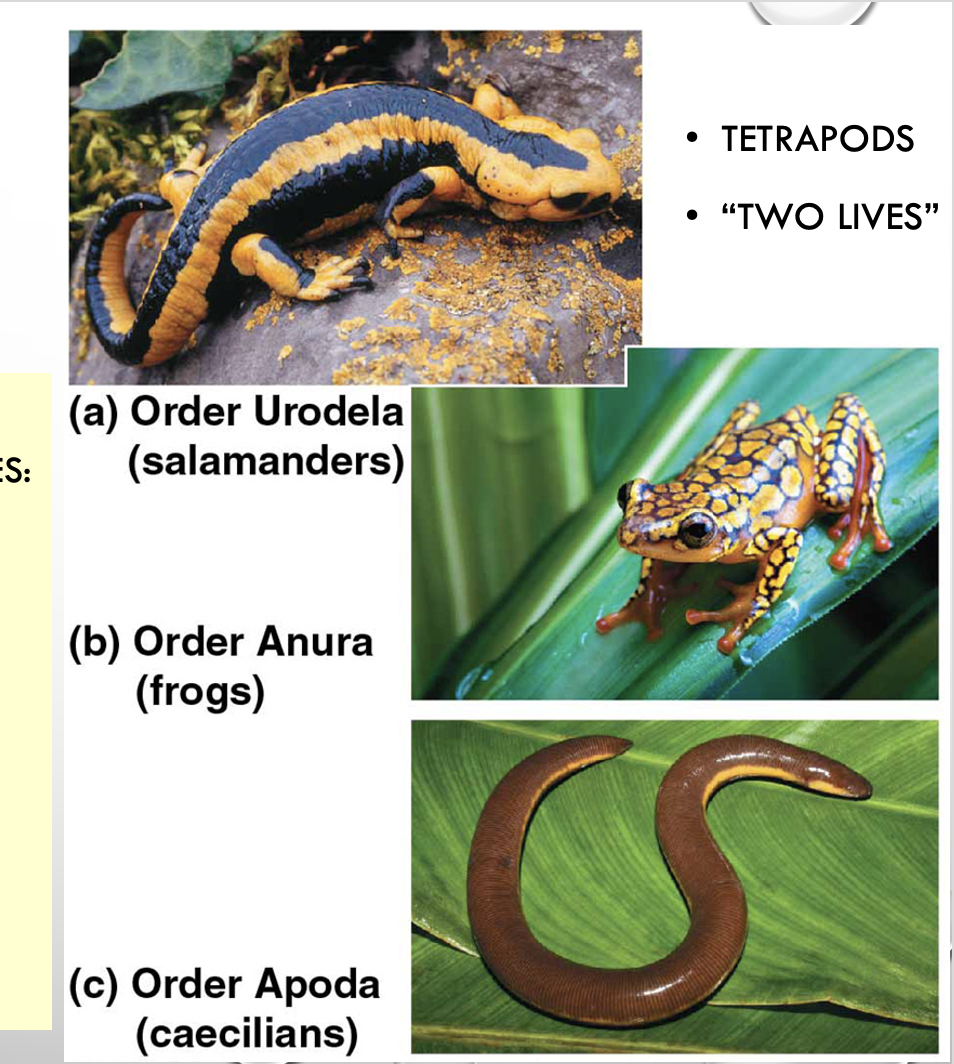
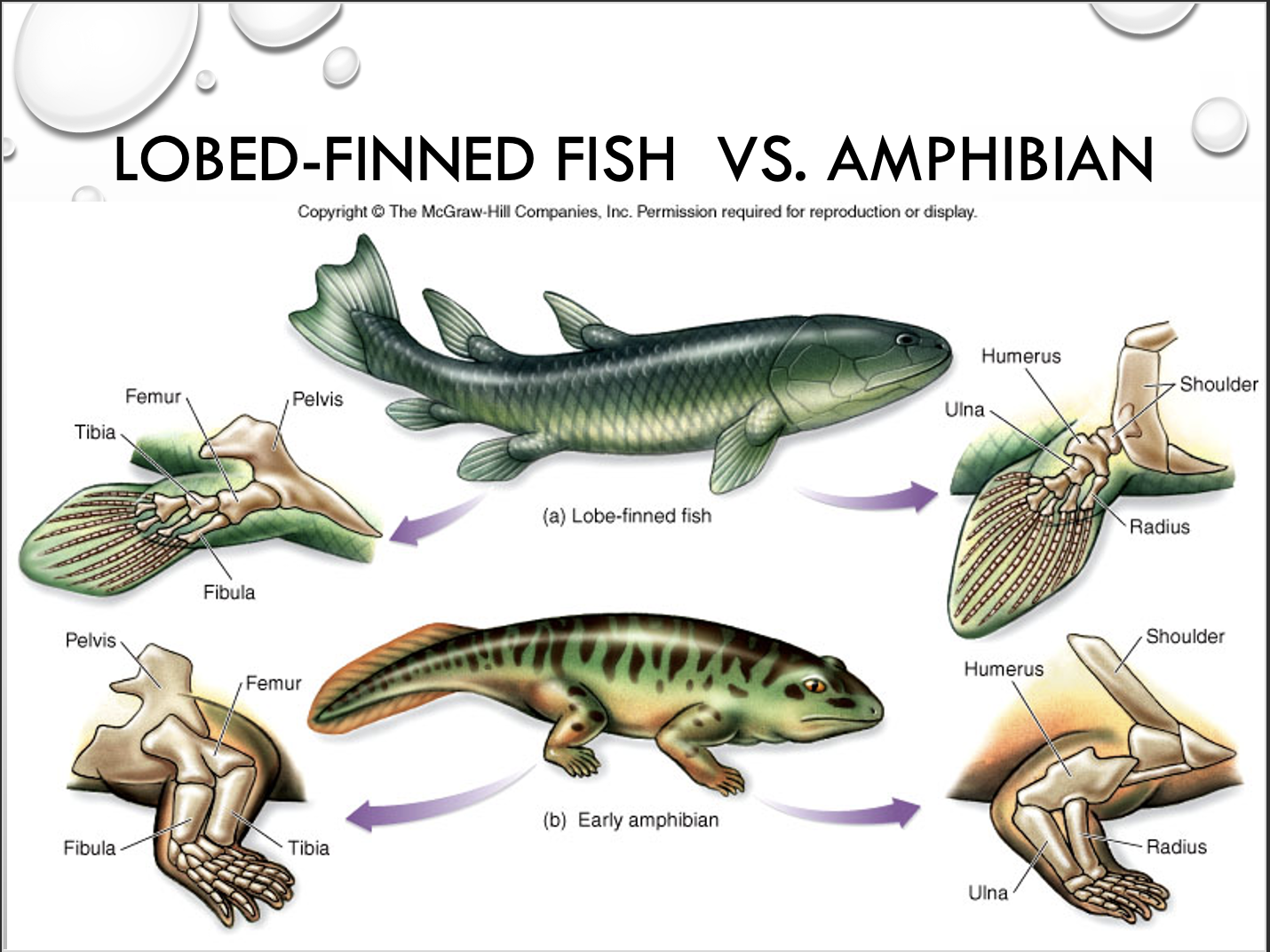

amphibians
SYNAPOMORPHY= FOUR LIMBS WITH DIGITS
salamanders, frogs, caecilians
tetrapods = four limbs with digits
Many live in water and land, but not all
undifferentiated, single-pointed teeth
not reptiles!
juveniles:
have gills
swim tail
webbed feet
swim like fish
adults
may have lungs for air
moist skin
needs water for reproduction
amniotes
includes: reptiles, mammals, birds
amphibians and amniotes split from a common ancestor
Amniote eggs develop on land, no need for water, but require moisture.
Extra membrane layers outside the embryo allow for development inside the enclosed egg.
gas exchange
waste excretion
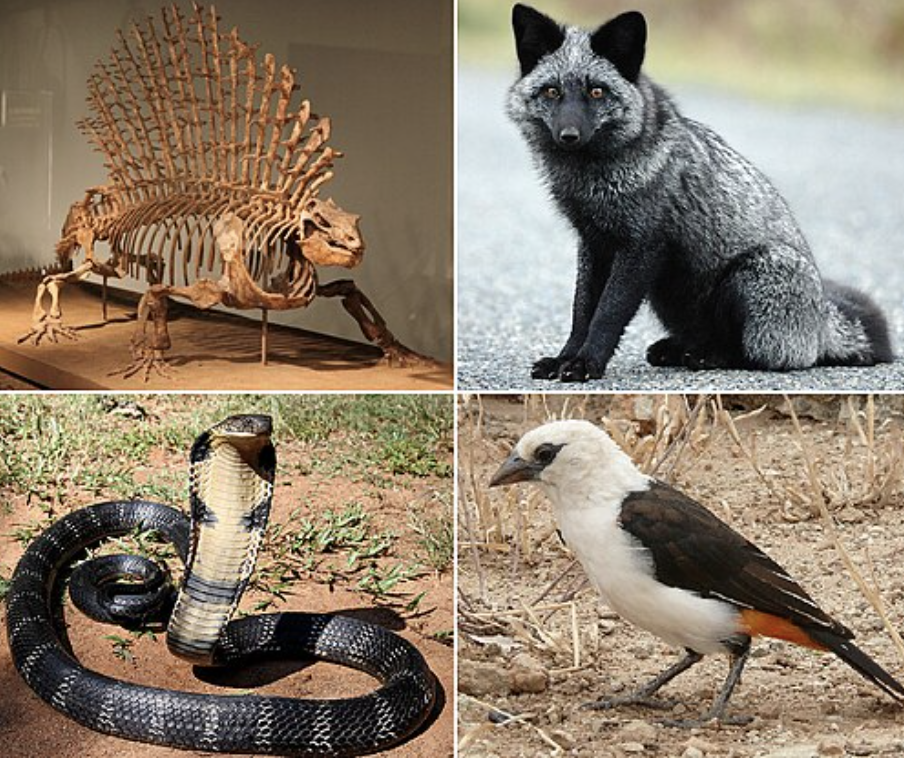

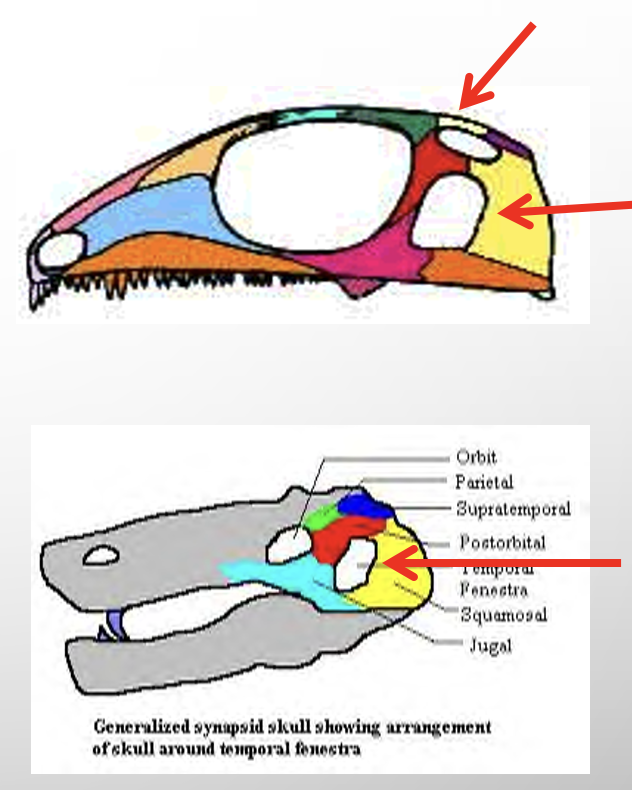
reptiles
SYNAPOMORPHY= AMNIOTIC EGG
includes: snakes, lizards, alligators, turtles, robins, etc.
•Amniote eggs
•Breathing efficiency
•improved in amniotes due to the use of a rib cage to ventilate the lungs
•less dependent on gas exchange through the skin
•Leathery/ Dry skin (Keratinized cells)- less water loss through skin
•Kidneys – More concentrated Urine, less water loss
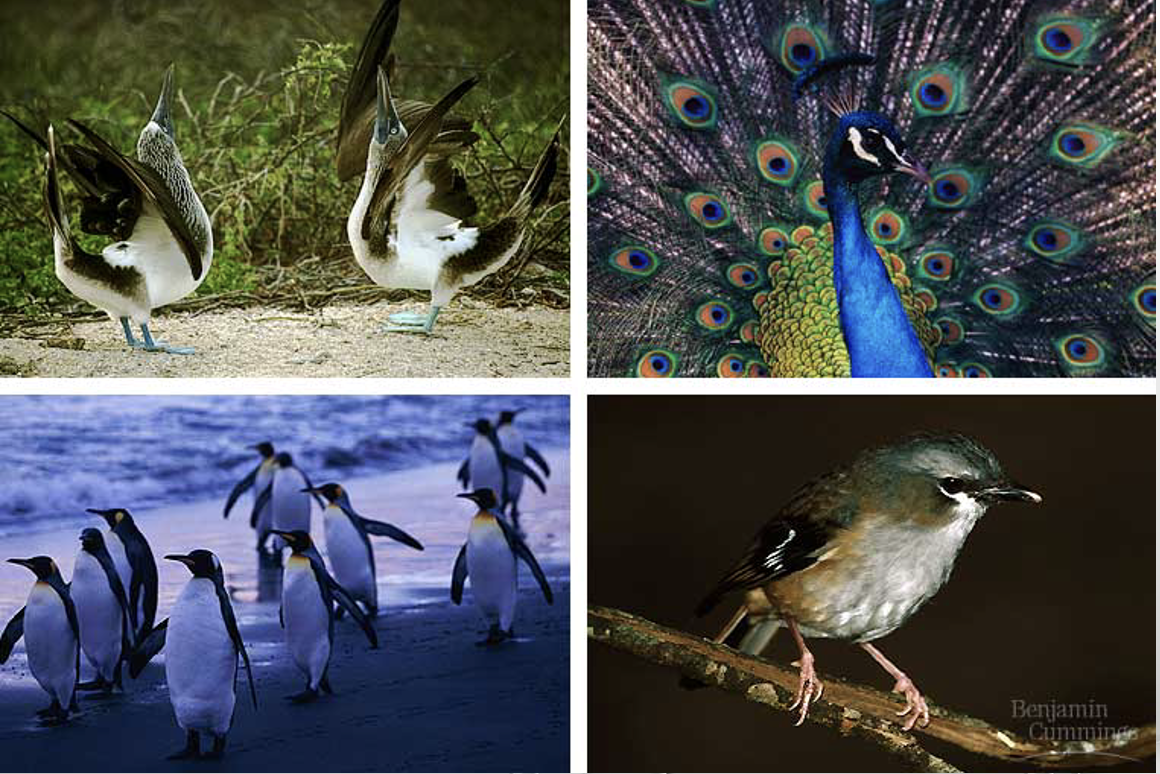

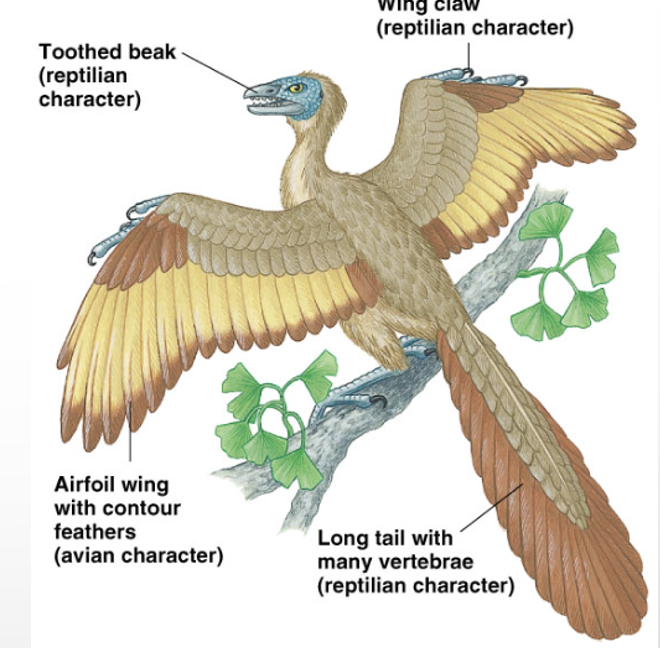
aves (birds with vertebrates)
SYNAPOMORPHY= FLIGHT AND FEATHERS
includes: peacocks, penguins, seagulls
origins of flight arose 4 times
pterosaurs (flying reptiles)
bats
insects
birds
2 theories
tree-down hypothesis = tree-down hypothesis proposes that flight evolved from tree-dwelling ancestors who first glided down from heights before developing powered flight
ground-up hypothesis = flight evolved from fast-running ground animals using wings for balance and lift
lungs + air sacs, 4-chambered heart
one ovary
no teeth
warm-blooded
mammals
SYNAPOMORPHY= warm blooded + high metabolisms + fat layer under skin for insulation + sweat glands to cool
efficient respiratory and circulatory systems
legs move under body
specialized teeth (shearing, crushing, or grinding) —> food
hair
mammary glands (milk to feed the young)
auricles (pinna) = external earlobes
extended care of young
more learned behaviors
Cyclostomes (jawless fish)
SYNAPOMORPHY= SKULL AND BACKBONE COMPOSED OF VERTEBRAE
craniates with simple vertebrae but jawless
mixini - hagfish (not a fish)
have cartilaginous, skull, and simple vertebrae
some of these fish attach to fish and eat their blood

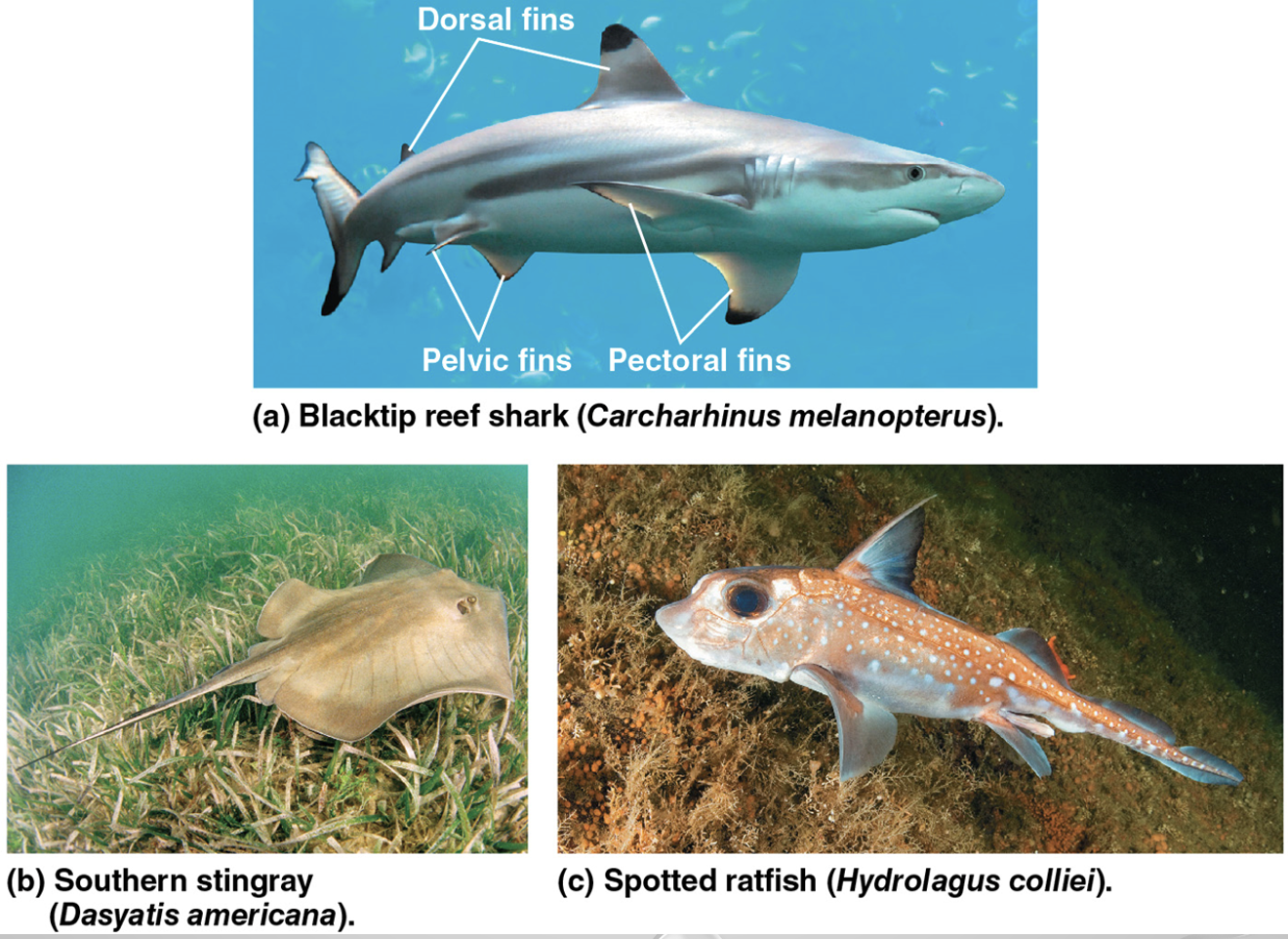
Chondrichthyes (cartilage fish)
SYNAPOMORPHY= TRUE JAWS, FIRST BONES
most are carnivores that have several rows of sharp teeth for tearing flesh
acute sense of sight and smell ability to detect electrical fields aid in prey capture
Sharks are swift swimmers but don’t maneuver well
paired pectoral and pelvic fins are for maneuvering
oil stored in liver for buoyancy but continual swimming is necessary to avoid sinking + gas exchange
actinopterygii (ray-finned fishes)
SYNAPOMORPHY= LUNGS or LUNG DERIVATIVES
include nearly all familiar aquatic Osteichthyes (bony-skeleton fish)
breathe water over gills
control buoyancy with air sac —> swim bladder
skin secretes mucus and is covered by flattened, bony scales in most fishes
Fins are supported mainly by long, flexible rays and are modified for maneuvering, defense, and other functions

actinistia (lobed-fins)
SYNAPOMORPHY= HINGED INTRACRANIAL JOINT IN SKULL THAT ALLOWS THE FRONT PART OF HEAD TO MOVE INDEPENDENTLY FROM REAR
rod shaped bones surrounded by thick layer of muscle in pelvic and pectoral fins
lobed fins may have been used by ancient species to amneuver across the substrate of aquatic habitats
Echinodermata
SYNAPOMORPHY= Pentaradial symmetry, water vascular system, endoskeleton
marine animals
includes starfish, sea urchins, sea cucumbers
