EXCRETORY-DIGESTIVE-SYSTEM-BIO2 (copy)
1/122
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
123 Terms
Excretion
rids the body of nitrogenous metabolites and other waste products
Cellular waste
this is what removed from the body which includes heat, water, salts, CO2, urea, and uric acid
Ammonia
-animals that excrete nitrogenous wastes this need access to lots of water
-in many invertebrates, this release occurs across the whole body surface
-most aquatic animals, including most bony fishes
Urea
-most terrestrial mammals and many marine species excrete ______, which is less toxic than ammonia
-in most vertebrates, _________ is produced in the liver
-circulatory system carries ________ to kidneys, where it is excreted
-conversion of ammonia to ________ is energetically expensive; excretion of ______ requires less water than ammonia
Uric Acid
-insects, land snails, and many reptiles, including birds, mainly excrete this
-is relatively nontoxic and does not dissolve readily in water
-can be secreted as a paste with little water loss
-is more energetically expensive to produce than urea
Protozoa
cell membrane (diffusion) contractile vacuole (excess water)
Flatworm (Planaria)
flame cells
Earthworm
nephridia, skin
Grasshopper
malphigian tubules, tracheae
Crayfish
kidneys, gills
Human
lungs, skin, liver, kidneys
Snake
kidneys
Lungs
excrete some waste products, e.g. CO2 and H2O
Skin
removal of waste through sweat glands
Liver
(via intestines) detoxifies blood, excretes bile pigments, and forms urea
Kidneys
-filters waste from the blood
-main organ of urinary system
-regulates electrolytes in blood
Urinary System
excretes waste and maintains homeostasis of body fluids
Ureters
narrow muscular tubes that take urine from the kidney to the urinary bladder
Urinary Bladder
muscular sacks that stores urine
Urethra
small tube that leads urine from bladder out of the body
Nephron
-about one million per idney
-microscopic units that filter blood of wastes
-H2O and waste taken from blood into nephron
-form urine
Glomerulus
-clump of capillaries
filtrate
most excretory systems produce urine by refining a _________ derived from body fluids
Filtration1
filtering of body fluids
Reabsorption2
reclaiming valuable solutes
Secretion3
adding nonessential solutes and wastes to the filtrate
Excretion4
processed filtrate containing nitrogenous wastes is released from the body
Bowman’s Capsule
blood filtrate produced in ________ __________ contains salts, glucose, amino acids, vitamins, nitrogenous wastes, and other small molecules
Thick ascending limb of the Loop of Henle
has low permeability to water, but it is permeable to ions
Proximal Tubule, concentrated
-reabsorption of ions, water, and nutrients
-molecules are transported actively and passively from the filtrate into the interstitial fluid and then capillaries
-as filtrate passes thru _______ _______, materials to be excreted become _________
-some toxic materials are actively secreted into the filtrate
Descending Limb of the Loop of Henle
-reabsorption of water continues thru channels formed by aquaporin proteins
-movement is driven by the high osmolarity of the interstitial fluid, which is hyperosmotic to the filtrate
-filtrate becomes increasingly concentrated
Ascending Limb of the Loop of Henle
-salt but not water is able to diffuse from the tubule into the interstitial fluid
-filtrate becomes increasingly dilute
-transport epithelial cells have plasma membranes of low permeability to water
Distal Tubule
-regulates the K+ and NaCl concentrations of body fluids
-controlled movements of ions (H+ and HCO3-) contributes to pH regulation
Collecting Duct
-carries filtrate thru the medulla to the renal pelvis
-one of the most important tasks is reabsorption of solutes and water
-urine is hyperosmotic to body fluids
Active Transport
picture someone paddling upstream in that lazy river. Active transport is like that. It's when the cell needs to use energy (usually in the form of ATP, the cell's energy currency) to move things across the membrane, even if it's going against the flow.
Passive Transport
Imagine a lazy river where things just float along without needing any energy to push them. That's a lot like ___________- in cells. It's when stuff like water, small molecules, and even some ions move across a cell membrane without the cell needing to spend any extra energy.
Plasma Osmolarity
-the _________ of blood _______, which is a measure of the hydration status
-measures the body’s electrolyte-water balance
Antidiuretic Hormone (ADH)
-also called vasopressin
-its molecules is released from the posterior pituitary bind to and activate membrane receptors on collecting duct cells
Freshwater Fish
-lives in water
-less concentrated than body fluids
-tends to gain water and lose salt
-does not drink water
-active transport by gills
-large volume of urine and is less concentrated than body fluids
Marine Bony Fish
-lives in water
-more concentrated than body fluids
-tends to lose water and gain salt
-drinks water
-active transport by gills
-small volume of urine and is slightly less concentrated than body fluids
Terrestrial Vertebrate
-lives in land
-tends to lose body water to air
-drinks water by mouth
-moderate volume of urine and is more concentrated than body fluids
Homeostatic Regulation of the Kidney
-mammals can control volume and osmolarity of urine in response to changes in salt intake and water availability
-combination of nervous and hormonal controls manages the osmoregulatory functions of the mammalian kidney, which contribute to homeostasis for blood pressure and blood volume
Why Alcohol is Diuretic?
-it inhibits the release of ADH
-inhibits pituitary secretion of anti-diuretic hormone (ADH), which acts on kidney to reabsorb water
-when ADH level drop, kidneys do not reabsorb as much water causing it to produce more urine
Bladder & Kidney Infections
caused by bacteria from colon/rectum entering urethra
Kidney Stones
crystallization of minerals salts & uric acid that block passage of urine
Kidney Disease
caused by long term diabetes, infections, & chemical poisoning
Gout
form of arthritis where excess production of uric acid leads to deposits of crystals in joints (esp. toes)
Hyperosmotic
Imagine a glass of water with a lot of salt dissolved in it. It's like the water is really thirsty because there's so much salt around. So, if you put a cell in this salty water, the water inside the cell will want to escape to dilute the saltiness outside.
Hypoosmotic
think of a glass of water that doesn't have much salt in it at all, just plain water. It's like the water outside the cell is not as thirsty because there's not much salt around. So, if you put a cell in this water, the water outside will want to rush into the cell to try to balance things.
Digestion
-breaking down food into chemical components that cells on an animal body can use as source of energy
Chemical energy
for cellular processes
Organic Building blocks
for macromolecules
Nutrients
Essential _______
Extracellular Digestion
food is broken down within the body, but inside a hallow sac or tube that opens to the external environment
Ingestion1
taking food into the body
Digestion2
breaking down food it can be: mechanical and chemical
Absorption3
moving nutrients across the lining of the digestive region and into the internal environment
Elimination4
expelling any leftover material that was not digested and absorbed
Coelom
is also called the body cavity
Digestive Tract
group of tissues or organs designed to breakdown food. __________ can be complete or incomplete
Filter Feeding
organisms that filter small particles, like plankton, from water, examples include whales and baleen sharks
Substrate Feeding
organisms that ingest organic material from material they live in, like soil or wood. Earthworms and caterpillar eating feces are the examples
Fluid Feeding
organisms that feed by sucking nutrient-rich fluids from a living host. Mosquitoes and leeches are examples
Bulk Feeding
Organisms that consume large pieces of food. Humans and many other animals are bulk feeders, eating whole plants or animals
Mammalian Mouth
humans have two sets of teeth over the course of a lifetime, their deciduous teeth or “baby teeth” are replaced by adult teeth and human adult teeth do not grow anymore
Mechanical Digestion
-starts when our teeth rip and crush food to increase the surface area of food particles
-breaking down food into smaller pieces through actions like chewing, grinding, and churning by muscles in the digestive system.
adult human
have all four tooth types (molar, premolar, canine, incisor) and are equally large
carnivore
with enlarged canine teeth and sharp premolars
herbivore
with reduced canines, and large, broad molars and premolars
Mammal’s Tongue
-is a bundle of membrane-covered skeletal muscle attached to the floor of the mouth
-movements of this help position food where teeth can chop or shred it
-mix food with saliva from salivary glandd
Salivary Glands
produce saliva that is a watery substance produced from the mouth of animals
Parotid
salivary gland that is situated around the external ear
Sublingual
salivary gland that is located below the tongue
Submandibular
salivary gland that is situated in the digastrics triangle of neck
Saliva
-contains glycoproteins that combine with water to form mucus
-the mucus helps small bits of food stick together in moist, easy to follow clumps
Salivary amylase
an enzyme in saliva begins the process of chemical digestion by breaking starch to disaccharides through hydrolysis
swallow, epiglottis
When you __________, the larynx rises, causing the _________ to fold over and cover the entrance to the larynx.
At the same time, vocal cords constrict, These actions block the route between the pharynx and larynx so food cannot enter the airway and CHOKE YOU.
when trachea open
-epiglottis up
-esophageal sphincter contracted
when esophagus opem
-epiglottis down
-glottis up and closed
-esophageal sphincter relaxed
Peristalsis process
-rings of smooth muscle contraction (indicated by the inward pointing arrows) travel in the mouth-to-anus direction along digestive tract.
-contraction between narrows the interior of the tract, pushing material inside it (green) through the tube
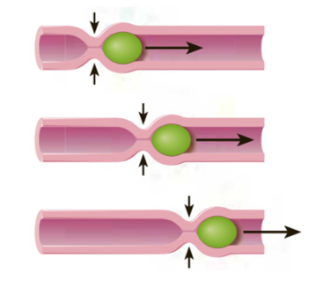
Peristalsis
-wave of smooth muscle contraction propelling food through the digestive tract
Stomach
-is a J-shaped, muscular, stretchable sac with a sphincter at either end
-acid and pepsin begin digestion (protein)
Rugae
-folds in the interior of the stomach
-smooths out as the stomach is filled with food, it can expand to hold about 1L of fluid
Functions of Stomach
-stores food
-mechanically breaks down food
-secretes substances that aid in chemical digestion
Gastrin
-arrival of food in the stomach triggers endocrine cells to secrete this
-it is secreted in the stomach lining into the blood
Gastrin Function
-acts on acid-secreting cells in the stomach lining to increase their acid output
-stimulates peristalsis in the stomach
Chyme
this contraction mixes gastric fluid with food forming a semiliquid mass called ________
Mucosa
glandular epithelium that lines the stomach and secrete gastric fluid
Gastric Fluid
(2L each day) - includes mucus, HCI, enzyme pepsin
1.5 and 3, pepsin
-pH of stomach is between __________ depending on the amount of acid secreted on it.
-high acidity activates ________
Chemical Digestion
-starts in the stomach (protein)
-its acidity denatures proteins exposing their peptide bonds to pepsin thus breaking them into smaller polypeptides
When stomach is EMPTY
contraction of smooth muscles slows and gastrin secretion slows
Gastroesophageal reflux (acid reflux)
-the sphincter at the entrance to the stomach (the Gastroesophageal sphincter) does not close properly or opens when it should be closed.
-ACID CHYME splashes into the esophagus, causing a burning pain commonly called heartburn or acid indigestion
secreted mucus, lining
a protective layer of ________ __________ prevents acid and enzymes in gastric fluid from damaging the stomach ___________
Ulcer (crater-like sore)
-most of this arise after acid-tolerant HELICOBACTER PYLORI bacteria infect cells of the stomach lining.
-H. pylori degrades the protective mucus and makes chemicals that increase gastrin secretion, causing the stomach to secrete extra acid
-overuse of nonsteroidal anti-inflammatory drugs such as ibuprofen or aspirin can also cause a stomach ______
Multiple Stomach Chambers
-ruminants like cattle, goats, sheep, antelope, and deer are hoofed grazers that have ________________
-1st and 2nd chamber contains MICROBES that can breakdown cellulose
-In 2nd chamber, solid foods is stored and forms a CUD that is regurgitated—moved back into the mouth for a second round of chewing
-fluid rich in nutrients moves from the 2nd chamber to the 3rd and 4th chambers, and finally to the intestine
Small Intestine
-only small in terms of its diameter—about 2.5 cm (1 inch), it is the longest segment of the gut
-uncoiled, adult small intestine would extend about 5 to 7 meters (16 to 23 feet)
Duodenum
-region of small intestine
-receives food from the stomach
Jejunum
-region of small intestine
-further break down food particles that have been partially digested in the stomach and duodenum
Ileum
-region of small intestine
-empties to the large intestine