Spanish in the Americas Quiz
1/31
Earn XP
Description and Tags
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
32 Terms
Aztec Empire
A South American Native American Empire, created by the Mexica people, with a population of 5-6 million. Very loosely controlled with frequent rebellions. Very innovative empire (canals + bridges), frequent trade (food, textiles, materials)
How did the Aztecs maintain control?
Religion: sacrificed slaves and enemies to the sun god (to maintain the safety of the empire); justified expansion as the Sun God needs sacrifice to help the Aztecs survive. Fear of conquest and death prevented rival nations from attacking.
Displays of wealth and riches attracted allies
Inca Empire
LargeER Mesoamerican Empire in the Andes Mountains, starting from a small Quechua community. The Emperor claimed to be a descendant of nobility. population of 10-12 million people
How did the Incas maintain control?
Subjects were sorted into groups and looked over by assigned officials. Conquered people relocated to prevent revolt, and the Quechua language was taught to all people. People were free to follow whatever gods they chose while also recognizing Incan gods. Rewards we’re given to loyal subjects
mita system
Originally an Incan public service system, later taken by the Spanish to force slave labor onto the Incan and other Native populations. Specifically in mines, for example, Potosi.
Tenochtitlan
Capital of the Aztec Empire, taken by the Spanish in 1521
Christopher Columbus
First Spaniard to land in Hispaniola, started sending slaves when there wasn’t gold to profit off of
Taino People
Natives to most Caribbean islands
Montecuzoma II or Montezuma II
The 9th Aztec Emperor, first contact of the Spanish and Aztecs during his reign. Killed during the siege of Tenochtitlan. Began by treating the Spanish with kindness and caution, which gave the Spaniards time to permeate the Aztec defenses.
Encomiendero
A Spanish conquistador with a grant from the Crown granted rights over Natives, their land, and their goods. ‘Benefits’ for Natives were christianization and protection from death outside the land they worked on. Very much treading into chattel slavery.
Chattel Slavery
A form of slavery where individuals are treated and traded like personal property or live-stock
Papal Bull ‘Inter caetera’
An order issued by Pope Alexander VI declared that Catholic Monarchs had all lands ‘to the west and south’ and were entrusted/promised to them.
Hernan Cortès
The Spanish conquistador who conquered the Aztec Empire in 1519, originally from a lower-class background and was looking for a passage to Asia, landed in Mexico. He allied with conquered peoples who disliked the Aztec Empire to overthrow them, combined with greater technology and weapons. Spanish married royal women after the fact for power, wealth, and knowledge.
Three G’s of Globalization
Gold, Glory, God
Doña Marina (La Malinche or Malinal) b.1505
“Mother of Mestizo Culture) From the community between Mayans and the Aztecs, step-dad sold her into slavery to the Mayan Cheiftan in Tabasco. Given to Cortez after he conquered Tabasco. Acted as a translator for Cortez due to her language versatility, which is the main reason the Spaniards conquered the Aztecs. To this day, debated whether to be either a victim or a traitor.
Treaty of Tordisillas
Signed by Spain and Portugal in 1494, the agreement divided the newly discovered lands in the west. Created to prevent tensions between the two countries, and increase colonization as well as conquest. Any land within the assigned area ‘not belonging to Christian Kings’ was up for grabs.
enconmienda
A grant given to an encomendero
silver mining
one of the largest markets using native slave labor, silver went to Spain to make their currency of pesos
small pox
European disease brought over by Europeans starting in the 1490s, responsible for the death of 90% of the Native population
Mercantilism
An economic theory that emphasizes maximizing exports and minimizing imports, relying on the exploitation of colonies to benefit the mother country. Success depends on the quantity of riches accumulated. This theory dominated Western Europe until the 1700s, with the switch to capitalism.
Iberian
(Portugal, Spain, and Andorra) The Iberian Peninsula is a small collection of European countries off the south-western coast of Europe
conquistadores
A Spanish or Portuguese soldier who explored, conquered, and colonized land from the 1400s to the 1600s (ex, Cortez, Pizarro)
Francisco Pizzaro
A Spanish conquistador who overtook and colonized the Incas in 1533, originally landing in Peru. He swept through the Incas in less than a generation. He landed in a time of tension as the previous ruler had died from disease, and his sons were fighting for the throne. Helped by the Inca population, who were against the current ruler. Lost most of his men in the process.
Columbian Exchange
The exchange of culture, plants, disease, animals, and technology from the Americas to the “Old World” (Africa, Asia, Europe). Truly only benefited specific areas of the old world/
Mestizo
Children of Spanish and Indigenous parents
criollos/creoles
Born in the colonies with parents of Spanish decent
mulato
Children of Spanish and African parents
peninsulares
Spanish born in Spain
zambos
Children of Indigenous and African parents
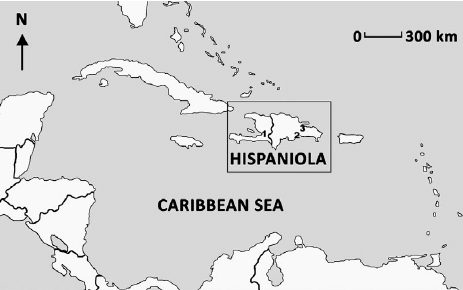
Hispanola (Haiti + DR)
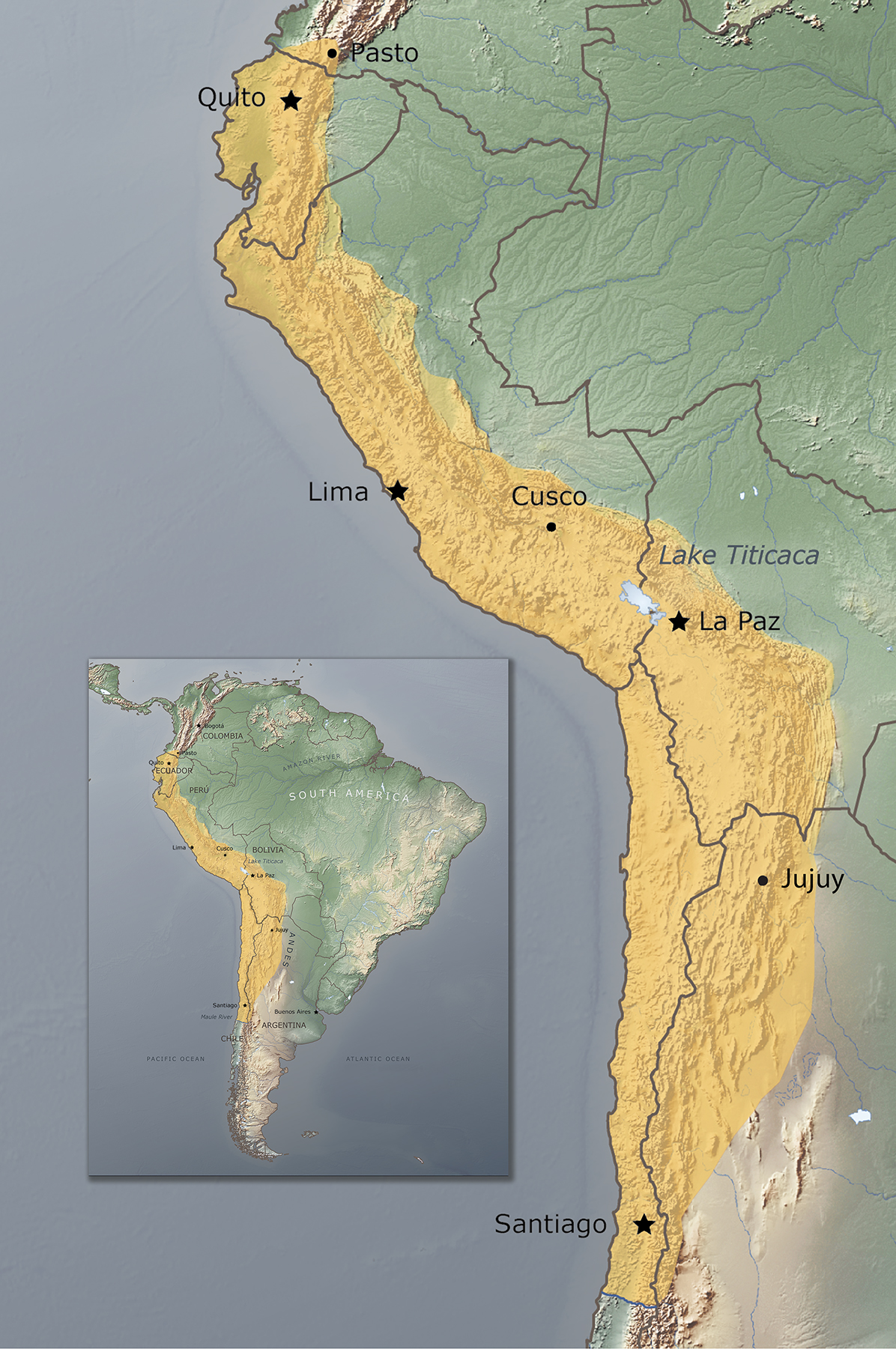
Inca Empire
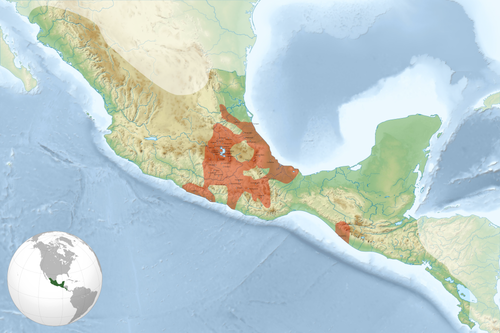
Aztec Empire