P - S2023 - Describing Motion
5.0(2)Studied by 18 people
Card Sorting
1/29
Last updated 6:10 PM on 2/15/23
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
30 Terms
1
New cards
reference point
starting point you choose to describe the location, or position, of an object
2
New cards
position
an object's distance and direction from a reference point
3
New cards
motion
the process of changing position
4
New cards
displacement
the difference between the initial (first) position and the final position of an object (vector quantity)
5
New cards
distance
how much ground an object has covered during its motion (scalar quantity)
6
New cards
scalar
quantities that are described by a magnitude (or numerical value) alone
7
New cards
vector
quantities that are described by both a magnitude and a direction
8
New cards
speed
a measure of the distance an object travels per unit of time (scalar quantity)
9
New cards
constant speed
the rate of change of position in which the same distance is traveled each second
10
New cards
instantaneous speed
speed at a specific instant in time
11
New cards
average speed
the total distance traveled divided by the total time taken to travel that distance
12
New cards
average speed formula

13
New cards
velocity
the speed and the direction of a moving object (vector quantity)
14
New cards
units for speed & velocity
meters per second (m/s)
15
New cards
acceleration
a measure of the change in velocity during a period of time (vector quantity)
16
New cards
average acceleration formula

17
New cards
units for acceleration
meters per second per second (m/s/s or m/s^2)
18
New cards
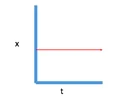
p-t graph - object at rest
19
New cards
p-t graph - constant, positive velocity

20
New cards
p-t graph - constant, negative velocity

21
New cards
p-t graph - accelerating in the positive direction

22
New cards
p-t graph - accelerating in the negative direction

23
New cards
p-t graph - decelerating in the positive direction

24
New cards
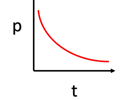
p-t graph - decelerating in the negative direction
25
New cards
p-t graph - constant positive velocity, then higher constant positive velocity

26
New cards
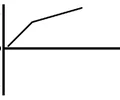
p-t graph - higher constant positive velocity, then lower constant positive velocity
27
New cards
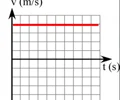
v-t graph - constant positive velocity; no acceleration
28
New cards
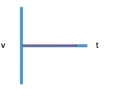
v-t graph - object at rest
29
New cards
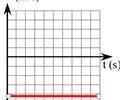
v-t graph - constant negative velocity, no acceleration
30
New cards
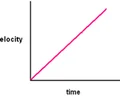
v-t graph - positive acceleration
Explore top notes
Environmental Psychology: Design Guidelines for Homes, Offices, Classrooms, & Hospitals
Updated 1255d ago0.0(0)
Environmental Psychology: Design Guidelines for Homes, Offices, Classrooms, & Hospitals
Updated 1255d ago0.0(0)