semisolid dosage forms: creams, ointments, gels
1/86
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
87 Terms
ointments are semisolid preparations intended for external application to _______
skin or mucous membranes (oral, ocular, otic, vaginal)
t/f: topical preparations are only used for local effects
false. may be local or systemic. if it is systemic it is a transdermal
what is notable to consider if a pregnant pt is prescribed a certain cream
whether the cream is a transdermal/has systemic effects
are systemic effects possible from non-transdermal creams
yes. if they are misused (ex: put cream all over body when intended for one area) then too much can get absorbed and reach bloodstream
which pts cannot be given retinols/ vit d derivatives and why
pregnant/nursing pts
-highly teratogenic, cause abnormalities in fetus
what does "absorbed" mean for creams// where is the drug?
in blood or in lymph (not just on skin surface)
breast milk tends to be _________ and causes _______ drugs to accumulate
acidic; basic drugs accumulate
topical vs transdermal products
topical= skin is target organ (may or may not have active drug)
transdermal= designed for systemic effects
what can non-medicated ointments be used for
1. emollients (softening)
2. protective barriers (anti-dehydrants)
3. base or vehicle
explain how protective barrier ointments/ anti-dehydrants (ex: aquaphor) can help in the healing process of wounds
barrier keeps wound sterile
what are the 4 types of bases
1. oleaginous/ hydrocarbon
2. absorption
3. water-removable
4. water-soluble
oleaginous base characteristics
- emollient effect
- prevent moisture escape
- occlusive dressings
- remain on skin for long periods without drying due to immiscibility with water
t/f: while oleaginous bases provide an emollient effect, they may dry out over time
false. there is no water in oleaginous bases so they do not dry out
what could too much moisture on areas of healing lead to? which ointment can help with this?
-too much moisture might cultivate bacterial infections
- oleaginous bases trap moisture BUT they also prevent bacteria from reaching the wound= more sterile
t/f: an oleaginous base helps protect the fluidity of granulation tissue
true. oleaginous bases prevent moisture escape, help with healing, and keep wounds sterile
petrolatum, white petrolatum, yellow ointment, white ointment, and mineral oil are all examples of
oleaginous bases
which type of base is petrolatum? what is it obtained from?
oleaginous; discovered when drilling for petrol/gas
why doesnt petroleum have an expiration date
completely hydrophobic= no bacteria grow in it
what is white petrolatum
decolorized petrolatum
which oleaginous base is often used as a levigating agent
mineral oil (liquid petrolatum)
hydrophilic petrolatum, anhydrous lanolin, lanolin, and cold cream are all examples of
absorption bases
relate absorption base function in relation to water
oleaginous in nature but draws fluid out (absorbs fluid, does not trap it in)
2 types of absorption bases
1. emulsifiable bases- allow water incorporation to form w/o emulsion
2. emulsified bases- already w/o emulsions that allow for more water incorporation
can absorption bases be easily removed from the skin with water? why or why not?
no. external phase is oleaginous
which base is useful as pharmaceutical adjuncts to incorporate SMALL volumes of aqueous solutions into HYDROCARBON bases
absorption bases
t/f: you may mix an aqueous solution with an absorption base to incorporate it into a hydrocarbon base
true
explain why oleaginous/absorption bases often have low pt compliance (what are some cons that annoy pts)
oily and ruins clothes. not easily washed out. pts dont want to wear it even though it is the most effective
identify the hydrophilic component in hydrophilic petrolatum:
cholesterol, stearyl alcohol, white wax, white petrolatum
stearyl alcohol (OH groups are aqueous)
is cholesterol ionic/non? lipophilic or hydrophilic?
nonionic, very lipophilic
= makes a good emulsifying agent
what is lanolin? what is anhydrous lanolin?
purified wax-like substance from sheep wool
- no more than 0.25% of water
anhydrous lanolin: non-hydrophilic, but may draw in a little water
which type of base is lanolin
absorption (oleaginous but may absorb some water)
water-removable bases characteristics
- o/w emulsions resembling creams
- easily washed from skin (must still scrub)
- may be diluted w water/aqs
- can absorb serious discharges
which base is an o/w emulsion resembling creams
water-removable bases
which base can be diluted with water or other aqueous solutions
water-removable bases (outer phase is water)
what kind of discharges can water-removable bases absorb
serous exudates (NOT granulation tissue)
ex: purulent, hemorrhagic
are parabens needed in water-removable bases? why?
yes
1. parabens are preservatives. water-removable bases are o/w so bacteria may grow in H2O
2. parabens also help in not becoming dehydrated/ preventing evaporation/ preserves stability
what is the purpose of sodium lauryl sulfate (SLS)
emulsifier/surfactant; help incorporate oil and water
water-soluble bases characteristics
- NO oleaginous components
- completely water washable/ greaseless
- mostly used to incorporate solids
which base is the most hydrophilic and completely water washable
water-soluble bases
which base has the lowest emollient/ protective effect and is the most likely to evaporate
water-soluble bases
polyethylene glycol ointment is an example of
water-soluble base
if 6-25% of an aqueous solution is to be incorporated in PEG ointment, replace ___g of PEG3350 with an equal amount of __________
50g, stearyl alcohol
identify the base:
-occlusive
-non water washable
-hydrophobic
- greasy
hydrocarbon/oleaginous
identify the base:
-emollient
-occlusive
-anhydrous
-absorb water
-greasy
absorption base
identify the base:
- water washable
- nongreasy
- can be diluted with water
- nonocclusive
water-removable
identify the base:
- water washable
- non-occlusive
-nongreasy
- lipid free
water-soluble
how can we control the release rate of a drug from ointment base? why would we want to?
"like dissolves like"
= lipophilic base will release lipophilic molecule slower than an aqueous molecule
- fast release = acute, need relief now (ex: infection)
- slow release= for longer duration of action (ex: immune)
lipophilic drug X is in a lipophilic base. is this for short or long duration of action?
long duration bc slower rate of release
if we want better penetration of a topical, what kind of drug molecule would you select
cells are made of phospholipid membranes, if we want deeper penetration we need lipophilic drug, rather than aqueous. best drug would have some of both. consider adding penetration enhancer
characterize lipophilic drugs by release rate and penetration
- release slower from lipophilic bases
- penetrate through skin better
when is the following base usually used
- ointment:
- cream:
- lotion:
ointment: dry scaly skin
cream: weeping/oozing surfaces
lotion: intertriginous areas/ friction
2 methods for ointment preparation
1. incorporation-levigation: physically mixed until homogenous
2. fusion: components melted together and cooled w constant mixing
what is one limitation to the fusion method of ointment preparation
all ingredients must be heat stable since fusion requires melting
______ are semisolid dosage forms that may be w/o, o/w, or wwb
creams
t/f: ointments are preferred for mucous membranes, rectal, and vaginal
false. creams
what is vanishing cream
o/w emulsion with HIGH water content
- humectant (preserves moisture/ softens skin)
- forms thin layer after water evaporates
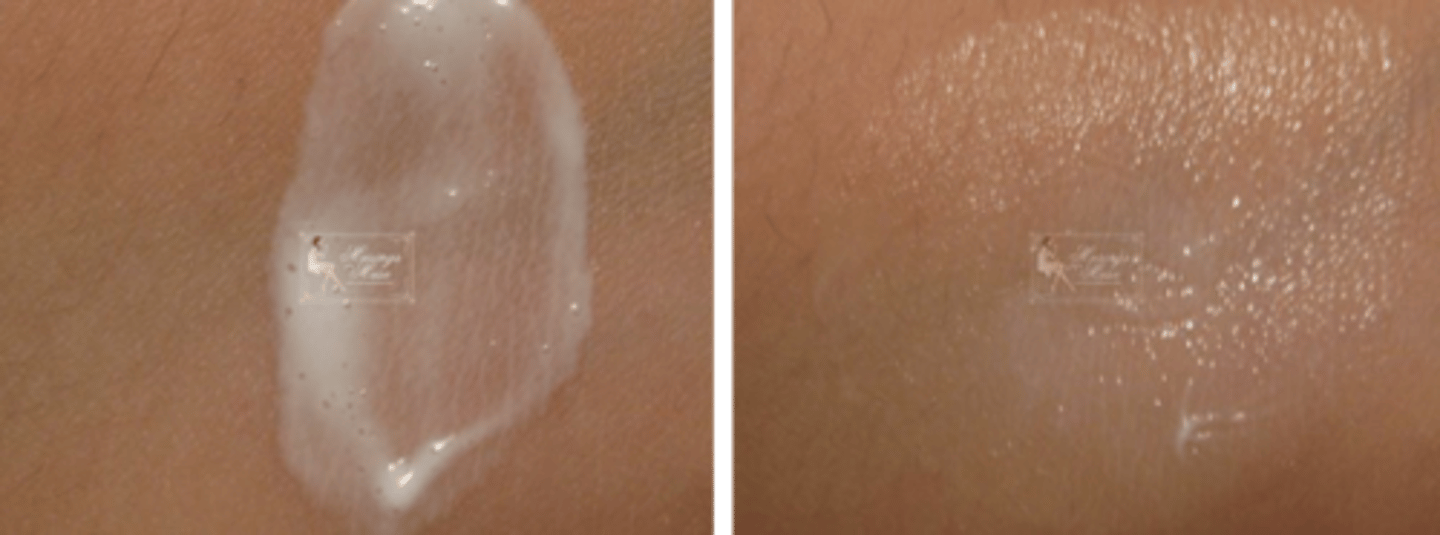

pt A comes in complaining that her cream isnt working. as soon as she spreads it, it disappears and she has to reapply. how would you explain/counsel pt
vanishing cream is o/w emulsion that appears clear as you spread it out and SA increases & water evaporates. tell pt that the drug/oil is on the skin, even if you cant see it
describe the makeup of gels/jellies
suspensions made up of small inorganic particles or large organic molecules in liquid
an organic compound may need to be suspended in _____ before adding to gel
emulsifier (ex: alcohol)
single phase vs two phase gel system
single= macromolecules uniformly distributed w no boundary btwn molecule and liquid
2= gel mass has distinct flocules of particles (ex: magma)
what is magma defined as
- two phase gel system
- when the dispersed phase particle size is large, it may separate out

milk of magnesia
makeup?
use/moa?
ex of magma (2 phase gel system)
gelatinous precipitate of Mg(OH)2
- for heart burn, stomach ulcers, gastritis
- coats surface of stomach, does not stop primary patho (HCl)
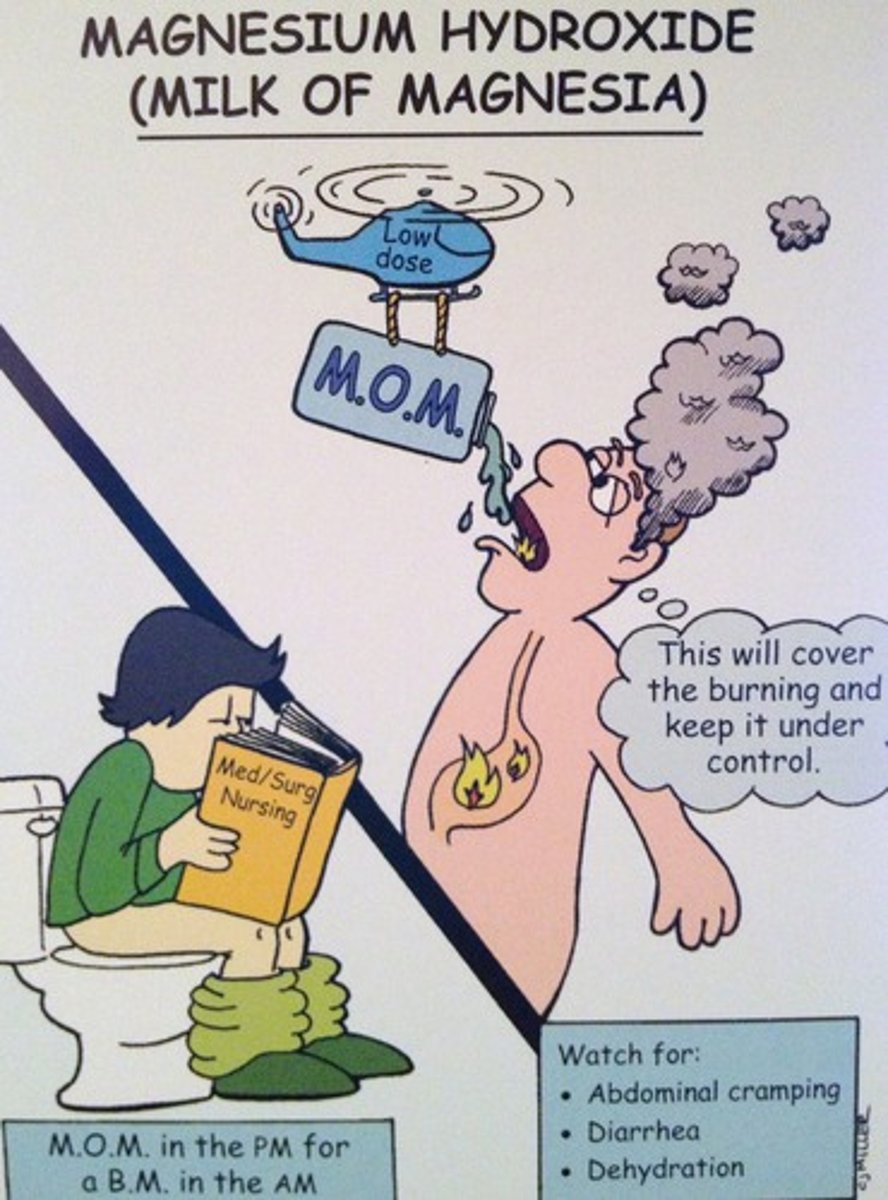

t/f: milk of magnesia lowers HCl production responsible for GERD
false. it coats the stomach, it does not stop HCl poduction
Gels may thicken on standing, forming a _______, & must be shaken before use to liquefy the gel & enable pouring.
thixotrope
thixotrope
formed by gel thickening; must shake before using
t/f: a transdermal cream will be found in blood/lymph
true. transdermal implies that it passed through skin and reached blood (systemic)
what is usually added to topical agents to increase transdermal efficacy
penetration enhancers (lipophilic/organic)
= DMSO, EtOH, PG, glycerin, urea, SDS, poloxamers, terpenes
what are penetration enhancers
added to topicals for transdermal prep. they are lipophilic and help active drug pass through all of the skin layers and eventually reach blood
examples of penetration enhancers
DMSO, EtOH, PG, glycerin, PEG, urea, SDS, poloxamers, terpenes
pluronic lecithin organogel
aids in rapid penetration of active drugs through the skin (for transdermals) (penetration enhancer)

what are pastes
semisolid preparations of stiff consistency and contain a high percentage of finely dispersed solids

how are pastes prepared?
whats notable about them?
- made same as ointments or by heating
- they are stiff, remain in place, absorb serous secretion
- stick to hairy parts
which vehicle base would you choose if you need it to stay on skin and not move
paste, plasters
what are plasters
solid or semisolid adhesive masses spread on a backing of paper, fabric, moleskin, or plastic
- provide prolonged contact at site
- can be unmedicated= protection/support (casts)
which type of vehicle is often needed in callouses or corn removal
plasters bc they have prolonged contact that can get past the hard skin barrier. creams will not work
(if pt feels pain, STOP therapy. it has reached viable skin)
layers of epidermis
stratum corneum, stratum lucidum, stratum granulosum, stratum spinosum, stratum basale
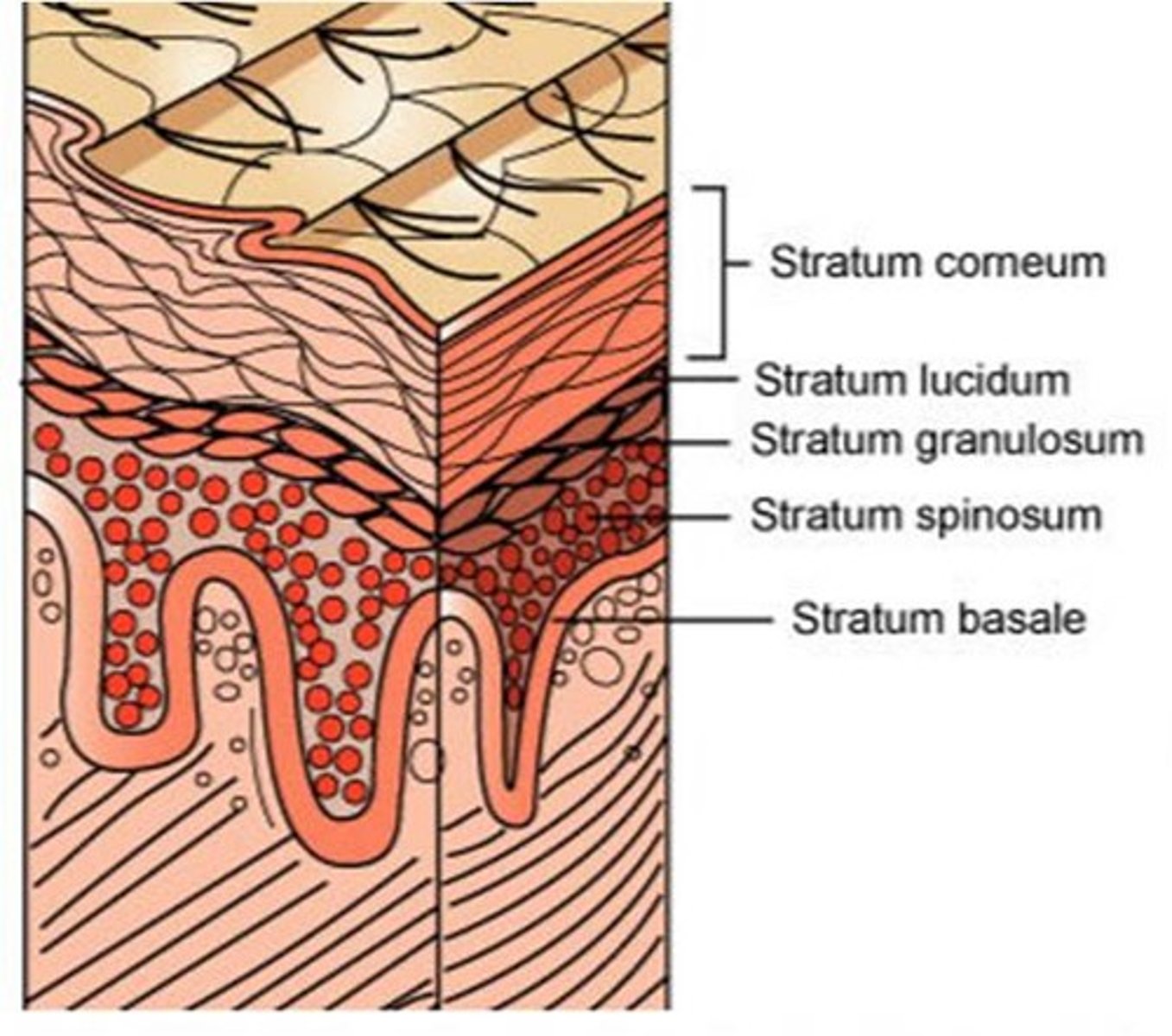
which layer of the dermis is the primary barrier to topicals bc of its thickness
stratum corneum
t/f: the first thing a cream must penetrate is the stratum corneum
false. it must penetrate the top layer of waterproof protein- keratin. stratum corneum is independant and follows it
ways for drug entry through skin
- hair follicles (minor)
- gland ducts (minor)
- epidermis (large)
- hair and glands is minor bc theyre SA is so small
what does the rate of dug movement through keratinized SC depend on
- drug concentration (need higher gradient for penetration)
- aqueous solubility
- o/w partition coefficient
describe preferred solubility of compounds that need to pass through skin. what if skin is broken?
-both aqueous and lipid solubility
- if skin is broken, faster absorption
t/f: generally, topical patches go on thick skin to control penetration
false. they are usually applied to thin skin
= abdominal, pelvic, inner arm
(unless if you are treating the thick skin)
t/f: we can determine the concentration of a drug at the site of absorption of the topical
false. we do not know how much of a drug is on the skin. we can only tell for transdermals since we can take a blood sample.
-for skin, the only way is to do a punch biopsy
-this is why clinical efficacy varies among patients
t/f: unless specified, bandages should not cover topicals
true
t/f: an immediate rxn after applying a topical for the first time is a type 1 hypersensitivity rxn
false. we need to be sensitized first to have an allergic rxn. immediate rxn at first time is usually physicochemical
why do the eyes/ears/nose/vagina need higher monitoring when using topicals
thin and specialized epithelium.
pay attention to microbial and particulate content
how can drugs enter the eye
most= simple diffusion through cornea
alternate= conjunctiva and sclera