AP Macro Unit Two
1/39
Earn XP
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
40 Terms
Gross Domestic Product
The dollar value of all final goods and services produced within a country in one year
What is not included in the GDP?
Intermediate goods, non production transactions, non market and illegal activities
GDP Per Capita
GDP/Population - better measure of a nation’s standard of living
Give five reason why some countries have higher GDPs
Economic systems, rule of law, capital stock, human capital, and natural resources
Expenditures Approach
Add up all the spending on final goods and services produced in a given year. Includes consumer spending, business investments, government spending, and net exports.
Income Approach
Add up all the income earned from selling all final goods and services produced in a given year. This includes labor income, rental income, interest income, and profit.
Value-Added Approach
Add up the dollar value added at each stage og the production process
Factor Payments
Payment for the factors of production, namely rent, wages, interest, and profit
Components of Consumer Spending
Durable goods, non-durable goods, and services
When is Inventory Counted for GDP?
The year it was produced, not sold
Formula for percent change
(final - initial) / initial
Limitations of GDP
Doesn’t count money spent on bad things, doesn’t count non production societal goods such as volunteering, or non market transactions
Unemployment
Workers that are actively looking for a job but aren’t working
Unemployment Rate
Percent of people in the labor force who want a job but are not working
Who is considered in the labor force?
At least 16; not in the military, retired, or in school full time; not institutionalized; able and willing to work
Friction Unemployment
Temporary unemployment between jobs
Seasonal Unemployment
A type of frictional unemployment, which is due to time of year and nature of the job
Structural Unemployment
Changed in the labor force that make some skills obsolete
Creative Destruction
The permanent loss of jobs as a result of some skills becoming obsolete
Technological Unemployment
Type of structural unemployment where automation and machinery replace workers
Cyclical Unemployment
Unemployment caused by a recession; demand for goods fall and workers are laid off
Natural Rate of Unemployment
Friction + structural. Should be around 4-6%
Problem with low unemployment?
Prices rise since consumers spend more and producers bid up price of resources
Criticisms of the Unemployment Rate
Discouraged workers aren’t counted, labor force participation rate excluded, underemployed workers are considered equally employed, and it doesn’t show disparity for minorities and teenagers
Why is high inflation bad?
banks don’t land and people don’t save which decreases investment and the GDP
Deflation
Decrease in general prices or a negative inflation rate; causes hoarding of resources
Disinflation
Prices increasing at slower rates
Inflation Rate
(final year - first year) / first year
Price Indices
Index numbers assigned each year that show how prices have changed relative to a specific base year
Consumer Price Index
(Price of market basket / price of market basket in base year) x 100
Problems with the Consumer Price Index
Substitution Bias: As prices increase for the fixed market basket, consumers buy less of these products and more substitutes that may not be part of the basket
New Product: May not include newest products
product Quality: Ignores both improvements and decline in product quality
Who is hurt by inflation?
Lenders, savers, people with fixed incomes
Who is helped by inflation?
Borrowers,
Nominal
Measured in dollars
Real
Adjusted for inflation
Costs of Inflation
Menu Costs: Costs money to change listed prices
Shoe Leather Costs: The costs of transactions increase
Unit of Account Cost: Money doesn’t reliably measure the value of goods/services
GDP Deflator
(Nominal GDP / Real GDP) x 100
Business Cycle
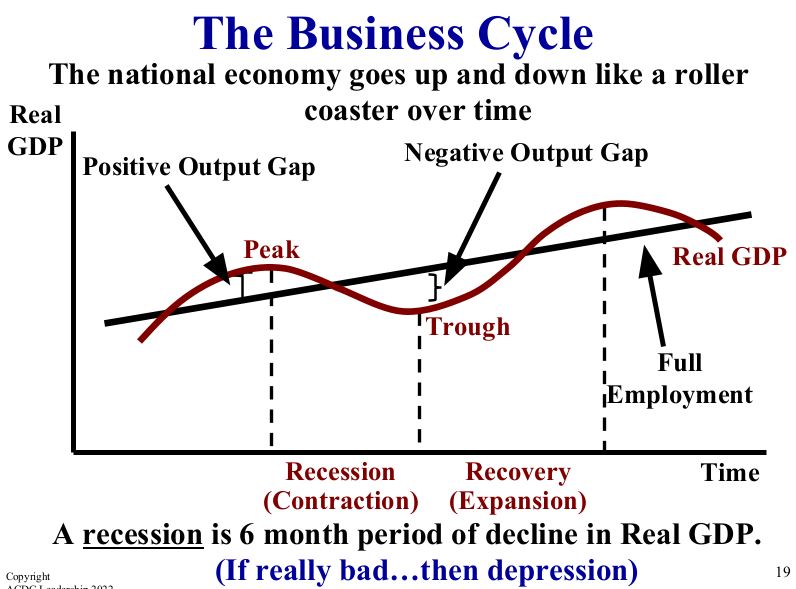
How long until a recession is official?
Six months
Real ____ Rate
Nominal ____ - Inflation rate
*Works for wage, interest, and any value rate!!