CH17: CARBOXYLIC ACIDS & THEIR DERIVATIVES
1/189
Earn XP
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
190 Terms
What is the functional group structure of a carboxylic acid?
–COOH (carbonyl + hydroxyl group).
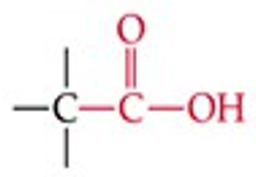
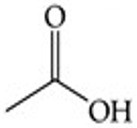
Recognize this line structure:
Carboxylic acid.
What is the suffix for carboxylic acids?
-ic acid.
What is the functional group structure of an anhydride?
Two carbonyls (C=O) bonded through an oxygen atom (–CO–O–CO–).
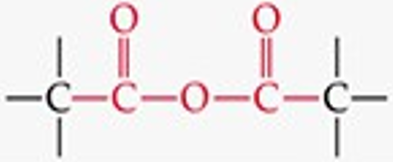
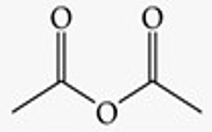
Recognize this line structure:
Anhydride.
What is the suffix for anhydrides?
None.
What is the functional group structure of an ester?
–COOR (carbonyl bonded to –OR group).
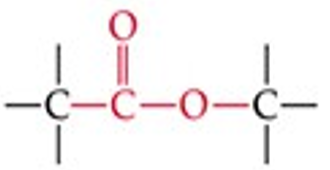
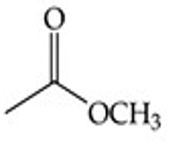
Recognize this line structure:
Ester.
What is the suffix for esters?
-ate.
What is the functional group structure of an amide?
–CONH₂ (carbonyl bonded to NH₂).
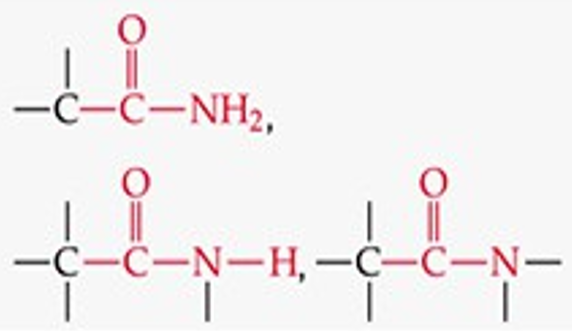
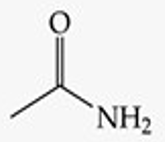
Recognize this line structure:
Amide.
What is the suffix for amides?
-amide.
4 properties of ACIDS
SOUR
RED
rxn w/ some metals to produce hydrogen gas
rxn w/ bases to form salt & water
4 properties of BASES
BITTER
BLUE
slippery feeling on skin (rxn w/ fats/oils on skin)
rxn w/ acids to form salt & water (neutralization rxn)
Acid-Base Theories — Summary Chart (KNOW)

Similar to amines, primary, secondary, and tertiary amides are _____, with either ____, ____, or _____.
carbon atoms directly bound to a N atom
1, 2, or 3 Cs, respectively
Common derivates of carboxylic acids are ________.
anhydrides, esters, and amides
O=C-OH is a _______.
carboxyl functional group
O=C-OR is
an alkoxide
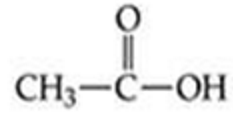
ID this structure
acetic acid
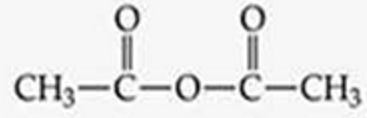
ID this structure
acetic anhydride
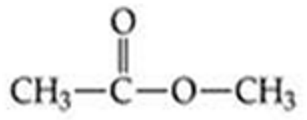
ID this structure
methyl acetate
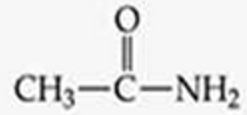
ID this structure
acetamide
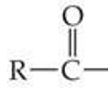
ID this group
acyl group
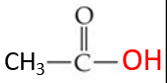
ID this group + specific compound’s name
acetyl group
acetic acid
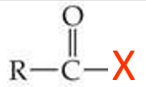
ID this group
carbonyl compound
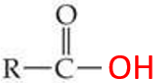
ID this group
carboxylic acid
When an R group bonds to the carbonyl group, it is called _______
an acyl group. R can be H, alkyl, or aryl
An important acyl group in biochemistry is the_____
acetyl group, in which R is a methyl group
Carboxylic acid structural definition
The acyl group bonds to –OH, and after dissociation of H+ becomes carboxylate ion.
Esters structural definition
The acyl group bonds to –OR (Alkoxy group)
Amides structural definition
The acyl group bonds to nitrogen. An amide containing -NH2 group is a primary amide, one with -NHR is a secondary amine, and one with –NR2 is a tertiary amide
Carboxylic acid derivatives are generated through the ___________, including alkoxyl (ester!) and amino groups (amide!)
substitution of the -OH group with different substituents
In substitution reaction, an atom or group of atoms in a molecule is _________.
replaced by another atom or group of atoms
carboxylic acids undergo substitution reactions where _________.
-OH is substituted by another group

ID this reaction
substitution rxn
Carboxylic acids form their derivatives by _________
carbonyl-group, reversible, substitution reactions
Carboxylic acids react with alcohols to form ______
esters and water
The OH in carboxylic acid is substituted by _____.
OR group (ethoxy)
ethoxy definition
instead of alkoxy, with 1 C, this has two Cs.
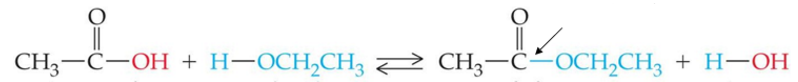
ID this rxn and the indicated bond
formation of an ester from carboxylic acid and an alcohol
ester bond
Carboxylic acids react with ammonia or amines to form ________.
amides
Carboxylic acid reacts with _________ to form secondary amide
primary amine

ID this rxn and the indicated bond
formation of an amide from a carboxylic acid and ammonia
amide bond
alcohol general molecular formula
H-OR’
ammonia general molecular formula
NH3
primary amine general molecular formula
R-NH2
secondary amine general molecular formula
H-NR’2
carboxylic acids reacts with secondary amines to form ______
tertiary amides
ester general molecular formula
RCOOR’
primary amide general molecular formula
RCO-NH2
secondary amide general molecular formula
RCO-NHR’
tertiary amide general molecular formula
RCO-NR’2
carbonyl group substitution rxns are also called
acyl transfer rxns b/c the rxn can be considered as the transfer of the acyl group
The reaction involving the replacement of one functional group attached to a carbonyl carbon (C=O) with another is generally called _________.
carbonyl-group substitution reactions
carbonyl-group substitution reaction is ______. Hence the carboxylic acid derivatives can all be ________ to carboxylic acids
reversible
hydrolyzed (rxn w/ H2O) back
one of the fuels used by our body for energy is ______.
fatty acids
Before fatty acid can be metabolized, it has to be activated by reacting with ____ to form ______.
coenzyme A (H-SCoA)
fatty acyl-CoA
activation of coenzyme A (H-SCoA) is a _____ rxn b/c the –OH group in carboxylic acid is substituted by coenzyme A
carbonyl-group substitution / acyl transfer
(acyl group is transferred to coenzyme A)
_______, such as fatty acyl-CoA and acetyl-CoA, play a crucial role in biochemistry, particularly in metabolic pathways
Thioesters (sulfur bond in thiols or thioesters)
Acid anhydride (or simply anhydride) can be synthesized by _______.
a condensation rxn, at high temp, b/t 2 carboxylic acids.
______ consist of phosphorus atoms in place of the carbon atoms in acid anhydrides
Phosphate anhydrides
phosphate anhydrides contain ______ bonds, which are high-energy bonds (energy released when broken) present in molecules like ATP.
phosphoanhydride
Similar to acid anhydrides, phosphate anhydrides are formed from the _______.
condensation reaction of two phosphate groups
_________ are also vital for various biochemical processes, including energy metabolism and genetic information storage
Phosphate esters and diesters
Carboxylic acids are a family of organic compounds that contain one or more ________
carboxyl functional group (-COOH)
The carboxyl functional group is so-named because it contains the _____
carbonyl group (-C=O) and a hydroxyl group (-OH)
In the carboxyl group, the carbonyl carbon is bonded to:
An _____ atom by a double bond,
A ______ by a single bond;
A ______ by a single bond.
oxygen
hydroxyl group (-OH)
hydrogen atom or a hydrocarbon chain (R, straight chain saturated or unsaturated, a ring or aromatic)
With two electronegative oxygen atoms, the carboxyl groups are highly _______
polar, with three polar covalent bonds
Alcohol behaves differently depending upon if it is bound to ____
carboxyl group vs. alkyl group
Carboxylic acids have a general formula _________
R-COOH, where R can be a hydrogen, derived from alkane, alkene, aliphatic or cyclic, or aromatic
A _____ may contain more than one carboxyl groups
carboxylic acid compound
Succinic acid has _____ carboxyl groups and citric acid contains _____ carboxyl groups
two
three
ID this by its common and IUPAC names and know its major source: HCOOH
Common: formic acid
IUPAC: methanoic acid
Major source: ants (L. formica)
ID this by its common and IUPAC names and know its major source: CH3COOH
common: acetic acid
IUPAC: ethanoic acid
major source: vinegar (L. acetum)
ID this by its common and IUPAC names and know its major source: CH3CH2COOH
common: propionic acid
IUPAC: propanoic acid
major source: milk (Gk. protus prion)
ID this by its common and IUPAC names and know its major source: CH3CH2CH2COOH
common: butyric acid
IUPAC: butanoic acid
major source: butter (L. butyrum)
fatty acids commonly have ______ carbons
12—24
dicarboxylic acids general molecular formula
HO2C-(R)-CO2H
Dicarboxylic acids contain ____ carboxylic groups
two
________ is the stinging toxin in ant bites
Formic acid
ID this: H2C=CHCOOH
acrylic acid
ID this: CH3CH=CHCOOH
crotonic acid
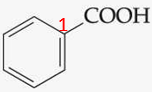
ID this
benzoic acid — simplest aromatic carboxylic acid
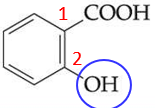
ID this
salicylic acid - or 2-hydroxybenzoic acid (IUPAC name), a reactant that forms aspirin
biological functions of this compound: fatty acids
energy source
biological functions of this compound: amino acids
make proteins
biological functions of this compound: citric acid
Intermediate in the citric acid cycle (KREBS), reducing NAD and FAD to generate energy
NADH/H+ is the _____ agent, and NAD is the _____ agent
reducing
oxidizing
fatty acids yield more energy per gram basis than ________
carbohydrates
Polyunsaturated fatty acids = _____
contains more than 1 C=C
Monounsaturated fatty acids = ______
contains 1 C=C
in a polyunsaturated fatty acid chain the C=C are always ____.
3 Cs apart
_______ are building blocks of proteins
Standard amino acids
four groups contain in an amino acid
amino group, NH2
carboxyl group, COOH
a hydrogen, H
an R group, or side-chain that makes each amino acid unique
_____ is the smallest amino acid, w/ 2 Hs, 1 NH2, and 1 COOH
Glycine
________ is the second smallest amino acid, w/ 1 methyl group, 1 H, 1 NH2, and 1 COOH
Alanine
functional group ranking
Carboxylic acid
Ester
Amide
Aldehyde
Ketone
Alcohol
Thiol
Amine
Ether
Alkyne = alkene
Alkyl = halide
_______ has three carbons, with each carbon bonds to a carboxyl group; is a tricarboxylic acid
Citric acid
______ is a component of the Krebs cycle, a key metabolic pathway involved in cellular respiration. Generates energy!!
Citric acid