p: unit 2, topic 1 - linear motion and force
1/23
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
24 Terms
what is a physical quantity and give an example
PE
property that can be measured
e.g. length (m), mass (kg)
speed
FRSS
formula: speed = distance/time
rate: the rate at which an object moves
scalar quantity
SI unit: ms^-1
what are scalar quantities and give examples
MDE
magnitude: the types of physical quantities that are described only by a magnitude
direction: no direction
e.g. time (s), speed (ms^-1)
what is a vector quantity and give an example
DP AE
direction: physical quantity that has both magnitude and direction
positive: can be positive or negative
algebraically: can be depicted algebraically or graphically
e.g. displacement, velocity
how to notate vectors
BAT
bold letters
arrow notation
tilde: using a tilde (same thing above the fancy spanish N)
distance
ESS
entire: the entire length travelled by an object
scalar quantity
SI unit: metres (m)
displacement
OVS
overall: the overall change in position of an object
vector quantity
SI unit: metres (m)
velocity
FRVS
formula: velocity = displacement/time
rate: the rate of change of an object’s displacement
vector quantity
SI unit: ms^-1
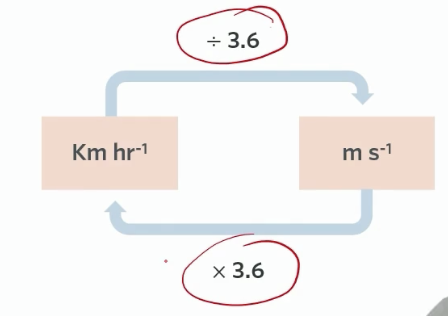
conversion from km hr^-1 to ms^-1
acceleration
VV PSQF
velocity: rate of change of velocity
vector quantity
pos: can be pos or neg
SI unit: ms^-2
quickly: refers to how quickly an object is speeding up or slowing down
formula: acceleration = change in velocity/time
average velocity
OF
overall: describes the overall rate of motion across a journey
formula: total displacement/total time
instantaneous velocity
SSV
specific: describes how fast an object is moving at a specific moment
slope: represented by the slope of a position-time graph
velocity: velocity can be read directly off the graph for a given point in time
what are the 3 main graphs of motion that help us to depict displacement, velocity and acceleration of an object
DVA
displacement-time
velocity-time
acceleration-time
displacement-time graphs
TDD VNY
time is the independent variable (x-axis)
displacement is the dependent variable (y-axis)
directly: can be read directly off graph
velocity: given by gradient
negative gradient means change in direction
y-intercept shows the position from which the object begins
error bars
UPF
uncertainty: graphically represent the uncertainty in the data
precise: help convey how precise/reliable the data is
fit: can be used to insert maximum and minimum lines of best fit
line of best fit
TSV
trendline: aka trendline
straight line drawn through a scatter plot of data points that best represents the relationship between the variables
visualise: used to visualise the trend/correlation in the data and make predictions about one variable based on the value of another
what are the 3 lines of best fit
AMM
average
minimum
maximum
velocity-time graphs
DTV AID
displacement: given by area under the curve
total: displacements above the x-axis are added, and areas under the x-axis are subtracted to give the total displacement
velocity: read directly from graph
acceleration: given by gradient slope
instantaneous velocity can also be determined for a particular point in time
displacement: can be constructed from the gradient of the displacement-time graph
acceleration-time graphs
VA
velocity: given by area under the graph
acceleration: can be read directly off the graph
SUVAT
the variables arising in a situation involving constant acceleration
S: displacement (m)
U: initial velocity (ms^-1)
V: final velocity (ms_-1)
A: acceleration (ms^-2)
T: time (s)
what are the three main equations of motion?
final velocity

displacement

final velocity squared

definition of gravity
the force that attracts objects with mass toward each other, particularly pulling them toward Earth’s centre
acceleration due to gravity
CG VMP
constant: objects fall at a constant (uniform) rate close to the Earth’s surface
gravity: this constant is gravity, g, and its value is 9.8ms^-2 close to the Earth’s surface
velocity: as an object falls to the ground, its velocity increases by 9.8ms^-1
mass: applies to all objects, regardless of mass
planet: varies based on planet