American Government: Stories of a Nation Unit 1
1/81
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
82 Terms
politics
the process of influencing the actions and policies of government
government
the rules and institutions that make up that system of policy making
democracy
a system of government where power is held by the people
Adopted from histories and philosophies of ancient Greek and Rome.
Note that early foundational documents like the federalist papers often consider the US to be a republic NOT a democracy, using a definition of democracy closer to what we'd now consider "direct democracy" in contrast to a republic's elected representatives.
inalienable rights
rights the government cannot take away
The Declaration of Independence declares "that all men are created equal, that they are endowed by their Creator with certain unalienable Rights, that among these are Life, Liberty and the pursuit of Happiness"

linkage institutions
channels that connect individuals with government, including elections, political parties, interest groups, and the media
participatory democracy
a theory that widespread political participation is essential for democratic government

Elitist Democracy
a theory of democracy that the elites have a disproportionate amount of influence in the policymaking process

pluralist theory
a theory of democracy that emphasizes the role of groups in the policymaking process
Political Institutions
the structure of government, including the executive, legislature, and judiciary
constitutional republic
a democratic system with elected representatives in which the Constitution is the supreme law

Declaration of Independence
the document (mostly written by Jefferson) recording the proclamation of the second Continental Congress (4 July 1776) asserting the independence of the colonies from Great Britain
Drew upon ideas of the Enlightenment, such as natural rights, social contract, and popular sovereignty.

ideals of democracy
natural rights, popular sovereignty, social contract, limited government
(according to the College board)
natural rights
the right to life, liberty, and property, which government cannot take away
Popularized in the enlightenment by John Locke, a variant of these with "pursuit of happiness" in place of "property" is found in the Declaration of Independence.
social contract
people allow their governments to rule over them to ensure an orderly and functioning society
An idea from the enlightenment. The declaration of independence uses this idea in asserting that Parliament broke essentially broke its social contract so the colonists were right to rebel. "That whenever any Form of Government becomes destructive of these ends [securing rights], it is the Right of the People to alter or to abolish it"
limited government (and ways of achieving of limited government)
government structure in which government actions are limited by law.
CB wants you to know that we have limited government through: separation of powers, checks and balances, federalism, and republicanism
popular sovereignty
the idea that the government's right to rule comes from the people.
Referenced in the Declaration of Independence: "That to secure these rights, Governments are instituted among Men, deriving their just powers from the consent of the governed"
republicanism
a system in which the government's authority comes from the people
Majority rule with minority rights
the democratic principle that a government follows the preferences of the majority of voters but protects the interests of the minority
another expression of democratic ideals, combining popular sovereignty (majority rule) and natural rights (minority rights)
Articles of Confederation
A weak constitution that governed America during the Revolutionary War.
Shays' Rebellion
Rebellion led by Daniel Shays of farmers in western Massachusetts in 1786-1787, protesting mortgage foreclosures. It highlighted the need for a strong national government just as the call for the Constitutional Convention went out.

Faction
a group of self-interested people who use the government to get what they want, trampling the rights of others in the process
Federalist 10 addresses the problems this as an issue

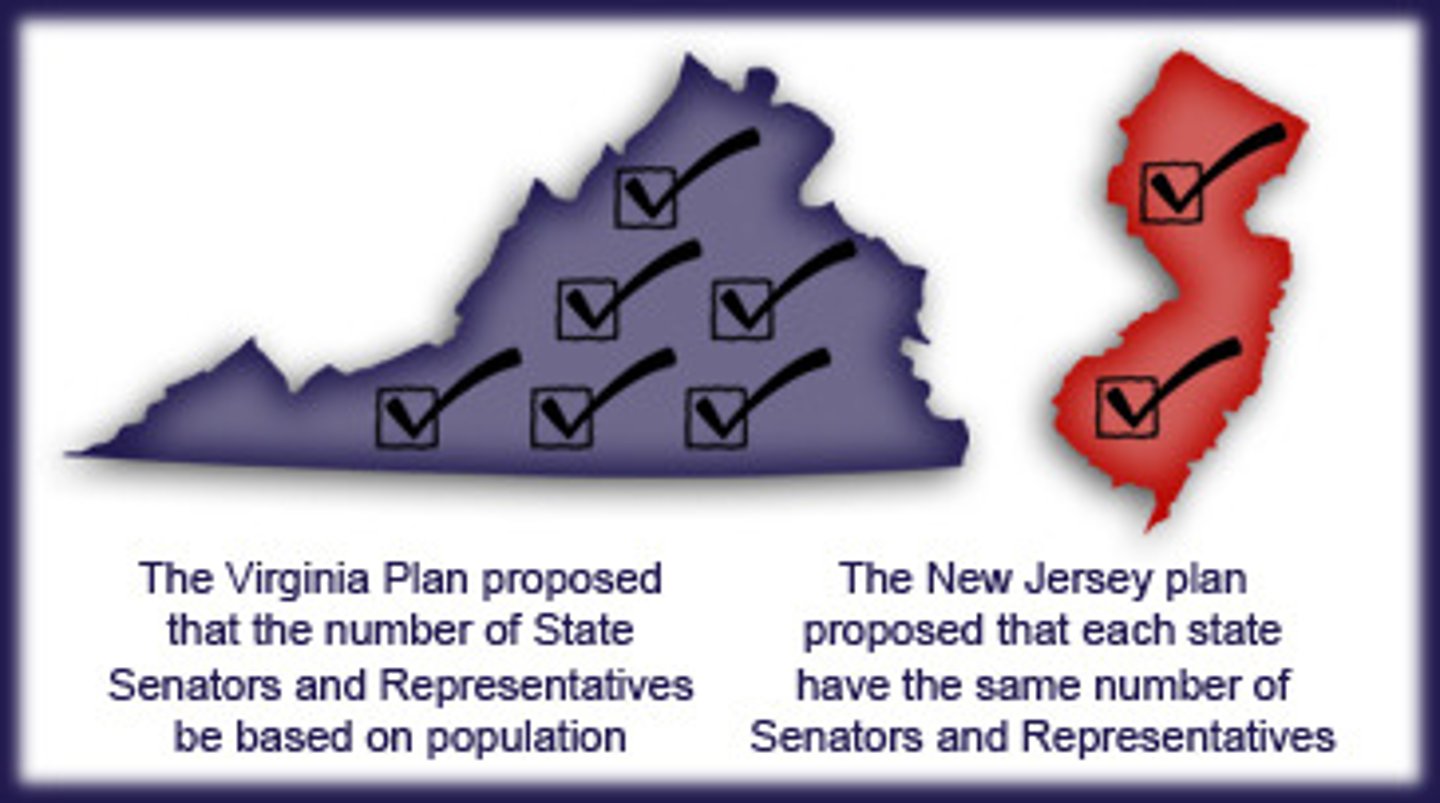
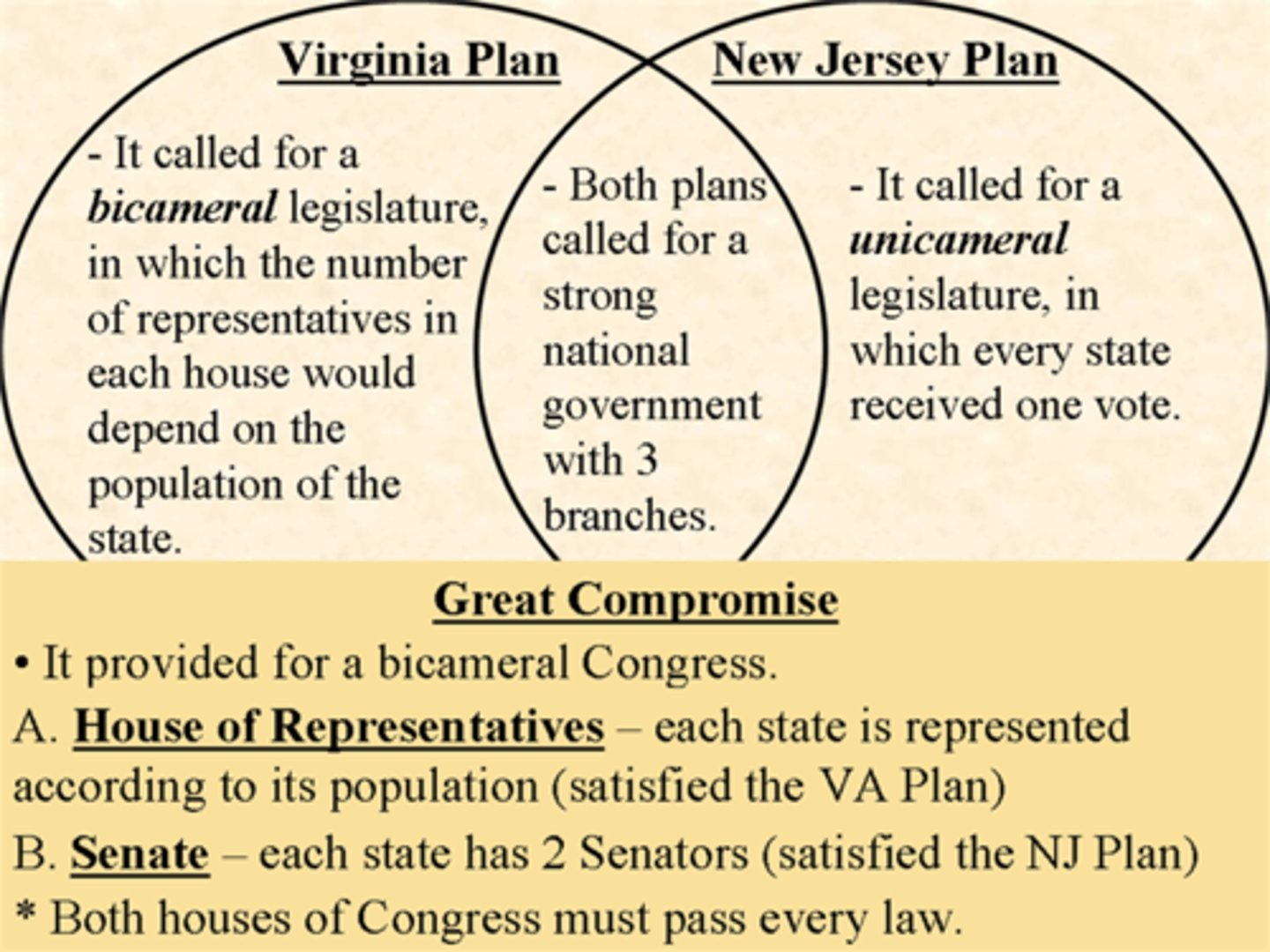
New Jersey Plan
a plan of government that provided for a unicameral legislature with equal votes for each state
(favored and was favored by small states)
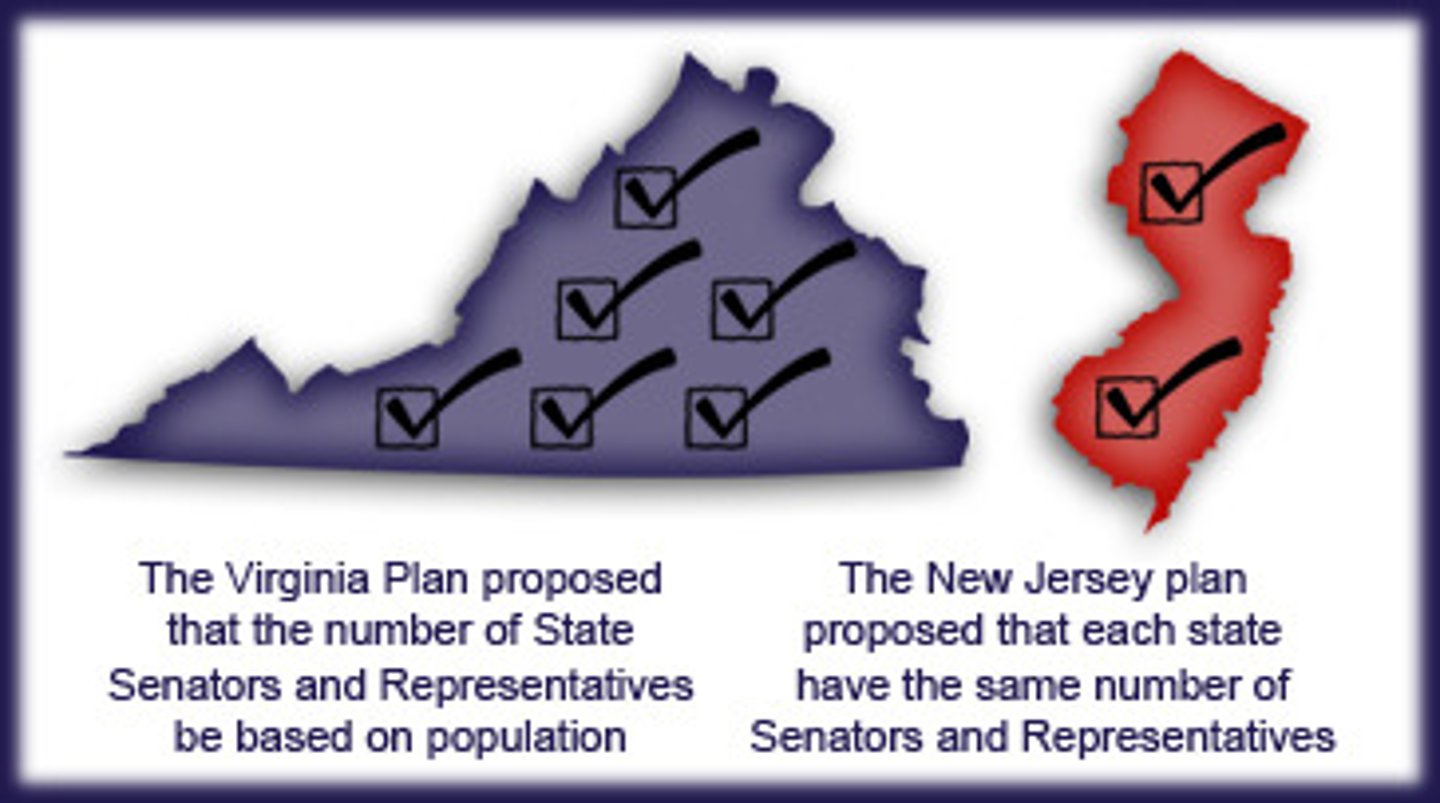
Virginia Plan
a plan of government calling for a three-branch government with a bicameral legislature, where more populous states would have more representation in Congress
(favored and was favored by large states)
Bicameral
a two-house legislature
The Virginia Plan and the Great Compromise called for this type of legislature.
Unicameral
One-house legislature
The articles of confederation had this type of legislature, the New Jersey plan also suggested this type of legislature.
Connecticut (Great) Compromise
an agreement for a plan of government that drew upon both the Virginia and New Jersey Plans; it settled issues of state representation by calling for bicameral legislature with a House of Representatives apportioned proportionately and a Senate apportioned equally.
3/5ths Compromise
an agreement reached by delegates at the Constitutional Convention that a slave would count as three-fifths of a person in calculating a state's representation
writ of habeas corpus
the right of people detained by the government to know the charges against them
Suspension of the writ of habeas corpus is forbidden by Article I, section 9 of the Constitution.
Bills of Attainder
when the legislature declares someone guilty without a trial
Forbidden by Article I Section 9 of the constitution
ex post facto law
a law punishing people for acts that were not crimes at the time they were committed
Forbidden by Article I Section 9 of the constitution
separation of powers
a design of government that distributes powers across institutions in order to avoid making one branch too powerful on its own
The US constitution uses this.
An idea popularized by Montesquieu during the Enlightenment.
Checks and Balances
A system that allows each branch of government to limit the powers of the other branches in order to prevent abuse of power
Federalists
supporter of the proposed constitution, who called for a strong national government
(Note: also later referred to a political party)
Amendment
a constitutional provision for a process by which changes may be made to the constitution
Article 5 of the constitution puts forward a process for these in US.
Anti-Federalist
a person opposed to the proposed constitution who favored stronger state governments
Bill of Rights
The first ten amendments to the Constitution.
Federalists agreed to add a bill of rights to the constitution as a compromise to end the Ratification debate.

Federalist paper 10
an essay in which Madison argues that the dangers of faction can be mitigated by a large republic and republican government
mnemonic fact10n
Federalist paper 51
an essay in which Madison argues that separation of powers and federalism will prevent tyranny
Brutus 1
an Antifederalist Paper arguing that the country was too large to be governed as a republic and that the Constitution gave too much power to the national government
Federalism
the sharing of power between the national government and the states.
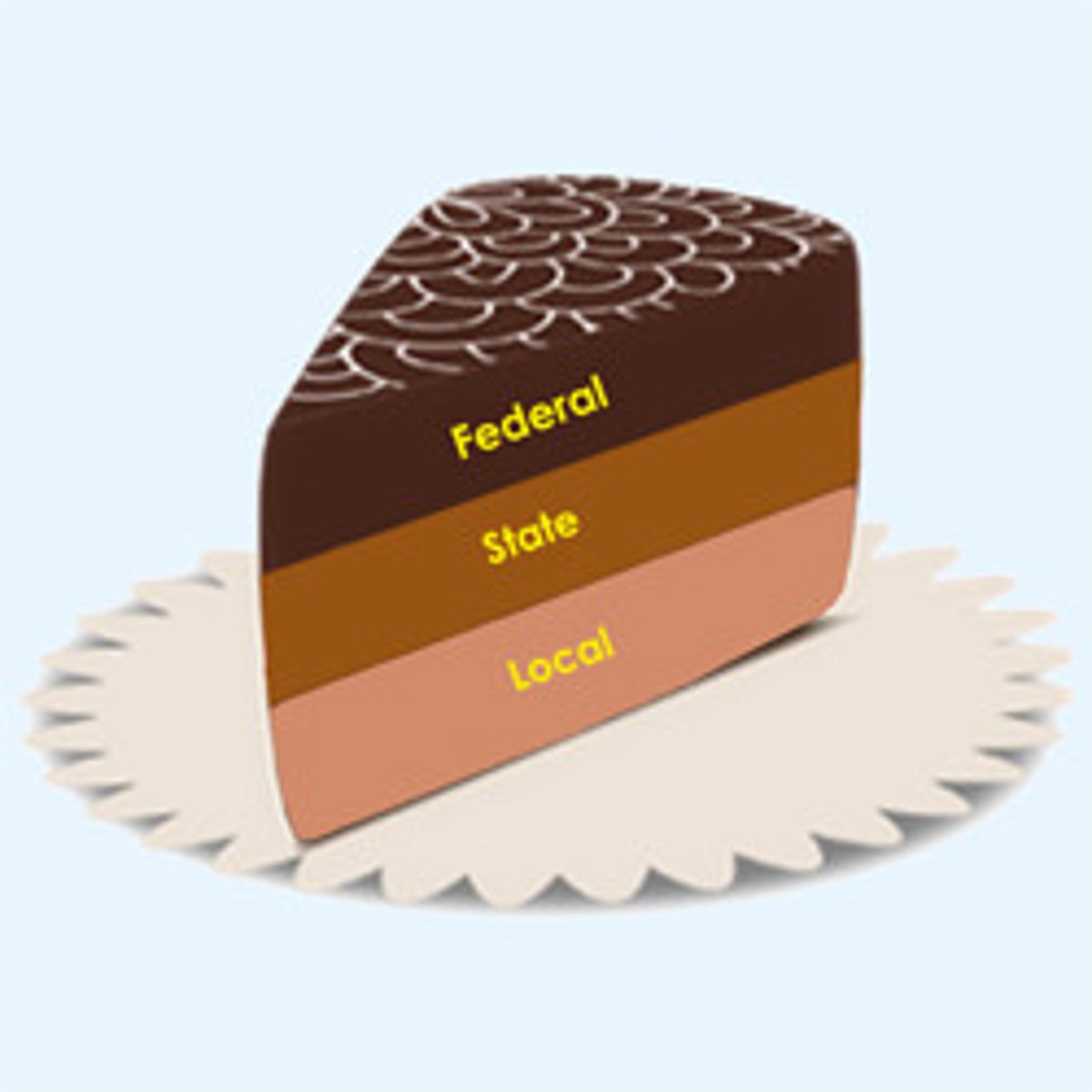
confederal system
a system where the subnational governments [such as states in the US] have most of the power
Examples: The EU, the US under the Articles of Confederation, Switzerland.
unitary system
a system where the central government has all of the power over subnational governments [such as the states in the case of the US]
Examples: UK, China, most countries
federal system
a system of government where power is divided between the national and state governments.
Examples: US, Mexico, Nigeria, Russia (in theory)
enumerated or expressed powers
powers explicitly granted to the national government through the Constitution; also called expressed powers
exclusive powers
powers only the national government may exercise
implied powers
authority of the federal government that goes beyond its expressed powers; powers not granted specifically to the national government but considered necessary to carry out the enumerated powers
Necessary and Proper or elastic Clause
language in Article I, Section 8, granting Congress the powers necessary to carry out its enumerated powers
Used to justify the implied powers of the federal government in addition to its enumerated powers
commerce clause
grants Congress the authority to regulate interstate business and commercial activity
Has had a strong impact on modern American Federalism
Supremacy Clause
The constitutional provision that makes the Constitution and federal laws superior to all conflicting state and local laws.
Found in Article VI of the Constitution
Tenth Amendment
reserves powers not delegated to the national government to the states and the people; the basis of federalism
reserved powers
powers not given to the national government, which are retained by the states and the people
concurrent powers
powers granted to both states and the federal government in the Constitution
Full Faith and Credit Clause
constitutional clause requiring states to recognize the public acts, records, and civil court proceedings from another state
Extradition
the requirement that officials in one state return a defendant to another state where a crime was committed
Privileges and Immunity Clause
prevents states from discriminating against people from out of state
Dual Federalism
a form of American federalism in which the states and the nation operate independently in their own areas of public policy
The US largely used this model of Federalism until FDR's New Deal
selective incorporation
the process through which the Supreme Court applies fundamental rights in the Bill of Rights to the states on a case-by-case basis
Cooperative Federalism
a form of American federalism in which the states and the national government work together to shape public policy
Largely began with FDR's New Deal in response to the Great Depression.
grants-in-aid
federal money provided to states to implement public policy objectives
Fiscal Federalism
the federal government's use of grants-in-aid to influence policies in the states
categorical grants
grants-in-aid provided to states with specific provisions on their use
unfunded mandates
federal requirements that states must follow without being provided with funding
block grant
a type of grants-in-aid that gives states more authority in the disbursement of federal funds
revenue sharing
when the federal government apportions tax money to the states with no strings attached
Devolution
returning more authority to state or local governments
McCulloch v. Maryland
Supreme Court ruling (1819) confirming the supremacy of national over state government
Found that Maryland could tax the 2nd bank (which McCulloch worked for).
Gibbons v. Ogden
Commerce clause case (1824). Decision greatly enlarged Congress' interstate commerce clause power by broadly defining the meaning of "commerce" to include virtually all types of economic activity.
New York had granted a monopoly to Ogden to routes in NY and between NY and NJ, Gibbons a license by the federal government. Found unanimously for Gibbons.
Pair with Lopez & Morrison cases (limiting commerce power).

Fourteenth Amendment
constitutional amendment that provides that persons born in the United States are citizens and prohibits states from denying persons due process or equal protection under the law
Protections Bill of rights are now applied to the states via "Selective Incorporation" through the 14th amendment.
Thirteenth Amendment
constitutional amendment that outlaws slavery
US vs Lopez
the Supreme Court ruled that Congress had exceeded its constitutional authority under the Commerce Clause when it passed a law prohibiting gun possession in local school zones.
liberty
social, political, and economic freedoms
american political culture
the set of beliefs, customs, traditions, and values that Americans share
republic
a government ruled by representatives of the people
constitution
a document that sets out the fundamental principles of governance and establishes the institutions of government

James Madison
"Father of the Constitution" (also 4th president of the US)
Pushed for a new constitution to replace the Articles of Confederation. Helped come up with the original Virginia Plan for the Constitution. One of the authors of the federalist papers, including 10 and 51.

Importation Compromise
Congress could not prohibit the slave trade until 1808, but imported slaves could be taxed.
legislative Branch
the institution responsible for making laws
the two chambers of Congress, the house of representatives and the senate, make up the this branch of government in the US
executive Branch
the institution responsible for carrying out laws passed by the legislative branch
This branch is headed by the President in the US
Articles of the Constitution
1. Legislative Branch
2. Executive Branch
3. Judicial Branch
4. States
5. Amendments
6. Supremacy
7. Ratification
Mnemonic Device Initialism: Lazy Elephants Jump Slowly And Sit Regularly
Mnemonic Device Acronym: - LEJSASR ~Ledge Sass-er

formula grant
Federal categorical grants distributed according to a formula specified in legislation or in administrative regulations.
John Marshall
Long serving chief justice of the U.S. Supreme Court (1801-1835). Generally a federalist who expanded federal power as Chief Justice even after the Federalist Party had began to lose influence to the Democratic-Republicans. Responsible for a number of important cases including a some required cases.
Marbury v Madison
McCulloch v Maryland
(also Gibbons v Ogden)
Questionable Mnemonic: Marshall and the M and M cases.

Classification of US Government
[Constitutional] Federal Presidential Republic
Constitutional: constitution provides fundamental law
Federal: National (Federal) government and subnational (state) governments share power.
Presidential: The leader and executive branch is a separate branch of the government. (In the Parliamentary system the executive is chosen by and a part of the legislature.)
Republic: citizens or their elected representatives hold political power. (Also think of Direct vs Indirect Democract.)