Photoelectric Effect
1/7
Earn XP
Description and Tags
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
8 Terms
What is the photoelectric effect?
When light above a certain threshold frequency hits a metal surface, electrons are emitted.
The frequency problem
Photoelectric emission only occurs when the frequency of the incident radiation is above a certain value, the threshold frequency.
However, according to wave theory, photoelectrons should be emitted at all frequencies.
The intensity problem
The maximum kinetic energy of the emitted photoelectrons only depends on the frequency of the incident radiation, not the intensity
The intensity of the incident radiation is instead proportional to the number of photoelectrons emitted per second.
Issue:
According to wave theory, E is proportional to amplitude squared.
So higher intensity should cause higher KE
So increasing intensity should increase the electric field strength (EFS)
F = e(EFS), so if EFS increases, the KE should increase.
But this doesn’t happen.
Time delay problem
If the incident radiation is above threshold frequency, photoelectric emission occurs without delay as soon as the incident radiation is directed at the surface
According to wave theory, there should be a time delay before electrons are emitted. We do not observe this.
How does Einstein’s photon theory solve the intensity problem, the frequency problem and the time-delay problem?
His Solution:
Light is made up of particles (photons)
E = hf
How does it help?
A single electron can absorb a single photon and in doing so gain energy = hf. (1-1 interaction)
If hf > ϕ, then electrons will be emitted. (ϕ = minimum energy required to remove electrons from the surface of the metal → work function)
KEmax = hf - ϕ
KE represents left over energy. (KE electrons have from the energy left over from what was needed to remove electrons)
Intensity - number of photons per second per unit area. Doubling intensity will double the number of photons
How does this solve the problems?
Intensity:
Doubling the intensity causes the number of photons per second to double. So, the number of electrons emitted per second doubles.
Frequency:
If the frequency is less than the threshold frequency then hf < ϕ so no electrons are emitted.
Time Delay:
Since the electron absorbs all the energy at once, emission is rapid.
Why do emitted photoelectrons have a range of KE’s up to a maximum value
Electrons have varying depth within surface
Electron-Electron interactions
Distribution of initial energy states
What is the stopping potential?
Electrons that escape from the metal surface can be attracted back to it by giving the surface enough positive charge. This can be achieved by connecting the positive terminal of a cell to the metal plate
The value of the potential difference that causes the current to reduce to zero is called the stopping potential, Vs
At this voltage, all the KE of the electron is used to do work to overcome the attraction to the positive plate.
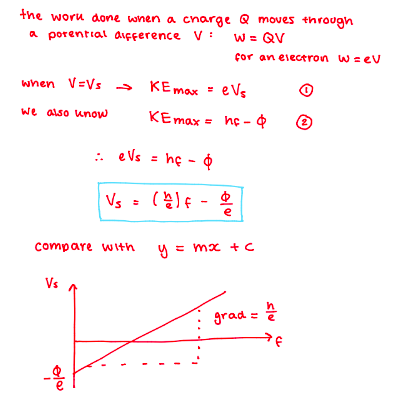
Use Vs = (h/e) f - ϕ/e to sketch a graph and understand how this can be used to determine Planck’s constant.
The gradient would be equivalent to h/e.