Geography - Tectonic Hazards
1/123
Earn XP
Description and Tags
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
124 Terms
lithosphere
cold, rigid, brittle
asthenosphere
hot, weak, plastic
mesosphere
hot but stronger due to high pressure
moho
boundary between solid crust and semi-solid mantle/asthenosphere
continental crust
less dense, thicker (30 - 75cm), older
oceanic crust
more dense, thinner (5 - 10cm), younger
pangea
made up of Laurasia and Gondwana land
continental drift theory
Alfred Wegner → theory was disregarded as unable to explain the mechanism behind the movement
evidence of continental drift
jigsaw fit of continents e.g. South America and Africa
location and mapping of volcanic activity
fossils of the same pre-historic aquatic animals have been found in continents that are now far apart (mesosauras = freshwater reptile in Africa + South America and Glossepten’s leaf = found in Antarctica + Australia but different climates and extinct nearly 220 millions years ago)
same rock sequences in Scotland + Canada
‘ring of fire’
most tectonically active area in the world
How did the thoery of plate tectonics evolve?
identification of mid-Atlantic ridge - mountains 1000 miles wide and 25—m high was discovered by 2 plates moving apart
echo sounders used to prove the crust and ocean floors found to be thinner
paleomagnetism - Earth’s magnetic field reverses every 400,000 years and lava preserves record of magnetic film at that time due to orientation of iron particles
Benioff zone - depth of EQs get larger the further away from the boundary/zone due to oceanic crust sinking
convection currents
heat transferring from one area to another
rising and sinking convection currents within the mantle allow the slabs of crust to float in the same direction as the diverging or converging currents in the asthenosphere
‘slab pull’ vs ‘ridge push’
‘slab pull’ = where the weight of a subducting plate ‘pulls’ the rest of the plate downwards into the mantle due to gravity
‘ridge push’ = due to mid-ocean ridges lying at higher elevation than the rest of the ocean floor, gravity causes the ridge to push on the crust that lies further away
convergent boundaries
plates moving towards each other (either destructive or collision)
destructive plate boundaries
either oceanic + continental or BOTH oceanic
the denser oceanic curst subducts beneath the less dense continental or oceanic plate. Due to high pressure and heat it melts and this magma rises through the continental or oceanic plate as is less dense, leading to VOLCANOES
friction in the Benioff zone between the plates creates stress and eventually rocks will fracture and slip, meaning EARTHQUAKES
e.g. Nazca Plate and South American Plate
submarine volcano
formed if two oceanic plates converge and when the magma cools, a volcanic island is built e.g. Indonesia
collision boundaries
continental and continental
creates fold mountains but NOT volcanoes as no new magma being created
stress created by the pressure causes rocks to fracture and therefore earthquakes are very common
e.g. Indian and Eurasian Plate
divergent boundaries
plates moving away from each other
constructive plate boundary when both oceanic plates
magma rises and cools as it enters the cooler ocean which forms submarine volcanoes and volcanic islands
forms new oceanic crust e.g. Mid Atlantic Ridge
constructive plate boundary when both continental
convection currents thin the crust causing it to begin to fracture, forming volcanoes as magma rises
causes continental crust to split apart forming more oceanic crust
e.g. East Africa being pulled apart
conservative boundary
plates moving in the same/opposite direction/rubbing together
EARTHQUAKES occur when stress is released due to sudden plate movement after locking together
e.g. North American plate and the Juan de Luca plate creating the San Andreas fault
shallow focus earthquakes
close to the surface
often more powerful as they don’t have time before losing their energy
focus (hypocentre)
origin of the earthquake
epicentre
lies directly above the focus
mantle plumes + hot spot volcanoes
occur when an area of the mantle experiences increased temperatures and therefore increased upwelling of magma beneath the crust
movement of plate above can cause a chain of volcanoes to form (the one directly above the plume is more active)
e.g. Hawaii
both continental and oceanic plates
Midlands EQ (2002)
4.8 on Richter scale
epicentre = Dudley, west of Birmingham
caused by movement along the old fault line known as the Malvern Lineament
intra-plate earthquakes
occur along faults (cracks in the earths lithosphere where sections of a plate are fractured) due to friction and the buildup of stress and pressure
shadow zone
the area of the Earth where seismograms cannot detect an earthquake since it does not receive any direct P or S waves (104-140 degrees)
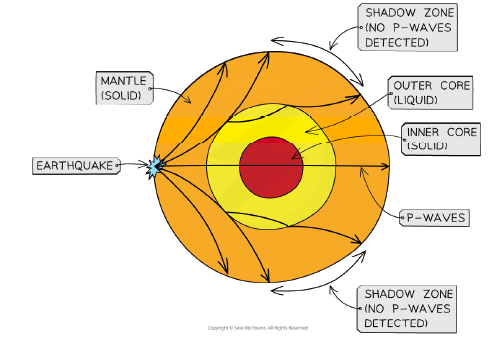
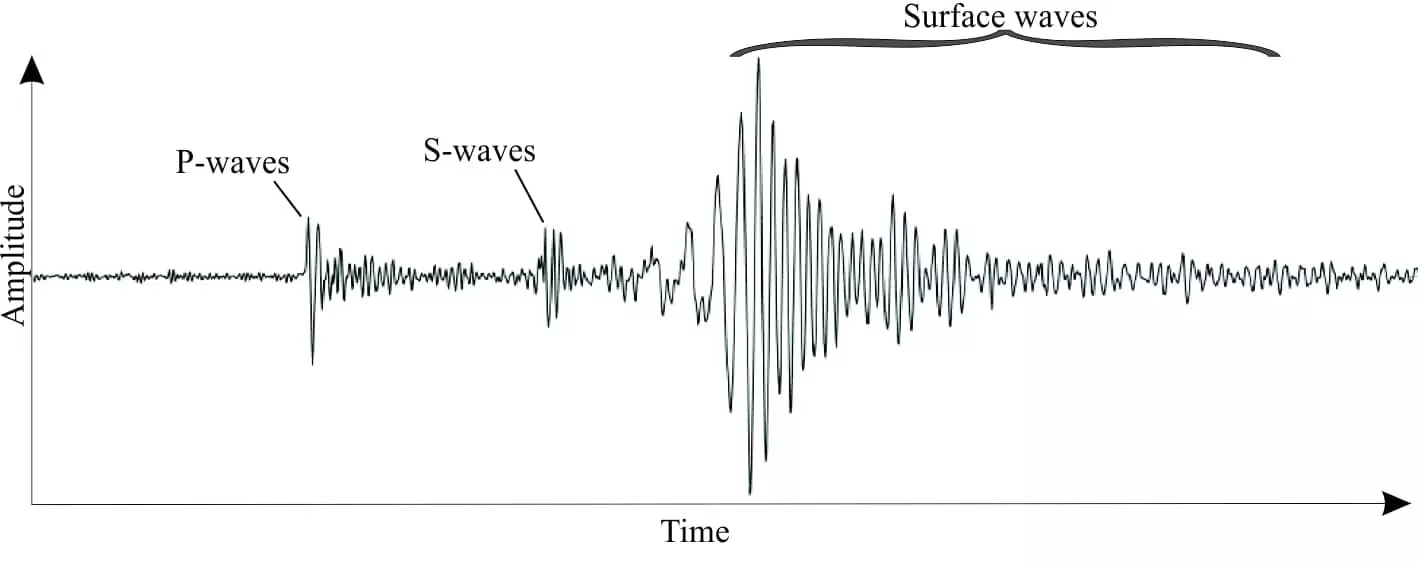
P-wave (primary)
travel in a linear fashion (parallel to the flow of particles )
fastest moving wave (6km/s)
travel though solids and liquids
body wave and can travel through anything (from crust to core)
travel in a push and pull motion
S-wave (seconday)
travel 3km/s
can only travel through solids not liquids (cannot go through outer core)
particles vibrate perpendicular to the direction of the wave
body wave
L-wave (surface/rayleigh)
complex rolling motion (ground moves up and sideways)
can only travel through the surface (solid) and energy decreases with distance from epicentre
slowest velocity
responsible for most structural damage and sometimes visible
seismograms
the velocities of all seismic waves are variable and dependent upon the density and composition of the rocks through which they travel (higher density = higher velocity)
seismographs
an inert weight is attached by a spring, which acts as a shock absorber which keeps the pen stationary whilst the rest of the instrument moves
Mercalli scale
records intensity or damage caused and is based on observations by those who experienced the event and the scale of resulting damage (I - XII)
Richter scale
assigned numbers in a logarithmic scale from 1 to 9.9 (increases 10x strength for each one e.g. 10x difference between a level 4 and 5 EQ)
Moment Magnitude Scale
measures the size of earthquakes in terms of energy released (same scale as Richter scale)
How to accurately pinpoint the epicentre of earthquakes
figure out the lag time between the arrival of P and S waves
using s = d/t, a distance between the epicentre and recording station is produced giving a possible radius
using multiple recording stations, the possible radius’ would overlap giving the epicentre p
primary effects of EQs
ground shaking → measured using a seismometer
ground rupturing → occurs when the EQ movement along a fault actually breaks the surface
secondary effects of EQs
damage to structures → depends upon building materials (metal = effective, bricks and concrete = can’t cope), underlying geology and age of building
building collapse e.g. Haiti - 250,000 collapsed
liquefaction → ground water migrates toward the surface causing sediment to behave like quicksand e.g. LA - Loma Prieta EQ
landslides → destabilises soil pulled down by gravity
tsunamis → EQ occurring underwater e.g. 10ft waves after Haiti
fires → may break gas pipes which leak gas and so any sparks would ignite
avalanches → destabilises snow
Bam (2003) - impacts + responses
6.8 magnitude yet destroyed 70% of buildings
26,271 deaths and 500 missing (even 3 months later
high death toll as people asleep
cut electricity, water supplies and phone services
Responses
40+ countries sent aid
emergency centres set up as main hospital collapsed
long term cost of reconstruction = $1 billion
Haiti EQ (2010) - impacts + responses
7.0 magnitude
170,000 deaths + 250,000 buildings collapsed
one of worlds poorest countries
Responses
planeloads of water, food, tents, medicine and rescue equipment to Port-au-Prince
mass graves created to stop spread of disease
Nepal aid workers defecated in river causing 5000 further deaths from cholera
Paso Rables EQ (2003) - impacts + responses
3 deaths and 40 badly injured as high agricultural design
7.1 magnitude yet less deaths than Bam
75,000 homes and businesses lost power but restored rapidly
Response
low destruction so little responses
Nepal EQ (2015) - impacts + responses
7.8 magnitude
9000 deaths and received many aftershocks
7000 schools + hospitals destroyed
25% loss of electricity
harvests almost completely lost with a massive drop in tourism
catalysed avalanche on Mt Everest killing 300
Kathandu is population dense
Responses
made 16 transitional shelters for hundreds of thousands of people who became homeless
500 million Nepall rupees for relief from government
preparedness undermined as government buildings lost
causes of tsunamis
the continental crust and oceanic crust lock together causing the continental crust to be dragged downwards (if destructive boundary)
eventually the force of movement overcomes friction and the overlying crust is sprung upwards, displacing large volumes of water
coastal uplift - tsunami travels in both directions
wave approaches land causing its energy to compress into a smaller space, so gains height
characteristics of tsunamis (x5)
travel at speeds of up to 400-500 mph in deep ocean but only 100mph in shallow
can reach up to 100 feet or more and crash inland
shallow water = slows down, short wavelength but large height
deep water = faster, long wavelength but flat
waves retreating is a sign that a tsunami is approaching
Indian Ocean tsunami
230,000 deaths (deadliest tsunami)
displaced millions from their home - forced to live in temporary shelters or with host families
loss of jobs and income for thousands in fishing and tourism industry
agricultural loss e.g. rice paddies and fish reserves destroyed
tourism showed sharp decline
reached Thailand, Indonesia etc. (51m high)
Hunga Tonga volcano
4 deaths whilst 84,400 affected by volcanic ash fall and tsunami waves
contaminated water supplies
600 structures destroyed or severely damaged
80% population affected
caused an estimated US$90.4 million in damages (18.5% of Tonga’s GDP)
agricultural loss - destroyed crop lands and reduced crop yields
tourism industry hindered due to damages and fear
fissure volcano
linear volcanic vent through which lava erupts, usually without an explosion (gentle slopes + basaltic lava)
shield volcano
volcano with gently sloping sides due to layers of solidified basaltic lava
dome volcano
roughly circular mound-shaped volcano with steep convex slopes from thick, fast cooling andesitic lava
cinder cone volcano
a steep, conical hill consisting of layers of fine ash and cooled andesitic lava
composite cone volcano
a volcano with layers of solid andesitic lava and fine ash with not only the central vent but also side vents
caldera volcano
an extremely explosive volcanic crater which is usually formed by a major explosion leading to the collapse of the mouth of a volcano
basaltic lava
low silica content and erupts at highest temperatures (1000 - 1200 degrees)
very low viscosity and fast flows with high density (effusive)
rates of 100km/hr and flows around 50km from source
found near oceanic hotspots e.g. Hawaii
andesitic lava
higher in aluminum and silica
temperatures are lower (800 - 1000 degrees) - more viscous
found at destructive subduction margins e.g. Mt Edna or in the Andes
rhyolitic lava
high silica content and high viscosity (10x slower than basaltic lava)
high gas and ash rich (pyroclastic)
lower temperatures (650 - 800 degrees)
explosive eruptions
found at continental hotspots due to mantle plume melting e.g. Yellowstone
tephra as a primary hazard of volcanoes
any solid material ejected from a volcano e.g. ash or volcanic bomb
the size of the particles that fall out are largest near the volcano and get progressively smaller
lava as a primary hazard of volcanoes
quite predictable and rarely leads to death despite being fast-flowing
can impact infrastructure, destroy crop land and tourist facilities
main secondary hazard = fires
pyroclastic flows as a primary hazard of volcanoes
contains extremely hot gas, ash, lava and dust which can reach 800 degrees and travel at 200km/hr e.g. Mt St Helens destroyed 15km3 of timber
volcanic gases as a primary hazard of volcanoes
include CO2, CO, H2, SO2 and Cl2 which are greenhouse gases - can be deadly e.g. emissions of CO2 from Lake Nyos in Cameroon suffocated 1700 people
lahars as a secondary hazard of volcanoes
mudflows of wet volcanic debris and are a hazard of vulcanism
caused when heavy rainfall turns new ash deposits into fast flowing mud rivers or if pyroclastic flow meets a river or snow e.g. Mt St Helens
Johulhlaups as a secondary hazard of volcanoes
glacial outburst floods
caused if a subglacial volcano erupts causing the overlying ice to melt producing huge quantities of water which leads to flooding e.g. Grimsvotn in Iceland
fires as a secondary hazard of volcanoes
hot magma and volcanic bombs may cause wildfires, destroying wildlife and nature etc.
Lake Nyos, Cameroon (1986)
released vast amounts of CO2 killing 1700 people due to suffocation
due to a landslide hitting the lake (which lies above a pocket of magma) causing a large cloud of CO2 to be emitted
killed 3500 livestock
Mt St Helens, USA (1980)
destructive plate boundary between Juan de Fuca and the North American plate
VEI of 5 - only 57 deaths due to remote place and when the volcano collapsed, it focused the blast laterally toward the north
pyroclastic flows caused extensive damage, rhyolitic lava caused large explosion and ash caused suffocation
Kilauea, Hawaii (2018)
almost continually active since 1983 with effusive eruptions
0 deaths but injured 23
700 houses destroyed and SO2 released
insurance increased 6x
Nevada del Ruiz, Columbia (1985)
killed 23,000 in town of Armero (40km away)
VEI 3 but led to melting of 20% of snow and ice at the summit causing lahars
infrastructure destroyed and cost of response was 20% of GDP
Volcanic Explosivity Index (VEI)
given as a number based on the amount of material ejected from the eruption (scale of 1-8)
super eruption = VEI 8
an increase of 1 on the VEI is a 10x increase in explosivity
volume of products, eruption cloud height and qualitative observations used
hazard
a naturally occurring process or event that has the potential to affect people
vulnerability
the ability to anticipate, cope with, resist and recover from a natural hazard
disaster
an event that causes significant social, environmental and economic damage
resilience
the ability to protect lives, livelihoods and infrastructure from destruction, and to restore areas after a natural hazard has occurred
hazard risk equation
risk = (vulnerability x hazard) / resilience
the ‘Pressure-release model’
underlying causes of a disaster based on the idea that a disaster happens when two opposing forces interact
vulnerability is a process that starts with dynamic pressures which are political and economic systems that control who has power in a society and who has access to resources
example of PAR mdoel
poor (root cause), don’t spend time or money enforcing building regulations (dynamic pressures), leads to poorly built infrastructure (unsafe living conditions)
factors that increases vulnerability
level of education e.g. people per doctor
government policies
location of country e.g. landlocked
landscape of a country (geology)
infrastructure
magnitude of disaster
wealth (GDP)
climate - worse weather = worse infrastructure
quality of healthcare system
preparation/monitoring levels
coastal or low-lying
access to clean water
population density = more people = greater vulnerability
primary effects of Haiti EQ
316,000 deaths and more than 1 million made homeless
1 in 5 jobs lost, 30,000 commercial buildings collapsed
port destroyed, road and rail links blocked meaning hard to spread aid
sea levels in the local area changed, some parts of land sinking into water
secondary effects of Haiti EQ
5000 people in a refugee camp died of cholera as a UN force from Nepal defecated in upland rivers
looting and sporadic violence observed due to delay in disease distribution
transport links destroyed and damage to communication and electrical networks
How have root causes led to unsafe living conditions in Haiti?
magnitude 7 + relatively shallow increased ground shaking
epicentre only 24km from Port-au-Prince which is the most densely populated city in Haiti (2 million people)
developing country - poor and limited resources
80% Haitians lived in poverty (slum-like housing densely packed and poorly constructed)
high level of corruption so no building regulations
deforestation led to loose soil e.g. landslides
lack of disaster preparation
rapid urbanisation rates leading to overpopulation
hazard profiles
they compare the physical processes that all hazards share, and help decision makers to identify and rank the hazards (help compare across hazards)
advantages of hazard profiles
compare physical processes that all hazards share
helps rank and compare hazards
allows for specific management to be considered
identifies hazards that require the most resources and attention
disadvantages of hazard profiles
reliability when comparing different events is limited
difficulty comparing across hazards
for planning it is better to consider hazards as individual hazards
trends in disasters
World Meteorological organisation say number of disasters over last 50 years increased fivefold but number of deaths fallen by 2/3
increased due to weather disasters from climate change and easier to record disasters
death rates fallen from improvements in planning, prediction and reaction as well as better infrastructure, healthcare and education etc.
biological disasters e.g. Covid19
World Data for disaster trends (x5)
number of deaths from disasters has decreased from over 500,000 in 1920 to around 50,000 in 2010
total amount of economic damage is increasing but dictated by disasters in HICs as spend more
severity of hurricanes set to increase 2-11%
economic inflation means cost cannot represent how destructive a hazard was as may be different
responsible for 0.1% deaths in the world (45,000 per year)
how does climate change affect the frequency/hazard of disasters
as weather warms and ice melts, the release of ice can trigger EQs as well as remove support from the slopes which may lead to landslides which can destabilise the magma chamber and trigger an eruption
temperature increase also contributes to the increase in droughts, fires, tropical storms etc.
how does population increase affect the frequency/hazard of a disaster
more than half the population live in cities → densely packed and poor conditions, increasing by 80 million a year
how does sea level rise increase the frequency/hazardous of a disaster
increase tsunami and hurricane hazard as amplifies it and increases magnitude
how does social media increase the frequency/hazardous of a disaster
e.g. Twitter sending alerts once marked by official accounts like the Police
mega disasters
large scale disasters either spatially, economically or socially which often require international support
Eyjafjallajokul eruption, Iceland (2010) x7
composite volcano - VEI 3 but produced large volume of very fine ash which combined with easterly blowing winds, blew ash across Europe
phreamagmatic eruption - cool water from glacier above and magma mixed creating vast volumes of ash which disrupted air travel (airlines lost £130 million a day, 17,000 flights cancelled during first day)
near shutdown of agricultural sector in Kenya causing refrigerate storehouses to fill up + 5000 staff temporarily laid off
led to some UK citizens to sail their own boats across the English Channel to pick up stranded tourists (150,000)
2.8 million tonnes of CO2 was released
Nissan plant in Japan had to stop producing cars as one part from Ireland so couldn’t import it
World Bank estimate African countries lost $65 million due to loss of exports
Japanese Tohoku tsunami (2011) x8
agriculture accounts for 3-4% of Japan’s employment and seawater contamination affected rice crops for years
magnitude 9 EQ + no deaths BUT triggered tsunami 40m high and travelled 10km inland killing 19,747 (5000 aftershocks + Japan have regular EQ drills and emergency SMS system)
more than 120,000 buildings destroyed and $235 billion spent (worlds costliest disaster) - 39,000 evacuees whilst 1000 still in temporary housing in 2021
level 7 nuclear meltdown and release of radioactive material as electrical power + backup generators were overwhelmed so lost cooling abilities
UK temporarily stopped their power plants
200,000 residents evacuated due to Fukushima powerplant
main Tohoku Expressway was closed for 3 months and 20,000 people stranded
Japanese docks, ships and household items arrived on US and Canadian shores for years (5 million debris)
tsunami broke the Sulzberger ice shelf in Antarctica
multiple hazard zones
places where a number of physical hazards combine to creates an increased level of risk for a country's and its population
‘disaster hotspot’ e.g. Philippines
general info on Philippines (x12)
population = 106 million
more than 7000 islands
average GDP is $8100 (relatively low = LIC)
25.4% agriculture sector
life expectancy = 70 years
high levels of deforestation
0.8 doctors per 1000 people
unemployment rate = 2.41%
population below poverty line = 16.7%
rapidly urbanising era e.g. Manilla - 2000 people per square km
mountainous landscape means limited space for urbanisation → cramped housing near coast
found within the Pacific ‘ring of fire’
floods in Philippines
38 events since 1990 and 1147 killed
‘flash floods’ caused by EQ, typhoons etc.
e.g. 2006 EQ - triggered a flood due to material from the Parker volcano entering the Maughan lake
typhoons in the Philippines
on belt of SE Asian typhoons
6-7 per year
e.g. Typhoon Haiyan (worst tropical storm to reach land = category 5)
earthquakes in the Philippines
24 major EQs since 1990
e.g. 2006 EQ - killed 15 and damaged 800 buildings - triggered landslide from the Parker volcano into the Maughan lake = FLOOD
volcanoes in the Philippines
25 major eruptions with 1,700,000 people affected and 3000 deaths
e.g. Mount Pinatubo - ash spread over 100km radius with 20 million tonnes of material ejected - triggered by a 7.7 magnitude EQ (killed 1600 in Manilla) - typhoon meant rain and ash swelled on roofs causing collapse and mudslides
landslides in the Philippenes
e.g. Guinsaugan landslide (2006) - killed 1150 people and engulfed a whole village - caused by 70cm of rain over 10 days combined with a 2.6 magnitude EQ + deforestation causing destabilisation of slopes
droughts in the Philippenes
e.g. Geneva drought (2016) - caused by significantly increasing temperatures and not enough rain
left 43% of the country in drought with 1 farmer dying and 13 injured due to the conditions
crop yields decreased as not enough water
3 characteristics of tropical revolving storms
strong winds - over 100mph except within the eye where winds = 0mph
storm surge - raised sea levels that move with the storm (coastal flooding)
heavy rain leads to flooding