SIE EXAM
1/165
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
166 Terms
Par Value
Arbitrary value for accounting purposes
non marginable and marginable securities
Marginable: exchange listed securities, US government securities, OTC securities listed on the fed marginable securities list
Non marginable: options, mutual fund shares, new issues that have been publicly traded for less than 30 days, and penny stocks
Authorized stock
Fixed number of shares that may be issued when a corporation is formed
Issued shares
Authorized shares that have been sold
Treasury stock is considered issued shares that have been repurchased by the company and are not considered outstanding.
Outstanding shares
Total number of shares in circulation
Outstanding shares = issued shares - treasury stock
Aggregate value
Outstanding shares x Par value = aggregate value
Preemptive rights
Distributed to shareholders when a company is issuing new shares. Short term securities that give the owner the option to buy shares at a reduced price.
Only common stock gets pre emptive rights
Have a life of about 4-8 weeks. Not redeemable
Stock split
Can be forward or reverse. Must adjust par, so $1 par would go to $.5 after (2:1) split.
assume x:y; for price adjustment: y/x
for share adjustment: x/y
Current yield
Annual income / market price
Earnings per common share
Earnings available for common/ common shares outstanding
Treasury stock
Shares repurchased by a corporation after issuance.
treasury stock does not vote or receive dividends
Statutory Voting vs Cumulative
Statutory: Votes must be cast evenly
Cumulative: Can divide total votes as desired. Good for small investors
Preferred stock
Can be callable, cumulative, convertible, and participating.
Cumulative stock is guaranteed dividends.
Convertible stock gives the opportunity for growth- most sensitive to price changes
Participating gives extra dividends.
based on market interest rates
common stockholder
owner in a corporation. common stock is not callable
warrants
give the holder an option to buy stock at a premium of the current market price. usually have a life around 5 years
offered as a sweetener
0 coupon bonds
purchase at a discount and receive no interest payments, but receive more at maturity than the purchase price.
no reinvestment risk
serial bond
bond issues with single issue dates and different maturities and interest rates. often used by municipals
series bond
same maturity but have different issuance dates and often pay different interest rates.
bond quotes
if there is no fraction, add a 0 to the quote for $
corporate bonds are 1/8 of par. ex if quoted 80 8/32 =80.25 and move decimal to the right for $802.5
government bonds are 1/32. some are 1/64
term bonds are quoted in % of par. serial bonds are quoted on a yield basis
bid / ask spread
investor pays the dealer the ask when buying and bid when selling.
98.16 ask = 98 and 16/32 cents
basis points
refers to the yield. each % of the yield = 100 bps. 1bps = .0001 or 1/100th of a percent
bond point
1% of par
selling at par
coupon rate = current yield = YTM
selling at a discount
coupon rate < current yield < YTM
below par
most likely to never be called by an issuer
selling at a premium
coupon rate > current yield > YTM
nominal yield
the coupon rate or stated interest
annual income / par
current yield
the return an investor is earning
annual income / market price
term bond
same interest rates and maturities
callable bond
issuer can redeem the bond @ a predetermined price (% of par) before maturity
likely to be called when interest rates drop
issuer buy back
Yield to worst
must be disclosed to client. this is the lesser of the YTC or YTM
YTC > YTM
for a bond trading at a discount
YTM would be yield to worst
YTC < YTM
for a bond trading at a premium
YTC would be yield to worst
put bonds
have lower coupon rates and higher interest rates. benefit to the investor
bondholder buyback
once exercised, the bond price will not fall below the option price if rates rise
bond payouts
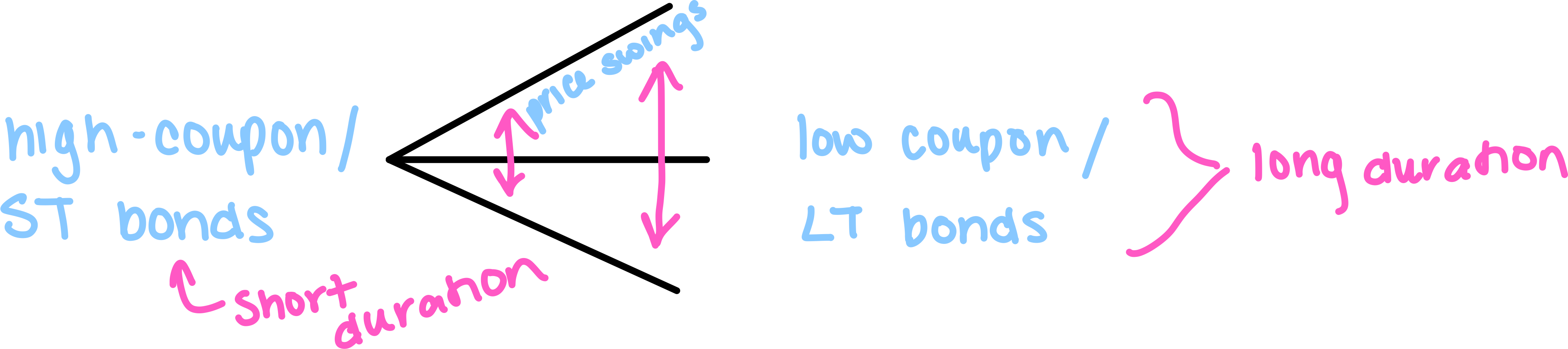
adjustable rate bonds
fluctuate with the market. as interest rates drop, the rate on the bond drops
are protected from interest rate risk
call protection
prevents a callable bond from being called the first few years of its life.
benefit is greatest when the bond is most likely to be called (rates are falling / prices are rising)
yield to call
the yield of a callable bond, assuming it is held until its first call date
call premium
price above par where the issuer has the right to call in the bonds from bondholders prior to maturity
trust indenture act of 1939
all corporate issues of $50 mil or more must have a trust indenture, with the exception of munis and government issues
trustee is appointed by the issuer and protects interests of bondholders
bond types
secured - mortgage, equipment trust certifications, collateral trust bonds
unsecured - debentures, junk bonds, guaranteed bonds
other - income bonds. not suitable when seeking income because payments are not guaranteed
convertible bonds
conversion ratio = par/ conversion price
conversion value = conversion ratio x market price
parity price of stock and bonds
PP of stock = bond mkt value / conversion ratio
PP of bonds = conversion ratio x market price of common
treasury securities
Tbills: > 1 yr. $100-$5mil. no interest. quote in yield
Tnote: 2-10 yr. $100-5mil. semiannual interest. quoted as 1/32
Tbond: 10-30 yr. $100-5 mil. semiannual interest. quoted as 1/32
unqualified muni
a muni with an unconditional affirmation that there are no legal issues
GO bond
muni debt backed by the full faith, credit, and taxing power of the muni
unsecured bonds
ad valorem tax
need voter approval
have statutory debt limits
used for roads, schools, and muni buildings
CAB
capital appreciation bonds. muni zero discount
good for munis close to debt limit
revenue bonds
backed by the revenue from a specific project
higher coupons and riskier
no voter approval, but must do feasibility study
self supporting
used for tolls, hospitals, utility companies
bond tax status
US govt and govt agencies: subject to federal, exempt from state
private govt agency or corporate: subject to federal and state
munis: exempt from both if a resident
money market debt
ST debt and those < 1 yr maturity. large denominations
if maturity is < 270 days, not registered to the SEC
Fed buys MM from primary dealers to increase debt availability since it puts cash into banks
GAN
comes from federal transit funding
RAN
comes from federal highway funding
special tax bonds
backed by taxes other than an ad valorem tax like liquor, gas, cigarette, or sales tax.
non self supporting
federal funds
overnight loans between member institutions of the federal reserve system
debentures
secured by the full faith and credit of the issuer
3 investment companies
face amount certificate companies (obsolete) management companies, unit investment trust
management corporation
open end (mutual funds) and closed end (publicly traded fund)
open end is only common shares
closed end is negotiable and not redeemable
UIT
fixed UIT (fixed trust) and non fixed UIT (variable annuity)
fixed is mainly bonds but also stocks'
non fixed is only mutual funds
mutual funds
established by a sponsor and shares are sold by the fund distributor.
offers professional money management and diversification. must have 75-5-10 diversification (securities - per issuer- voting)
always require a prospectus
largest expense is the management fee
can easily be redeemed (liquid). must pay redemption proceeds within 7 days
LT gain is taxed at preferential rate, ST is at ordinary
load fund
MF with a sales charge
sales charge can’t exceed 8.5% of POP
POP
NAV + sales charge
12-b1 fund
max sales charge can be 7.25%
12-b1 fee can’t exceed 1% of average annual net assets
of the 1%, .75% can be used for marketing and distributing, and .25% for admin expenses
MF Class A
NAV: NAV + sales charge
sales charge: front end with breakpoints
12b-1: low
good for: large / LT accounts
MF Class B
NAV: NAV
sales charge: back end unless held for long enough
12-b1: high but can convert to class A
good for: 5-7 year hold
MF Class C
NAV: NAV
sales charge: none
12-b1: very high
good for: 1-2 year hold
expense ratio
total expenses / total net assets
ETFs
traded on an exchange like a stock, but are usually registered as open-end
linked to a specific index
nontraditional ETFs are okay for short term investing
private REITs
not listed on exchanges and aren’t registered with the SEC. not liquid
95% REITs income must be RE related income
Registered non-listed REITs
registered with the SEC but not on an exchange. not liquid
listed REITs
registered with SEC and on an exchange or OTC. very liquid and can use margin and short
no load fund
MF that markets and sells their own shares
12-b1 can not exceed .25% of net assets
passively managed
oil and gas programs
exploratory: find where gas likely is - 100% deduction for intangible and tangible drilling costs
developmental: find properties near producing oil and gas wells - deduction for intangible and tangible drilling costs
income: purchase existing producing wells - oil depletion allowance
breakpoint sale
when a customer buys just beneath the breakpoint level so they didn’t get the benefit of the lower sales charge
NAV
(total assets - liabilities) / # of outstanding shares
increases when fund receives dividends or interest and when liabilities decrease.
figured using forward pricing
MF types riskiest —> least risky
-special situation fund (bankruptcy, takeover)
-sector / specialty fund (1 industry or area)
-growth fund ( growing common stocks)
-balanced (bonds and pref stock)
-value (blue chip common stocks)
-income (large cap/ blue chip pref stocks and bonds)
-money market fund (Tbills, BAs, commercial paper)
dividend dates (DERP)
declaration date- when company declares dividend
Ex-dividend- 1st day a stock trades and purchaser will not receive upcoming dividend
record date- purchasers of stock must settle no later than the record date to receive dividend
payable date- the actual day checks will be sent
**ex dividend date is the same as the record date
cost basis
purchase price (including commissions or markups) x number of shares
**only includes amount paid for the securities. excludes commission price when selling
TIPS
Tnotes and Tbonds whose interest adjusts based on inflation (uses real interest rate)
no purchasing power risk
STRIPS
government 0 coupon bonds
no reinvestment risk
trading markets
primary (IPOs) and secondary
Secondary:
first market- exchanges
second market- OTC
third market- OTC trading of listed securities
fourth market- institutional trading systems
broker vs dealer
broker (agent):
charges commission
no inventory is held
no risk to firm
dealer (principal):
markup / markdown
inventory is held
risk to firm
**firm can’t be the broker and dealer on the same transaction
**markups can not exceed 5%. exceptions: MFs max is 8.5% and Munis are exempt but have similar rules
SLOBS and BLUSS
Sell Limits over the market Buy Stop (SLOBS)
Buy Limit under the market Sell Stops (BLUSS)
-cash dividends adjust these orders on the ex-date
**Stops are to “stop the pain”. You would be happy to take profits at a limit because it is an opportunity for the client
** Stock splits and dividends affect all order (# of shares inc, price dec)
-new shares = share x (1+div%)
-new price = price / (1+div%)
types of orders
market orders: filled immediately
limit orders: filled at specific price
stop orders: turns into a market order when price is hit
stop limit: turns into limit order when price is hit
buy call
right to buy
profit = unlimited
loss = premium
breakeven = strike + premium
sell call
obligation to sell
profit = premium
loss= unlimited
breakeven = strike + premium
buy put
right to sell stock
profit= strike price - premium
loss = premium paid
breakeven = strike price - premium
sell put
obligation to buy
profit = premium
loss = strike price - premium
breakeven = strike price - premium
premium =
IV + time value
new account form
name and address, if legal age, registered rep, principal signature, and if a corporation, the name who will transact business
must be sent 30 days of account open and every 3 years to update
customer signature nor education need to be included, unless margin account then signature is needed
KYC
must make an effort to obtain financial status, tax status, investment objectives
suitability questionnaire rules
must obtain:
investment objective
investment experience
age
financial needs
tax status
investment time horixon
liquidity needs
risk tolerance
**must be updated every 36 months
Regulation S-P
can’t disclose nonpublic personal info with 3rd parties
Regulation BI
best interest
disclosure obligation requires written disclosure of material facts before or when a recommendation is made
can never be waived
does not apply to institutions
Reg T
initial margin: 50%. must be at least $2,000
min maintenance margin: long = 25% short = 30% of the closing price of the security that day
covers borrowing between customers and brokers
an extension request gives a customer 2 additional business days to pay for a securities purchase
FRB determines if an OTC stock is marginable
equity value =
market value of security - amount owed broker
equity % =
equity value / market value of security
Reg U
covers borrowing between banks and brokers
fiduciary account
ONLY the fiduciary can trade. cash accounts only
revocable vs irrevocable trust accounts
revocable: can be eliminated by the trustor
irrevocable: permanent and assets aren’t included in tax purposes
living vs testamentary trust accounts
testamentary accounts are initiated upon death
charitable trust
can give assets to charity upon death
can deduct the fair market value of the securities as long as they have been held for 12 months