AP Macro Unit 5
5.0(4)Studied by 188 people
0%Unit Mastery
0%Exam Mastery
Build your Mastery score
Supplemental Materials
Card Sorting
1/41
Earn XP
Description and Tags
Last updated 11:09 PM on 12/19/22
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
42 Terms
1
New cards
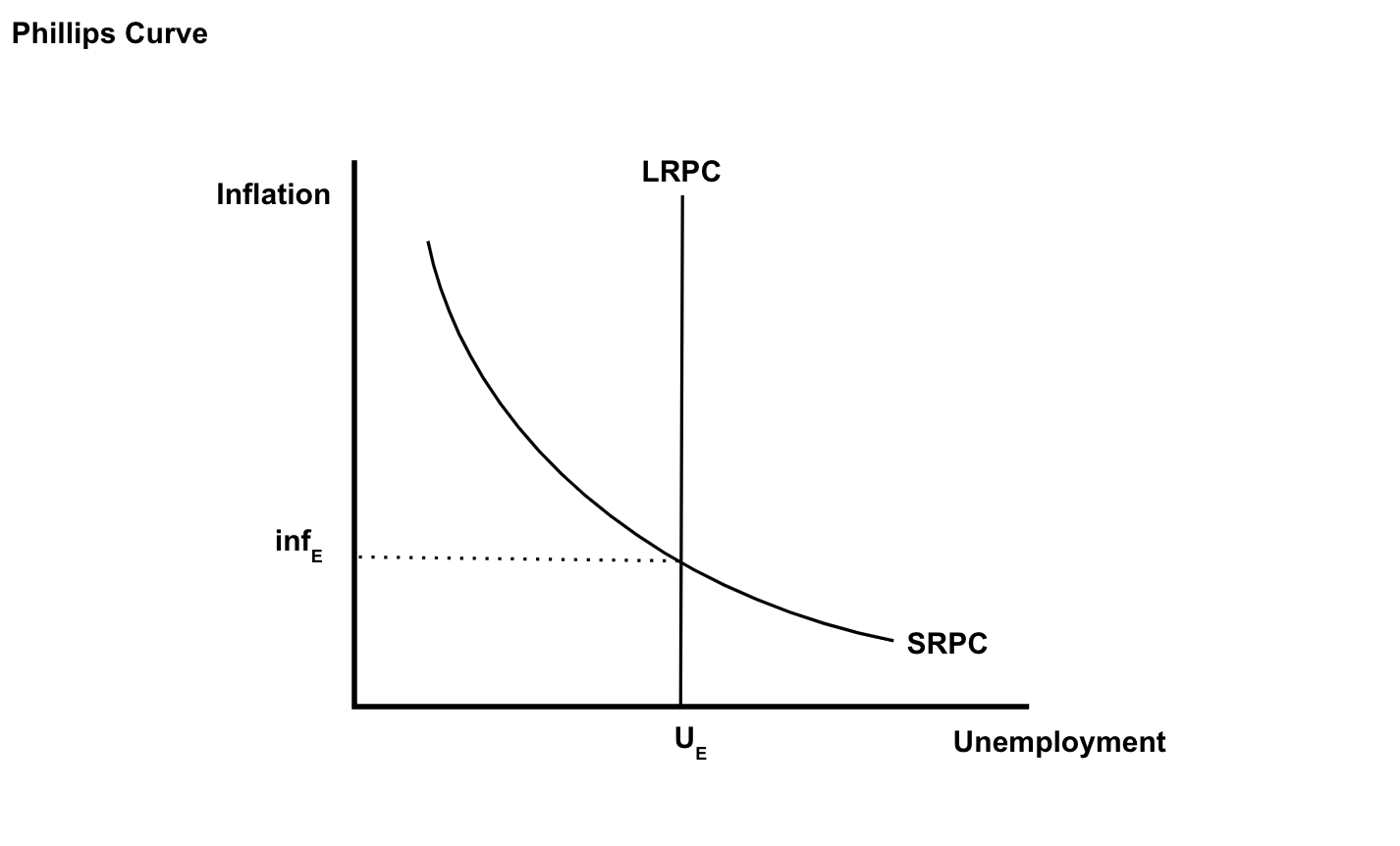
The Phillips Curve
shows the tradeoff between inflation and unemployment
→ in general, there is an inverse relationship unemployment and inflation
→ in general, there is an inverse relationship unemployment and inflation
2
New cards
Short Run Phillips Curve
when the economy is overheating, there is low unemployment but high inflation
→ higher expected inflation shifts SRPC to the right
→ higher expected inflation shifts SRPC to the right
3
New cards
What happens when AS falls causing stagflation?
increase in unemployment and inflation
4
New cards
Short Run v. Long Run
in the long run, there is no trade off between inflation and unemployment
→ the LRPC is vertical at the Natural Rate of Unemployment
→ the LRPC is vertical at the Natural Rate of Unemployment
5
New cards
When AD increases/decreases
point on SRPC moves along the curve
6
New cards
When SRAS increases/decreases
whole SRPC curve shifts
7
New cards
Quantity Theory of Money
money supply and price level in an economy are in direct proportion to one another
8
New cards
M \* V *= P* \* Y
M = money supply
V = velocity
P = price level
Y = quantity of output (Real GDP)
\
→ assume the velocity is relatively constant because people’s spending habits are not quick to change, and that output (Y) is not affected by the quantity of money because it is based on production, not the value of the stuff produced
V = velocity
P = price level
Y = quantity of output (Real GDP)
\
→ assume the velocity is relatively constant because people’s spending habits are not quick to change, and that output (Y) is not affected by the quantity of money because it is based on production, not the value of the stuff produced
9
New cards
What happens in the long-run when the central bank increases the money supply?
→ short-run spending eventually leads to higher resource prices and inflation
→ if inflation is bad enough, banks don’t lend and the economy tanks
→ MS↑, nominal interest rates↓, investment spending↑, AD↑, SRAS↓, PL↑, demand for money↑
→ if inflation is bad enough, banks don’t lend and the economy tanks
→ MS↑, nominal interest rates↓, investment spending↑, AD↑, SRAS↓, PL↑, demand for money↑
10
New cards
Budget Deficit
when annual government spending and transfer payments are greater than tax revenue
11
New cards
Budget Surplus
when annual government spending and transfer payments are less than tax revenue
12
New cards
The National Debt
the accumulation of all the budget deficits over time
→ if the government increases spending without increasing taxes they will increase the annual deficit and the national debt
→ if the government increases spending without increasing taxes they will increase the annual deficit and the national debt
13
New cards
Neutrality of Money
money has no real effect on equilibrium
14
New cards
Expansionary Monetary Policy in the short-run
real output↑, price level↑, interest rates↓
15
New cards
Expansionary Monetary Policy in the long-run
real output no change, price level↑, interest rates indeterminate
16
New cards
Contractionary Monetary Policy in the short-run
real output↓, price level↓, interest rates↑
17
New cards
Contractionary Monetary Policy in the long-run
real output no change, price level↓, interest rates indeterminate
18
New cards
Automatic stabilizers in a recessionary gap
AD↑, real GDP↑, PL↑, budget towards deficit, national debt↑
19
New cards
Automatic stabilizers in an inflationary gap
AD↓, real GDP↓, PL↓, budget towards surplus, national debt↓
20
New cards
Tax cuts and government spending increases
AD↑, real GDP↑, PL↑, towards deficit, national debt↑
21
New cards
Government spending cuts and tax increases
AD↓, real GDP↓, PL↓, towards surplus, national debt↓
22
New cards
What is the long-run impact of higher real interest rates?
less economic growth because investment falls, less capital stock
23
New cards
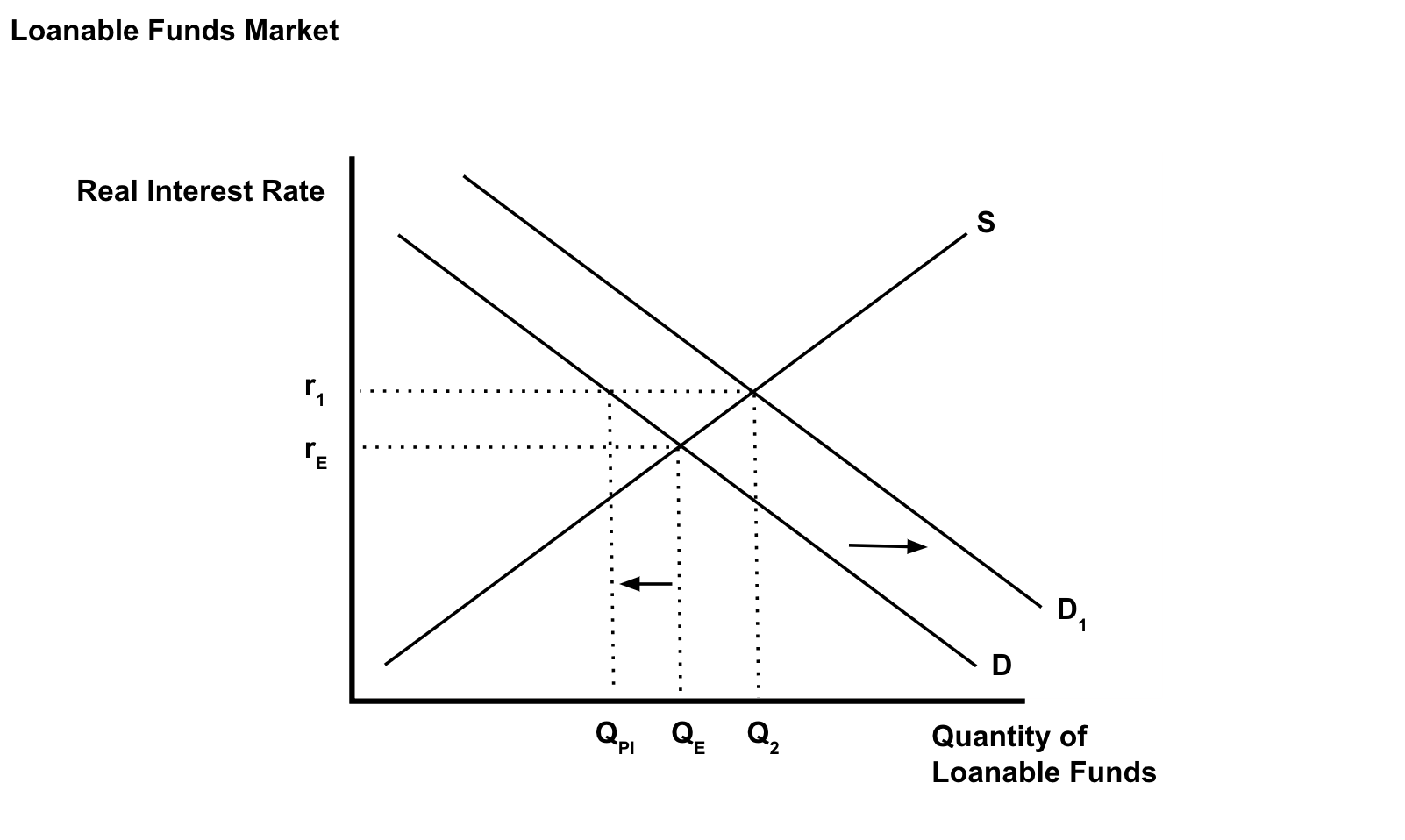
Assume the government increases government spending -- what will happen to the demand for loanable funds, the real ir, and private domestic investment?
→ demand increases
→ real interest rate increases
→ private investment decreases
→ real interest rate increases
→ private investment decreases
24
New cards
Crowding Out
the adverse effect of government borrowing on interest-sensitive private sector spending
25
New cards
Which monetary policy would help accommodate or reinforce a contractionary fiscal policy?
sell bonds, increase reserve ratio, or increase discount rate
→ ir↑, bond prices↓
→ MS↓, bank reserves↓
→ quantity of loanable funds demanded by private sector↓
→ AD↓
→ ir↑, bond prices↓
→ MS↓, bank reserves↓
→ quantity of loanable funds demanded by private sector↓
→ AD↓
26
New cards
Which monetary policy would help accommodate or reinforce an expansionary fiscal policy?
buy bonds, decrease reserve ratio, or decrease discount rate
→ ir↓, bond prices↑
→ MS↑, bank reserves↑
→ quantity of loanable funds demanded by private sector↑
→ AD↑
→ ir↓, bond prices↑
→ MS↑, bank reserves↑
→ quantity of loanable funds demanded by private sector↑
→ AD↑
27
New cards
Real GDP Per Capita
the real GDP divided by the population
28
New cards
Growth Rate
the change in real GDP per capita over time
29
New cards
Why do some countries have more economic growth?
( 1 ) Economic System
( 2 ) Rule of Law
( 3 ) Capital Stock
( 4 ) Human Capital
( 5 ) Natural Resources
( 2 ) Rule of Law
( 3 ) Capital Stock
( 4 ) Human Capital
( 5 ) Natural Resources
30
New cards
Productivity
output per unit of input
31
New cards
Capital Stock
machinery and tools purchased by businesses that increase their output
32
New cards
What government policies most likely result in long-run economic growth?
( 1 ) Education/training spending
→ increases human capital
( 2 ) Infrastructure spending
→ increases physical capital
( 3 ) Production/investment incentive programs
→ increases physical capital
→ increases human capital
( 2 ) Infrastructure spending
→ increases physical capital
( 3 ) Production/investment incentive programs
→ increases physical capital
33
New cards
Supply-side Fiscal Policies
government policies designed to increase production by reducing business taxes and/or regulations
34
New cards
Why are Supply-side Fiscal Policies controversial?
( 1 ) Providing tax breaks to businesses might disproportionately benefit the wealthy
( 2 ) It assumes that corporations will spend tax cuts on investment rather than pay out shareholders
( 2 ) It assumes that corporations will spend tax cuts on investment rather than pay out shareholders
35
New cards
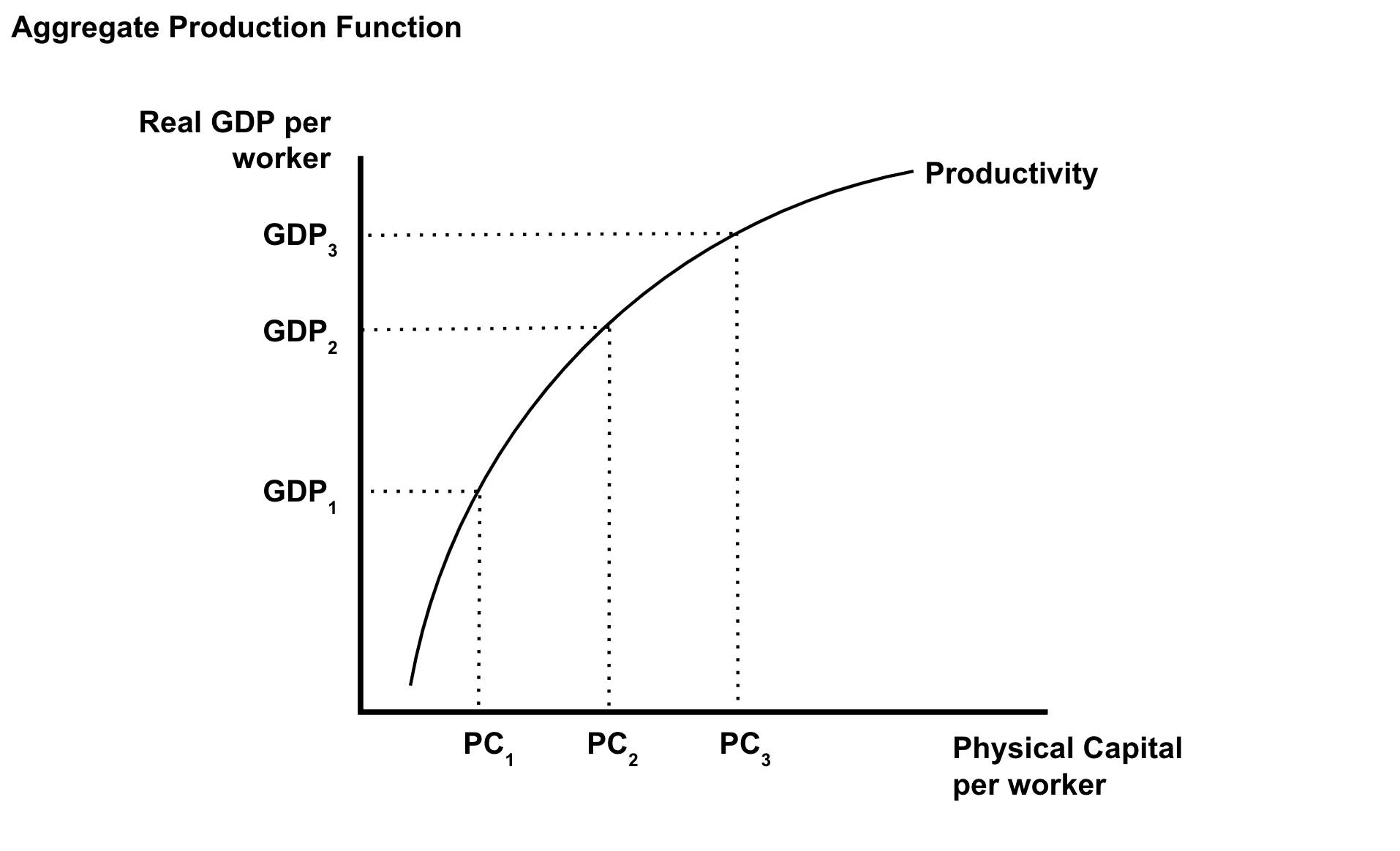
Aggregate Production Function
36
New cards
What Shifts the Long-Run Phillips Curve?
anything that changes the natural rate of unemployment (LRAS)
37
New cards
Velocity of Money
the average number of times a dollar is spent and respent
38
New cards
When the economy is at full employment, why will an increase in the money supply have no effect on real output in the long-run?
an increase in money supply doesn’t change the amount of physical capital in the economy or the real output that can be produced
39
New cards
Difference Between the Budget Deficit and the National Debt
a budget deficit is the amount that the government overspends in a year, while the national debt is the total accumulated debt over the years from deficit spending
40
New cards
How does the existence of a large national debt affect government spending in the future?
future spending falls because the government must pay interest on the debt and will not have funds for alternative uses
41
New cards
What influences productivity?
( 1 ) Technology
( 2 ) Amount/quality of physical capital
( 3 ) Amount/quality of human capital
( 2 ) Amount/quality of physical capital
( 3 ) Amount/quality of human capital
42
New cards
What happens in the long-run when lower interest rates lead to more investment?
AD, SRAS, and LRAS shift to the right