Transport Mechanism Across Membrane: Passive and Active Transport
1/24
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
25 Terms
plasma membrane
semi-permeable layer surrounding the cell
consists of phospholipid bilayer with several types of sugars and proteins embedded
protects all components of the cell from the outside environment as
structure
separates the cytoplasm
provides structural support to the cell
fluid mosaic model
phospholipids
cholesterol
proteins
glycolipid and glycoprotein
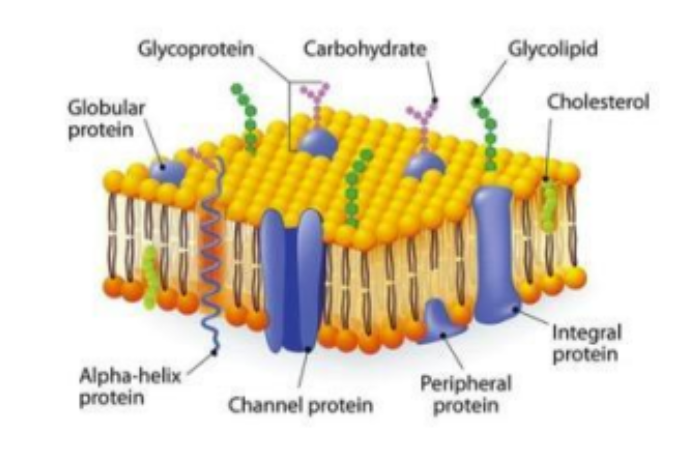
phospholipids
fatty acid chain and phosphate group
fatty acid tails - inwards
phosphate heads - outwards
cholesterol
sterol to stabilize the membrane and reduce fluidity
proteins
integral or peripheral, variety of roles
glycolipid and glycoprotein
surface of membrane
phospholipids
contains hydrophilic head
saturated fatty acids contain single bonds only
unsaturated contains double bonds producing kinks on chains (healthier)
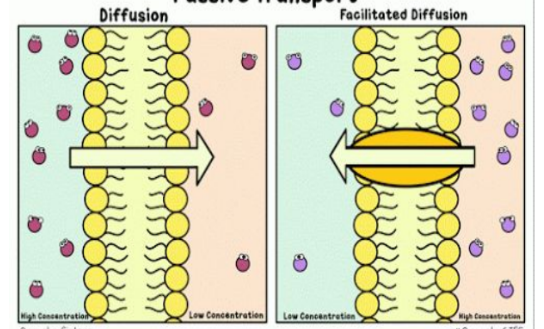
passive transport
does not require cell energy
high to low concentration
molecules more randomly
passive transport
diffusion
facilitated diffusion
osmosis
active transport
requires cell energy (ATP)
low to high concentration
ative transport
carrier mediated active transport
endocytosis
exocytosis
diffusion
spontaneous movement of particles (high to low)
continues until all molecules are evenly spaced (equilibrium is reached)
simple diffusion
small and nonpolar molecules can pass through the plasma membrane easily
temperature and size are factors that can affect the rate of diffusion
simple diffusion
food coloring
perfume
tea
breathing
soda
calcium
facilitated diffusion
diffusion with the help of transport proteins
specific!! they “select“ only certain molecules to cross the membrane
transports larger or charged molecules
facilitated diffusion
glucose and amino acid transport
gas transport
ion transport
cholesterol molecules
passive transport
osmosis
diffusion of water (high to low)
isotonic solution
concentration of solute inside and outside of the cell is the same
water goes in both directions
water in = water out
molecules in equilibrium
normal state for animal cells
cell in homeostasis
hypotonic
water enters the cell
cell swells and bursts
give plant cells shape and support
cytolysis
cell swells and bursts
hypertonic
water moves out of the cell
cell shrinks due to water loss
plasmolysis
shrinking of cell due to water loss
osmosis
blood cells shrinking in a hypertonic solution
fruits and veggies shrinking
can kill slugs or snails
reason behind getting thirsty
plants survival
importance of transport mechanisms
plays an important role in homeostasis
movement of substances into and out of the cell enables to keep cell conditions within normal ranges