L33: Osmolality & Urinary Specific Gravity
1/49
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
50 Terms
Osmolality
total solute concentration /kg of water
Osmolarity
total solute concentration /L of water
Urine specific gravity
measures urine solute concentration using refractive index
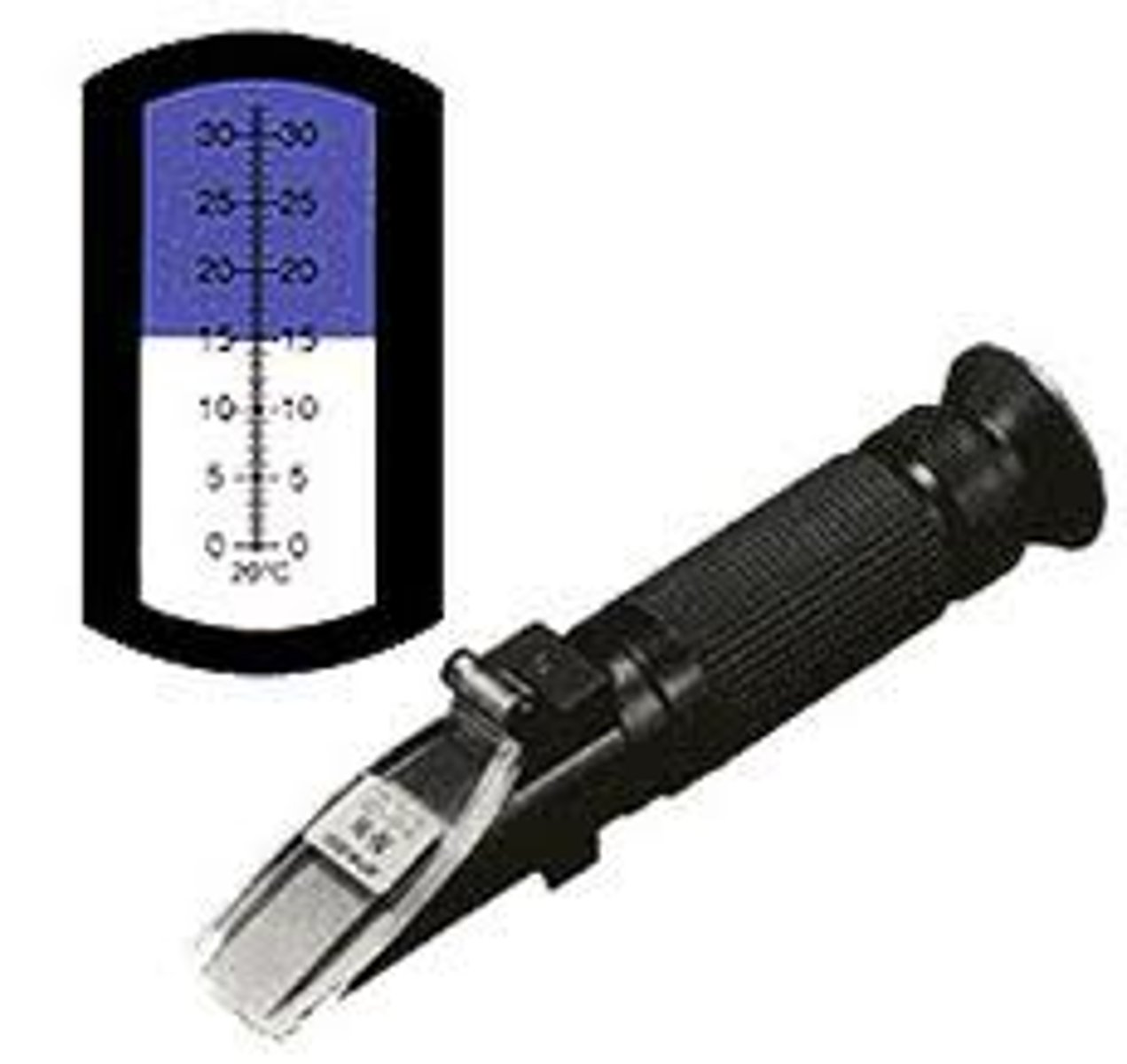
Refractometer
measures serum & plasma protein, or urine solute concentrations by refractive index

Osmometer
measures solute concentration in plasma based on depression of freezing point
Feline dehydration USG should be
>1.040
Canine dehydration USG should be
>1.030
Large animals dehydration USG should be
>1.025
What does the refractometer measure in urine samples of healthy patients?
urine specific gravity due to refractive index of total solutes
What analytical teat assesses urine solute concentration by refractometry?
urine specific gravity
How can you estimate osmolality from USGref?
use last two digits x 30
USGref overstimates the solute concentration if there is
high protein (> 4+) or glucose (> 3+)
What substances when increased can overestimate solute concentration by increasing USGref?
proteins & glucose
Glomerular filtration (passive)
substances filter from plasma to tubules (excluding proteins/Albumin)
What tubular segment reabsorbs water under the influence of ADH?
collecting duct
Osmolality in each segment of the nephron
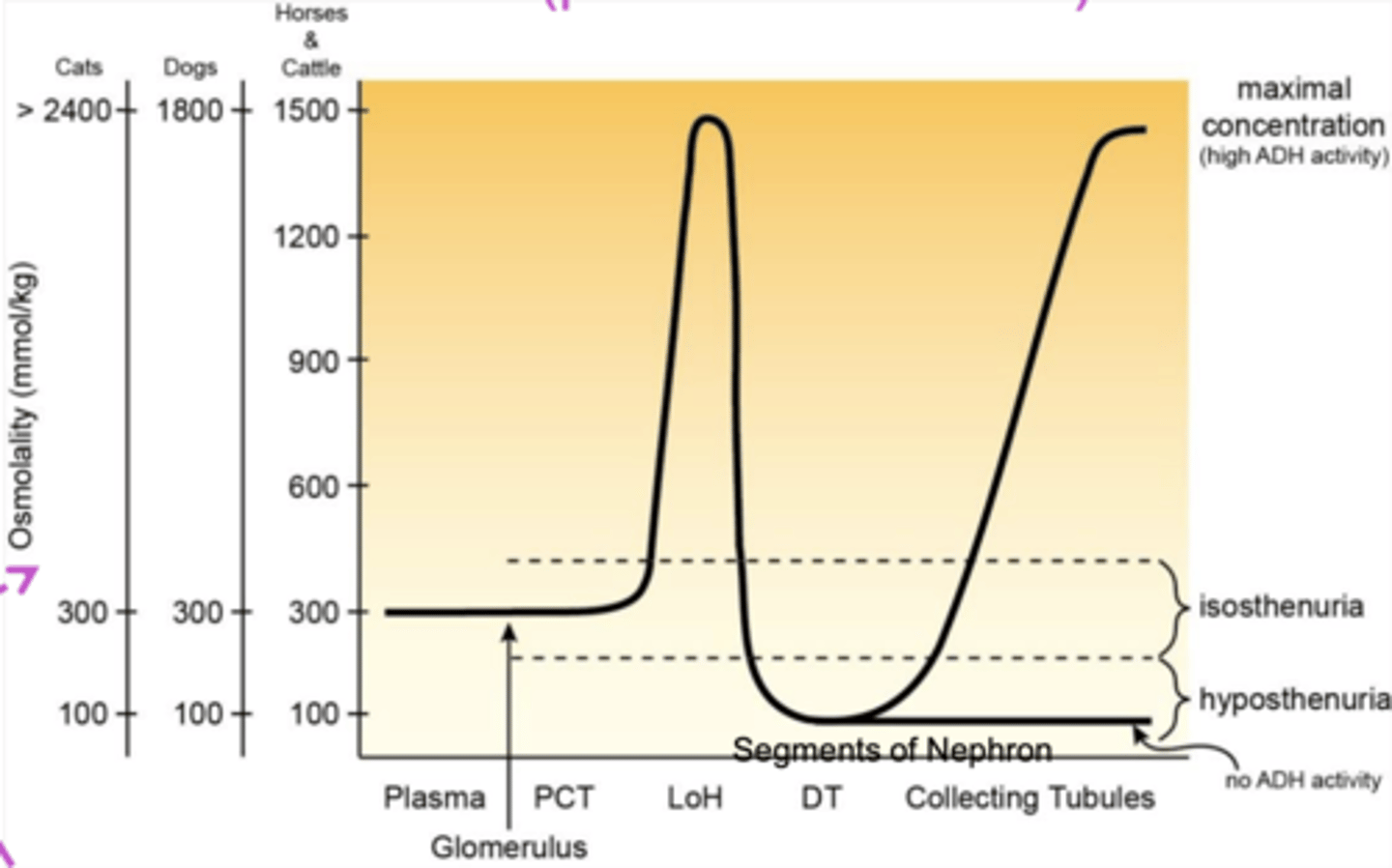
Proximal collecting tubule
removes volume, no change in urine concentration
- 75% water reabsorbed
- 75% solute reabsorbed
- osmolality of proximal tubular fluid is same as plasma (300 mmol/kg)
Descending loop of Henle
removes water, increases solute concentration
- urine becomes more concentrated (higher osmolality 1500 mmol/kg)
Ascending loop of Henle
removes solute, dilutes solute concentration
- removes Na, K, Cl, fCa, Mg
- water stays in tubules, urine becomes more dilute
Collecting duct
ADH stimulates removal of water - increased concentration & osmolality
- if does not remove water - stays dilute
To produce concentrated urine
1. ADH must be present (from posterior pituitary)
2. tubules must respond to ADH
3. concentration gradient must be present
What portion of the nephron reabsorbs water and electrolytes resulting in osmolality same as plasma?
proximal convoluted tubule
For kidneys to produce a urine with a specific gravity of 1.001-1.003 or osmolality of ~100 mmol/kg, what nephron segment must be functional?
ascending loop of Henle (diluting limb of the nephron)
For kidneys to produce a urine with a specific gravity of 1.030 (osmolality ~1500 mmol/kg), which portion of the nephron must be functional?
all segments must be functional
Hypersthenuria
very concentrated, high USG
dogs: >1.050
cats: >1.060
Eusthenuria
concentrated
dogs: 1.015-1.045
cats: 1.035-1.060
Isosthenuria
same osmolality as plasma
1.007-1.013
Hyposthenuria
low concentration, low USG
< 1.007
In dehydrated dogs, hypersthenuria should be above
1.030
In dehydrated cats, hypersthenuria should be above
1.040
Proteinuria is caused by
damaged filtration barrier (glomerulus)
Glucosuria is caused by
diabetes mellitus
High USGref =
low urine volume
Low USGref =
high urine volume
> 1.030 for dogs and >1.040 for cats is evidence of
adequate concentrating ability in dehydrated states
In what context do you interpret USGref?
hydration status & treatment, azotemia, polyuria, oliguira or anuria
UA results: 1.035, other findings negative. What is the conclusion?
hydration status: normal
blood volume: OK
plasma osmolality: OK
ADH release: ↑
tubule response to ADH: OK
concentration gradient: OK
water conservation: OK
conclusion: conserving water
UA results: 1.060, dehydrated. What is the conclusion?
hydration status: dehydration
blood volume: ↓↓
plasma osmolality: OK
ADH release: ↑↑
tubule response to ADH: ↑↑
concentration gradient: OK
water conservation: ↑↑
conclusion: conserving water in a dehydrated state
UA results: 1.003, other findings negative. What is the conclusion?
hydration status: overhydration
blood volume: ↑
plasma osmolality: OK
ADH release: No
tubule response to ADH: N/A
concentration gradient: OK
water conservation: ↓↓
conclusion: hyposthenuric- ascending LOH functioning, do not need ADH
UA results: 1.010, well hydrated healthy animal. IV fluids or drinks H20. What is the conclusion?
hydration status: well hydrated
blood volume: ↑
plasma osmolality: OK
ADH release: little
tubule response to ADH: N/A
concentration gradient: OK
water conservation: ↓
conclusion: isosthenuric value due to well hydration state
UA results: 1.010, dehydrated animal. What is the conclusion?
hydration status: dehydrated
blood volume: ↓↓
plasma osmolality: OK
ADH release: ↑↑
tubule response to ADH: poor (due to nephron damage)
concentration gradient: poor
water conservation: ↓↓
conclusion: isosthenuric value, unable to concentrate when dehydrated most likely due to nephron damage
UA results: 1.025 (eusthenuria), 4+ glucose = 1.015. What is the conclusion?
hydration status: dehydrated
blood volume: ↓↓
plasma osmolality: ↑↑ (glucose)
ADH release: ↑↑
tubule response to ADH: ↑
concentration gradient: ↓↓
water conservation: not enough for dehydration
conclusion: osmotic diuresis / medullary washout
UA results: 1.020, dehydration, hyponatremia, hypochloremia. What is the conclusion?
hydration status: dehydrated
blood volume: ↓↓
plasma osmolality: ↓↓ (NaCl)
ADH release: ↑↑
tubule response to ADH: ↑
concentration gradient: ↓ (NaCl)
water conservation: ↓↓
conclusion: hypoadrenocorticism (Addison's), NaCl necessary for medullar concentration gradient
UA results: 1.002, other findings negative, hyposthenuric value. What is the conclusion?
hydration status: dehydrated
blood volume: ↓↓
plasma osmolality: OK
ADH release: ↑↑
tubule response to ADH: No
concentration gradient: OK
water conservation: ↓
conclusion: CT not responding to ADH (renal diabetes insipidus), hypercalcemia/pyometra/liver failure
UA results: 1.002, dehydrated, hyposthenuric value. What is the conclusion?
hydration status: dehydrated
blood volume: ↓↓
plasma osmolality: OK
ADH release: No
tubule response to ADH: OK
concentration gradient: OK
water conservation: ↓
conclusion: lack of ADH from brain- central diabetes insipidus
A cat presents with a USGref of 1.065. What condition is most likely causing the USG result?
dehydration: hypersthenuria > 1.060 (very concentrated urine)
A cat presents with mild dehydration. The cat was treated at a veterinary clinic with IV fluids. Following the treatment, USG was 1.002. What condition is most likely causing the USG result?
overhydration: from fluid therapy, dilute urine (1.002)
A cat presents with dehydration and glucosuria of 4+ and USG of 1.025. What condition is most likely causing the USG?
osmotic or solute diuresis: from diabetes (water follows solutes), isosthenuria
A cat presents with severe dehydration and anorexia for three months with oliguria. USG is 1.011. What condition is most likely causing the USG result?
damage to nephrons: kidney disease
An intact-female-dog presents for fever, inflammatory leukogram, and high urine volume with USG of 1.003. What condition is most likely causing the USG?
collecting tubule not responding to ADH: endotoxins from pyometria inhibit tubular response to ADH