IZA Test 2
0.0(0)
Card Sorting
1/100
Earn XP
Description and Tags
Animal Transfers, Exhibit Design,Government and Legislation, Mixed Species Exhibits, Taxonomy
Study Analytics
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
101 Terms
1
New cards
Taxonomy
Study of naming, describing, and classifying all living organisms, constantly evolving process
2
New cards
Morphological (taxonomy)
What it looks like
3
New cards
Behavioral (taxonomy)
What it acts like
4
New cards
Molecular data (taxonomy)
Genetic make-up
5
New cards
Taxonomy Order
Domain, Kingdom, Phylum, Class, Order, Family, Genus, Species
6
New cards
3 more common species concepts
Morphological, Biological, Phylogenetic
7
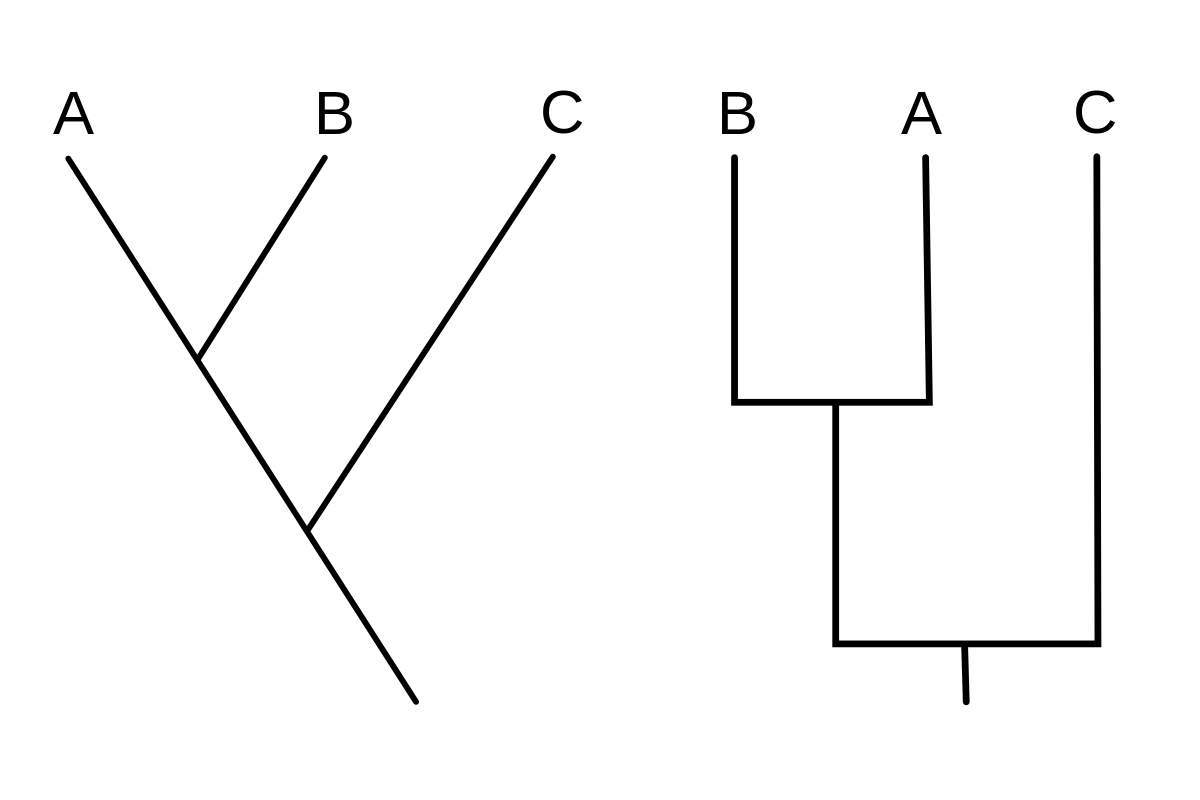
New cards
Cladogram
branching diagram showing the relationship between species.
8
New cards
Taxon Advisory Groups (TAG)
makes management decisions for a group of related animals (ex. Ape TAG, Galliformes TAG, Crocodillian TAG)
9
New cards
Species Survival Plans (SSP)
Maintain sustainable populations of a species.
Operate under a TAG.
Operate under a TAG.
10
New cards
How taxonomy affects how we display animals?
Based on behavior/biology of related group
11
New cards
How taxonomy affects our care of animals.
Closely related groups often require similar care.
12
New cards
Sub-species
Not quite different enough to be its own species, but still different.
13
New cards
How do zoos adjust their programs when taxonomy changes?
- Ignore it.
- Split or lump groups together.
- Split or lump groups together.
14
New cards
Genetics and Taxonomy
- Multiple ways to analyze DNA.
- Mitochondrial DNA is becoming more popular.
- Genetics is changing the way we classify animals.
- Mitochondrial DNA is becoming more popular.
- Genetics is changing the way we classify animals.
15
New cards
How do new species occur? (8)
- Area
- Genetic Diversity
- Habitat Heterogeneity
- Geographic Barriers
- Reproductive Barriers
- Population Size
- Hybridization
- Genome Duplication
- Genetic Diversity
- Habitat Heterogeneity
- Geographic Barriers
- Reproductive Barriers
- Population Size
- Hybridization
- Genome Duplication
16
New cards
Allopatric Speciation
Occurs when a species separates into two separate groups which are isolated from one another.
A physical barrier (mountain range or a waterway) makes it impossible for them to breed with one another.
A physical barrier (mountain range or a waterway) makes it impossible for them to breed with one another.

17
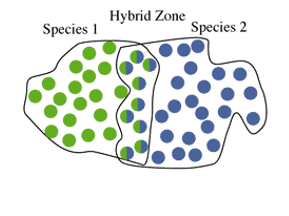
New cards
Parapatric Speciation
when new species evolve in contiguous, yet spatially segregated habitats.
Can be some hybridization where the 2 populations overlap.
Can be some hybridization where the 2 populations overlap.
18
New cards
Hybrid Zone
In parapatric Speciation, the place where two species can still interbreed with each other.
19
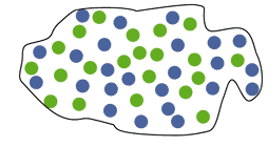
New cards
Sympatric Speciation
occurs when there are no physical barriers preventing any members of a species from mating with another, and all members are in close proximity to one another.
20
New cards
Founder Effect
Reduced genetic diversity resulting from a population descended from a small number of ancestors.
21
New cards
Zoogeography
Study of the distribution of animals.
Determination of areas characterized by specific groups of animals.
Determination of areas characterized by specific groups of animals.
22
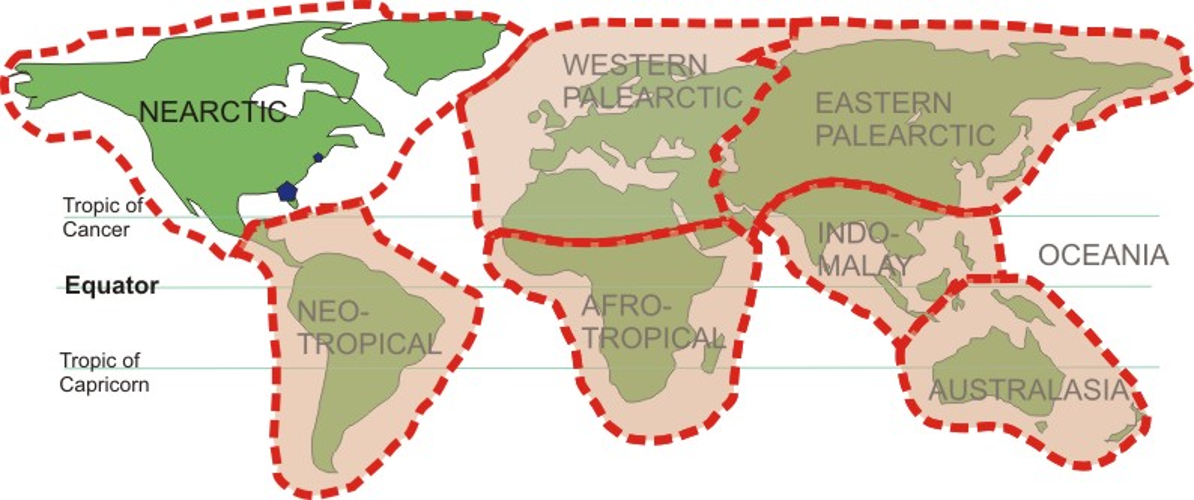
New cards
Biogeographic Realms
Divided according to biological evolutionary history and distribution of terrestrial organisms in ecosystems.
23
New cards
8 Biogeographic Realms
- Nearctic
- Palaearctic
- Neotropical
- Afrotropic
- Indomalayan
- Australasia
- Oceanian
- Antarctic
- Palaearctic
- Neotropical
- Afrotropic
- Indomalayan
- Australasia
- Oceanian
- Antarctic
24
New cards
Nearctic Species
Pronghorn Antelope
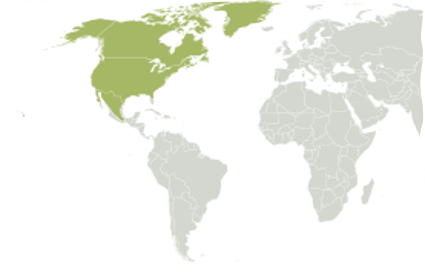
25
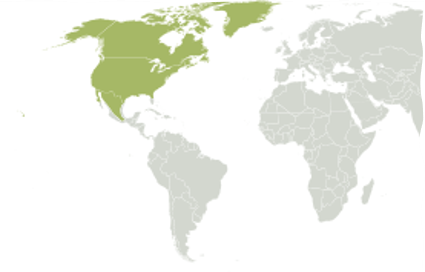
New cards
Nearctic Region
Most of North America (Greenland, Central FL, highlands of Mexico)
26
New cards
Nearctic Biomes
- Arctic tundra
- Boreal Forests
- Temperate Broadleaf forests of coastal mountain regions
- Temperate coniferous forests
- Mid-winter to cold-winter deserts, shrublands
- Boreal Forests
- Temperate Broadleaf forests of coastal mountain regions
- Temperate coniferous forests
- Mid-winter to cold-winter deserts, shrublands
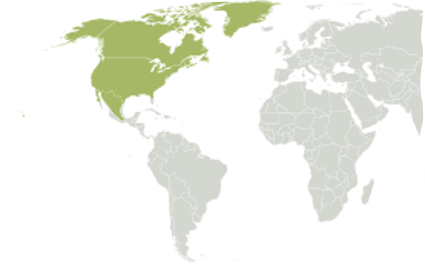
27
New cards
Palaearctic Species
Tiger
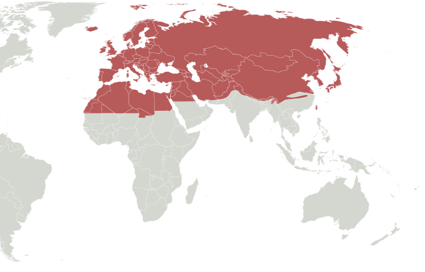
28
New cards
Palaearctic Region
- Largest Biogeographic realm
- Bulk of Eurasia and North Africa
- Northern and Central parts of Arabian peninsula
- Bulk of Eurasia and North Africa
- Northern and Central parts of Arabian peninsula
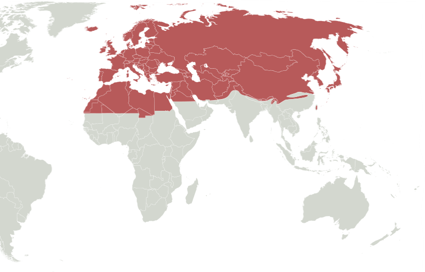
29
New cards
Palaearctic Biomes
- Freshwater and terrestrial ecoregions
- Sahara and Arabian Deserts
- Sahara and Arabian Deserts
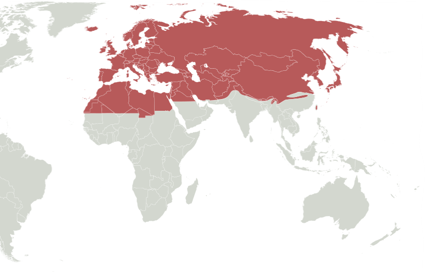
30
New cards
Neotropical Species
Toucan
31
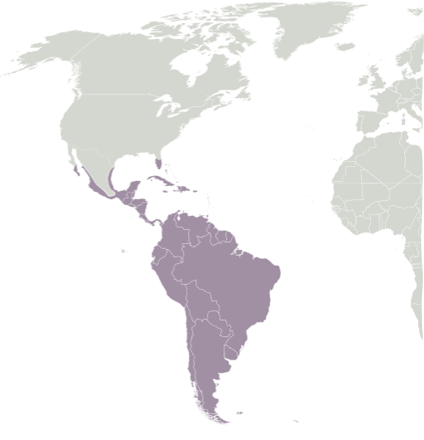
New cards
Neotropical Region
Tropical terrestrial ecological regions of South America, Central America, and the Caribbean
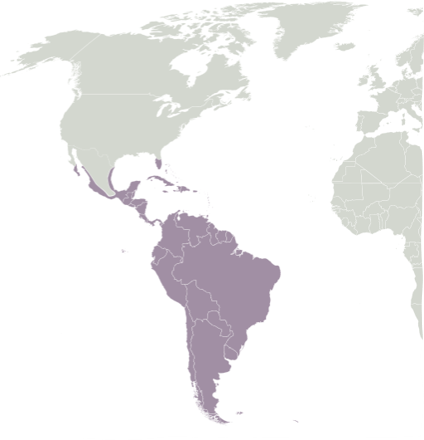
32
New cards
Neotropical Biomes
- Moist Broadleaf forests
- Amazon Rainforest
- Humid forest and wetlands
- Amazon Rainforest
- Humid forest and wetlands
33
New cards
Afrotropic Species
Rhino
34
New cards
Afrotropic Region
- Trans-Saharan Africa
- Arabia
- Arabia
35
New cards
Afrotropical Biomes
- Lowland tropical forest
- Savanna
- Grassland
- Desert
- Savanna
- Grassland
- Desert
36
New cards
Indomalayan Species
Wrinkled Hornbill
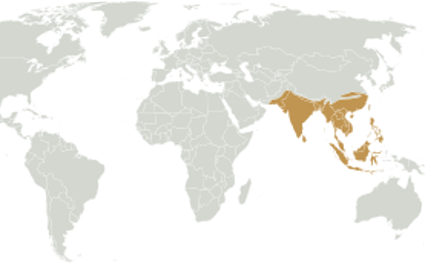
37
New cards
Indomalayan Region
- Indian sub-continent
- Southeast Asia
- Southern China
- Indochina
- Sunda shelf
- Ecoregions of the Philippines
- Southeast Asia
- Southern China
- Indochina
- Sunda shelf
- Ecoregions of the Philippines
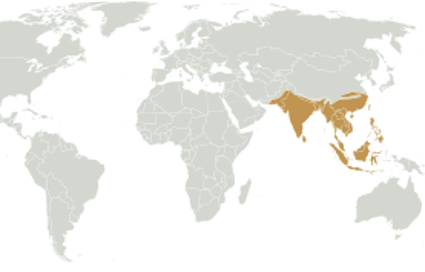
38
New cards
Australasia Species
Major Mitchell's cockatoo
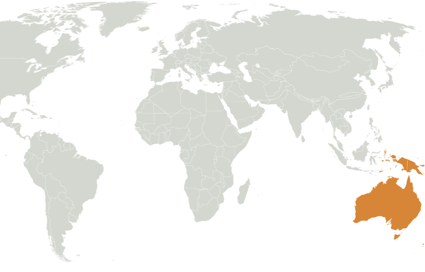
39
New cards
Australasia Region
- Australia
- New Guinea
- New Zealand
- Eastern Indonesian archipelago
- Solomon Islands
- New Caledonia
- New Guinea
- New Zealand
- Eastern Indonesian archipelago
- Solomon Islands
- New Caledonia
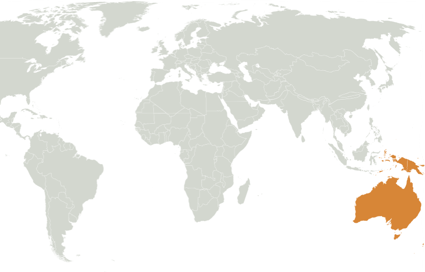
40
New cards
Australasia Biomes
- Similar flora to Antarctic realms and Southeast Asia
- Wallace's line serves as biological dividing line
- Wallace's line serves as biological dividing line
41
New cards
Oceanian Species
Solomon's Island Eclectus parrots
42
New cards
Oceanian Regions
- Polynesia
- Micronesia
- Fiji
- One of the smallest and youngest realms
- Micronesia
- Fiji
- One of the smallest and youngest realms
43
New cards
Oceanian Biomes
- Volcanic high islands
- Coral atolls
- Coral atolls
44
New cards
Antarctic Species
Emperor's Penguin
few species due to cold temperatures
few species due to cold temperatures
45
New cards
Antarctic Region
- Antarctica
- island groups in southern Atlantic & Indian Oceans
- island groups in southern Atlantic & Indian Oceans
46
New cards
Antarctic Biome
- Tundra
- Ice Sheets
- Ice Sheets
47
New cards
3 ways that zoos are organized:
- Taxonomic
- Zoogeographic
- Habitat
- Zoogeographic
- Habitat
48
New cards
Taxonomic Zoo Organization
Based on the classification of animals
49
New cards
Zoogeographic Zoo Organization
Based on geographic location of animals
50
New cards
Habitat Zoo Organization
Based on the preferred habitat of the animals
51
New cards
Carl Hagenbeck
- Tierpark Hagenbeck
- Larger, more naturalistic exhibits
- No obvious form of cantainment (moats)
- Mixed-species exhibits with species from the same region
- Larger, more naturalistic exhibits
- No obvious form of cantainment (moats)
- Mixed-species exhibits with species from the same region
52
New cards
Heini Hediger and William Conway
exhibits should address biologicaland behavioral needs of the animals
53
New cards
Where was the 1st naturalistic predator-prey exhibit in North America
African Plains exhibit at the Bronx Zoo
54
New cards
Exhibit design changes in 1990s-present
- enrichment opportunities in exhibits
- training walls/demonstrations
- training walls/demonstrations
55
New cards
Exhibit design changes in the present
- Incorporating choices for animals into exhibits
- visitor connections with live animals
- visitor connections with live animals
56
New cards
3 Clients for Exhibit Design
- Animals
- Zoo Staff (Keepers, Vets, Hort, Maintenance)
- Public
- Zoo Staff (Keepers, Vets, Hort, Maintenance)
- Public
57
New cards
Needs for Zoo Staff in Exhibit Design
- Easy to clean
- Ability to rotate exhibit furniture
- Facilitate animal captures/medical procedures
- Easy maintenance of plants, pools, barriers
- Ability to rotate exhibit furniture
- Facilitate animal captures/medical procedures
- Easy maintenance of plants, pools, barriers
58
New cards
Needs for Animals in Exhibit Design
- Safe Barriers
- Useable space
- Natural behaviors
- Shelter/Space to get away from people
- Food and water
- Useable space
- Natural behaviors
- Shelter/Space to get away from people
- Food and water
59
New cards
Needs for Guests in Exhibit Design
- Easy to see animals (natural behavior/active)
- Shade
- Area to sit and watch animals
- Graphics (animal info, conservation info)
- Shade
- Area to sit and watch animals
- Graphics (animal info, conservation info)
60
New cards
Holding Area uses
- Overnight
- Sick/injured animals
- Mother and offspring
- Exhibit construction
- Sick/injured animals
- Mother and offspring
- Exhibit construction
61
New cards
Needs for Off-Display areas
- Should work for training
- Should have the same standards as on-display areas
- Should have the same standards as on-display areas
62
New cards
Intraspecific
Within the same species
63
New cards
Conspecifics
Members of the same species
64
New cards
Interspecific
Between different species
65
New cards
Benefits of Mixed-Species to the Public
- More dynamic to watch
- More educational opportunities
- Use "flashier" species with others to draw attention to them
- More educational opportunities
- Use "flashier" species with others to draw attention to them
66
New cards
Benefits of Mixed-Species to the Animals
- Opportunities for interactive behaviors
- More naturalistic environment
- More complex behaviors
- Good for possible reintroduction programs
- More naturalistic environment
- More complex behaviors
- Good for possible reintroduction programs
67
New cards
Risks of Mixed-Species to the Public
- May witness aggression/possible injuries
- May not understand what they are seeing
- May not understand what they are seeing
68
New cards
Risks of Mixed-Species to the Animals
- Correct diets
- Hybridization
- Undesirable behavior
- Interspecific/Intraspecific Aggression (Breeding, competition for resources
- Hybridization
- Undesirable behavior
- Interspecific/Intraspecific Aggression (Breeding, competition for resources
69
New cards
According to the textbook there is usually more ______-species aggression
Intra-species
70
New cards
Why would interspecific aggression be more common?
the animals may not be able to interpret the other species behavior/warning signals
71
New cards
Things a keeper needs to interpret aggression
- Source of the aggression
- One time occurance or continutous
- Possible solutions
- One time occurance or continutous
- Possible solutions
72
New cards
Benefits for keepers working mixed-species
- Can work with a variety of animals in one enclosure
- Allows for lots of problem-solving opportunities
- Allows for lots of problem-solving opportunities
73
New cards
Difficulties for keepers working mixed-species
- Training
- Shifting
- Manaement for medical treatments
- Diets
- Captures
- Breeding
- Shifting
- Manaement for medical treatments
- Diets
- Captures
- Breeding
74
New cards
Considerations for mixed-species exhibits
- Preferred areas in enclosure
- Diet
- Natural history
- Individual history
- Breeding
- Disease transfer
- Diet
- Natural history
- Individual history
- Breeding
- Disease transfer
75
New cards
When to transport animals?
- Breeding Loans
- Exhibit Loans
- Donations
- Sales
- SSP recommendations
- Placing offspring
- Closing/opening an exhibit
- Replace animals that have passed away
- Adding to an enclosure
- Exhibit Loans
- Donations
- Sales
- SSP recommendations
- Placing offspring
- Closing/opening an exhibit
- Replace animals that have passed away
- Adding to an enclosure
76
New cards
Animal needs during transfer
- Food
- Water
- Bedding (absorbs feces/urine, provides warmth, traction)
- Temperature control
- Perches (depends on the animal)
- Cover
- Light
- Water
- Bedding (absorbs feces/urine, provides warmth, traction)
- Temperature control
- Perches (depends on the animal)
- Cover
- Light
77
New cards
US Fish and Wildlife Service (US FWS)
Endangered Species Act
78
New cards
National Marine Fisheries Service
Marine Mammal Protection Act (MMPA
79
New cards
US Dept. of Agriculture (USDA)
Animal and Plant Health Inspection Service (APHIS)
80
New cards
US Center for Disease Control (CDC)
Importation of certain animals
81
New cards
US Transportation and Security Administration (TSA)
Animal Transport by Air (IATA)
82
New cards
Occupational Safety and Health Administration (OSHA)
Staff Safety regulations
83
New cards
US Department of Homeland Security
Inspection of importation/exportation of animals
84
New cards
Game Management
- The act of making land produce sustained annual crops of wild game for recreational use.
- Grows natural species in an environment with few changes to enhance yield.
- An observer wouldn't be able to tell the difference between managed and unmanaged yield.
- Grows natural species in an environment with few changes to enhance yield.
- An observer wouldn't be able to tell the difference between managed and unmanaged yield.
85
New cards
Game Farming
- Intensified version of game management
- Propagates wild species in confinement, usually for later release to supplement wild stock.
- Propagates wild species in confinement, usually for later release to supplement wild stock.
86
New cards
Hunting Regulations
- Restriction of hunting
- Predator control
- Reservation of game (parks, refuges)
- Artificial replenishment
- Environmental controls
- Predator control
- Reservation of game (parks, refuges)
- Artificial replenishment
- Environmental controls
87
New cards
pre-1860's who owned game
Royalty or land-owning nobility
88
New cards
pre-1860's how did the poor feed themselves
Poaching
89
New cards
1830's Wildlife management in the US
- Game licenses
- Specific hunting seasons
- Specific hunting seasons
90
New cards
Tragedy of the Commons
- William Forster Llyod, made widely known in Garrett Hardin essay.
- A resource is widely used by a population
- Individuals aren't concerned about preserving it for themselves or the good of everyone.
- Eventually the resource is depleted and cannot be used by anyone.
- A resource is widely used by a population
- Individuals aren't concerned about preserving it for themselves or the good of everyone.
- Eventually the resource is depleted and cannot be used by anyone.
91
New cards
1st National Park
Yellowstone
92
New cards
Gifford Pinchot
- Conservationist
- Utilitarian: planned use and renewal of resources
- Value of nature is equal to the value of human use
- Utilitarian: planned use and renewal of resources
- Value of nature is equal to the value of human use
93
New cards
John Muir
Preservationist: some areas should be completely protected from any human use
94
New cards
Teddy Roosevelt's view on wildlife
Wildlands to be renewable organic resources which might last forever if harvested scientifically (not faster than produced)
95
New cards
Roosevelt's Doctrine of Conservation
- Recognized all outdoor resources as one integral whole
- Recognized their conservation through wise use as a public responsibility and their private ownership as a public trust
- Recognized science as a tool for discharging that responsibility.
- Recognized their conservation through wise use as a public responsibility and their private ownership as a public trust
- Recognized science as a tool for discharging that responsibility.
96
New cards
Aldo Leopold
- Father of Wildlife Management
97
New cards
A Sand County Almanac (1949)
- By Aldo Leopold
- Introduced the idea of a responsible relationship between people and the land.
- The Land Ethic
- Introduced the idea of a responsible relationship between people and the land.
- The Land Ethic
98
New cards
Wildlife Management 1970-present
- Broader environmental movement
- focus shifted away from game species and includes ecosystems
- focus shifted away from game species and includes ecosystems
99
New cards
E.O. Wilson
- Father of biodiversity and biogeography
- recognized keystone species and their importance
- Conservation advocacy
- recognized keystone species and their importance
- Conservation advocacy
100
New cards
Jane Goodall
- Promotion of animal welfare
- breaking down perceived differences between humans and animals
- known for chimp research
- breaking down perceived differences between humans and animals
- known for chimp research