Receptive Fields and the Visual System
1/27
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
28 Terms
Retinal Ganglion Cells (RGCs)
Receive signals from photoreceptors via the bipolar cells and amacrine cells and send action potentials to the brain via the optic nerve
Retinal Bipolar Cells
transmit signals between photoreceptors and ganglion cells
Amacrine and Horizontal Cells
Receive input from photoreceptors and send signals laterally within the retina. May send inhibitory signals to adjacent photoreceptors, bipolar or ganglion cells.
Lateral Inhibition
Mediated by the amacrine and horizontal cells. In RGCs, firing rate is reduced when areas of the retina adjacent to the excitatory portion of its receptive field are stimulated due to this process.
Centre-Surround Antagonism
Common arrangement found in receptive fields where the neural response to light placed in the centre is opposite to that in the surround. Stimulation of the inhibitory surround/centre counteracts the centre/surrounds excitatory response, causing a decrease in the neurons firing rate.
Receptive Field
the region of the sensory surface that, when stimulated, causes a change in the firing rate of that neuron
Simple Cells
Neurons in the primary visual cortex (V1) that respond maximally to straight-edge stimuli in a certain position and orientation
Orientation Tuning Curve
determined by measuring the responses of a simple cortical cell to bars with different orientations
Complex Cells
Neurons in the visual cortex that respond best to bars with a particular orientation moving in a specific direction
End-Stopped Cells
Neurons in the visual cortex that respond best to corners or bars of a specific length that are moving in a particular direction.
On-Centre Cell
A cell that increases firing in response to an increase in light intensity in the centre of its receptive-field and decreases firing in response to light in the surround of its receptive field
Off-Centre Cell
A cell that increases firing in response to a decrease in light intensity in the centre of its receptive-field (or increases firing in response to an increase in light intensity in the surround of its receptive-field and decreases firing in response to light in the centre of its receptive field)
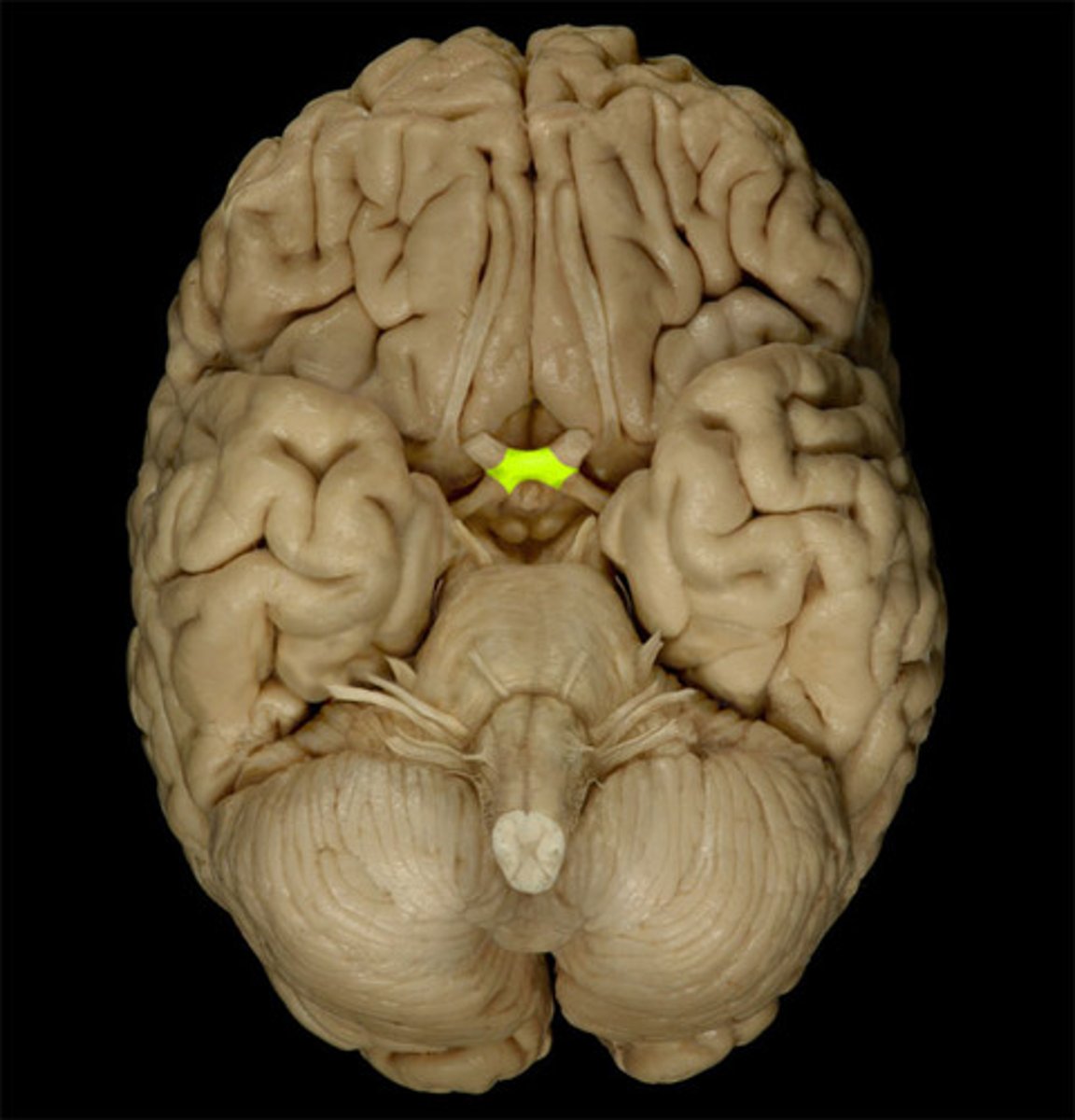
Optic Chiasm
Point at which the part of the optic nerve coming from the nasal retina in each eye decussates to the contralateral side of the brain.
Nasal Retina
Part of retina for each eye that is located close to the nose. Receives light incoming from temporal portion of the visual field.
Temporal Retina
Part of retina for each eye that is located close to the ears. Receives light incoming from nasal portion of the visual field.
Lateral Geniculate Nucleus (LGN)
A structure in the thalamus that receives input from the retinal ganglion cells and has input and output connections to the visual cortex. Left side receives input from right visual field and vice versa.
Hubel and Wiesel
Won a Nobel prize for their research on feature detectors in visual cortex - discovered simple, complex, and end-stopped (hypercomplex) cells
Hartline (1938)
Discovered and coined the term 'receptive field' by recording from ganglion cell axons in the optic nerve of a frog
Kuffler (1953)
Demonstrated the presence of centre-surround receptive fields in mammalian retinal ganglion cells by stimulating the retina of cats
Centre-Surround Receptive Fields
The organisation of receptive fields in RGCs and cells within the lateral geniculate nucleus
Retinotopic Map
Organisation in the LGN and primary visual cortex in which each cortical area corresponds with a specific area of the retina
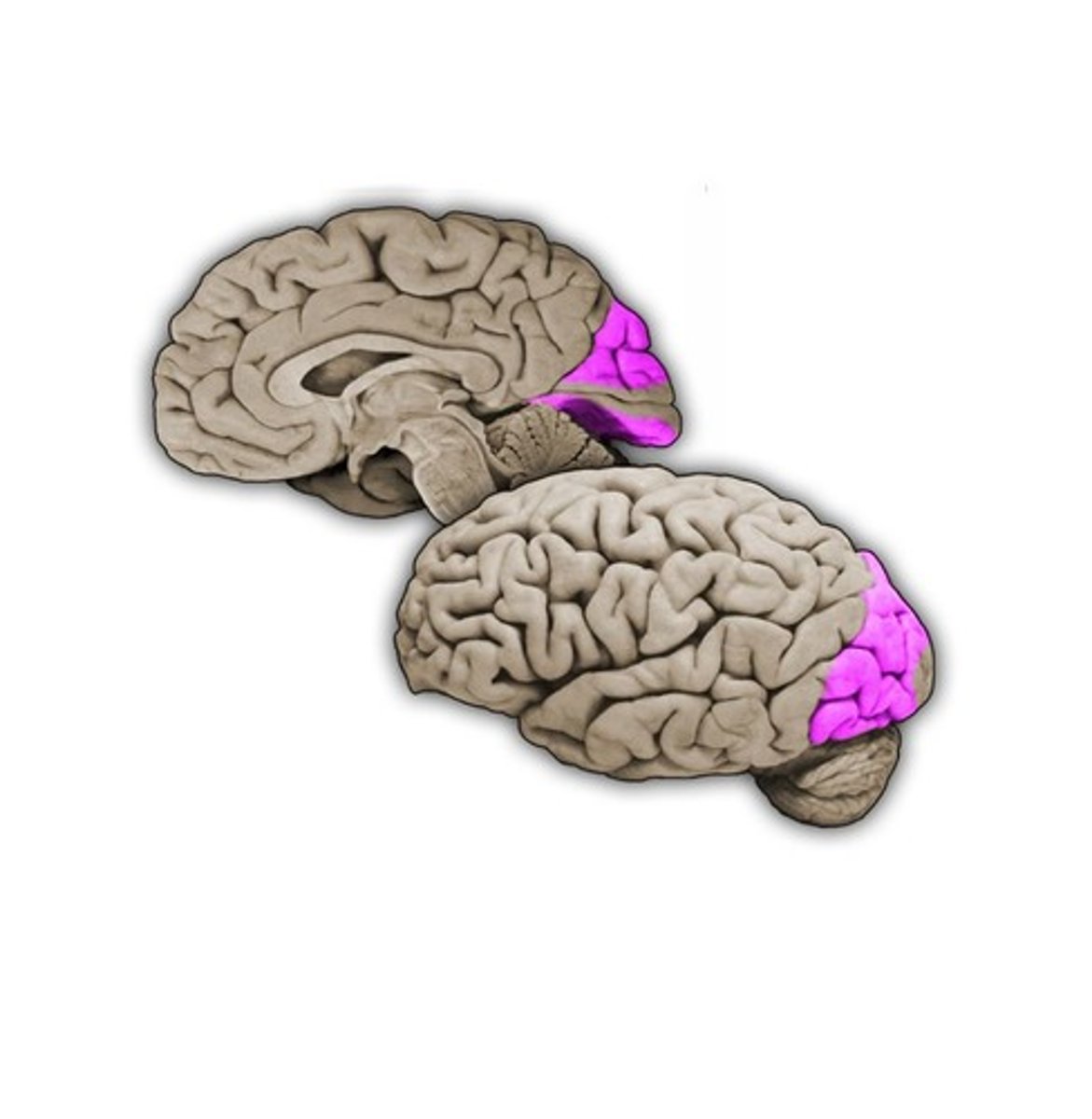
Primary Visual Cortex
The region of the cerebral cortex in the posterior medial occipital lobe that receives visual information from the lateral geniculate nucleus. Also known as area V1.
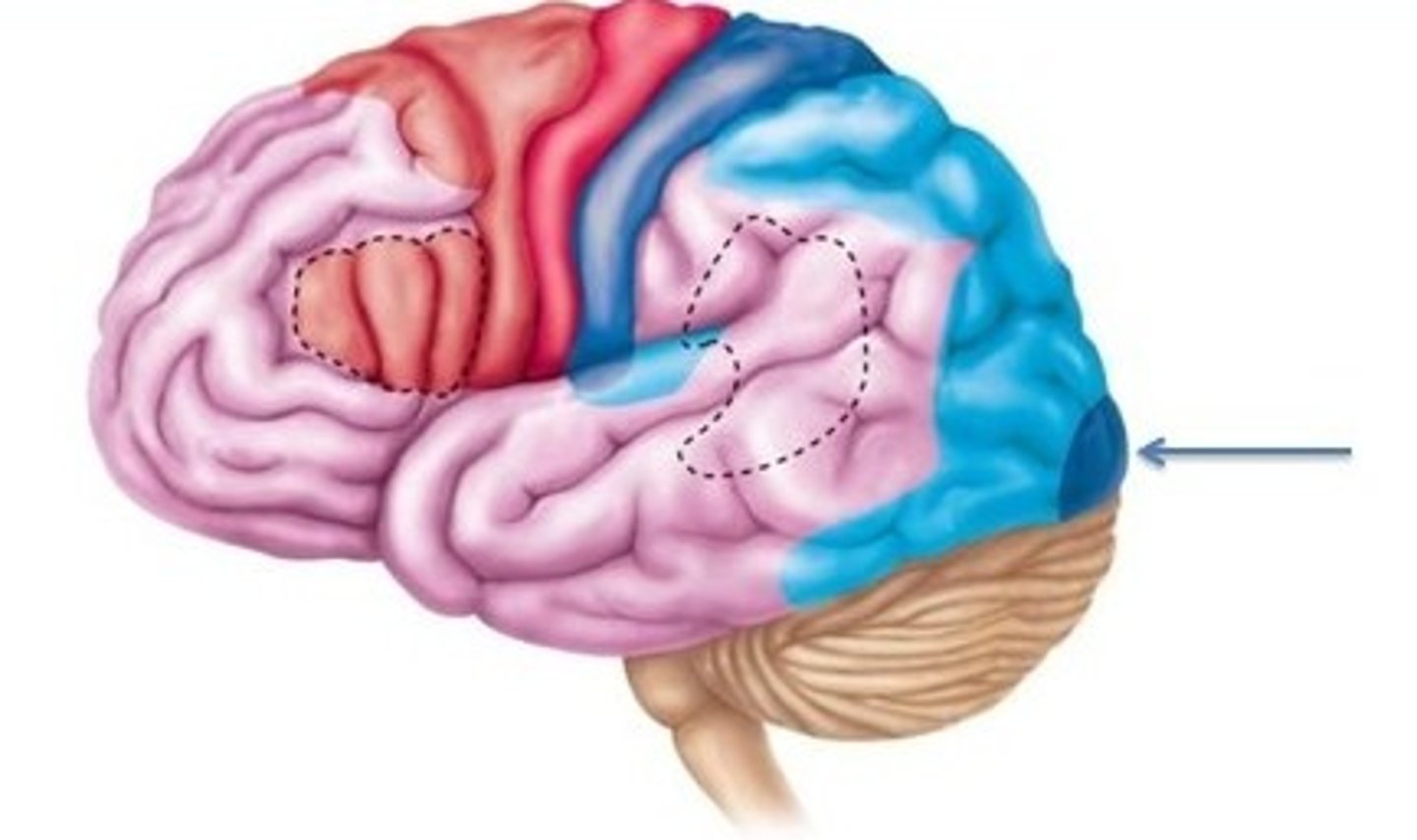
Visual Association Cortex
Includes areas V2-5. Processes increasingly complex visual information provided by the feature detectors in area V1 allowing us to perceive colour, shape, objects and movement.
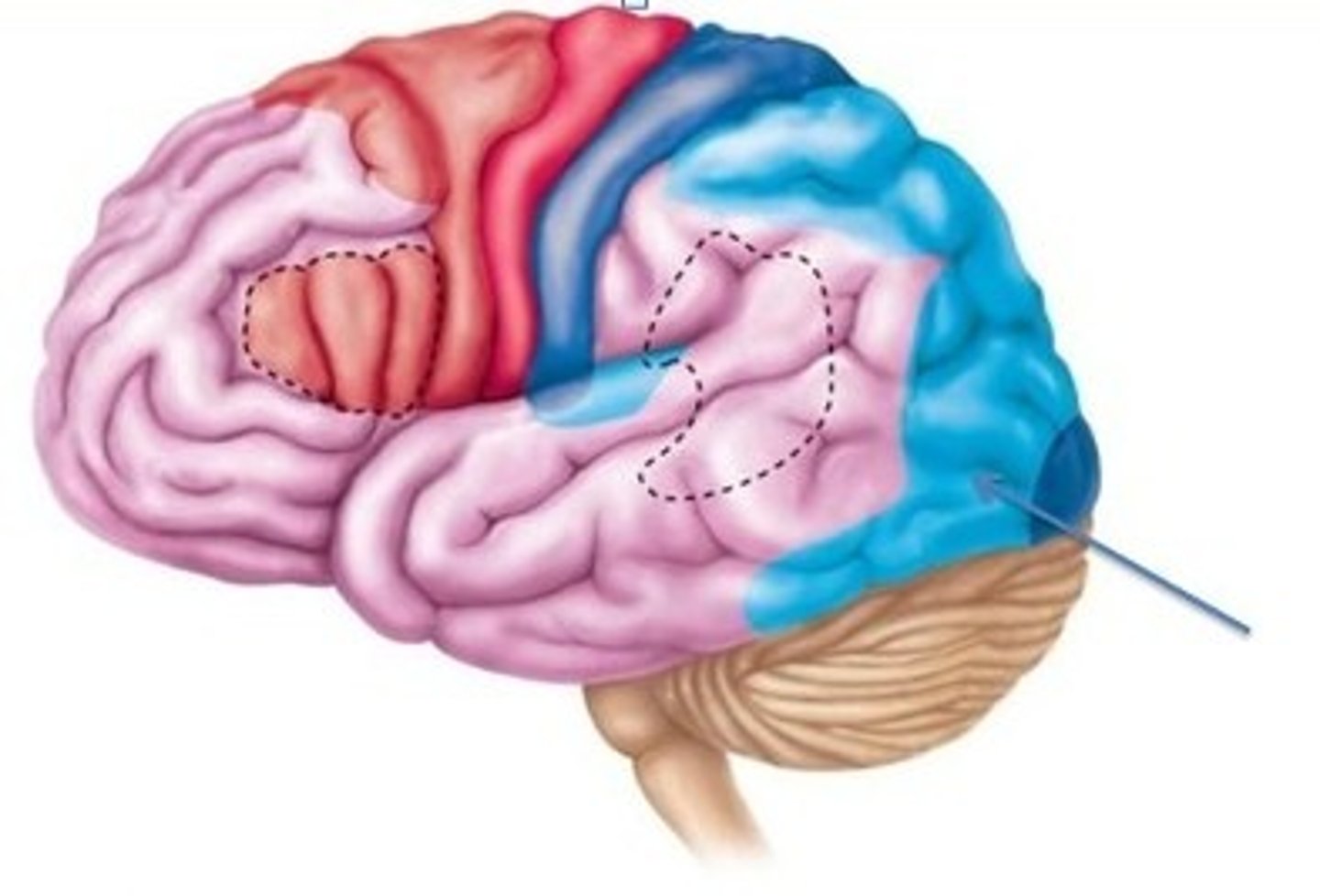
Dorsal Visual Stream
Pathway that originates in the occipital cortex and projects to the parietal cortex. Otherwise known as the 'where' pathway, it processes information that facilitates our perception of the location of objects and how action is to be guided toward objects.
Ventral Visual Stream
Pathway that originates in the occipital cortex and projects to the temporal cortex. Otherwise known as the "what" pathway, it processes information that facilitates our perception of form, structure and recognition allowing us to determine what an object is.
Striate Cortex
Another term for the primary visual cortex.
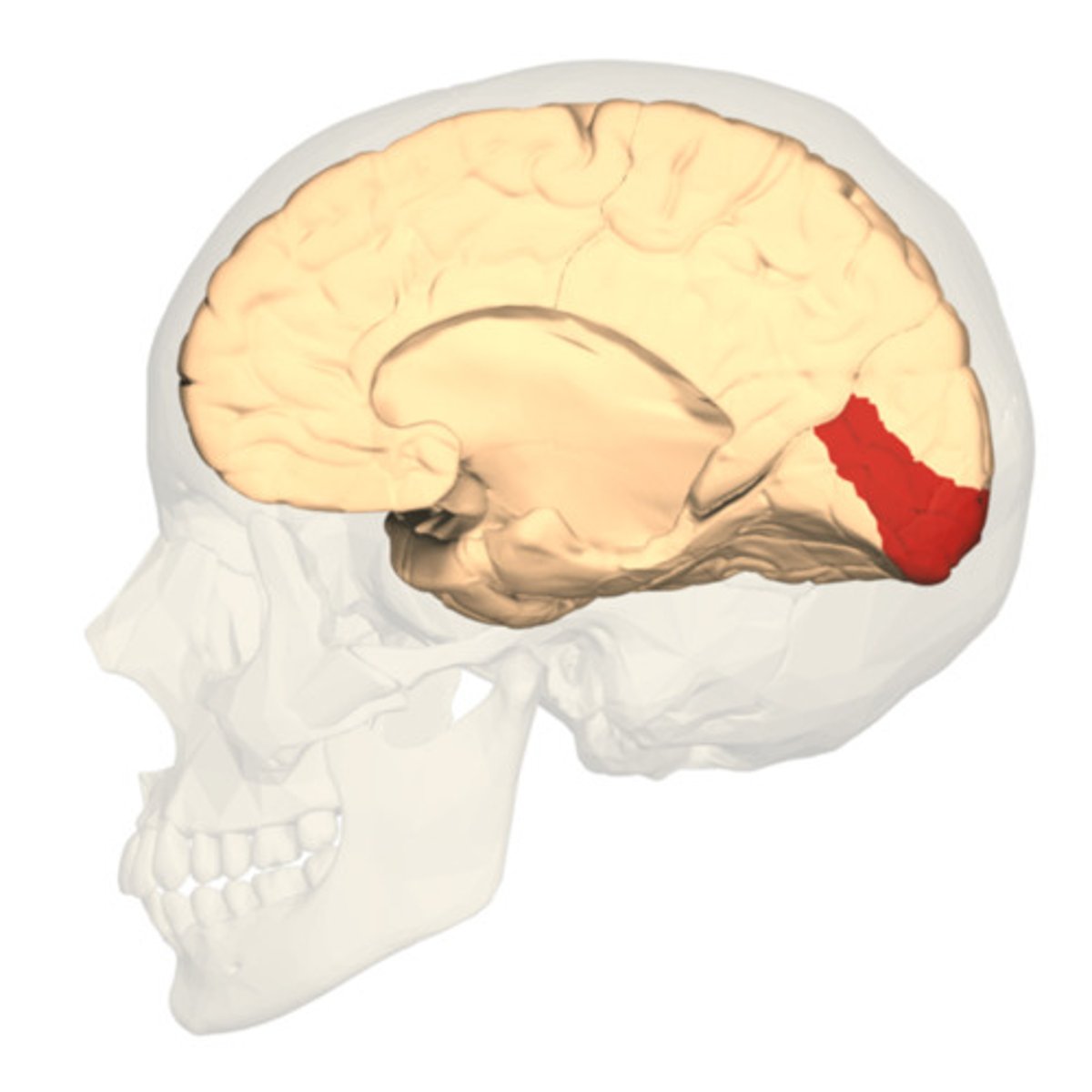
Extrastriate Cortex
Another term for the visual association cortex
Feature Detectors
neurons that respond selectively to very specific features of more complex stimuli (such as orientation, movement, colour, shape etc.)