Kin 312 The Stages of Learning
5.0(1)
Card Sorting
1/19
Earn XP
Description and Tags
Last updated 4:41 AM on 9/22/25
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
20 Terms
1
New cards
Two Models Used to Identify the Stages of Learning Motor Skills
1) Fitts and Posner three-stage model
2) Gentile two-stage model
2) Gentile two-stage model
2
New cards
The Basis for The Learning Stage Models (Time/Amount of Practice Continuum)
3
New cards
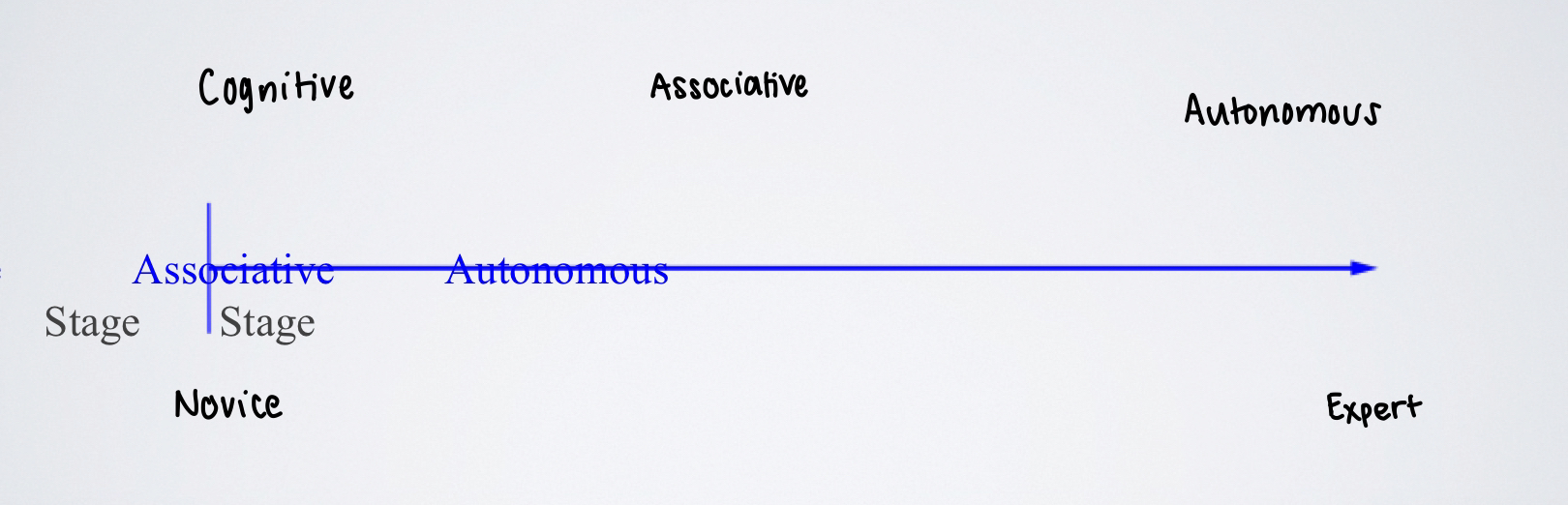
Fitts and Posner Model: Three Stages
1) Cognitive (novice)
2) Associative
3) Autonomous (expert)
2) Associative
3) Autonomous (expert)
4
New cards
Fitts and Posner Model: Cognitive Stage
Person characteristics
-questions concern what to do to achieve the goal of the skill
-involved in cognitive and movement problem-solving activity
-movements demand large amounts of conscious attention
-aware of making errors, but doesn't know how to correct them
Performance characteristics
-"in the ballpark" movement pattern
-large number of errors
-errors tend to be "big"
-high amount of trial-to-trial variability (poor consistency).
ex) skier falls down a hill and loses their equipment
-questions concern what to do to achieve the goal of the skill
-involved in cognitive and movement problem-solving activity
-movements demand large amounts of conscious attention
-aware of making errors, but doesn't know how to correct them
Performance characteristics
-"in the ballpark" movement pattern
-large number of errors
-errors tend to be "big"
-high amount of trial-to-trial variability (poor consistency).
ex) skier falls down a hill and loses their equipment
5
New cards
Fitts and Posner Model: Associative Stage
Person characteristics
-performer "associates" environmental cues with required movements
-reduced amount of attention demanded at movement level
-increased capability to perform simultaneous tasks
-increased capability to detect errors
Performance characteristics
-refinement of movement pattern
-errors are fewer and smaller
-trial-to-trial variability decreases
ex) baseball batter takes in environmental features (ball, pitcher posture) while swinging
-performer "associates" environmental cues with required movements
-reduced amount of attention demanded at movement level
-increased capability to perform simultaneous tasks
-increased capability to detect errors
Performance characteristics
-refinement of movement pattern
-errors are fewer and smaller
-trial-to-trial variability decreases
ex) baseball batter takes in environmental features (ball, pitcher posture) while swinging
6
New cards
Fitts and Posner Model: Autonomous Stage
Person characteristics
-very little, if any, attention demanded at movement level (automatic)
-capable of performing simultaneous tasks
-capable of detecting and correcting errors
Performance characteristics
-consistent trial-to-trial movement pattern
-errors are few and small
-very little, if any, attention demanded at movement level (automatic)
-capable of performing simultaneous tasks
-capable of detecting and correcting errors
Performance characteristics
-consistent trial-to-trial movement pattern
-errors are few and small
7
New cards
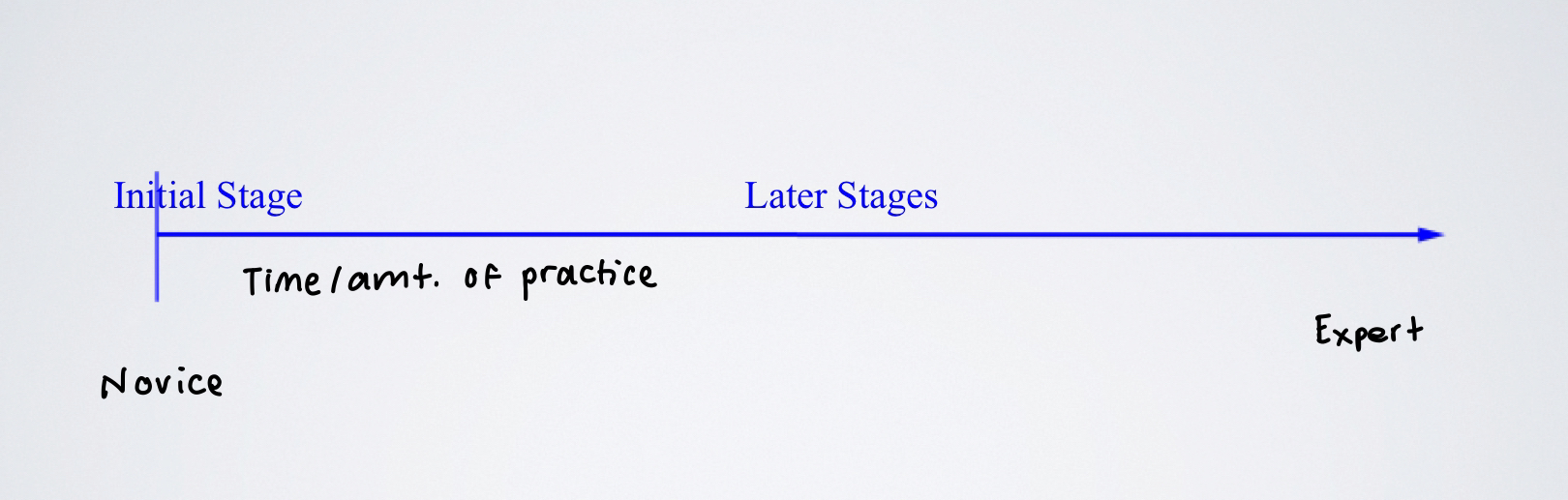
Gentile Model: Two Stages
1) Initial Stage
2) Later Stages
2) Later Stages
8
New cards
Gentile Model: Initial Stage
Characteristics
-performance emphasis: develop movement pattern that allows some degree of success at achieving the action goal
--"The action goal is not achieved consistently and the movement lacks efficiency". (Gentile, 2000)
-person begins to learn to discriminate regulatory from non-regulatory environmental conditions
-other performance characteristics similar to Cognitive Stage in Fitts and Posner model
-performance emphasis: develop movement pattern that allows some degree of success at achieving the action goal
--"The action goal is not achieved consistently and the movement lacks efficiency". (Gentile, 2000)
-person begins to learn to discriminate regulatory from non-regulatory environmental conditions
-other performance characteristics similar to Cognitive Stage in Fitts and Posner model
9
New cards
Gentile Model: Later Stages
Person Emphasizes:
-developing capability to adapt movement patterns to situation demands
-becoming more consistent at achieving action goal
-involves refining movement pattern developed in Initial Stage
-increasing economy of effort (efficiency of effort--no "wasted effort") while performing the skill
-achieving specific goals for performing closed and open motor skills
-developing capability to adapt movement patterns to situation demands
-becoming more consistent at achieving action goal
-involves refining movement pattern developed in Initial Stage
-increasing economy of effort (efficiency of effort--no "wasted effort") while performing the skill
-achieving specific goals for performing closed and open motor skills
10
New cards
Gentile Model: Later Stages-Closed Skills
-goal: fixation
-focus on increasing consistency of producing same movement pattern each time skill is performed
-increase capability to adapt to non-regulatory conditions (ex: fatigue, anxiety, wind, noise)
-focus on increasing consistency of producing same movement pattern each time skill is performed
-increase capability to adapt to non-regulatory conditions (ex: fatigue, anxiety, wind, noise)
11
New cards
Gentile Model: Later Stages-Open Skills
-goal: diversification
-focus on increasing capability to adapt to changing spatial and temporal regulatory conditions
-increase capability to modify movement characteristics of movement pattern as needed
(ex: ping pong game)
-focus on increasing capability to adapt to changing spatial and temporal regulatory conditions
-increase capability to modify movement characteristics of movement pattern as needed
(ex: ping pong game)
12
New cards
7 Concepts that Explain the Stages of Learning
1) Rate of Improvement
2) Body & Limb Segment Coordination
3) Muscle Activation During Performance
4) Energy Cost
5) Kinematic Goal Achievement
6) Visual Attention
7) Demand for Conscious Attention
2) Body & Limb Segment Coordination
3) Muscle Activation During Performance
4) Energy Cost
5) Kinematic Goal Achievement
6) Visual Attention
7) Demand for Conscious Attention
13
New cards
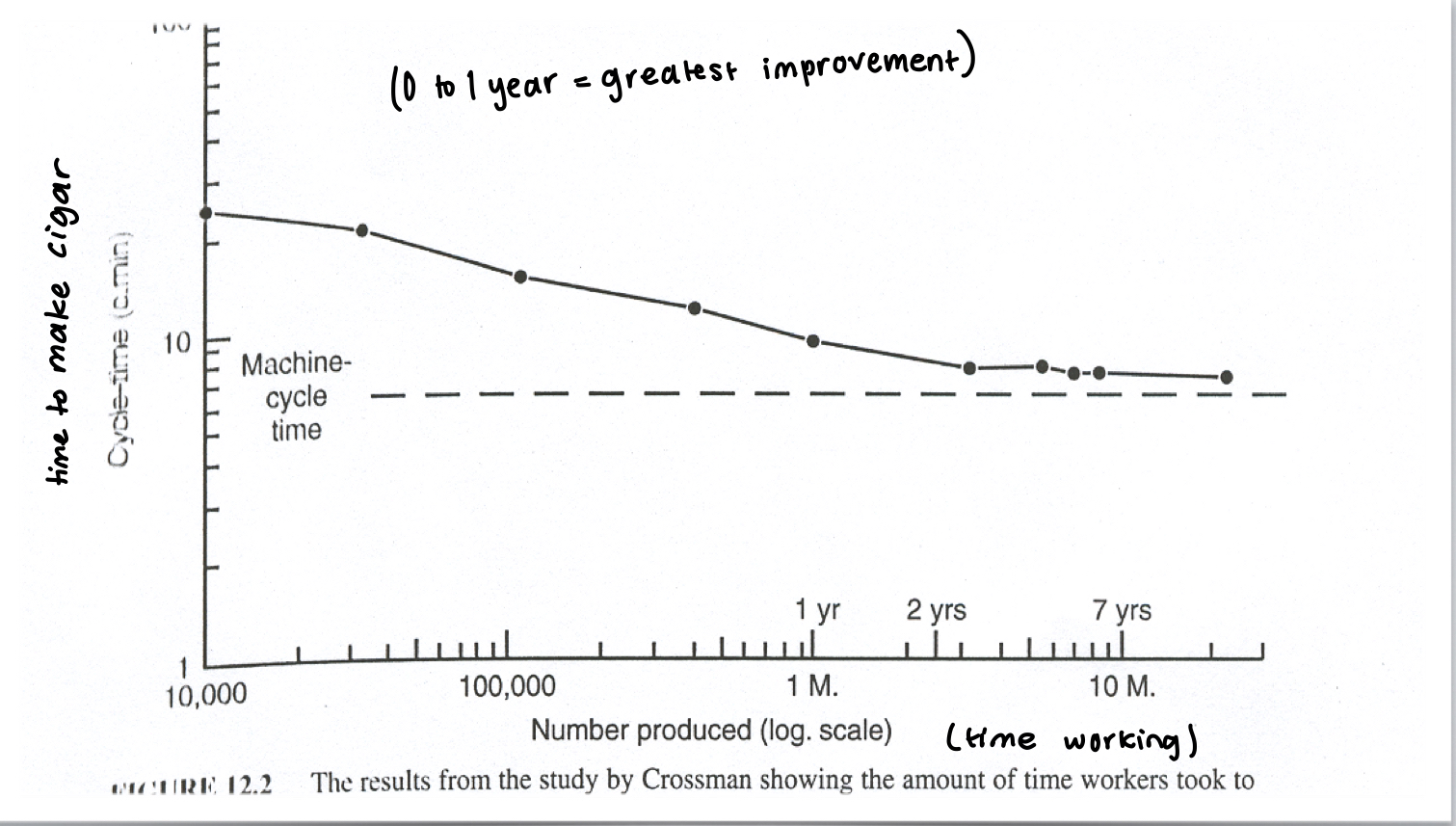
Rate of Improvement
-power law of practice
ex) Crossman's study of cigar makers who ranged from 1 to 7 years of experience
ex) Langley Study of Beginning Bowlers:
o assessed what students were trying to correct at the beginning, middle, and end of a 10-week bowling class
-first week: general lack of ball control related to inconsistency and aiming
-middle week: specific movement errors related to specific desired outcomes
-final week: specific errors related to consistency and aiming of a hook
-What do people do as they improve performance so that the Power Law characterizes the rate of improvement?
o change their emphasis on the types of performance errors they try to correct:
-gross errors
-movement errors
-accuracy and consistency errors
ex) Crossman's study of cigar makers who ranged from 1 to 7 years of experience
ex) Langley Study of Beginning Bowlers:
o assessed what students were trying to correct at the beginning, middle, and end of a 10-week bowling class
-first week: general lack of ball control related to inconsistency and aiming
-middle week: specific movement errors related to specific desired outcomes
-final week: specific errors related to consistency and aiming of a hook
-What do people do as they improve performance so that the Power Law characterizes the rate of improvement?
o change their emphasis on the types of performance errors they try to correct:
-gross errors
-movement errors
-accuracy and consistency errors
14
New cards
Body and Limb Segment Coordination
-Progresses from "freezing to freeing" degrees of freedom
-For a multi-joint movement: initial control strategy, person performs skill by moving some joints as only 1 joint (freezing); eventually develops a functional synergy of those joints (freeing)
-For a multi-joint movement: initial control strategy, person performs skill by moving some joints as only 1 joint (freezing); eventually develops a functional synergy of those joints (freeing)

15
New cards
Muscle Activation During Performance
-Decrease in number of muscles activated
-develop sequences of muscle activation (ex: Jaegers dart throwing experiment)
-Energy cost:
increase in efficient use of energy (ex: decrease in energy cost)
-Energy use involves:
o physiological (O2, calories)
o mechanical (=work rate/metabolic rate)
-develop sequences of muscle activation (ex: Jaegers dart throwing experiment)
-Energy cost:
increase in efficient use of energy (ex: decrease in energy cost)
-Energy use involves:
o physiological (O2, calories)
o mechanical (=work rate/metabolic rate)
16
New cards
Kinematic Goal Achievement
progresses from spatial to temporal goals

17
New cards
Visual Attention
-from erratic to more specific visual search
-develops faster visual focus on correct cues
-increases capability to shift visual attention
-develops faster visual focus on correct cues
-increases capability to shift visual attention
18
New cards
Demand for Conscious Attention
-decrease due to CHUNKING
-systematically increase number of parts in a "chunk"
ex) learning to shift gears while driving a stick shift
-systematically increase number of parts in a "chunk"
ex) learning to shift gears while driving a stick shift

19
New cards
Characteristics of "Experts"
-in sports, the level of expertise considered here is commonly referred to as an "elite" or "world-class" athlete
-some similarities across domains of expertise (ex: musicians, athletes, artists): minimum of 10 years of deliberate practice (involves regular schedule of intense, work like practice)
-some differences across domains of expertise: expertise is domain specific; little transfer of capabilities from expertise domain to one in which expert has no experience
-some similarities across domains of expertise (ex: musicians, athletes, artists): minimum of 10 years of deliberate practice (involves regular schedule of intense, work like practice)
-some differences across domains of expertise: expertise is domain specific; little transfer of capabilities from expertise domain to one in which expert has no experience
20
New cards
Expertise: a Conundrum-2 Contradictory Occurrences
1) If 'experts' perform skill "automatically", why do they not perform perfectly all the time?
-external factors
-inconsistent with movement
2) Can an expert lose the capability to perform like an expert?
- many stories of professional sports about athletes who "lost it" during the peak of their careers and never regained the previously achieved level of performance
-external factors
-inconsistent with movement
2) Can an expert lose the capability to perform like an expert?
- many stories of professional sports about athletes who "lost it" during the peak of their careers and never regained the previously achieved level of performance