Bio module 1-anatomy and physiology
1/67
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
68 Terms
Anatomy
study of the structural basis of body function
Physiology
study of functional relevance of human structure
Gross anatomy
structures visible to the eye
study using surface observation or dissection
Histology
the study of tissue
observed under a microscope
specimens are thinly spliced and stained
Surface anatomy
study of external structures of the body sh. what you can see
Systemic anatomy
study of one organ system at a time
Regional anatomy
study of multiple organ systems at the same time in a specific region of the body
Inspection
take a look; simplest method
Palpation
to feel structures with fingertips
Percussion
tapping on the body and listening for sounds of abnormalities
Auscultation
listening to sounds made by the body
Medical imaging
allows viewing inside of body without surgery
Noninvasive
no penetration of skin or orifices
Invasive
penetration of skin and body orifices
Radiography
photogrophy of internal structures with x-rays
Computed Tomography CT scan
Produces an image of a slice of body and is useful for identifying tumors, aneurysms, and kidney stones
Magnetic resonance imaging
uses magnetic field and radio waves to produce image
Positron Emission tomography PET scan
an injection of radioactively labeled glucose highlights the most active areas of the body
Sonography
uses a handheld device against skin to emit high frequency ultrasound
this option avoids the harmful effects of X-rays and is both cheap and portable however does not produce very sharp image
an echocardiography is a sonographic exam of a beating heart
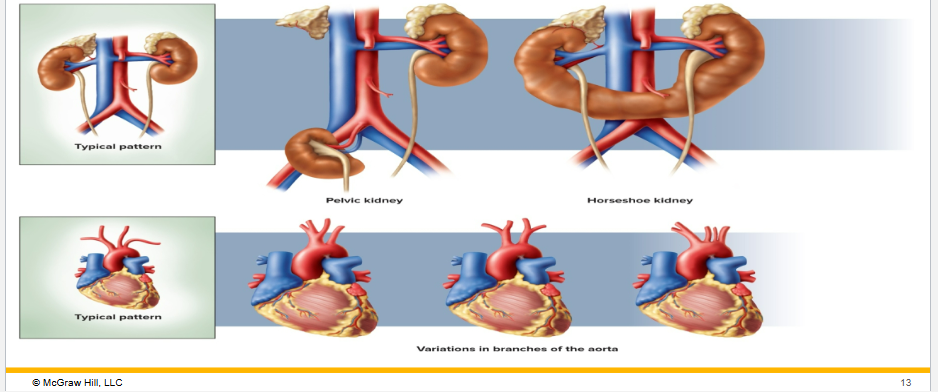
Anatomical variation
individuals vary in their anatomy and some people lack certain organisms
Neurophysiology
the study of the nervous system
Pathophysiology
the study of mechanisms of disease
What are the 8 biological qualities of living things?
organization
cells
metabolism
development
excitability
homeostasis
reproduction
evolution
Organization
expend energy to survive
disease and death result from breakdown in order
Cells
living things are compartmentalized into the smallest functional unit within our bodies (cells)
Metabolism
sum of all internal chemical change within an organism ex. converting food and drink into energy
Development
the change in form or function over the lifetime of an organism
involves growth and differentiation
growth: an increase in size
differentiation: cells and tissues with no specialized function
transform into cells committed to a particular task
Excitability
the ability of organisms to sense and react to stimuli sh. to feel
Homeostasis
ability to achieve internal stability despite a changing environment
What are some examples of homeostasis
blood pressure
body weight
body temperature
Reproduction
organisms are able to produce copies of themselves and pass their genes on to offspring
Evolution
ability to have genetic change in the population over time
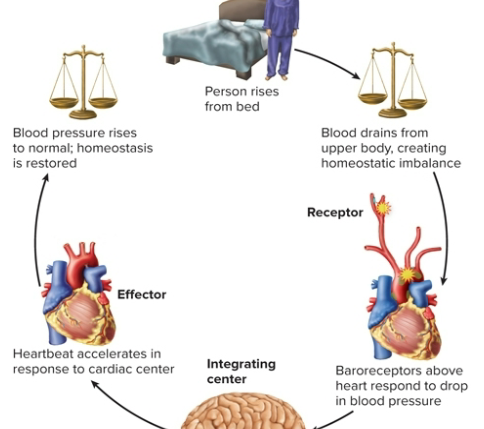
What does homeostasis consist of?
a feedback loop
Receptor
as structure that senses changes in the body
ex. tempature receptors on skin
Integrating control center
processes information and makes response decision
ex. cardiac control center in brain
Effectors
structures that carry out response to restore homeostasis
Negative feedback
a process where the body senses a change and activates mechanisms that reverse it. does not produce absolute constancy and values may fluctuate around a set point.
ex. is key mechanism for maintaining homeostasis and health
Positive feedback
A cycle where change in the body leads to greater change in same direction
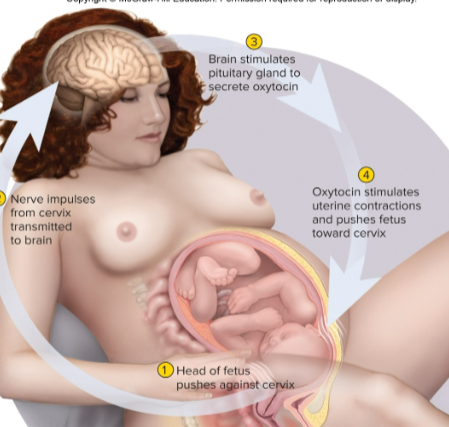
What are some examples of positive feedback?
childbirth, clotting, and protein creation
organism
a whole complete individual
organ system
a group of organs that carry out a basic function
organ
multiple tissue types that work to carry out a function
ex. heart kidneys bones
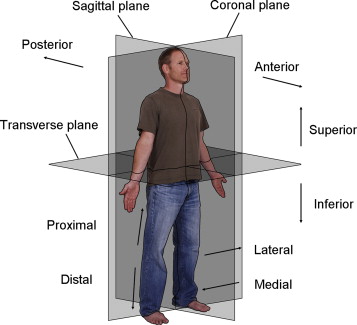
sagittal plane
extends vertically and divides the body into right and left portions
midsagittal divides the body into equal right and left portions while parasagittal divides body into unequal right and left portions
frontal plane
extends vertically and divides the body into frontal and back positions
transverse plane
divides the body into upper and lower positions
Body cavities that contain internal organs are lined by what type of membrane?
serous membrane that secretes a water flow
Cranial cavity
enclosed by skull and contains the brain
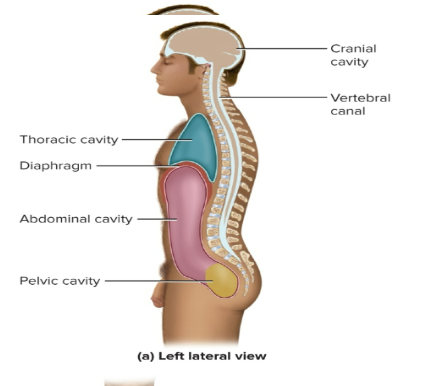
Vertebral canal
Space that passes down the vertebral column (spine)
continuous with cranial cavity
Membrane
a thin sheet of tissue covering an organ surface, lining a space, or separating other tissues from each other
Meninges
a layer of three membranes that lines both the cranial cavity and vertebral to protect nervous tissue from hard bone
Which muscle separates the thoracic cavity from the abdominopelvic cavity?
the diaphragm
Mediastinum
a partition that divides the thoracic cavity into right and left portions
contains the esophagus, trachea, heart and major blood vessels
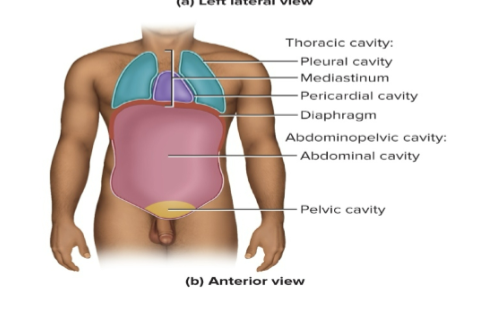
What does the thoracic cavity contain?
mediastinum
pericardium
pleura
Pericardium
two layered serous membrane that surrounds the heart
Pleura
two layered membrane enclosing the lungs
What are the names for the two layers of a membrane?
visceral (innermost)
parietal (outermost)
Abdominal cavity
contains most of the digestive organs
Pelvic cavity
contains lowermost part of large intestine, urethra, bladder and reproductive organs
Peritoneum
a serous membrane lining the abdominopelvic cavity and peritoneal cavity
Peritoneal cavity
the space between the parietal and visceral peritoneum
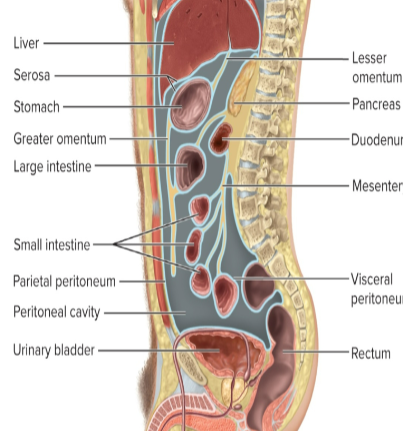
Retroperitoneal organs
covered by peritoneum only on side facing the cavity
lie against the posterior body wall
kidneys and pancreas
Intraperitoneal organs
fully encircled by peritoneum and suspended from posterior body wall by by mesenteries
loops of small intestines
Tissue
a group of similar cells or cell products that work to carry out a function
Physiological variation
physiology is more variable than anatomy
Differs with sex, age, weight, diet, physical activity,
environment
health care workers must make adjustments for characteristics
Organelles
microscopic structures that carry out cells individual functions
ex. nuclei, mitochondria and lysosomes
Composed of molecules, which are made of atoms
The anatomical position
views of body are based on slices with sections and planes
Parietal peritoneum
outer layer of peritonium, lines the abdominal wall
Visceral peritoneum
Mesentery suspends certain
abdominal viscera from body wallSerosa covers some visceral
surfaces